-
日撸Java三百行(day19:字符串匹配)
目录
一、字符串的一些基础知识
字符串(String)是用一对双引号括起来的零个或多个字符组成的有限序列,在java中,字符串是被作为对象来处理的。常用的字符串可以分为以下两大类:
- String类:创建之后不允许再做修改的字符串常量
- StringBuffer类:创建之后允许再做修改的字符串变量
毫无疑问,字符串是计算机处理信息的基础,毕竟我们向计算机输入的信息本质上都是字符串,而计算机所谓的“打印”实际上也是以字符串的形式显示出来的。所以,要想学好计算机,学会并熟练使用字符串以及字符串的各种操作(比如拼接、比较、截取、查找和替换等)是必不可少的。下面,我们就来进行一些基础的字符串操作,话不多说,上代码!
二、代码实现
其实字符串也是一种线性表,它和之前的栈、队列一样,有顺序存储结构、链式存储结构这两种存储方式,今天我们采用的是顺序存储结构,即以顺序表(数组)为底层进行模拟。
1.字符类的创建
相信经过这几天的学习,大家对类的创建已经差不多熟练了,这里就不过多阐述了。
- public class MyString {
- /**
- * The maximal length.
- */
- public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
- /**
- * The actual length.
- */
- int length;
- /**
- * The data.
- */
- char[] data;
- /**
- *********************
- * Construct an empty char array.
- *********************
- */
- public MyString() {
- length = 0;
- data = new char[MAX_LENGTH];
- }// Of the first constructor
- /**
- *********************
- * Construct using a system defined string.
- *
- * @param paraString
- * The given string. Its length should not exceed MAX_LENGTH - 1.
- *********************
- */
- public MyString(String paraString) {
- data = new char[MAX_LENGTH];
- length = paraString.length();
- // Copy data.
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- data[i] = paraString.charAt(i);
- } // Of for i
- } // Of the second constructor
注意,为了后续操作方便,这里我们使用了charAt()方法+for循环,从而将字符串paraString复制到之前定义的数组data中。
2.字符类的遍历
- /**
- *********************
- * Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
- *********************
- */
- public String toString() {
- String resultString = "";
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- resultString += data[i];
- } // Of for i
- return resultString;
- } // Of toString
同样的,我们重写toString()方法来实现字符串遍历。
3.字符串匹配
进行代码模拟之前,我们先来了解一下什么是字符串匹配。所谓“字符串匹配”,就是给定一个模式字符串(相当于原字符串的子串),判断其是否存在于主字符串(即原字符串)中,如果存在,确定该模式串出现的位置。显然,模式串的长度(patternLength) ≤ 主串的长度(mainLength)。
具体操作的方法为:将模式串的元素逐个与主串一一比对,直到在主串中找到某一段连续的部分与模式串完全匹配,此时模式串中第一个元素的下标即为该模式串出现的位置。
为了更好地理解字符串匹配的过程,我们用图来说明:
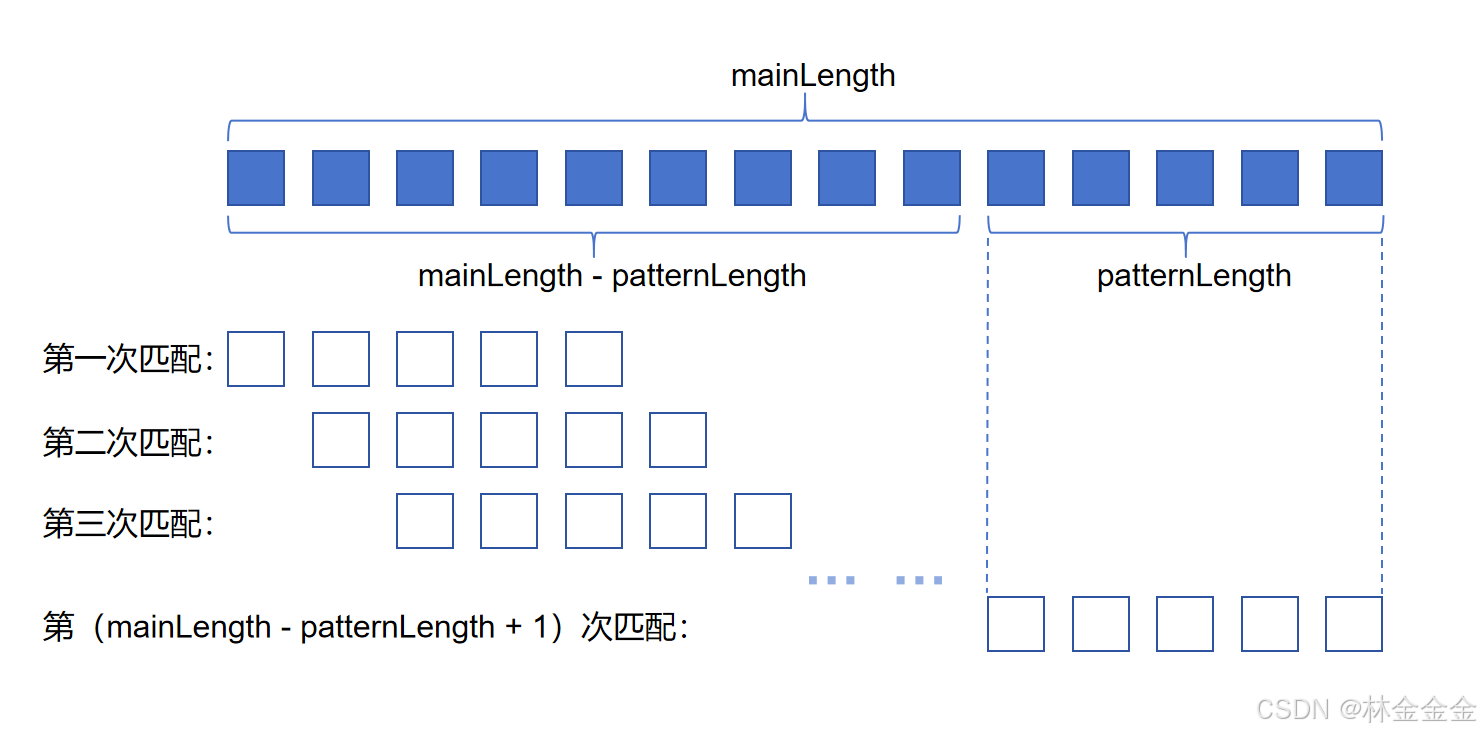
每次匹配,都是将模式串中的元素逐个(即从头到尾)与主串中的对应元素进行比对,若全部相同则匹配成功;若匹配过程中出现模式串的某个元素与对应元素不一样则立即停止,直接移动模式串进行下一次匹配。此外,由上图可以看出,最多需要进行mainLength - patternLength + 1次匹配。
理解字符串匹配的原理后,我们就可以开始代码实现了,如下:
- /**
- *********************
- * Locate the position of a substring.
- *
- * @param paraString The given substring.
- * @return The first position. -1 for no matching.
- *********************
- */
- public int locate(MyString paraMyString) {
- boolean tempMatch = false;
- for (int i = 0; i < length - paraMyString.length + 1; i++) {
- // Initialize.
- tempMatch = true;
- for (int j = 0; j < paraMyString.length; j++) {
- if (data[i + j] != paraMyString.data[j]) {
- tempMatch = false;
- break;
- } // Of if
- } // Of for j
- if (tempMatch) {
- return i;
- } // Of if
- } // Of for i
- return -1;
- } // Of locate
这里我们用到的是两层for循环,外层for-i循环是控制匹配次数的循环,因为最多匹配mainLength - patternLength + 1次且i的初始值为0,所以循环控制条件即为i < mainLength - patternLength + 1;而内层for-j循环则控制每次匹配时对模式串元素从头到尾进行比对,相当于对模式串进行一次遍历操作。注意,每次匹配时一旦出现比对失败就立即停止,马上进行下一次匹配,所以我们这里增加了一个if判断语句+break语句。
如果某次匹配全部比对成功,则执行完for-j循环后tempMatch仍为true,所以直接返回i,因为此时的i恰好就是模式串第一个元素当前所处的位置。
4.字符串截取
所谓“字符串截取”,顾名思义,就是从原字符串中截取某一部分的内容,有以下两种方法:
- 给定截取内容的开头下标以及整个截取内容的长度
- 给定截取内容的开头下标和结尾下标
通常我们用的是第一种方法,代码如下:
- /**
- *********************
- * Get a substring
- *
- * @param paraString The given substring.
- * @param paraStartPosition The start position in the original string.
- * @param paraLength The length of the new string.
- * @return The first position. -1 for no matching.
- *********************
- */
- public MyString substring(int paraStartPosition, int paraLength) {
- if (paraStartPosition + paraLength > length) {
- System.out.println("The bound is exceeded.");
- return null;
- } // Of if
- MyString resultMyString = new MyString();
- resultMyString.length = paraLength;
- for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
- resultMyString.data[i] = data[paraStartPosition + i];
- } // Of for i
- return resultMyString;
- } // Of substring
当然,在进行字符串截取之前,还需要提前判断我们想要截取的内容是否超出了原字符串的范围。这里我们通过if语句进行判断,当paraStartPosition + paraLength > length(即截取内容已超出原字符串的范围)时,输出" The bound is exceeded.",并返回null。如果没有超出范围,则从截取内容的开头下标开始遍历,将内容copy到结果字符串中。
5.数据测试
接着,我们进行如下的数据测试(注意,空格、标点符号等也算一个字符):
- 测试一:在字符串" I like ik. "中,进行模式串" ik "的匹配,可以预测结果应该为3(以首次匹配成功为准)
- 测试二:在字符串" I like ik. "中,进行模式串" ki "的匹配,原字符串中不存在模式串" ki ",所以应该返回-1
- 测试三:在字符串" I like ik. "中,截取开头下标为1,内容长度为2的字符串,预测结果为" l"
- 测试四:在字符串" I like ik. "中,截取开头下标为5,内容长度为5的字符串,可以预测结果为"e ik."
- 测试五:在字符串" I like ik. "中,截取开头下标为5,内容长度为6的字符串,显然此时已经超出范围,所以输出"The bound is exceeded."
- /**
- *********************
- * The entrance of the program.
- *
- * @param args Not used now.
- *********************
- */
- public static void main(String args[]) {
- MyString tempFirstString = new MyString("I like ik.");
- MyString tempSecondString = new MyString("ik");
- int tempPosition = tempFirstString.locate(tempSecondString);
- System.out.println("The position of \"" + tempSecondString + "\" in \"" + tempFirstString
- + "\" is: " + tempPosition);
- MyString tempThirdString = new MyString("ki");
- tempPosition = tempFirstString.locate(tempThirdString);
- System.out.println("The position of \"" + tempThirdString + "\" in \"" + tempFirstString
- + "\" is: " + tempPosition);
- tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(1, 2);
- System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
- tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(5, 5);
- System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
- tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(5, 6);
- System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
- } // Of main
6.完整的程序代码
- package datastructure;
- /**
- * My string. String is a class provided by the language, so I use another name.
- * It is essentially a sequential list with char type elements.
- *
- *@auther Xin Lin 3101540094@qq.com.
- */
- public class MyString {
- /**
- * The maximal length.
- */
- public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
- /**
- * The actual length.
- */
- int length;
- /**
- * The data.
- */
- char[] data;
- /**
- *********************
- * Construct an empty char array.
- *********************
- */
- public MyString() {
- length = 0;
- data = new char[MAX_LENGTH];
- }// Of the first constructor
- /**
- *********************
- * Construct using a system defined string.
- *
- * @param paraString
- * The given string. Its length should not exceed MAX_LENGTH - 1.
- *********************
- */
- public MyString(String paraString) {
- data = new char[MAX_LENGTH];
- length = paraString.length();
- // Copy data.
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- data[i] = paraString.charAt(i);
- } // Of for i
- } // Of the second constructor
- /**
- *********************
- * Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
- *********************
- */
- public String toString() {
- String resultString = "";
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- resultString += data[i];
- } // Of for i
- return resultString;
- } // Of toString
- /**
- *********************
- * Locate the position of a substring.
- *
- * @param paraString The given substring.
- * @return The first position. -1 for no matching.
- *********************
- */
- public int locate(MyString paraMyString) {
- boolean tempMatch = false;
- for (int i = 0; i < length - paraMyString.length + 1; i++) {
- // Initialize.
- tempMatch = true;
- for (int j = 0; j < paraMyString.length; j++) {
- if (data[i + j] != paraMyString.data[j]) {
- tempMatch = false;
- break;
- } // Of if
- } // Of for j
- if (tempMatch) {
- return i;
- } // Of if
- } // Of for i
- return -1;
- } // Of locate
- /**
- *********************
- * Get a substring
- *
- * @param paraString The given substring.
- * @param paraStartPosition The start position in the original string.
- * @param paraLength The length of the new string.
- * @return The first position. -1 for no matching.
- *********************
- */
- public MyString substring(int paraStartPosition, int paraLength) {
- if (paraStartPosition + paraLength > length) {
- System.out.println("The bound is exceeded.");
- return null;
- } // Of if
- MyString resultMyString = new MyString();
- resultMyString.length = paraLength;
- for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
- resultMyString.data[i] = data[paraStartPosition + i];
- } // Of for i
- return resultMyString;
- } // Of substring
- /**
- *********************
- * The entrance of the program.
- *
- * @param args Not used now.
- *********************
- */
- public static void main(String args[]) {
- MyString tempFirstString = new MyString("I like ik.");
- MyString tempSecondString = new MyString("ik");
- int tempPosition = tempFirstString.locate(tempSecondString);
- System.out.println("The position of \"" + tempSecondString + "\" in \"" + tempFirstString
- + "\" is: " + tempPosition);
- MyString tempThirdString = new MyString("ki");
- tempPosition = tempFirstString.locate(tempThirdString);
- System.out.println("The position of \"" + tempThirdString + "\" in \"" + tempFirstString
- + "\" is: " + tempPosition);
- tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(1, 2);
- System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
- tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(5, 5);
- System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
- tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(5, 6);
- System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
- } // Of main
- } // Of class MyString
运行结果

显然,运行结果与预测结果保持一致。
总结
总的来说,字符串不仅是计算机处理信息的基础,还涉及到很多应用程序的核心功能,所以掌握字符串及其相关操作对编程学习是非常重要的。此外,对于今天的字符串匹配操作,我们采用的是BF暴力算法,但其实还有KMP算法、Rabin-Karp算法、Boyer-Moore算法等。
-
相关阅读:
bed has inconsistent naming convention for record
TS类型全解
自己的项目 调查问卷Web (详细版)
C/C++统计数 2021年12月电子学会青少年软件编程(C/C++)等级考试一级真题答案解析
opencv 入门学习
接口
Python 写网络监控
redis + AOP + 自定义注解实现接口限流
告警:线上慎用 BigDecimal ,坑的差点被开了
力扣刷题day41|198打家劫舍、213打家劫舍II、337打家劫舍III
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80594618/article/details/141097297