-
竞赛 深度学习OCR中文识别 - opencv python
0 前言
🔥 优质竞赛项目系列,今天要分享的是
🚩 **基于深度学习OCR中文识别系统 **
该项目较为新颖,适合作为竞赛课题方向,学长非常推荐!
🥇学长这里给一个题目综合评分(每项满分5分)
- 难度系数:3分
- 工作量:3分
- 创新点:4分
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate
1 课题背景
在日常生产生活中有大量的文档资料以图片、PDF的方式留存,随着时间推移 往往难以检索和归类 ,文字识别(Optical Character
Recognition,OCR )是将图片、文档影像上的文字内容快速识别成为可编辑的文本的技术。高性能文档OCR识别系统是基于深度学习技术,综合运用Tensorflow、CNN、Caffe
等多种深度学习训练框架,基于千万级大规模文字样本集训练完成的OCR引擎,与传统的模式识别的技术相比,深度学习技术支持更低质量的分辨率、抗干扰能力更强、适用的场景更复杂,文字的识别率更高。本项目基于Tensorflow、keras/pytorch实现对自然场景的文字检测及OCR中文文字识别。
2 实现效果
公式检测

纯文字识别
3 文本区域检测网络-CTPN
对于复杂场景的文字识别,首先要定位文字的位置,即文字检测。
简介
CTPN是在ECCV
2016提出的一种文字检测算法。CTPN结合CNN与LSTM深度网络,能有效的检测出复杂场景的横向分布的文字,效果如图1,是目前比较好的文字检测算法。由于CTPN是从Faster
RCNN改进而来,本文默认读者熟悉CNN原理和Faster RCNN网络结构。

相关代码
def main(argv): pycaffe_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__) parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() # Required arguments: input and output. parser.add_argument( "input_file", help="Input txt/csv filename. If .txt, must be list of filenames.\ If .csv, must be comma-separated file with header\ 'filename, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax'" ) parser.add_argument( "output_file", help="Output h5/csv filename. Format depends on extension." ) # Optional arguments. parser.add_argument( "--model_def", default=os.path.join(pycaffe_dir, "../models/bvlc_reference_caffenet/deploy.prototxt.prototxt"), help="Model definition file." ) parser.add_argument( "--pretrained_model", default=os.path.join(pycaffe_dir, "../models/bvlc_reference_caffenet/bvlc_reference_caffenet.caffemodel"), help="Trained model weights file." ) parser.add_argument( "--crop_mode", default="selective_search", choices=CROP_MODES, help="How to generate windows for detection." ) parser.add_argument( "--gpu", action='store_true', help="Switch for gpu computation." ) parser.add_argument( "--mean_file", default=os.path.join(pycaffe_dir, 'caffe/imagenet/ilsvrc_2012_mean.npy'), help="Data set image mean of H x W x K dimensions (numpy array). " + "Set to '' for no mean subtraction." ) parser.add_argument( "--input_scale", type=float, help="Multiply input features by this scale to finish preprocessing." ) parser.add_argument( "--raw_scale", type=float, default=255.0, help="Multiply raw input by this scale before preprocessing." ) parser.add_argument( "--channel_swap", default='2,1,0', help="Order to permute input channels. The default converts " + "RGB -> BGR since BGR is the Caffe default by way of OpenCV." ) parser.add_argument( "--context_pad", type=int, default='16', help="Amount of surrounding context to collect in input window." ) args = parser.parse_args() mean, channel_swap = None, None if args.mean_file: mean = np.load(args.mean_file) if mean.shape[1:] != (1, 1): mean = mean.mean(1).mean(1) if args.channel_swap: channel_swap = [int(s) for s in args.channel_swap.split(',')] if args.gpu: caffe.set_mode_gpu() print("GPU mode") else: caffe.set_mode_cpu() print("CPU mode") # Make detector. detector = caffe.Detector(args.model_def, args.pretrained_model, mean=mean, input_scale=args.input_scale, raw_scale=args.raw_scale, channel_swap=channel_swap, context_pad=args.context_pad) # Load input. t = time.time() print("Loading input...") if args.input_file.lower().endswith('txt'): with open(args.input_file) as f: inputs = [_.strip() for _ in f.readlines()] elif args.input_file.lower().endswith('csv'): inputs = pd.read_csv(args.input_file, sep=',', dtype={'filename': str}) inputs.set_index('filename', inplace=True) else: raise Exception("Unknown input file type: not in txt or csv.") # Detect. if args.crop_mode == 'list': # Unpack sequence of (image filename, windows). images_windows = [ (ix, inputs.iloc[np.where(inputs.index == ix)][COORD_COLS].values) for ix in inputs.index.unique() ] detections = detector.detect_windows(images_windows) else: detections = detector.detect_selective_search(inputs) print("Processed {} windows in {:.3f} s.".format(len(detections), time.time() - t)) # Collect into dataframe with labeled fields. df = pd.DataFrame(detections) df.set_index('filename', inplace=True) df[COORD_COLS] = pd.DataFrame( data=np.vstack(df['window']), index=df.index, columns=COORD_COLS) del(df['window']) # Save results. t = time.time() if args.output_file.lower().endswith('csv'): # csv # Enumerate the class probabilities. class_cols = ['class{}'.format(x) for x in range(NUM_OUTPUT)] df[class_cols] = pd.DataFrame( data=np.vstack(df['feat']), index=df.index, columns=class_cols) df.to_csv(args.output_file, cols=COORD_COLS + class_cols) else: # h5 df.to_hdf(args.output_file, 'df', mode='w') print("Saved to {} in {:.3f} s.".format(args.output_file, time.time() - t))CTPN网络结构

4 文本识别网络-CRNN
CRNN 介绍
CRNN 全称为 Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network,主要用于端到端地对不定长的文本序列进行识别,不用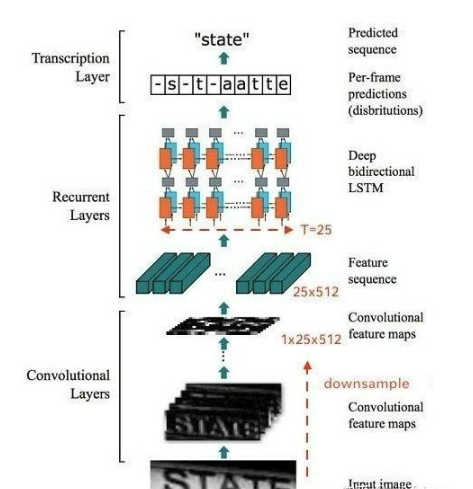
整个CRNN网络结构包含三部分,从下到上依次为:
- CNN(卷积层),使用深度CNN,对输入图像提取特征,得到特征图;
- RNN(循环层),使用双向RNN(BLSTM)对特征序列进行预测,对序列中的每个特征向量进行学习,并输出预测标签(真实值)分布;
- CTC loss(转录层),使用 CTC 损失,把从循环层获取的一系列标签分布转换成最终的标签序列。
CNN
卷积层的结构图:
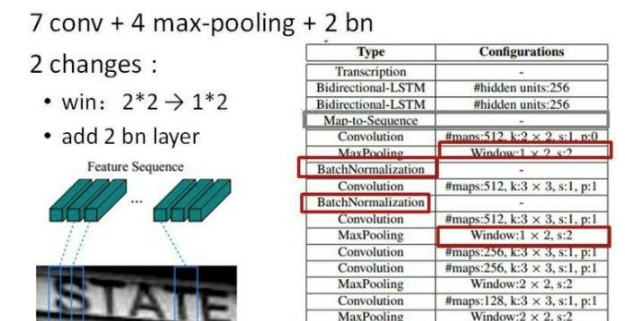
这里有一个很精彩的改动,一共有四个最大池化层,但是最后两个池化层的窗口尺寸由 2x2 改为 1x2,也就是图片的高度减半了四次(除以 2^4
),而宽度则只减半了两次(除以2^2),这是因为文本图像多数都是高较小而宽较长,所以其feature
map也是这种高小宽长的矩形形状,如果使用1×2的池化窗口可以尽量保证不丢失在宽度方向的信息,更适合英文字母识别(比如区分i和l)。CRNN 还引入了BatchNormalization模块,加速模型收敛,缩短训练过程。
输入图像为灰度图像(单通道);高度为32,这是固定的,图片通过 CNN
后,高度就变为1,这点很重要;宽度为160,宽度也可以为其他的值,但需要统一,所以输入CNN的数据尺寸为 (channel, height,
width)=(1, 32, 160)。CNN的输出尺寸为 (512, 1, 40)。即 CNN 最后得到512个特征图,每个特征图的高度为1,宽度为40。
Map-to-Sequence
我们是不能直接把 CNN 得到的特征图送入 RNN 进行训练的,需要进行一些调整,根据特征图提取 RNN 需要的特征向量序列。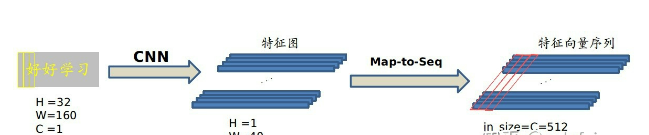
现在需要从 CNN 模型产生的特征图中提取特征向量序列,每一个特征向量(如上图中的一个红色框)在特征图上按列从左到右生成,每一列包含512维特征,这意味着第
i 个特征向量是所有的特征图第 i 列像素的连接,这些特征向量就构成一个序列。由于卷积层,最大池化层和激活函数在局部区域上执行,因此它们是平移不变的。因此,特征图的每列(即一个特征向量)对应于原始图像的一个矩形区域(称为感受野),并且这些矩形区域与特征图上从左到右的相应列具有相同的顺序。特征序列中的每个向量关联一个感受野。
如下图所示:
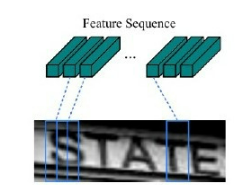
这些特征向量序列就作为循环层的输入,每个特征向量作为 RNN 在一个时间步(time step)的输入。
RNN
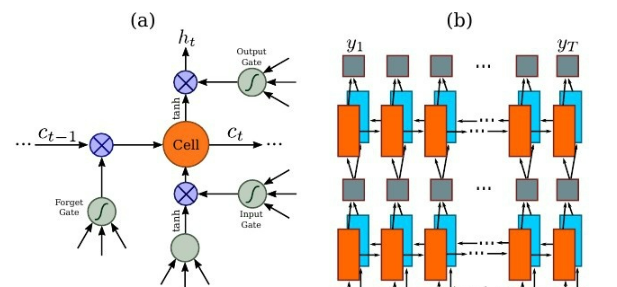
因为 RNN 有梯度消失的问题,不能获取更多上下文信息,所以 CRNN 中使用的是 LSTM,LSTM
的特殊设计允许它捕获长距离依赖,不了解的话可以看一下这篇文章 对RNN和LSTM的理解。LSTM
是单向的,它只使用过去的信息。然而,在基于图像的序列中,两个方向的上下文是相互有用且互补的。将两个LSTM,一个向前和一个向后组合到一个双向LSTM中。此外,可以堆叠多层双向LSTM,深层结构允许比浅层抽象更高层次的抽象。这里采用的是两层各256单元的双向 LSTM 网络:
通过上面一步,我们得到了40个特征向量,每个特征向量长度为512,在 LSTM 中一个时间步就传入一个特征向量进行分
我们知道一个特征向量就相当于原图中的一个小矩形区域,RNN
的目标就是预测这个矩形区域为哪个字符,即根据输入的特征向量,进行预测,得到所有字符的softmax概率分布,这是一个长度为字符类别数的向量,作为CTC层的输入。因为每个时间步都会有一个输入特征向量 x^T ,输出一个所有字符的概率分布 y^T ,所以输出为 40 个长度为字符类别数的向量构成的后验概率矩阵。
如下图所示:
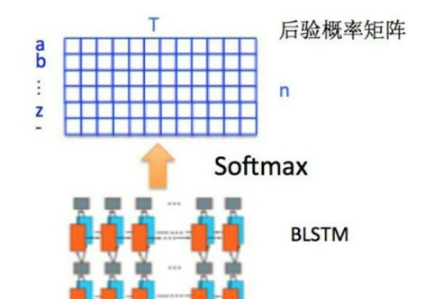
然后将这个后验概率矩阵传入转录层。
CTC loss
这算是 CRNN 最难的地方,这一层为转录层,转录是将 RNN
对每个特征向量所做的预测转换成标签序列的过程。数学上,转录是根据每帧预测找到具有最高概率组合的标签序列。端到端OCR识别的难点在于怎么处理不定长序列对齐的问题!OCR可建模为时序依赖的文本图像问题,然后使用CTC(Connectionist Temporal
Classification, CTC)的损失函数来对 CNN 和 RNN 进行端到端的联合训练。相关代码
def inference(self, inputdata, name, reuse=False): """ Main routine to construct the network :param inputdata: :param name: :param reuse: :return: """ with tf.variable_scope(name_or_scope=name, reuse=reuse): # centerlized data inputdata = tf.divide(inputdata, 255.0) #1.特征提取阶段 # first apply the cnn feature extraction stage cnn_out = self._feature_sequence_extraction( inputdata=inputdata, name='feature_extraction_module' ) #2.第二步, batch*1*25*512 变成 batch * 25 * 512 # second apply the map to sequence stage sequence = self._map_to_sequence( inputdata=cnn_out, name='map_to_sequence_module' ) #第三步,应用序列标签阶段 # third apply the sequence label stage # net_out width, batch, n_classes # raw_pred width, batch, 1 net_out, raw_pred = self._sequence_label( inputdata=sequence, name='sequence_rnn_module' ) return net_out
5 最后
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
-
相关阅读:
post请求同时上传文件并传递其他参数的前后端写法
民安智库(第三方市场调研公司)物业满意度入户调查
Kotlin学习之2
【DRAM存储器十五】DDR介绍-关键技术之DLL和prefetch
宝塔面板网站解决跨域问题
使用Python批量发送个性化邮件
【gcc】RtpTransportControllerSend学习笔记 3:gcc 算法
带头双向循环链表增删查改实现(C语言)
SpringBoot概念_项目的创建_和运行
Vue的快速入门(01)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/iuerfee/article/details/140243491