-
【GPT-SOVITS-04】SOVITS 模块-鉴别模型解析
说明:该系列文章从本人知乎账号迁入,主要原因是知乎图片附件过于模糊。
知乎专栏地址:
语音生成专栏系列文章地址:
【GPT-SOVITS-01】源码梳理
【GPT-SOVITS-02】GPT模块解析
【GPT-SOVITS-03】SOVITS 模块-生成模型解析
【GPT-SOVITS-04】SOVITS 模块-鉴别模型解析
【GPT-SOVITS-05】SOVITS 模块-残差量化解析
【GPT-SOVITS-06】特征工程-HuBert原理1.SOVITS 鉴别器
1.1、概述
GPT-SOVITS 在鉴别器这块在SOVITS原始版本上做了简化,先回顾下SOVITS的鉴别器。主要包含三类:
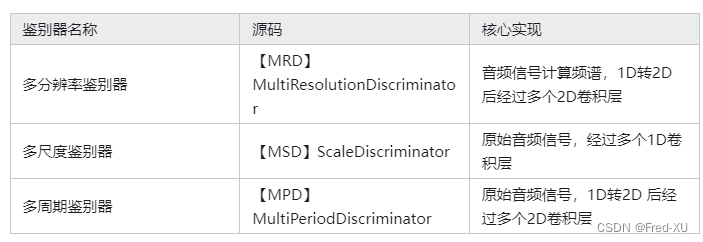
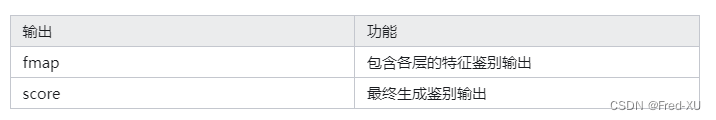
各个鉴别器的输出都包括两类,即各层中间输出和最终结果输出,分别用来计算特征损失和生成损失。如下:
1.2、MRD举例

import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.nn.utils import weight_norm, spectral_norm class DiscriminatorR(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, hp, resolution): super(DiscriminatorR, self).__init__() self.resolution = resolution self.LRELU_SLOPE = hp.mpd.lReLU_slope norm_f = weight_norm if hp.mrd.use_spectral_norm == False else spectral_norm self.convs = nn.ModuleList([ norm_f(nn.Conv2d(1, 32, (3, 9), padding=(1, 4))), norm_f(nn.Conv2d(32, 32, (3, 9), stride=(1, 2), padding=(1, 4))), norm_f(nn.Conv2d(32, 32, (3, 9), stride=(1, 2), padding=(1, 4))), norm_f(nn.Conv2d(32, 32, (3, 9), stride=(1, 2), padding=(1, 4))), norm_f(nn.Conv2d(32, 32, (3, 3), padding=(1, 1))), ]) self.conv_post = norm_f(nn.Conv2d(32, 1, (3, 3), padding=(1, 1))) def forward(self, x): fmap = [] # 获取频谱,这里是做了窗口傅里叶变换 # 傅里叶变换时,频谱数量、窗口的移动、窗口大小由参数 resolution 决定 x = self.spectrogram(x) x = x.unsqueeze(1) for l in self.convs: # 与其他鉴别器一样经过conv-1d 和 leak-relue 形成中间层特征 x = l(x) x = F.leaky_relu(x, self.LRELU_SLOPE) # 中间层特征被保存在 fmap 中 fmap.append(x) x = self.conv_post(x) fmap.append(x) x = torch.flatten(x, 1, -1) # 返回各层的中间层特征 fmap 和 最终输出 x return fmap, x def spectrogram(self, x): n_fft, hop_length, win_length = self.resolution x = F.pad(x, (int((n_fft - hop_length) / 2), int((n_fft - hop_length) / 2)), mode='reflect') x = x.squeeze(1) x = torch.stft(x, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=win_length, center=False, return_complex=False) #[B, F, TT, 2] mag = torch.norm(x, p=2, dim =-1) #[B, F, TT] return mag class MultiResolutionDiscriminator(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, hp): super(MultiResolutionDiscriminator, self).__init__() self.resolutions = eval(hp.mrd.resolutions) self.discriminators = nn.ModuleList( [DiscriminatorR(hp, resolution) for resolution in self.resolutions] ) def forward(self, x): ret = list() # 这里做了一个不同尺度的 DiscriminatorR """ 在 base.yml 中 mrd 的参数如下,有四个不同的尺度: mrd: resolutions: "[(1024, 120, 600), (2048, 240, 1200), (4096, 480, 2400), (512, 50, 240)]" # (filter_length, hop_length, win_length) use_spectral_norm: False lReLU_slope: 0.2 """ for disc in self.discriminators: ret.append(disc(x)) return ret # [(feat, score), (feat, score), (feat, score)]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
2.GPT-SOVITS 鉴别器
2.1、主要更改
GPT-SOVITS 鉴别器结构与 SOVITS基本类似,只是去除了多分辨率鉴别器,其余基本一样,包括多周期鉴别器的尺度也是 2, 3, 5, 7, 11。其返回结果也包含最终【生成鉴别结果】和各层输出【特征鉴别结果】两类。
class MultiPeriodDiscriminator(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, use_spectral_norm=False): super(MultiPeriodDiscriminator, self).__init__() periods = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11] discs = [DiscriminatorS(use_spectral_norm=use_spectral_norm)] discs = discs + [ DiscriminatorP(i, use_spectral_norm=use_spectral_norm) for i in periods ] self.discriminators = nn.ModuleList(discs) def forward(self, y, y_hat): y_d_rs = [] y_d_gs = [] fmap_rs = [] fmap_gs = [] for i, d in enumerate(self.discriminators): y_d_r, fmap_r = d(y) # 原始音频输入,返回鉴别结果 y_d_g, fmap_g = d(y_hat) # 推测音频输入,返回鉴别结果 y_d_rs.append(y_d_r) y_d_gs.append(y_d_g) fmap_rs.append(fmap_r) fmap_gs.append(fmap_g) return y_d_rs, y_d_gs, fmap_rs, fmap_gs- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
2.2、损失函数
y_d_hat_r, y_d_hat_g, fmap_r, fmap_g = net_d(y, y_hat) with autocast(enabled=False): loss_mel = F.l1_loss(y_mel, y_hat_mel) * hps.train.c_mel loss_kl = kl_loss(z_p, logs_q, m_p, logs_p, z_mask) * hps.train.c_kl loss_fm = feature_loss(fmap_r, fmap_g) loss_gen, losses_gen = generator_loss(y_d_hat_g)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
如前文所述,这里特征损失基于各层输出,计算逻辑在 feature_loss
def feature_loss(fmap_r, fmap_g): loss = 0 for dr, dg in zip(fmap_r, fmap_g): for rl, gl in zip(dr, dg): rl = rl.float().detach() gl = gl.float() loss += torch.mean(torch.abs(rl - gl)) return loss * 2- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
最终生成损失判别基于最终结果,计算逻辑在 generator_loss
def generator_loss(disc_outputs): loss = 0 gen_losses = [] for dg in disc_outputs: dg = dg.float() l = torch.mean((1 - dg) ** 2) gen_losses.append(l) loss += l return loss, gen_losses- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
-
相关阅读:
【C++】类和对象的知识点
2022.11组队学习——跨模态视频搜索VCED
一种HNR与路由交换设备间信令协议的设计与实现
linux-文件服务
【Windows】手动配置静态IPv4
Android 12.0 framework层设置后台运行app进程最大数功能实现
地标识别易语言代码
文未有福利 | 接口自动化你不懂?听HttpRunner的作者怎么说
AntDesignVue动态创建下拉菜单
图像处理:坐标变换
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Fredric_2014/article/details/136788619
