-
java继承和重写(代码演示)
java中的继承和重写
概念
继承
在 Java 中,继承是面向对象编程中的重要概念,它允许一个类(称为子类)继承另一个类(称为父类)的属性和方法。子类可以继承父类的非私有属性和方法,并且可以添加新的属性和方法,或者重写父类的方法。
重写
重写是指子类重新定义父类中已有的方法。当子类需要修改父类中的方法实现时,可以通过重写来实现。重写的方法必须具有相同的名称、参数列表和返回类型。在子类中使用 @Override注解可以帮助编译器检查是否正确地重写了父类的方法。
代码演示
定义三个类,person,student,test
其中令student继承person
然后重写student中继承父类的方法
使用test来进行输出测试观察
person
public class person { public int age=18; public String name="order"; public void talk(){ System.out.println("person talked"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
student
public class student extends person { public String name="liu"; public int score=99; public void talk(){ System.out.println("student talked"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
test
public class test { public static void main(String[] args){ student stu1 = new student(); stu1.talk(); System.out.println(String.valueOf(stu1.age)+" "+String.valueOf(stu1.score)+" "+stu1.name); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
首先令student继承person,新增一个score的属性
并且不给name属性赋值
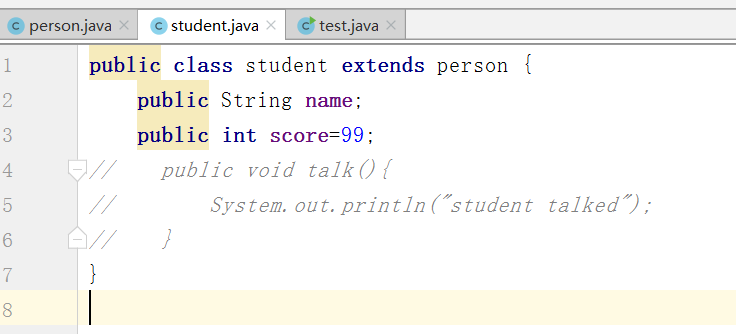
使用test输出看看结果
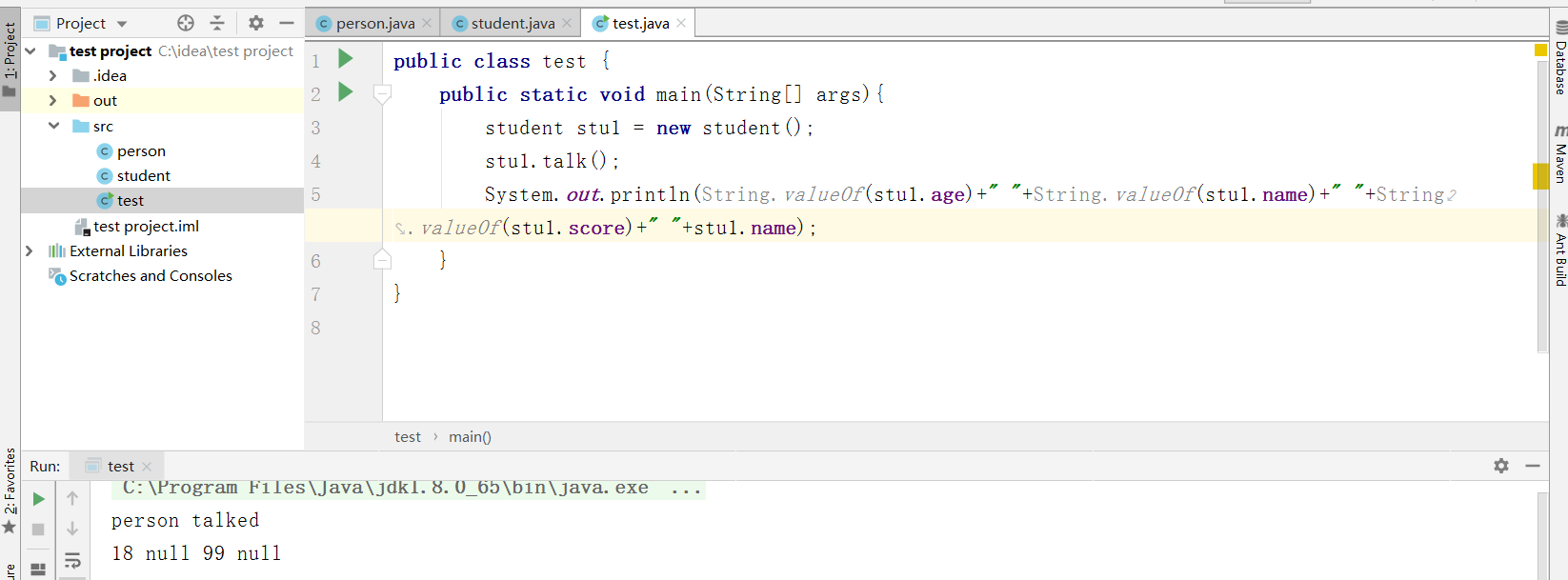
会发现,定义属性但是不赋值的话,输出值为空,但是如果不定义的属性就会继承父类的值
在student中重写talk方法
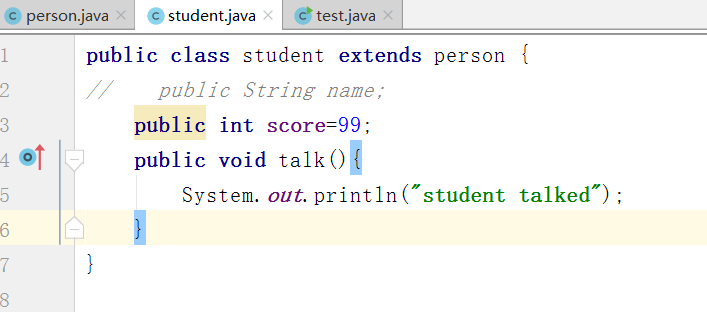
test输出测试就会发现执行了重写后的方法
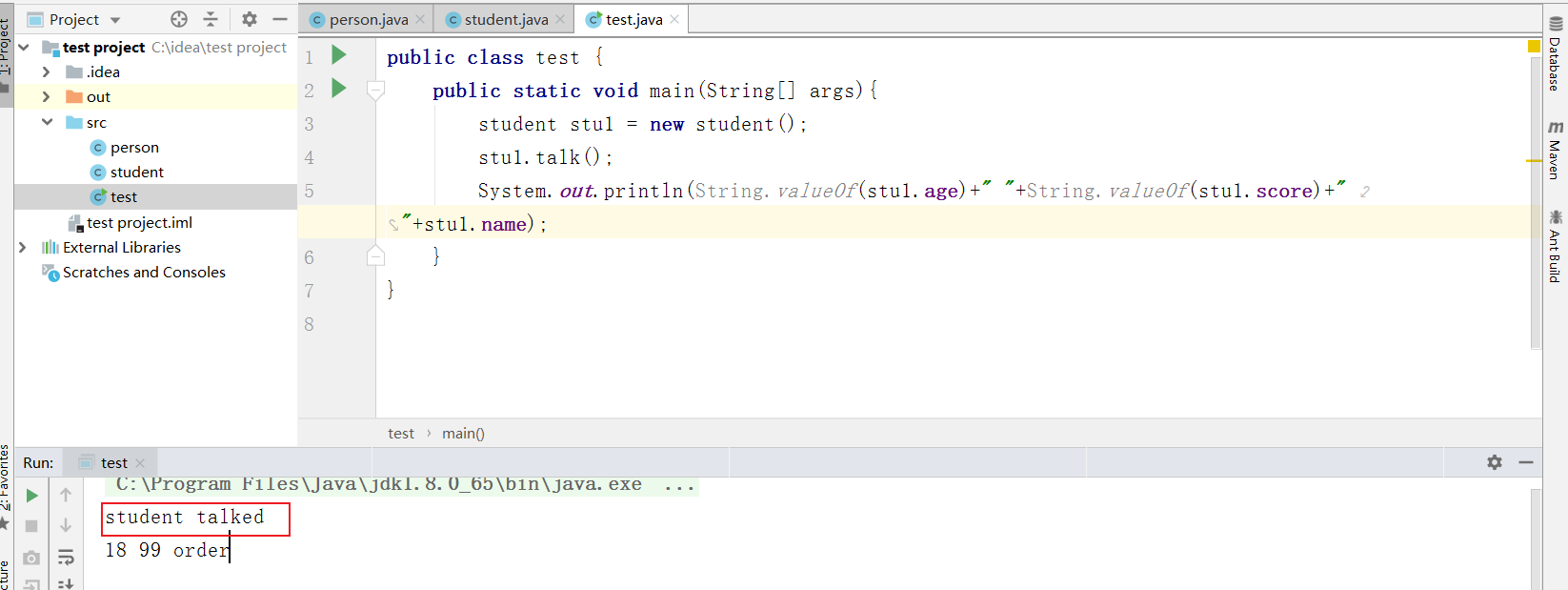
-
相关阅读:
【王道数据结构】第三章 栈和队列
C++内存模型与名称空间总结,看这一篇就够了
9.20华为机试-后端
串口数据包收发
服务端如何推送消息给客户端?
【Java基础】ArrayList类概述、常用方法及存储字符串并遍历
一次 MDIO 配置 switch 的调试过程,88e1512 switch mv88e6xxx
【C++设计模式】(五)创建型模式 — 建造者模式
月子会所信息展示服务预约小程序的作用是什么
(面试)SpringBoot启动原理-源码(深入)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_58683895/article/details/134558446