-
在SpringBoot中使用EhCache缓存
在使用EhCache缓存之前,我们需要了解的是EhCache缓存是啥?
Ehcache的概述
Ehcache是一个开源的Java缓存框架,用于提供高效的内存缓存解决方案,他可以用于缓存各种类型的数据,包括对象,查询结果,方法调用的结果等。
Ehcache具有以下特点:
- 内存缓存:Ehcache主要用于将数据存储在内存中,用以提供更快速的访问速度,他使用内存管理技术,可以有效的管理缓存中的对象。
- 可拓展性:Ehcache支持分布式缓存,可以在多个节点上部署,用以提供更高的容量和吞吐量,它还支持缓存的持久化,可以将缓存数据写入磁盘,以防止数据丢失。
- 灵活的配置选项:Ehcache提供了丰富的配置选项,可以根据应用程序的需求进行灵活的配置。可以通过设置缓存的大小,过期时间啊,淘汰策略等等。
- 支持缓存策略:Ehcache支持多种缓存策略,包括LRU(最近最少使用)、LFU(最不经常使用)、FIFO(先进先出)等。你可以根据数据的访问模式选择适合的缓存策略。
- 与Spring集成:Ehcache可以与Spring框架无缝集成,通过简单的配置即可在Spring应用程序中使用。它还支持与其他Java框架的集成,如Hibernate、MyBatis等。
在Spring Boot中,当我们使用缓存功能的时候,Spring Boot中自动侦测可用的缓存提供者,Spring Boot有按照相关的顺序进行缓存提供者侦测:
Generic:Spring Boot首先尝试使用通用的缓存抽象,即org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口的实现。这个抽象可以适用于多种缓存提供者,如Ehcache、Caffeine、Redis等。JCache (JSR-107):如果没有找到通用的缓存提供者,Spring Boot会尝试使用JCache标准(JSR-107)的实现。JCache是Java EE的一部分,定义了一套缓存API和规范。Ehcache 2.x:如果没有找到JCache的实现,Spring Boot会尝试使用Ehcache 2.x作为缓存提供者。Ehcache是一个流行的Java缓存框架,它提供了丰富的功能和配置选项。Hazelcast:如果没有找到Ehcache 2.x,Spring Boot会尝试使用Hazelcast作为缓存提供者。Hazelcast是一个开源的分布式缓存和计算平台,它提供了高性能和可扩展性。Infinispan:如果没有找到Hazelcast,Spring Boot会尝试使用Infinispan作为缓存提供者。Infinispan是一个高度可扩展的分布式缓存平台,它支持多种缓存模式和数据分布策略。Couchbase:如果没有找到Infinispan,Spring Boot会尝试使用Couchbase作为缓存提供者。Couchbase是一个面向文档的NoSQL数据库,它也提供了缓存功能。Redis:如果没有找到Couchbase,Spring Boot会尝试使用Redis作为缓存提供者。Redis是一个高性能的键值存储数据库,它也可以用作缓存。Caffeine:如果没有找到Redis,Spring Boot会尝试使用Caffeine作为缓存提供者。Caffeine是一个基于Java的高性能缓存库,它提供了快速的内存缓存解决方案。
除了按照以上顺序侦测外,我们可以通过配置属性
spring.cache.type来强制指定,假设没有强制指定,那么我们该如何知道我们当前使用了什么缓存呢?很简单此时debug就派上用场了,我们可以通过debug去查看cacheManager对象的实例来判断当前使用了什么缓存。当我们不指定具体的第三方的缓存时候,Spring Boot的Cache模块会使用ConcurrentHashMap来存储,而实际生产使用的时候,因为我们可以可能需要更多其他特性,往往就会采用其他缓存框架。
使用EhCache
引入相关依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>net.sf.ehcachegroupId> <artifactId>ehcacheartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <scope>providedscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
在application.yml中配置我们需要的配置:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.jpa.show-sql=true spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
创建一个实体类:
@Entity //@Data //@NoArgsConstructor public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long id; private String name; private Integer age; public User(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public User() { } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
User实体类的数据访问(内部含缓存注解)
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "users") public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> { @Cacheable User findByName(String name); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
在resources目录下创建一个ehcache.xml文件
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="ehcache.xsd"> <cache name="users" maxEntriesLocalHeap="200" timeToLiveSeconds="600"> cache> ehcache>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
创建一个测试类,单元测试
@Slf4j @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ApplicationTests { @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; @Autowired private CacheManager cacheManager; @Test public void test() throws Exception { System.out.println("CacheManager type : " + cacheManager.getClass()); // 创建1条记录 userRepository.save(new User("AAA", 10)); User u1 = userRepository.findByName("AAA"); System.out.println("第一次查询:" + u1.getAge()); User u2 = userRepository.findByName("AAA"); System.out.println("第二次查询:" + u2.getAge()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
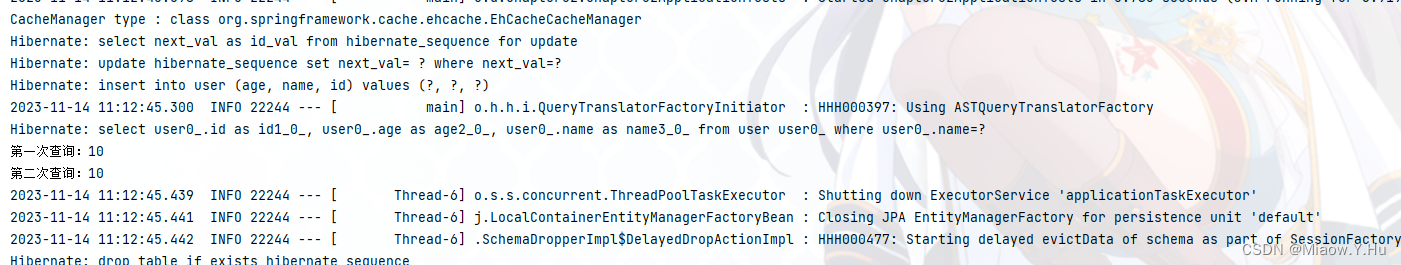
至此,我们可以看到第一行:CacheManager type : class org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager,并且第二次查询的时候,并没有输出SQL语句,所以走的事缓存获取。 -
相关阅读:
子数组的最小值之和(java)
SaaSBase:什么是探马SCRM?
如何利用ChatGPT进行论文撰写?
Python、C、C扩展、Cython 差异对比,98%的人都不知道
6款好用到爆的神级电脑软件,个个让人相见恨晚,堪称办公必备
在RT-Thread下为MPU手搓以太网MAC驱动-3
【JAVA】 Java 性能比较差的代码写法及替换方案
Python线程和进程
spring源码1--自定义Autowired实现
[NLP Begin] Classical NLP Methods - HMM
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45922256/article/details/134393583
