-
Springboot监控
1. 监控的理解
什么是监控?就是通过软件的方式展示另一个软件的运行情况,运行的情况则通过各种各样的指标数据反馈给监控人员。例如网络是否顺畅、服务器是否在运行、程序的功能是否能够整百分百运行成功,内存是否够用,等等等等。
这里的监控就是对软件的运行情况进行监督,但是springboot程序与非springboot程序的差异还是很大的,为了方便监控软件的开发,springboot提供了一套功能接口,为开发者加速开发过程。
一般来说我们监控如下信息:- 监控服务状态是否处于宕机状态
- 监控服务运行指标
- 监控程序运行日志
- 管理服务状态
2. Actuator
Actuator是spring boot的一个附加功能,可帮助你在应用程序生产环境时监视和管理应用程序。可以使用HTTP的各种请求来监管,审计,收集应用的运行情况。Spring Boot Actuator提供了对单个Spring Boot的监控,信息包,含:应用状态、内存、线程、堆栈等等,比较全面的监控了Spring Boot应用的整个生命周期。特别对于微服务管理十分有意义。
Actuator监控分成两类:原生端点和用户自定义端点;自定义端点主要是指扩展性,用户可以根据自己的实际应用,定义一些比较关心的指标,在运行期进行监控。
原生端点是在应用程序里提供众多Web接口,通过它们了解应用程序运行时的内部状况。
原生端点又可以分成三类:- 应用配置类:可以查看应用在运行期的静态信息:例如自动配置信息、加载的
springbean信息、yml文件配置信息、环境信息、请求映射信息; - 度量指标类:主要是运行期的动态信息,例如堆栈、请求链、一些健康指标、metrics信息等;
- 操作控制类:主要是指shutdown,用户可以发送一个请求将应用的监控功能关闭。
Actuator提供了13个接口,具体如下表所示。



2.1 体验Actuator
使用Actuator功能与springBoot使用其他功能一样简单,只需要在pom.xml中添加如下依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
为了保证actuator暴露的监控接口的安全性,需要添加安全控制的依赖spring-boot-
start-security依赖,访问应用监控端点时,都需要输入验证信息。Security依赖,可以
选择不加,不进行安全管理。配置文件
#展示细节,除了always还有when-authorized,never,默认值是never management.endpoint.health.show-details= always #开放所有接口 management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=* # 自定义信息 和接口/info相对应 要求是以info开头 info.app.name =spring-boot-actuator info.app.version =1.1.0 info.app.test = test #改变监控指标的路径 将 /actuator/ 自定义为 /monitor management.endpoints.web.base-path=/monitor- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
配置完成之后,启动项目就可以继续验证各个监控功能了。
2.2属性详解
在Spring Boot2.x中为了安全期间,Actuator只开放了两个端点/actuator/health和
/actuator/info。可以在配置文件中设置打开。默认情况下
management.endpoint.health.show-details= always 可展示健康的详细信息

配置了以info开头的自定义信息之后显示如下info.app.name =spring-boot-actuator info.app.version =1.1.0 info.app.test = test- 1
- 2
- 3

可以打开所有的监控点management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*- 1
也可以选择打开部分
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include= beans,trace- 1
Actuator默认所有的监控点路径都在/actuator/*,当然如果有需要这个路径也支持定制。
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/monitor- 1
设置完重启后,再次访问地址就会变成/monitor/*
Actuator几乎监控了应用涉及的方方面面,我们重点讲述一些经常在项目中常用的属性。- health
health主要用来检查应用的运行状态,这是我们使用最高频的一个监控点。通常使用此接口
提醒我们应用实例的运行状态,以及应用不”健康“的原因,比如数据库连接、磁盘空间不够默认情况下health的状态是开放的,添加依赖后启动项目,:需要添加
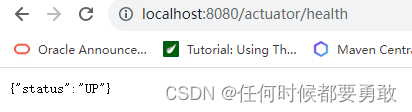
management.endpoint.health.show-details= always 可展示健康的详细信息- 1
访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
health通过合并几个健康指数检查应用的健康情况。Spring Boot Actuator有几个预定义的健
康指标比如DataSourceHealthIndicator,DiskSpaceHealthIndicator,
MongoHealthIndicator,RedisHealthIndicator等,它使用这些健康指标作为健康检查的一部分。举个例子,如果你的应用使用Redis,RedisHealthindicator将被当作检查的一部分;
如果使用MongoDB,那么MongoHealthIndicator将被当作检查的一部分。可以在配置文件中关闭特定的健康检查指标,比如关闭redis的健康检查:
management.health.redis.enabled=false- 1
默认,所有的这些健康指标被当作健康检查的一部分。
- info
info就是我们自己配置在配置文件中以info开头的配置信息,比如我们在示例项目中的配置
是:
info.app.name =spring-boot-actuator info.app.version =1.1.0 info.app.test = test- 1
- 2
- 3
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/info返回部分信息如下:

3. beans
根据示例就可以看出,展示了bean的别名、类型、是否单例、类的地址、依赖等信息。
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
4. mappings
描述全部的uri路径,以及它们和控制器的映射关系 访问路径http://localhost:8080/actuator/mappings-
threaddump
/threaddump接口会生成当前线程活动的快照。这个功能非常好,方便我们在日常定位问题
的时候查看线程的情况。主要展示了线程名、线程D、线程的状态、是否等待锁资源等信
息。http://localhost:8080/actuator/threaddump
生产出现问题的时候,可以通过应用的线程快照来检测应用正在执行的任务 -
heapdump
返回一个GZip压缩的JVM堆dump
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/heapdump会自动生成一个
Jvm的堆文件heapdump,我们可以使用JDK自带的Jvm监控工具VisualVM打开此文件查
看内存快照。 -
conditions
Spring Boot的自动配置功能非常便利,但有时候也意味着出问题比较难找出具体的原因
使用conditions可以在应用运行时查看代码了某个配置在什么条件下生效,或者某个自动配
置为什么没有生效。查看路径 http://localhost:8080/actuator/conditions -
shutdown
开启接口优雅关闭Spring Boot应用,要使用这个功能首先需要在配置文件中开启:
management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true- 1
配置完成之后,启动示例项目,使用curl模拟post请求访问shutdown接口。

或者直接使用postman Post方式 请求 接口http://localhost:8080/actuator/shutdown
3.springboot Admin监控服务端
什么是Spring Boot Admin
Spring Boot Admin,这是一个开源社区项目,用于管理和监控SpringBoot应用程序。这个
项目中包含有客户端和服务端两部分,而监控平台指的就是服务端。我们做的程序如果需要
被监控,将我们做的程序制作成客户端,然后配置服务端地址后,服务端就可以通过HTTP
请求的方式从客户端获取对应的信息,并通过UI界面展示对应信息。下面就来开发这套监控程序,先制作服务端,其实服务端可以理解为是一个web程序,
收到一些信息后展示这些信息。3.1 服务端开发
- 导入springboot admin对应的starter,.版本与当前使用的springboot版本保持一致,并将其
配置成web工程
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId> <version>2.7.1version> <relativePath/> parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>de.codecentricgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-serverartifactId> <version>2.7.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- application.yml中配置
server: port: 9111 spring: boot: admin: ui: #服务端标题 title: 监控 client: instance: metadata: tags: environment: local #要获取的client的端点信息 可写可不写 probed-endpoints: health,env,metrics,httptrace:trace,threaddump:dump,jolokia,info,logfile,refresh,flyway,liquibase,heapdump,loggers,auditevents monitor: # 监控发送请求的超时时间 default-timeout: 20000 security: # 设置账号密码 user: name: admin password: admin # 服务端点详细监控信息 #management: # trace: # http: # enabled: true # endpoints: # web: # exposure: # include: "*" # endpoint: # health: # show-details: always- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 主启动类中配置
@SpringBootApplication @EnableAdminServer public class SpringbootServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootServerApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 业务类
springsecurity配置类
@Configuration public class SecuritySecureConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { private final String adminContextPath; public SecuritySecureConfig(AdminServerProperties adminServerProperties) { this.adminContextPath = adminServerProperties.getContextPath(); } @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // 登录成功处理类 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler = new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler(); successHandler.setTargetUrlParameter("redirectTo"); successHandler.setDefaultTargetUrl(adminContextPath + "/"); http.authorizeRequests() //静态文件允许访问 .antMatchers(adminContextPath + "/assets/**").permitAll() //登录页面允许访问 .antMatchers(adminContextPath + "/login", "/css/**", "/js/**", "/image/*").permitAll() //其他所有请求需要登录 .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() //登录页面配置,用于替换security默认页面 //.formLogin().loginPage(adminContextPath + "/login").successHandler(successHandler).and() //登出页面配置,用于替换security默认页面 //.logout().logoutUrl(adminContextPath + "/logout").and() .httpBasic().and() .csrf() .csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse()) .ignoringAntMatchers( "/instances", "/actuator/**" ); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
服务掉线的状态提醒
@Component public class WarnNotifier extends AbstractStatusChangeNotifier { public WarnNotifier(InstanceRepository repository) { super(repository); } @Override protected Mono<Void> doNotify(InstanceEvent event, Instance instance) { // 服务名 String serviceName = instance.getRegistration().getName(); // 服务url String serviceUrl = instance.getRegistration().getServiceUrl(); // 服务状态 String status = instance.getStatusInfo().getStatus(); // 详情 Map<String, Object> details = instance.getStatusInfo().getDetails(); // 当前服务掉线时间 Date date = new Date(); SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); String format = simpleDateFormat.format(date); // 拼接短信内容 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); str.append("服务名:【" + serviceName + "】 \r\n"); str.append("服务状态:【"+ status +"】 \r\n"); str.append("地址:【" + serviceUrl + "】\r\n"); str.append("时间:" + format +"\r\n"); return Mono.fromRunnable(()->{ // 这里写你服务发生改变时,要提醒的方法 // 如服务掉线了,就发送短信告知 }); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
3.2客户端的配置
- 依赖
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId> <version>2.7.1version> <relativePath/> parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>de.codecentricgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-clientartifactId> <version>2.7.1version> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 配置
server: port: 9222 spring: application: name: demo5 boot: admin: client: # spring-boot-admin 客户端配置 url: http://localhost:9111 #服务端连接地址 username: admin # 服务端账号 password: admin # 服务端密码 instance: prefer-ip: true # 服务端点详细监控信息 management: # health: # 检测服务状态是通过http://localhost:9111/actuator/health接口,可去掉不用检测项 # mail: # 健康检测时,不要检测邮件 # enabled: false trace: http: enabled: true endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*" endpoint: health: show-details: always logfile: # 日志(想在线看日志才配) external-file: ./logs/client-info.log # 日志所在路径- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
配置完成启动服务即可
之后访问http://localhost:服务端端口号/applications -
相关阅读:
3.2 Keepalived安装部署
【Xilinx】Zynq\MPSoc\Versal不同速度等级下的ARM主频
【LeetCode刷题-数组】--27.移除元素
防止PDF 盗版
asp毕业设计——基于asp+sqlserver的工厂设备管理系统设计与实现(毕业论文+程序源码)——工厂设备管理系统
基于Java毕业设计游泳馆管理平台源码+系统+mysql+lw文档+部署软件
Towards a Rigorous Evaluation of Time-series Anomaly Detection(论文翻译)
「前端+鸿蒙」核心技术HTML5+CSS3(十)
【HarmonyOS开发】设备调试避坑指南
线程的状态
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wyr1235/article/details/134380389
