-
Elasticsearch(十五)搜索---搜索匹配功能⑥--基于地理位置查询
一、前言
随着互联网+的热门,越来越多的传统行业将全部或者部分业务转移到互联网上,其中不乏一些和地理位置强相关的行业。基于地理位置的搜索功能,大大提升了人们的生活和工作效率。例如,外出旅行时,只需要用手机打开订酒店的应用软件,查找附近心仪的酒店下单即可;又或者打车行业,人们不用在寒冷的户外拦截出租车,只需要在室内打开打车APP定位到当前位置,然后确定目的地,系统就可以为附近的车辆派发订单。
幸运的是,ES为用户提供了基于地理位置的搜索功能。它主要支持两种类型的地理查询:一种是地理点(geo_point),即经纬度查询,另一种是地理形状查询(geo_shape),即支持点、线、圆形和多边形查询等。
从实用性来说,地理点(即geo_point)数据类型的使用的更多一些,本节也只对地理点类型进行介绍。
对应于geo_point字段类型的查询方式有3种,分别为geo_distance查询、geo_bounding_box查询和geo_polygon。
为了更方便专一的学习地理搜索,我们在hotel索引批量增加多条文档,内容如下:POST /hotel_location/_doc/_bulk {"index":{"_id":51}} {"title":"连锁酒店1","location":{"lat":"40.17836693398477","lon":"116.64002551005981"}} {"index":{"_id":52}} {"title":"连锁酒店2","location":{"lat":"40.19103839805197","lon":"116.5624013764374"}} {"index":{"_id":53}} {"title":"连锁酒店3","location":{"lat":"40.13933715136454","lon":"116.63441990026217"}} {"index":{"_id":54}} {"title":"连锁酒店4","location":{"lat":"40.14901664712196","lon":"116.53067995860928"}} {"index":{"_id":55}} {"title":"连锁酒店5","location":{"lat":"40.125057718315716","lon":"116.62963567059545"}} {"index":{"_id":56}} {"title":"连锁酒店6","location":{"lat":"40.19216257806647","lon":"116.64025980109571"}} {"index":{"_id":57}} {"title":"连锁酒店7","location":{"lat":"40.16371689899584","lon":"116.63095084701624"}} {"index":{"_id":58}} {"title":"连锁酒店8","location":{"lat":"40.146045218040605","lon":"116.5696251832195"}} {"index":{"_id":59}} {"title":"连锁酒店9","location":{"lat":"40.144735806234166","lon":"116.60712460957835"}}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
通过上面的步骤,我们完成了9条经纬度数据的插入;可以通过search语句查询一下结果
二、geo_bounding_box
geo_bounding_box语法又称为地理坐标盒模型,在当前语法中,只需选择一个矩阵范围(输入矩阵的左上角的顶点地理坐标和矩阵的右上角的顶点地理坐标,构建成为一个矩阵),即可计算出当前矩阵中符合条件的元素;

简单来说呢,就是给定两个坐标,通过这两个坐标形成对角线,平行于地球经纬度从而得到的一个矩阵。采用geo_bounding_box语法可以得到坐落于当前矩阵中的元素的信息;
假设如上图我这边给定两个坐标,分别是A(116.498353,40.187328) 和 B(116.610461,40.084509),这样我们就得到了一个矩阵。
ES的geo_bounding_box语法有很多种查询方式,但是需要注意的是我们要确定好哪个是左上角的坐标,哪个是右下角的坐标,并且这两个坐标不能互换。
那上面的例子通过A\B两点去找矩阵范围内的酒店,DSL如下GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_bounding_box": { "location": { "top_left": { "lat": 40.187328, "lon": 116.498353 }, "bottom_right": { "lat": 40.084509, "lon": 116.610461 } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
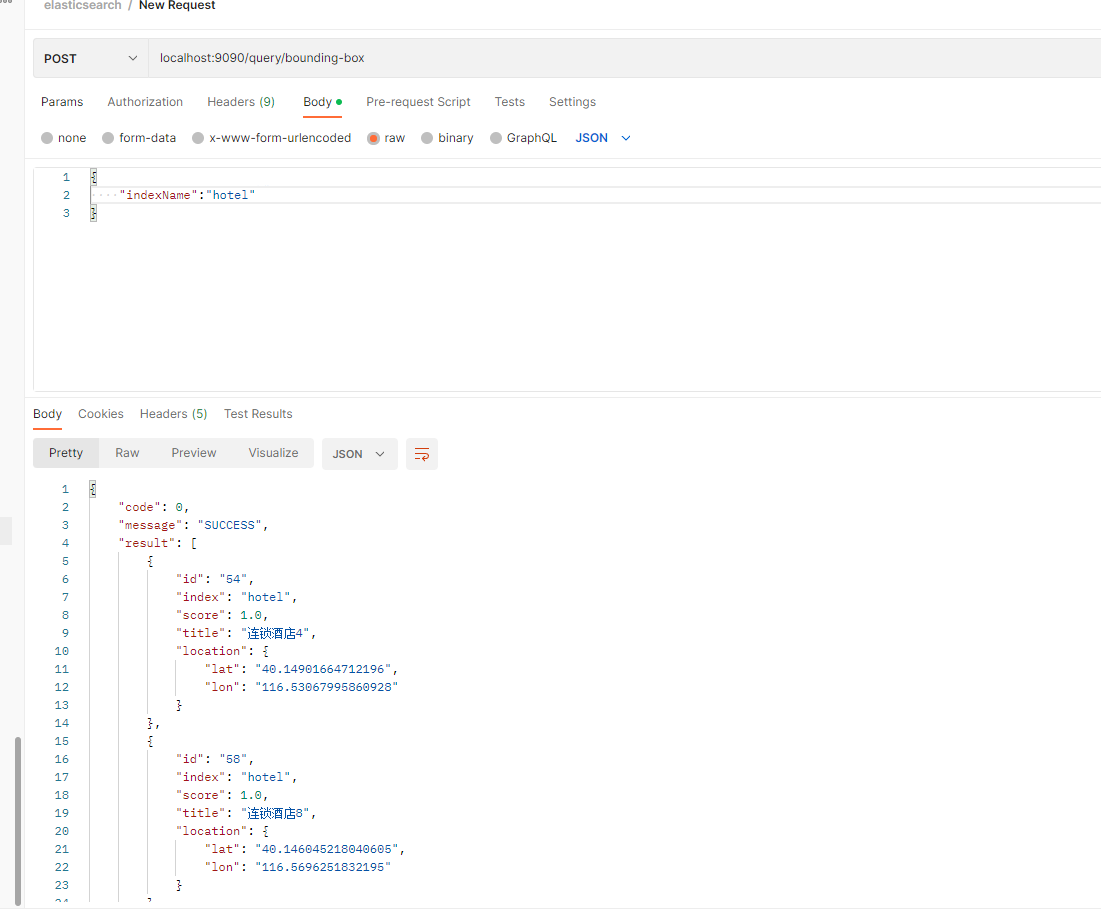
输出如下,可以看到有3家酒店位于这个矩阵范围中:
{ ... "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 3, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.0, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "hotel", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "54", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "title" : "连锁酒店4", "location" : { "lon" : "116.53067995860928", "lat" : "40.14901664712196" } } }, { "_index" : "hotel", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "58", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "title" : "连锁酒店8", "location" : { "lon" : "116.5696251832195", "lat" : "40.146045218040605" } } }, { "_index" : "hotel", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "59", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "title" : "连锁酒店9", "location" : { "lon" : "116.60712460957835", "lat" : "40.144735806234166" } } } ] } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
那么除了上面的查询的DSL语法之外,还有如下语法,获取的结果和上面DSL均相同:
- 基于经纬度数组的DSL语法
需要注意的是,数组形式的,经纬度顺序需调换一下
这样就不需要输入lat和lon了,直接通过数组表示经纬度GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_bounding_box": { "location": { "top_left": [116.498353,40.187328], "bottom_right": [116.610461,40.084509] } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 基于经纬度字符串的DSL语法
字符串不同于数组,经纬度顺序不需要调换
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_bounding_box": { "location": { "top_left": "40.187328,116.498353", "bottom_right": "40.084509,116.610461" } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 基于经纬度边界框WKT的DSL语法
可以看到先是A的经度,再是B的经度,然后是A的纬度,再是B的纬度,通过BBOX封装
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_bounding_box": { "location": { "wkt": "BBOX (116.498353,116.610461,40.187328,40.084509)" } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 基于经纬度GeoHash的DSL语法
//关于GeoHash可以参考两个网址 // 全球GeoHash地图 http://geohash.gofreerange.com/ // GeoHash坐标在线转换 http://geohash.co/ GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_bounding_box": { "location": { "top_left": "wx4udgz", "bottom_right": "wx4uj91" } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 基于经纬度顶点属性的DSL语法
相当于把top_left和bottom_right分成了四个
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_bounding_box": { "location": { "top": 40.187328, "left": 116.498353, "bottom": 40.084509, "right": 116.610461 } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
至此,采用上述6种方式计算的矩阵坐落元素所执行结果均一致,且逐个在地图上核实,所召回的建筑均真实的在上图的矩阵中;
计算某个矩阵或者是多边形中的元素,在Redis中目前是不支持的,在这方面ES表现的更为强大;通过上述的三种语法可以看到,ES可以很好的支持 矩阵、圆、多边形的空间地理检索,通过查看Redis的语法可以看到Redis目前只支持圆的空间地理检索;在java客户端使用
new GeoBoundingBoxQueryBuilder()构造geo_bounding_box请求,我们可以看到它有很多附加的方法

但是我们这次使用的主要是setCorners()设置两点距离,可以看到它支持geoHash,两点坐标,经纬度顶点等查询方法。

我们使用两点坐标来进行查询
Service如下:public List<Hotel> geoBoundingBoxQuery(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException { //新建搜索请求 String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName); SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); // 构造左上点坐标 GeoPoint topLeft = new GeoPoint(40.187328D, 116.498353D); // 构造右下点坐标 GeoPoint bottomRight = new GeoPoint(40.084509D, 116.610461D); GeoBoundingBoxQueryBuilder geoBoundingBoxQueryBuilder = new GeoBoundingBoxQueryBuilder("location") .setCorners(topLeft,bottomRight); searchSourceBuilder.query(geoBoundingBoxQueryBuilder); searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); return getQueryResult(searchRequest); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
这次getQueryResult(),我们需要将结果能够正常返回location这个属性
首先我们建立Location这个类,lat代表纬度,lon代表经度:import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class Location { private String lat; private String lon; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
然后在hotel索引类增加location属性,这个属性名和你建造索引用的是一样的:
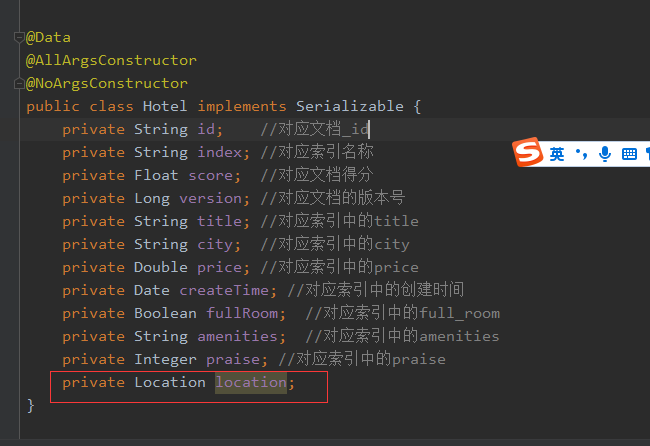
然后对getQueryResult进行改造,因为我们获取到location的json对象其实是类似于hashMap结构的对象,我们可以使用JSONUtil.toJsonStr(location)将其先转化为json字符串,然后通过JSONUtil.toBean(String jsonString,T)转化成我们的目标对象Location。
完整代码如下:private List<Hotel> getQueryResult(SearchRequest searchRequest) throws IOException { ArrayList<Hotel> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); RestStatus status = searchResponse.status(); if (status != RestStatus.OK) { return Collections.emptyList(); } SearchHits searchHits = searchResponse.getHits(); for (SearchHit searchHit : searchHits) { Hotel hotelResult = new Hotel(); hotelResult.setId(searchHit.getId()); //文档_id hotelResult.setIndex(searchHit.getIndex()); //索引名称 hotelResult.setScore(searchHit.getScore()); //文档得分 //转换为Map Map<String, Object> dataMap = searchHit.getSourceAsMap(); hotelResult.setTitle((String) dataMap.get("title")); hotelResult.setCity((String) dataMap.get("city")); Object price = dataMap.get("price"); if (price != null) { hotelResult.setPrice(Double.valueOf((String) price)); } //获取location Object location = dataMap.get("location"); if (location != null) { hotelResult.setLocation(JSONUtil.toBean(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(location), Location.class)); } resultList.add(hotelResult); } return resultList; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
然后回到controller调用:
@PostMapping("/query/bounding-box") public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> geoBoundingBoxQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) { try { List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.geoBoundingBoxQuery(hotelDocRequest); if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) { return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList); } else { return FoundationResponse.error(100,"no data"); } } catch (IOException e) { log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage()); return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage()); return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
postman调用截图:
三、geo_distance
ES中的geo_distance语法与Redis中的georadius语法类似,通过给定一个坐标和半径,圈出圆内的点。在ES可以定义一些排序规则返回召回结果集数据与当前坐标的距离,Redis中默认返回了距离;
与geo_bounding_box语法类似,geo_distance语法也有多种查询方式,如 经纬度属性、经纬度数组、经纬度字符串、GeoHash等,下面就简单的以 经纬度字符串为例进行演示,重新选定坐标,以纬度(116.5864,40.174697)为例,查询3km范围内的酒店GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_distance":{ "distance":"3km", "location":"40.174697,116.5864" } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
查询结果如下:
{ ... "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 1, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.0, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "hotel", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "52", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "title" : "连锁酒店2", "location" : "40.19103839805197,116.5624013764374" } } ] } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
而geo_distance和后面我们的sort排序用的很紧密,例如微信附近的人就可以通过该功能实现,其中结合sort可以返回当前位置与目标位置之间的距离。这个我们后面会介绍。
在Java客户端可以使用new GeoDistanceQueryBuilder()构造geo_distance查询,通过distance()设置以指定坐标点为中心的半径大小以及距离的单位,point()设置指定坐标点,service如下:public List<Hotel> geoDistanceQuery(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException { //新建搜索请求 String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName); SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); // 假设目标距离坐标 GeoPoint sourcePoint = new GeoPoint(40.174697D, 116.5864D); GeoDistanceQueryBuilder geoDistanceQueryBuilder = new GeoDistanceQueryBuilder("location") .distance("3", DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS).point(sourcePoint); searchSourceBuilder.query(geoDistanceQueryBuilder); searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); return getQueryResult(searchRequest); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
controller如下:
@PostMapping("/query/geo-distance") public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> geoDistanceQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) { try { List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.geoDistanceQuery(hotelDocRequest); if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) { return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList); } else { return FoundationResponse.error(100, "no data"); } } catch (IOException e) { log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage()); return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage()); return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
postman截图如下:

四、geo_polygon
ES的geo_polygon语法,可以通过指定多个坐标点,从而构成一个多边形,然后从当前多边形中召回坐落其中的元素进行召回;在当前语法中,最少需要3个坐标,从而构成一个多边形;
例如我在ES增加一个我公司的坐标(121.530533,31.085692)

POST /hotel/_doc/031 { "title":"上海闵行浦江智谷","location":{"lat":"31.085692","lon":"121.530533"} }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
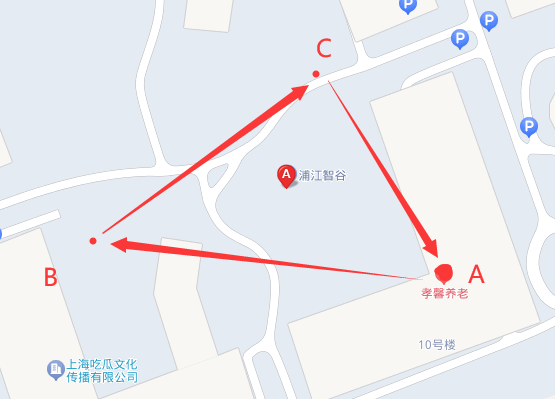
然后可以指定3个坐标,将公司位置坐落于这三个坐标中,看看公司位置是否可以检索出来,3个坐标在地图上的展示如下
坐标点A:(121.531257,31.085262)
坐标点B:(121.529694,31.085494)
坐标点C:(121.530632,31.086252)
ES的geo_polygon语法也支持多种语法,如 经纬度数组、经纬度字符串、GeoHash值等;这里就采用字符串演示了,另外两种语法不再赘述;其执行DSL如下
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_polygon": { "location": { "points": [ "31.085262,121.531257", "31.085494, 121.529694", "31.086252, 121.530632" ] } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
结果如下:
{ ... "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 1, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.0, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "hotel", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "031", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "title" : "上海闵行浦江智谷", "location" : { "lat" : "31.085692", "lon" : "121.530533" } } } ] } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
可以看到,通过三个点构建成一个三角形,当目标元素坐落于所构建的形状中,即可很好的将其召回;
到这里,关于ES的geo_point语法已经接近尾声了,简单的了解了一下ES的空间地理支持;下面再新增一种相对复杂一点的地形,看看geo_polygon语法可以很好的支持不。
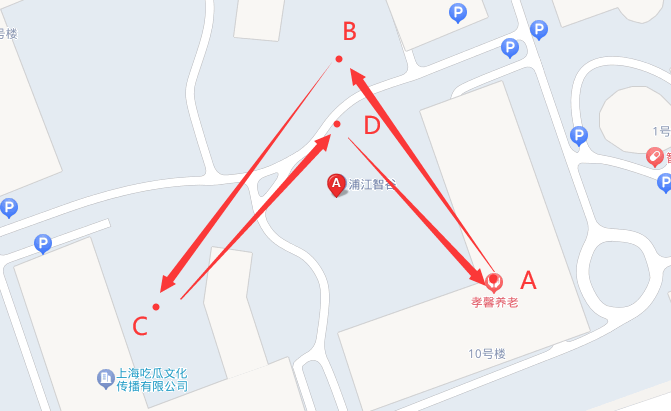
通过刚才的3个坐标,我们新增一个坐标,构建一个凹形的多边形,将目标节点剔除在多边形外,看看ES在这方面的支持如何,最终构建的多边形如下:
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "geo_polygon": { "location": { "points": [ "31.085262,121.531257", "31.086252, 121.530632", "31.085494, 121.529694", "31.085854,121.530524" ] } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
结果没有找到:
需要注意的是,查询语句输入的点的顺序是需要注意的,它会按照你输入的点的顺序构成不同的多边形,从而出现不同的结果,就像我上图那样的使用箭头标注顺序,如果我改变某个点的顺序,有可能就会把目标囊括进去从而和之前结果不一样。
那么在java客户端可以使用new GeoPolygonQueryBuilder ()构造geo_polygon查询,构造方法包含需要查询的字段以及可以接收一个GeoPoint数组,数组就和我们刚才DSL中输入的那些点是一样的,记住要按照顺序放,service如下:public List<Hotel> geoPolygonQuery(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException { //新建搜索请求 String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName); SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); // 假设目标距离坐标 ArrayList<GeoPoint> geoPoints = new ArrayList<GeoPoint>(); GeoPoint sourcePoint1 = new GeoPoint(31.085262D, 121.531257D); GeoPoint sourcePoint2 = new GeoPoint(31.085494D, 121.529694D); GeoPoint sourcePoint3 = new GeoPoint(31.086252D, 121.530632D); geoPoints.add(sourcePoint1); geoPoints.add(sourcePoint2); geoPoints.add(sourcePoint3); GeoPolygonQueryBuilder geoPolygonQueryBuilder = new GeoPolygonQueryBuilder("location", geoPoints); searchSourceBuilder.query(geoPolygonQueryBuilder); searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); return getQueryResult(searchRequest); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
controller如下:
@PostMapping("/query/geo-polygon") public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> geoPolygonQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) { try { List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.geoPolygonQuery(hotelDocRequest); if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) { return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList); } else { return FoundationResponse.error(100, "no data"); } } catch (IOException e) { log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage()); return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage()); return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
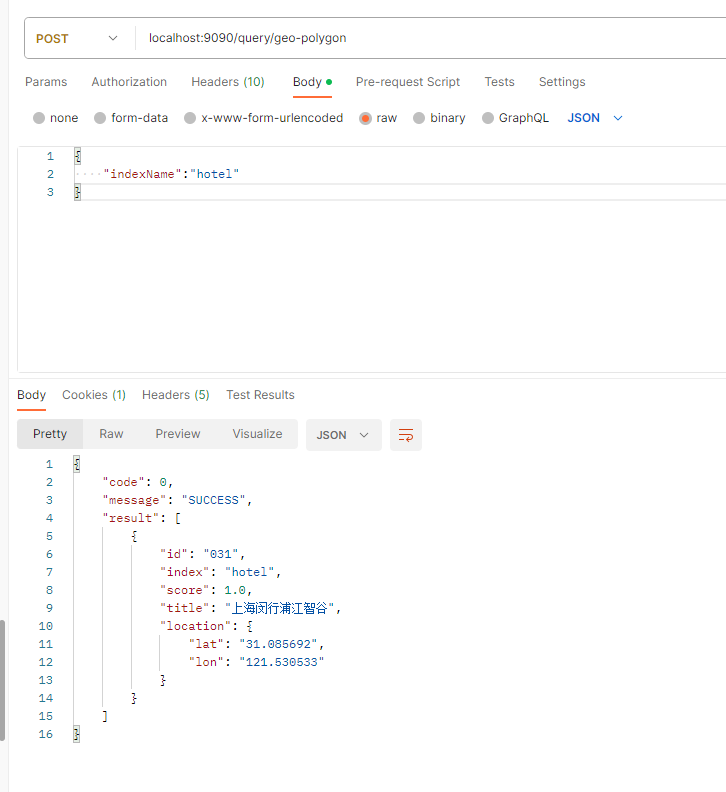
postman执行如下:
-
相关阅读:
SpringBoot 集成Mybatis
css高频面试题
【Go语言】Go语言中的指针
Linux: Swap与swappiness
什么是FD.IO/VPP?
【java】【SSM框架系列】【四】SpringBoot
唤醒桌面应用中休眠的宇宙结构(一)
java课堂互动应答系统mp4计算机毕业设计MyBatis+系统+LW文档+源码+调试部署
ARM术语
java项目-第102期基于ssm的校园二手交易平台-java毕业设计
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44754515/article/details/132472755