-
win10部署 Mistral-7B 文本生成模型
Mistral 7B
date : 2023年10月16日
人工智能创业公司Mistral AI以Apache 2.0授权开源Mistral 7B语言模型,Mistral 7B的特别之处在于其规模较小仅有73亿,但是在所有基准测试上,其表现都优于规模更大的语言模型Llama 2 13B,还具有编写程序代码以及处理8,000个token的能力。
整体来说,Mistral 7B在多个基准测试,包括常识推理、世界知识、阅读理解、数学和程序代码等,表现亮眼,除了明显优于Llama 2 13B之外,也和Llama 34B模型打成平手,其编写程序代码的能力接近CodeLlama 7B,并且在英文任务中表现良好。
在大规模多任务语言理解(MMLU)基准测试上,Mistral 7B的表现相当一个3倍大的Llama 2模型,但是却可大幅节省内存消耗,吞吐量也有所增加,其提供了更高的性价比。
Mistral 7B运用了群组查询注意力(GQA)加快推理速度,还使用滑动窗口注意力(SWA),以更小的成本处理较长的串行。群组查询注意力方法分组多个查询并且同时进行处理,通过这种方式,群组查询注意力机制能够减少重复计算,提高推理速度并降低运算成本。
关于 mistral ai开源的模型
基础模型 mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1
会话模型 mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.14-bit量化模型 Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-GGUF
使用了 Llama.cpp 技术既可以 cpu运行 又可以 GPU运行
不支持中文语言
部署流程
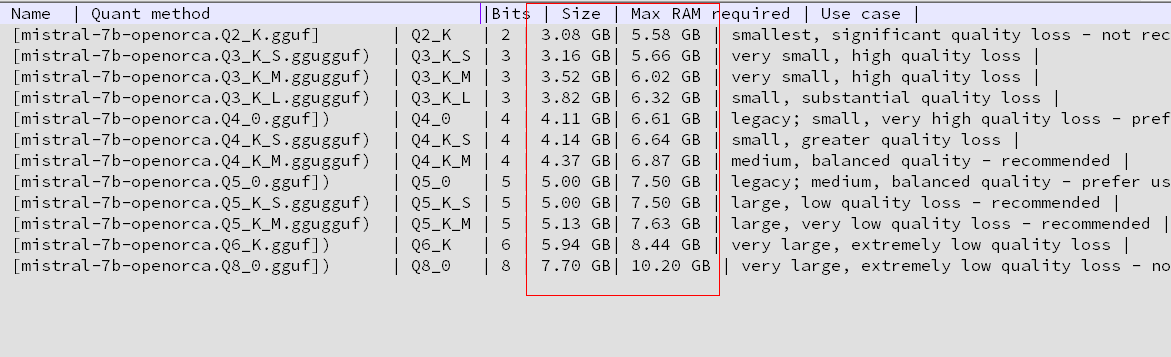
Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-GGUF
 https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-GGUF/tree/main
https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-GGUF/tree/main从上方网址下载合适大小的模型 放到 Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-GGUF/model/mistral-7b-openorca.Q5_K_M.gguf
在一个torch环境中安装 加速库
pip install ctransformers[cuda]CPU版 运行代码 run.py
路径:Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-GGUF/run.py
- from ctransformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
- # Set gpu_layers to the number of layers to offload to GPU. Set to 0 if no GPU acceleration is available on your system.
- # 根据你系统的 GPU 能力,设置 gpu_layers 参数来决定将模型的多少层放置在 GPU 上进行加速运算。如果你的系统无法进行 GPU 加速运算,则将 gpu_layers 参数设置为 0,这样模型将完全在 CPU 上运行。
- llm = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("./model/mistral-7b-openorca.Q5_K_M.gguf", model_file="./model/mistral-7b-openorca.Q5_K_M.gguf", model_type="mistral", gpu_layers=0)
- print(llm("AI is going to"))
GPU 加速运行代码 run.py
路径:Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-GGUF/run.py
- from ctransformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
- # Set gpu_layers to the number of layers to offload to GPU. Set to 0 if no GPU acceleration is available on your system.
- llm = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("./model/mistral-7b-openorca.Q5_K_M.gguf", model_file="./model/mistral-7b-openorca.Q5_K_M.gguf", model_type="mistral", gpu_layers=50)
- print(llm("AI is going to"))
生成效果
有一种黑色幽默的回答风格





用户:AI将
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AI:成为我们生活的一部分,不管我们喜欢与否。随着我们进入一个机器变得更加智能和自主的时代,我们的工作、生活和与他人互动的方式将发生重大变化。
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论人工智能如何改变我们的日常生活,以及可以采取哪些措施来确保技术的安全和负责任地集成。
人工智能及其对各个行业的影响:
1.医疗保健:人工智能已经开始彻底改变医疗保健,帮助医生更准确地诊断疾病,改善患者的预后,甚至帮助药物发现。机器学习算法可以分析大量的医学数据,以识别人类可能看不见的模式。这种能力有助于改善治疗决策、个性化用药和加强患者护理。
2.金融:人工智能正在整个金融部门用于检测欺诈、管理风险、优化投资组合配置,甚至自动化财富管理服务。人工智能聊天机器人也越来越受欢迎,因为它为客户提供即时查询答案,同时协助决策过程。
3.教育:人工智能有潜力通过根据学生的个人需求定制学习体验来改变教育。自适应学习平台可以调整
扩展 GUI版代码
- from ctransformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
- # Set gpu_layers to the number of layers to offload to GPU. Set to 0 if no GPU acceleration is available on your system.
- llm = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("./model/mistral-7b-openorca.Q5_K_M.gguf", model_file="./model/mistral-7b-openorca.Q5_K_M.gguf", model_type="mistral", gpu_layers=0)
- #print(llm("AI is going to"))
- import tkinter as tk
- import torch
- from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
- from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
- import os
- # 获取当前文件所在的目录路径
- current_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
- # 将当前目录和'model'连接起来,获得'model'文件夹的完整路径
- save_path = os.path.join(current_dir, 'creat_history.txt')
- def write_file(text):
- with open(save_path, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
- f.write(text + '\n')
- history=[]
- def answer(question):
- global history
- history=[]
- response = llm(question)
- print(f"Response from model: {response}") # Add this line for debugging
- return response
- # 创建主窗口
- root = tk.Tk()
- root.title("AI")
- root.geometry("800x600+{}+{}".format(root.winfo_screenwidth() // 2 - 400, root.winfo_screenheight() // 2 - 350))
- # 创建输入框和滚动条
- input_frame = tk.Frame(root)
- clear_button = tk.Button(root, text="清空", width=6, height=3)
- def clear_output():
- global history
- output_text.delete("1.0", tk.END)
- history=[]
- clear_button.config(command=clear_output)
- clear_button.pack(side="right", padx=60)
- # 创建输出框和滚动条
- output_frame = tk.Frame(root)
- output_label = tk.Label(output_frame, text="AI:")
- output_text = tk.Text(output_frame, height=26, width=87, padx=6, pady=6)
- output_scrollbar = tk.Scrollbar(output_frame)
- output_text.config(yscrollcommand=output_scrollbar.set)
- output_scrollbar.config(command=output_text.yview)
- output_label.pack(side="left", pady=10)
- output_text.pack(side="left", pady=10)
- output_scrollbar.pack(side="right", fill="y")
- output_frame.pack()
- output_text.tag_config("user", foreground='green')
- output_text.tag_config("ai", background='orange', foreground='white')
- input_label = tk.Label(input_frame, text="用户:")
- input_text = tk.Text(input_frame, height=10, width=67, padx=6, pady=6)
- input_scrollbar = tk.Scrollbar(input_frame)
- input_text.config(yscrollcommand=input_scrollbar.set)
- input_scrollbar.config(command=input_text.yview)
- input_label.pack(side="left")
- input_text.pack(side="left", pady=10)
- input_scrollbar.pack(side="right", fill="y")
- input_frame.pack()
- def show_text():
- # 清空 Tkinter Text 组件中的文本
- # output_text.delete('1.0', 'end')
- question = input_text.get("1.0", "end-1c")
- result = answer(question)
- output_text.insert("end", "用户:" + question, "user")
- output_text.insert("end", "\n" + '-'*78)
- output_text.insert("end", "\nAI:" + result)
- output_text.insert("end", '\n'+"="*78)
- output_text.insert("end", "\n\n\n")
- # 滚动到最底部
- output_text.yview_moveto(1.0)
- input_text.delete('1.0', 'end')
- # 创建按钮
- button_frame = tk.Frame(root)
- button = tk.Button(button_frame, text="回答", command=show_text, width=6, height=3)
- # 响应回车键 绑定
事件 - root.bind("
" , lambda event: show_text()) - def copy():
- global text
- text.event_generate("<
>" ) - def cut():
- global text
- text.event_generate("<
>" ) - def paste():
- global text
- text.event_generate("<
>" ) - # 创建右键菜单
- menu = tk.Menu(root, tearoff=0)
- menu.add_command(label="复制", command=copy)
- menu.add_command(label="剪切", command=cut)
- menu.add_command(label="粘贴", command=paste)
- # 绑定鼠标右键(第一个文本框)
- def show_menu1(event):
- global text
- text = input_text
- menu.post(event.x_root, event.y_root)
- input_text.bind("
" , show_menu1) - # 绑定鼠标右键(第二个文本框)
- def show_menu2(event):
- global text
- text = output_text
- menu.post(event.x_root, event.y_root)
- output_text.bind("
" , show_menu2) - button.pack(side="right", padx=60)
- button_frame.pack()
- root.lift()
- # 运行主循环
- root.mainloop()
-
相关阅读:
DO280分配持久性存储
Charles如何抓取https请求-移动端+PC端,学完不要去做坏事哦
kubernetes 静态存储与动态存储
【web开发】8、Django(3)
python到底是不是数据分析最好的语言
治愈系书单|林曦《只生欢喜不生愁》
mt7981支持leds驱动 - 修改5g led为普通led
Java版本spring cloud + spring boot企业电子招投标系统源代码
使用 Aspose.Words 处理word文件,然后转存pdf预览
java中HashMap的设计精妙在哪?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u013628121/article/details/133856525
