-
【数据结构】迷宫问题DFS非递归(c语言实现)
本来之前写过一个推箱子,就想着写个迷宫游戏,因为想着推箱子游戏里面也有墙,也有玩家的移动,比推箱子简单的是还不用判断前面是否有箱子的情况,但是自己写的迷宫游戏如果自己随机生成的迷宫地图的话,不一定会有通路,他要学一个什么随机迷宫的生成,刚看完懒猫老师的那个迷宫问题使用的是非递归DFS寻找迷宫是否有通路,用的是非递归DFS实现,然后随机迷宫生成用的是DFS递归写的,我真的要成两半了,今天分享给大家的是DFS算法找迷宫是否有出路,这个好像有的会作为数据结构的大作业还是啥的,用c语言实现,参考b站懒猫老师的课迷宫问题
1.问题展示

2.栈的所有有用的函数
因为要用栈实现,所以我们必须将有关栈的函数全部写出来,我们已经之前写过栈的初始化,等等,栈的实现,我们将他拷贝过来,或者你们直接去看我那一篇。
//栈的实现 #include#include #include typedef struct Stack//定义一个栈的结构体变量 { int * a; int top; // 栈顶 int capacity; // 容量 }Stack; void StackInit(Stack* ps) { assert(ps);//断言,防止为空指针 ps->a = NULL;//所指向的地址为空 ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;//容量和栈中元素个数均为0 } void StackPush(Stack* ps, int data) { assert(ps); if (ps->capacity == ps->top)//如果栈中的元素个数等于栈的容量时考虑扩容, { int newcapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;//如果刚开始时都等于0,就先给4个空间大小,后面如果满的话,容量扩大1倍 int* newnode = (int*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(int)* newcapcity);//申请空间,将申请好的空间首地址传给newnode指针 assert(newnode);//断言,防止malloc失败 ps->a = newnode;//将newnode保存的申请空间的首地址传给ps->a,让ps->a指向创建好的空间 ps->capacity = newcapcity;//容量大小更新为新容量大小 } ps->a[ps->top] = data;//像存数组一样存数据 ps->top++;//指向下一个 } // 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top ==0;//ps->top为栈中元素个数.==0栈中无元素,无元素要返回1, 无元素ps->t0p==0,这个表达式结果是1,返回1; } // 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!StackEmpty(ps));//防止栈内无元素,继续出栈 ps->top--; } // 获取栈顶元素 int StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//ps->top为栈中元素个数,由于数组下标是从0开始,所以栈顶元素下标为ps->top-1; } // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top; } // 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a);//free掉动态申请的内存 ps->a = NULL;//防止野指针 ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;//容量和栈中元素个数置为0 } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
但是不能直接用,所以我们必须加以修改,我们会将从入口到出口正确的路径坐标,以及每个坐标对应走向下一个坐标的方向保存在栈里面,由我之前实现的栈中一个元素变为三个元素,栈的实现做出以下改变,int * a,a指针不在指向一个int ,将inta改为proa;pro为结构体类型存放三个元素
typedef struct pro { int x; int y; int di; }pro; typedef struct Stack { pro* a; int top; // 栈顶 int capacity; // 容量 }Stack;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
由于一次压进三个数据,我们要修改入栈函数
void StackPush(Stack* ps, int data1, int data2, int data3)//入栈 { assert(ps); if (ps->capacity == ps->top) { int newcapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2; pro* tmp = (pro*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(pro) * newcapcity); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); } else { ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity = newcapcity; } } ps->a[ps->top].x = data1; ps->a[ps->top].y = data2; ps->a[ps->top].di = data3; ps->top++; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
由于每层由之前一个元素变为三个元素,所以要修改获取栈顶元素函数,返回栈顶地址,然后通过地址来访问三个元素中的每一个
// 获取栈顶元素 pro* StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); return ps->a+ps->top-1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
3.修改后的栈的实现
typedef struct pro { int x; int y; int di; }pro; typedef struct Stack { pro* a; int top; // 栈顶 int capacity; // 容量 }Stack; void StackInit(Stack* ps)//初始化栈 { ps->a = NULL; ps->top = 0; ps->capacity = 0; } void StackPush(Stack* ps, int data1, int data2, int data3)//入栈 { assert(ps); //assert(ps->a); if (ps->capacity == ps->top) { int newcapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2; pro* tmp = (pro*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(pro) * newcapcity); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); } else { ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity = newcapcity; } } ps->a[ps->top].x = data1; ps->a[ps->top].y = data2; ps->a[ps->top].di = data3; ps->top++; } // 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top == 0; } // 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); ps->top--; } // 获取栈顶元素 pro* StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); return ps->a+ps->top-1; } // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top; } // 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = ps->capacity = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
4. 定义二维数组作为迷宫的地图
我们这里将1看做墙,0看做空地可以走的地方,然后迷宫入口坐标为(1,1),我们定义二维数组为M*N的
#define N 10 #define M 10- 1
- 2
迷宫出口坐标为(M-2,N-2);
定义全局变量,方便使用int map[M][N] = { {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1}, {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

黑框标注的分别为入口和出口.
在定义一个结构体,表示要走的方向typedef struct direct { int conx; int cony; }direct;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
在主函数里面定义一个direct类型的数组,数组大小为四,存放上下左右走,坐标的变化,并且将他们赋值
direct des[4]; des[0].conx = 1;//向右走 des[0].cony = 0; des[1].conx = -1;//向左走 des[1].cony = 0; des[2].conx = 0;//向下走 des[2].cony = 1; des[3].conx = 0;//向上走 des[3].cony = -1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

向哪走就给对应坐标+上什么的,比如说我向右走,x+des[0].conx ,y+des[0].cony;5.定义一个栈,将其初始化,当用完时候将其销毁
int main() { direct des[4]; des[0].conx = 1;//向右走 des[0].cony = 0; des[1].conx = -1;//向左走 des[1].cony = 0; des[2].conx = 0;//向下走 des[2].cony = 1; des[3].conx = 0;//向上走 des[3].cony = -1; Stack st; StackInit(&st); StackDestroy(&st); StackDestroy(&scpy); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
6. DFS算法寻找迷宫是否有通路

bool findpath(int map[][N], direct des[], Stack* ps) { int line, col;//表示当前位置能走的下一个位置的坐标 int x, y, di;//表示当前位置的坐标,以及当前位置准备向下一个方向走的方向 int mapcon[M][N] = { 0 };//为了不修改原有的地图,重新创建一个二维数组 for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)//遍历地图,将原地图的二维数组的值拷贝到mapcon中 { for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { mapcon[i][j] = map[i][j]; } } mapcon[1][1] = -1;//走过的地方用-1标记 pro tmp;//保存当前位置的坐标,以及方向 tmp.x = 1; tmp.y = 1; tmp.di = -1;//刚开始在(1,1),将tmp.x,tmp.y赋值为1,刚开始还没有方向tmp.di = -1; StackPush(ps, tmp.x, tmp.y, tmp.di);//将当前位置信息压入st栈中 while (!StackEmpty(ps))//栈中不为空,开始循环 { tmp.x = StackTop(ps)->x; tmp.y = StackTop(ps)->y; tmp.di = StackTop(ps)->di;//获取栈顶元素到tmp中去,以便于回退 StackPop(ps);//出栈操作 x = tmp.x;//当前坐标改为回退之后的坐标 y = tmp.y;//当前坐标改为回退之后的坐标 di = tmp.di + 1;//开始di=0,方向向右 while (di < 4)//遍历当前位置的四个方向 { line = x + des[di].conx;//记录下一个位置的坐标 col = y + des[di].cony;//记录下一个位置的坐标 if (mapcon[line][col] == 0)//如果下一个坐标时0,为空地的话,就可以前进 { tmp.x = x;//保存当前位置坐标,以便于回退 tmp.y = y;//保存当前位置坐标,以便于回退 tmp.di = di;//保存当前位置坐标,以便于回退 StackPush(ps, tmp.x, tmp.y, tmp.di);//当前位置目前确定是通往出口路上的一个坐标,先入栈 x = line;//当前位置更新为下一个位置的坐标 y = col;//当前位置更新为下一个位置的坐标 mapcon[line][col] = -1;//留下足迹,标记为-1; if (x == M - 2 && y == N - 2)//是否到出口 return true;//有通路,跳出 else di = 0;//没到的话,将方向更新为向右 } else di++;//如果当前位置的方向不是空地的话,就换另一个方向判断 } } return false;//循环结束,无通路 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
7. 逆序打印坐标
如果有通路的话, findpath()函数返回1,由于栈是先入后出,所以栈顶元素是出口的坐标,怎么逆序打印从入口到出口的坐标呢?我们可以在创建一个栈,使用栈判空函数循环将st中的元素入栈到另一个栈中,就做到了在原先栈底元素,跑到了新栈的栈顶,实现了逆序打印
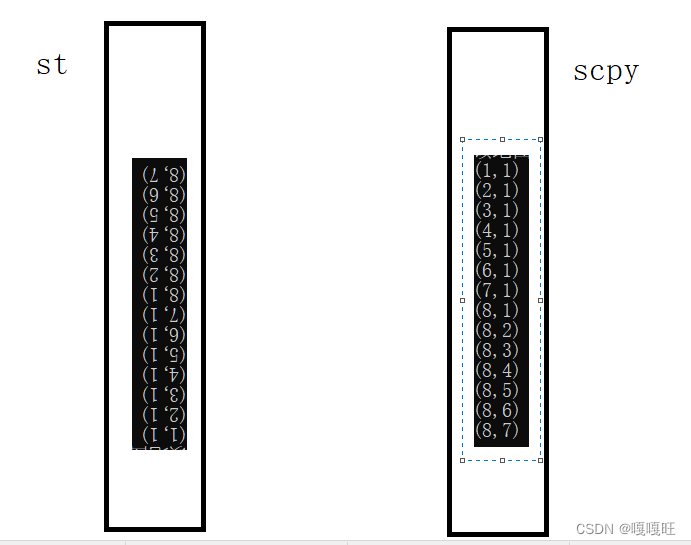
Stack st; Stack scpy;//定义一个栈用于倒翻数据 StackInit(&st); StackInit(&scpy);//新栈初始话 bool ret = findpath(map, des, &st);//返回1,地图有通路 if (ret == 1) { printf("该地图有通路\n"); while (!StackEmpty(&st))//原栈不为空的话 { int num1=StackTop(&st)->x; int num2 = StackTop(&st)->y; int num3= StackTop(&st)->di;//获取旧栈栈顶元素 /*printf("%d-%d ",num1,num2);*/ StackPop(&st);//栈顶元素出st栈 StackPush(&scpy, num1, num2, num3);//栈顶元素入新栈scpy } while (!StackEmpty(&scpy))//新栈scpy不为空, { int num1 = StackTop(&scpy)->x; int num2 = StackTop(&scpy)->y; int num3 = StackTop(&scpy)->di;//获取栈顶元素 printf("(%d,%d)\n", num1, num2);//打印栈顶元素 StackPop(&scpy);//新栈栈顶元素出栈 } } else { printf("该地图无通路\n"); } StackDestroy(&st);//销毁旧栈 StackDestroy(&scpy);//销毁新栈- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
只打印坐标,不要求方向,我就在栈中没画方向.
8.整体代码
#include#include #include #include #define N 10 #define M 10 int map[M][N] = { {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, {1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1}, {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}, }; typedef struct pro { int x; int y; int di; }pro; typedef struct direct { int conx; int cony; }direct; typedef struct Stack { pro* a; int top; // 栈顶 int capacity; // 容量 }Stack; void StackInit(Stack* ps)//初始化栈 { ps->a = NULL; ps->top = 0; ps->capacity = 0; } void StackPush(Stack* ps, int data1, int data2, int data3)//入栈 { assert(ps); //assert(ps->a); if (ps->capacity == ps->top) { int newcapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2; pro* tmp = (pro*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(pro) * newcapcity); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); } else { ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity = newcapcity; } } ps->a[ps->top].x = data1; ps->a[ps->top].y = data2; ps->a[ps->top].di = data3; ps->top++; } // 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top == 0; } // 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); ps->top--; } // 获取栈顶元素 pro* StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); return ps->a+ps->top-1; } // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top; } // 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = ps->capacity = 0; } enum Mine { SPACE, //空地 WALL,//墙 DEST, //目的地 PLAYER//玩家 }; bool findpath(int map[][N], direct des[], Stack* ps) { int line, col; int x, y, di; int mapcon[M][N] = { 0 }; for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { mapcon[i][j] = map[i][j]; } } mapcon[M - 2][N - 2] = 0; mapcon[1][1] = -1; pro tmp; tmp.x = 1; tmp.y = 1; tmp.di = -1; StackPush(ps, tmp.x, tmp.y, tmp.di); while (!StackEmpty(ps)) { tmp.x = StackTop(ps)->x; tmp.y = StackTop(ps)->y; tmp.di = StackTop(ps)->di; StackPop(ps); x = tmp.x; y = tmp.y; di = tmp.di + 1; while (di < 4) { line = x + des[di].conx; col = y + des[di].cony; if (mapcon[line][col] == 0) { tmp.x = x; tmp.y = y; tmp.di = di; StackPush(ps, tmp.x, tmp.y, tmp.di); x = line; y = col; mapcon[line][col] = -1; if (x == M - 2 && y == N - 2) return true; else di = 0; } else di++; } } return false; } int main() { srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); direct des[4]; des[0].conx = 1;//向右走 des[0].cony = 0; des[1].conx = -1;//向左走 des[1].cony = 0; des[2].conx = 0;//向下走 des[2].cony = 1; des[3].conx = 0;//向上走 des[3].cony = -1; Stack st; Stack scpy; StackInit(&st); StackInit(&scpy); bool ret = findpath(map, des, &st); if (ret == 1) { printf("该地图有通路\n"); while (!StackEmpty(&st)) { int num1=StackTop(&st)->x; int num2 = StackTop(&st)->y; int num3= StackTop(&st)->di; /*printf("%d-%d ",num1,num2);*/ StackPop(&st); StackPush(&scpy, num1, num2, num3); } while (!StackEmpty(&scpy)) { int num1 = StackTop(&scpy)->x; int num2 = StackTop(&scpy)->y; int num3 = StackTop(&scpy)->di; printf("(%d,%d)\n", num1, num2); StackPop(&scpy); } } else { printf("该地图无通路\n"); } StackDestroy(&st); StackDestroy(&scpy); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
9.编译运行

-
相关阅读:
ReactNative原理与核心知识点
OX08B40sensor的规格书
qt 重载信号,使用“&“方式进行connect()调用解决方案
(转)富文本编辑器——Vue2Editor
学生管理系统(Java版)
【react】手把手学习react - 元素条件渲染
低端电脑如何深度学习秘籍-使用mistGPU计算平台
自动化立体仓库控制系统-过程通信处理
Go 锁扩展
Scratch 第十四课-打地鼠游戏
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yyqzjw/article/details/133687690
