-
Linux系统编程(七):线程同步
参考引用
1. 同步概念
- 所谓同步,即同时起步、协调一致。不同的对象,对 “同步” 的理解方式略有不同
- 设备同步,是指在两个设备之间规定一个共同的时间参考
- 数据库同步,是指让两个或多个数据库内容保持一致,或者按需要部分保持一致
- 文件同步,是指让两个或多个文件夹里的文件保持一致
- 编程中、通信中所说的同步:“同” 字应是指协同、协助、互相配合。主旨在协同步调,按预定的先后次序运行
1.1 线程同步
- 线程同步,是指一个线程发出某一功能调用时,在没有得到结果之前,该调用不返回。同时其它线程为保证数据一致性,不能调用该功能
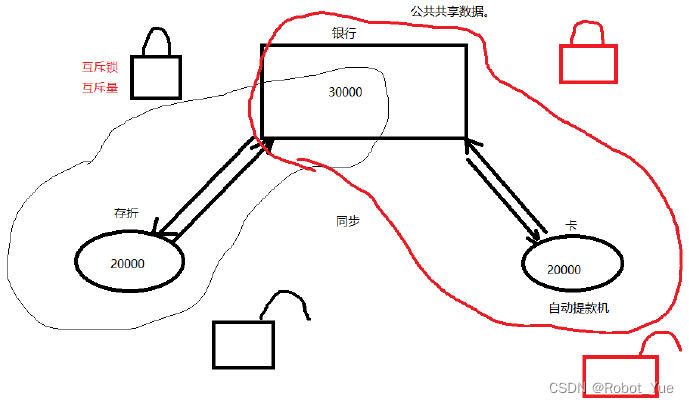
- 产生的现象叫做 “与时间有关的错误” (time related)。为了避免这种数据混乱,线程需要同步
- “同步” 的目的,是为了避免数据混乱,解决与时间有关的错误。实际上,不仅线程间需要同步,进程间、信号间等等都需要同步机制。因此,所有 “多个控制流,共同操作一个共享资源” 的情况,都需要同步
1.2 数据混乱原因
- 1、资源共享 (独享资源则不会)
- 2、调度随机 (意味着数据访问会出现竞争)
- 3、线程间缺乏必要的同步机制
以上 3 点中,前两点不能改变,欲提高效率,传递数据时资源必须共享。只要共享资源,就一定会出现竞争只要存在竞争关系,数据就很容易出现混乱。所以只能从第 3 点着手解决,使多个线程在访问共享资源的时候出现互斥
2. 互斥量 mutex
- Linux 中提供一把互斥锁 mutex (也称之为互斥量)。每个线程在对资源操作前都尝试先加锁,成功加锁才能操作,操作结束解锁。资源还是共享的,线程间也还是竞争的,但通过 “锁” 就将资源的访问变成互斥操作
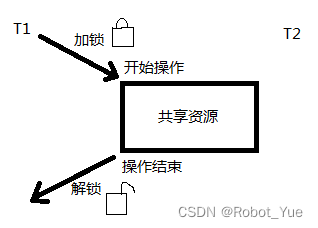
- 但应注意:同一时刻,只能有一个线程持有该锁。当 A 线程对某个全局变量加锁访问,B 在访问前尝试加锁,拿不到锁则 B 阻塞。C 线程不去加锁,而直接访问该全局变量,依然能够访问,但会出现数据混乱
- 所以,互斥锁实质上是操作系统提供的一把 “建议锁” (又称 “协同锁”),建议程序中有多线程访问共享资源的时候使用该机制,并没有强制限定
- 因此,即使有了 mutex,如果有线程不按规则来访问数据,依然会造成数据混乱
2.1 主要应用函数
#include// 返回值都是: 成功返回 0,失败返回错误号 // pthread_mutex_t 类型,其本质是一个结构体 // pthread_mutex_t mutex; 变量 mutex 只有两种取值 1、0 // 初始化一个互斥锁(互斥量) --> 初值可看作 1 // 参 1: 传出参数,调用时应传 &mutex // restrict 用来限定指针变量。被该关键字限定的指针变量所指向的内存操作,必须由本指针完成 // 参 2: 互斥量属性。是一个传入参数,通常传 NULL,选用默认属性(线程间共享) int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr); // 销毁一个互斥锁 int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 加锁。可理解为将 mutex-- (或 -1),操作后 mutex 的值为 0 int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 解锁。可理解为将 mutex++ (或 +1),操作后 mutex 的值为 1 int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 尝试加锁 int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
2.2 加锁与解锁
2.2.1 lock 和 unlock
- lock 尝试加锁,如果加锁不成功则线程阻塞,阻塞到持有该互斥量的其他线程解锁为止
- unlock 主动解锁函数,同时将阻塞在该锁上的所有线程全部唤醒,至于哪个线程先被唤醒,取决于优先级、调度。默认: 先阻塞、先唤醒
- 例如:T1 T2 T3 T4 使用一把 mutex 锁。T1 加锁成功,其他线程均阻塞,直至 T1 解锁。T1 解锁后,T2 T3 T4 均被唤醒,并自动再次尝试加锁。可假想 mutex 锁 init 成功初始值为 1,lock 功能是将 mutex–,而 unlock 则将 mutex++
2.2.2 lock 和 trylock
- lock 加锁失败会阻塞,等待锁释放
- trylock 加锁失败直接返回错误号 (如:EBUSY),不阻塞
- 在访问共享资源前加锁,访问结束后立即解锁。锁的 “粒度” 应越小越好
2.3 加锁步骤测试
- 创建锁 --> 初始化 --> 加锁 --> 访问共享数据 --> 解锁 --> 销毁锁
#include#include #include #include #include #include pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 定义一把全局互斥锁 void *tfn(void *arg) { srand(time(NULL)); while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 加锁,为 0 printf("hello "); sleep(rand() % 3); // 模拟长时间操作共享资源,导致 cpu 易主,产生与时间有关的错误 printf("world\n"); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁,为 1 sleep(rand() % 3); } return NULL; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { pthread_t tid; srand(time(NULL)); int ret = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); // 初始化互斥锁,为 1 if (ret != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "mutex init error: %s\n", strerror(ret)); exit(1); } pthread_create(&tid, NULL, tfn, NULL); while (1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 加锁 printf("HELLO "); sleep(rand() % 3); printf("WORLD\n"); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁 sleep(rand() % 3); } pthread_join(tid, NULL); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); // 销毁互斥锁 return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
$ gcc pthread_shared.c -o pthread_shared -pthread $ ./pthread_shared HELLO WORLD hello world HELLO WORLD ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3. 死锁
- 是使用锁不恰当导致的现象
- 线程试图对同一个互斥量 A 加锁两次(对一个锁反复 lock)
- 线程 1 拥有 A 锁,请求获得 B 锁;线程 2 拥有 B 锁,请求获得 A 锁(两个线程各自持有一把锁,请求另一把)
案例
#include#include #include #if 1 int var = 1, num = 5; pthread_mutex_t m_var, m_num; void *tfn(void *arg) { int i = (int)arg; if (i == 1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&m_var); var = 22; sleep(1); //给另外一个线程加锁,创造机会. pthread_mutex_lock(&m_num); num = 66; pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_var); pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_num); printf("----thread %d finish\n", i); pthread_exit(NULL); } else if (i == 2) { pthread_mutex_lock(&m_num); var = 33; sleep(1); pthread_mutex_lock(&m_var); num = 99; pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_var); pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_num); printf("----thread %d finish\n", i); pthread_exit(NULL); } return NULL; } int main(void) { pthread_t tid1, tid2; int ret1, ret2; pthread_mutex_init(&m_var, NULL); pthread_mutex_init(&m_num, NULL); pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, tfn, (void *)1); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, tfn, (void *)2); sleep(3); printf("var = %d, num = %d\n", var, num); ret1 = pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_var); //释放琐 ret2 = pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_num); if (ret1 == 0 && ret2 == 0) printf("------------destroy mutex finish\n"); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); printf("------------join thread finish\n"); return 0; } #else int a = 100; int main(void) { pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); a = 777; pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); printf("-----------a = %d\n", a); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); return 0; } #endif - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
$ gcc deadlock.c -o deadlock -pthread $ ./deadlock var = 33, num = 5 ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4. 读写锁
- 与互斥量类似,但读写锁允许更高的并行性。其特性为:写独占,读共享,写锁优先级高
4.1 读写锁状态
- 读写锁只有一把,但其具备两种状态
- 读模式下加锁状态 (读锁)
- 写模式下加锁状态 (写锁)
4.2 读写锁特性
- 读写锁是 “写模式加锁” 时, 解锁前,所有对该锁加锁的线程都会被阻塞
- 读写锁是 “读模式加锁” 时, 如果线程以读模式对其加锁会成功,如果线程以写模式加锁会阻塞
- 读写锁是 “读模式加锁” 时,既有试图以写模式加锁的线程,也有试图以读模式加锁的线程
- 读写锁会阻塞随后的读模式锁请求
- 优先满足写模式锁
- 读锁、写锁并行阻塞,写锁优先级高
读写锁非常适合于对数据结构读的次数远大于写的情况
4.3 主要应用函数
#include// 返回值 成功返回 0,失败直接返回错误号 // 初始化一把读写锁 // 参 2: attr 表读写锁属性,通常使用默认属性,传 NULL 即可 int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr); // 销毁一把读写锁 int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); // 以读方式请求读写锁 (简称:请求读锁) int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); // 非阻塞以读方式请求读写锁 (非阻塞请求读锁) int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); // 以写方式请求读写锁 (简称:请求写锁) int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); // 非阻塞以写方式请求读写锁 (非阻塞请求写锁) int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); // 解锁 int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
4.4 读写锁示例
- 3 个线程不定时 “写” 全局资源,5 个线程不定时 “读” 同一全局资源
#include#include #include int counter; // 全局资源 pthread_rwlock_t rwlock; void *th_write(void *arg) { int t; int i = (int)arg; while (1) { t = counter; // 保存写之前的值 usleep(1000); pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock); printf("=======write %d: %lu: counter=%d ++counter=%d\n", i, pthread_self(), t, ++counter); pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); usleep(9000); // 给 r 锁提供机会 } return NULL; } void *th_read(void *arg) { int i = (int)arg; while (1) { pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock); printf("----------------------------read %d: %lu: %d\n", i, pthread_self(), counter); pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); usleep(2000); // 给写锁提供机会 } return NULL; } int main(void) { int i; pthread_t tid[8]; pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL); for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, th_write, (void *)i); for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) pthread_create(&tid[i+3], NULL, th_read, (void *)i); for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) pthread_join(tid[i], NULL); pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock); // 释放读写琐 return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
$ gcc rwlock.c -o rwlock -pthread $ ./rwlock ----------------------------read 0: 140472231028480: 0 ----------------------------read 3: 140472205850368: 0 ----------------------------read 2: 140472214243072: 0 ----------------------------read 4: 140472197457664: 0 ----------------------------read 1: 140472222635776: 0 =======write 0: 140472256206592: counter=0 ++counter=1 =======write 1: 140472247813888: counter=0 ++counter=2 =======write 2: 140472239421184: counter=0 ++counter=3 ----------------------------read 2: 140472214243072: 3 ----------------------------read 3: 140472205850368: 3 ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
5. 条件变量
- 条件变量本身不是锁,但它也可以造成线程阻塞
- 通常与互斥锁配合使用,给多线程提供一个会合的场所
5.1 主要应用函数
#include// 返回值 成功返回 0,失败直接返回错误号 // 初始化一个条件变量 // 参 2: attr 表条件变量属性,通常为默认值,传 NULL 即可 int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr); // 销毁一个条件变量 int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond); // 函数作用(1、2 两步为一个原子操作) // 1、阻塞等待条件变量 cond (参 1) 满足 // 2、释放已掌握的互斥锁 (解锁互斥量),相当于 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 3、当被唤醒,pthread_cond_wait 函数返回时,解除阻塞并重新申请获取互斥锁 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex); // 限时等待一个条件变量 int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime); // 唤醒至少一个阻塞在条件变量上的线程 int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond); // 唤醒全部阻塞在条件变量上的线程 int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
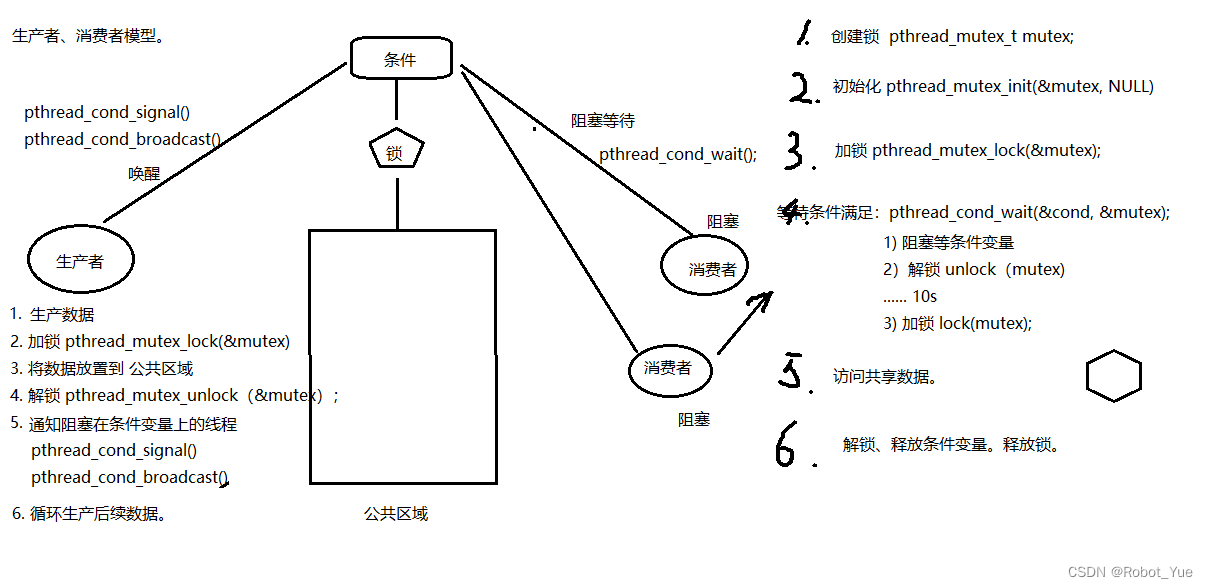
5.2 生产者消费者条件变量模型
- 线程同步典型的案例即为生产者消费者模型,而借助条件变量来实现这一模型,是比较常见的一种方法
- 假定有两个线程,一个模拟生产者行为,一个模拟消费者行为。两个线程同时操作一个共享资源 (一般称之为汇聚),生产者向其中添加产品,消费者从中消费掉产品
#include#include #include #include #include #include void err_thread(int ret, char *str) { if (ret != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "%s:%s\n", str, strerror(ret)); pthread_exit(NULL); } } struct msg { int num; struct msg *next; }; struct msg *head; pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; // 定义/初始化一个互斥量 pthread_cond_t has_data = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; // 定义/初始化一个条件变量 void *produser(void *arg) { while (1) { struct msg *mp = malloc(sizeof(struct msg)); mp->num = rand() % 1000 + 1; // 模拟生产一个数据` printf("--produce %d\n", mp->num); pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 加锁 互斥量 mp->next = head; // 写公共区域 head = mp; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁 互斥量 pthread_cond_signal(&has_data); // 唤醒阻塞在条件变量 has_data上的线程. sleep(rand() % 3); } return NULL; } void *consumer(void *arg) { while (1) { struct msg *mp; pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 加锁 互斥量 while (head == NULL) { pthread_cond_wait(&has_data, &mutex); // 阻塞等待条件变量, 解锁 } // pthread_cond_wait 返回时, 重新加锁 mutex mp = head; head = mp->next; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁 互斥量 printf("---------consumer id: %lu :%d\n", pthread_self(), mp->num); free(mp); sleep(rand()%3); } return NULL; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int ret; pthread_t pid, cid; srand(time(NULL)); ret = pthread_create(&pid, NULL, produser, NULL); // 生产者 if (ret != 0) err_thread(ret, "pthread_create produser error"); ret = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL); // 消费者 if (ret != 0) err_thread(ret, "pthread_create consuer error"); ret = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL); // 消费者 if (ret != 0) err_thread(ret, "pthread_create consuer error"); ret = pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL); // 消费者 if (ret != 0) err_thread(ret, "pthread_create consuer error"); pthread_join(pid, NULL); pthread_join(cid, NULL); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
$ gcc cond.c -o cond -pthread $ ./cond --produce 208 ---------consumer id: 140611653785344 :208 --produce 829 ---------consumer id: 140611645392640 :829 --produce 191 --produce 625 ---------consumer id: 140611662178048 :625 ---------consumer id: 140611653785344 :191 --produce 926 ---------consumer id: 140611645392640 :926 ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
5.3 条件变量的优点
- 相较于 mutex 而言,条件变量可以减少竞争
- 若直接使用 mutex,除了生产者、消费者之间要竞争互斥量以外,消费者之间也需要竞争互斥量,但如果汇聚 (链表) 中没有数据,消费者之间竞争互斥锁是无意义的
- 有了条件变量机制以后,只有生产者完成生产,才会引起消费者之间的竞争,提高了程序效率
6. 信号量
-
信号量相当于初始化值为 N 的互斥量
- 由于互斥锁的粒度比较大,如果希望在多个线程间对某一对象的部分数据进行共享,使用互斥锁是没有办法实现的,只能将整个数据对象锁住。这样虽然达到了多线程操作共享数据时保证数据正确性的目的,却无形中导致线程的并发性下降。线程从并行执行,变成了串行执行,与直接使用单进程无异
-
信号量,是相对折中的一种处理方式,既能保证同步,数据不混乱,又能提高线程并发
6.1 主要应用函数
#include// 返回值 成功返回 0,失败返回-1,同时设置 errno // 规定信号量 sem 不能 < 0 // 初始化一个信号量 // 参 1: sem 信号量 // 参 2: pshared 取 0 用于线程间; 取非 (一般为 1) 用于进程间 // 参 3: value 指定信号量初值 int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value); // 销毁一个信号量 int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem); // 给信号量加锁 -- int sem_wait(sem_t *sem); // 尝试对信号量加锁 -- (与 sem_wait 的区别类比 lock 和 trylock) int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem); // 限时尝试对信号量加锁 -- int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout); // 给信号量解锁 ++ int sem_post(sem_t *sem); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 信号量基本操作

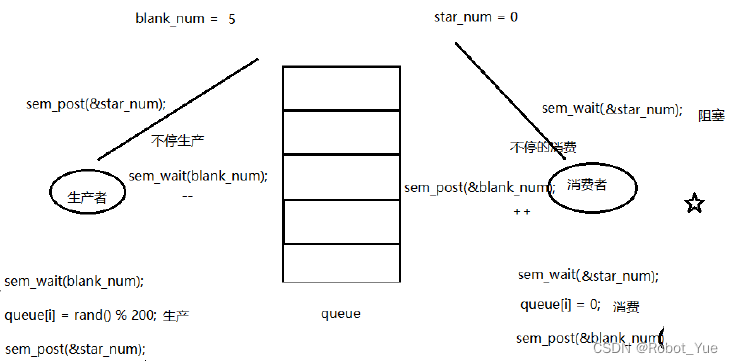
6.2 生产者消费者信号量模型

/*信号量实现 生产者 消费者问题*/ #include#include #include #include #include #define NUM 5 int queue[NUM]; // 全局数组实现环形队列 sem_t blank_number, product_number; // 空格子信号量, 产品信号量 void *producer(void *arg) { int i = 0; while (1) { sem_wait(&blank_number); // 生产者将空格子数--,为0则阻塞等待 queue[i] = rand() % 1000 + 1; // 生产一个产品 printf("----Produce---%d\n", queue[i]); sem_post(&product_number); // 将产品数++ i = (i+1) % NUM; // 借助下标实现环形 sleep(rand()%1); } } void *consumer(void *arg) { int i = 0; while (1) { sem_wait(&product_number); // 消费者将产品数--,为0则阻塞等待 printf("-Consume---%d\n", queue[i]); queue[i] = 0; // 消费一个产品 sem_post(&blank_number); // 消费掉以后,将空格子数++ i = (i+1) % NUM; sleep(rand()%3); } } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { pthread_t pid, cid; sem_init(&blank_number, 0, NUM); // 初始化空格子信号量为5, 线程间共享 -- 0 sem_init(&product_number, 0, 0); // 产品数为 0 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, producer, NULL); pthread_create(&cid, NULL, consumer, NULL); pthread_join(pid, NULL); pthread_join(cid, NULL); sem_destroy(&blank_number); sem_destroy(&product_number); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
$ gcc sem.c -o sem -pthread $ ./sem ----Produce---384 -Consume---384 ----Produce---916 -Consume---916 ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 所谓同步,即同时起步、协调一致。不同的对象,对 “同步” 的理解方式略有不同
-
相关阅读:
kubebuilder operator的运行逻辑
实时备案查询易语言代码
无法定位程序输入点packetgetreadevent于动态链接库wpcap.dll上
URP渲染管线场景优化实战 1.1 预配置及初始信息
efficientsam-pytorch基于point、box和segment everthing推理模型
centos 7.9系统安装向日葵
14.0、C语言——数据存储(2)
Kafka 认证二:ScramLoginModule 认证及 Java 连接测试
深入探究Python多进程编程:Multiprocessing模块基础与实战【第98篇—Multiprocessing模块】
axios从入门到源码分析之axios的理解和使用(一)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42994487/article/details/133437339
