-
第P7周—咖啡豆识别(1)
数据集及wen件目录介绍:

一、前期工作
1.1 数据详情
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torchvision.transforms as transforms
- import torchvision
- from torchvision import transforms, datasets
- import os,PIL,pathlib,warnings
- warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
- device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
- print(device)
- import os,PIL,random,pathlib
- data_dir = 'D:/P7/49-data/'
- data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
- data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
- classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[3] for path in data_paths]
- print(classeNames)
- image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*.png')))
- print("图片总数为:",image_count)

1.2 图片预处理:
详见:写文章-CSDN创作中心
 https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/133411331
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/133411331- train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
- transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
- # transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
- transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
- transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
- mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
- std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
- ])
- test_transform = transforms.Compose([
- transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
- transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
- transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
- mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
- std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
- ])
- total_data = datasets.ImageFolder("D:/P7/49-data",transform=train_transforms)
- print(total_data)

标签量化处理:
print(total_data.class_to_idx)
1.4 划分数据集
- train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
- test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
- train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
- print(train_dataset, test_dataset)

二、搭建VGG—16模型
2.1 搭建VGG模型
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- class vgg16(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(vgg16, self).__init__()
- # 卷积块1
- self.block1 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块2
- self.block2 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块3
- self.block3 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块4
- self.block4 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块5
- self.block5 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 全连接网络层,用于分类
- self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(in_features=512*7*7, out_features=4096),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4)
- )
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.block1(x)
- x = self.block2(x)
- x = self.block3(x)
- x = self.block4(x)
- x = self.block5(x)
- x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
- x = self.classifier(x)
- return x
- device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
- print("Using {} device".format(device))
- model = vgg16().to(device)
- print(model)
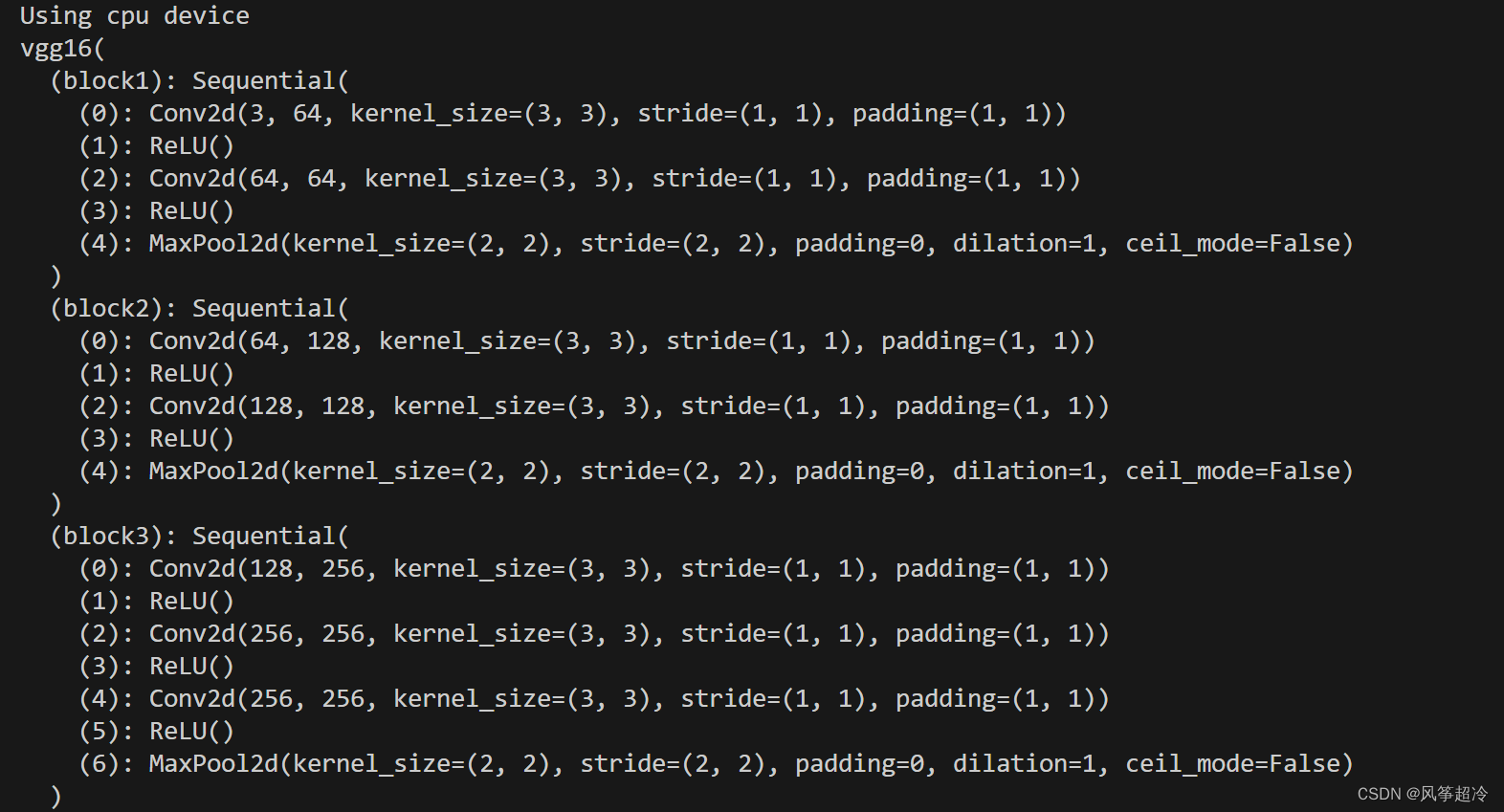
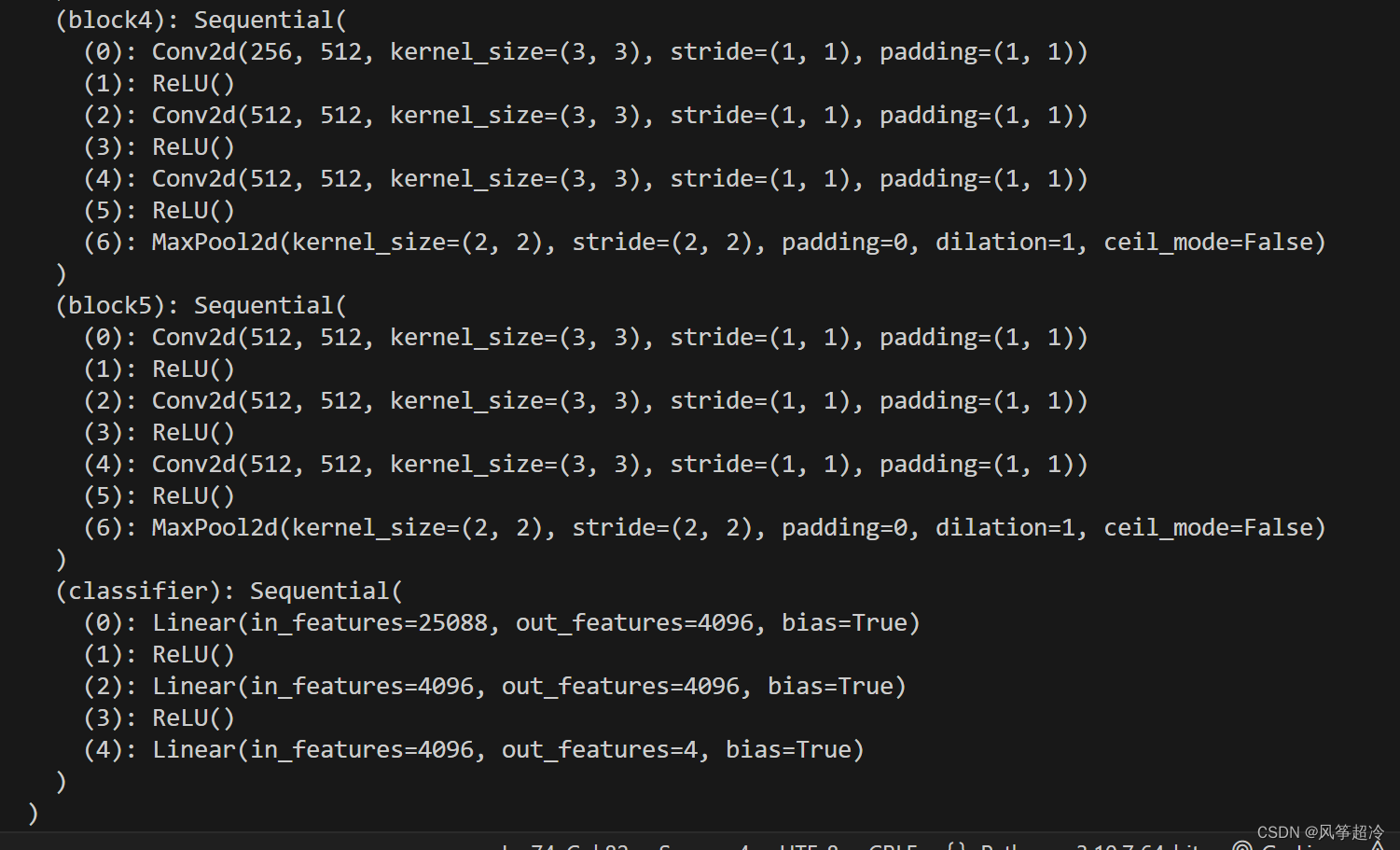
2.2 模型信息


三、模型训练
3.1 编写训练函数
- # 训练循环
- def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
- size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
- num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
- train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
- for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
- X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
- # 计算预测误差
- pred = model(X) # 网络输出
- loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
- # 反向传播
- optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
- loss.backward() # 反向传播
- optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
- # 记录acc与loss
- train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
- train_loss += loss.item()
- train_acc /= size
- train_loss /= num_batches
- return train_acc, train_loss
3.2 编写测试函数
- def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
- size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
- num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
- test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
- # 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
- with torch.no_grad():
- for imgs, target in dataloader:
- imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
- # 计算loss
- target_pred = model(imgs)
- loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
- test_loss += loss.item()
- test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
- test_acc /= size
- test_loss /= num_batches
- return test_acc, test_loss
3.3 模型训练 (完整代码)
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torchvision.transforms as transforms
- from torchvision import datasets
- import pathlib
- import warnings
- warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
- def main():
- device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
- print(device)
- data_dir = 'D:/P7/49-data/'
- data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
- data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
- classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[3] for path in data_paths]
- print(classeNames)
- image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*.png')))
- print("图片总数为:", image_count)
- train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
- transforms.Resize([224, 224]),
- transforms.ToTensor(),
- transforms.Normalize(
- mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
- std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
- ])
- test_transform = transforms.Compose([
- transforms.Resize([224, 224]),
- transforms.ToTensor(),
- transforms.Normalize(
- mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
- std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
- ])
- total_data = datasets.ImageFolder("D:/P7/49-data", transform=train_transforms)
- print(total_data)
- train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
- test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
- train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
- print(train_dataset, test_dataset)
- batch_size = 32
- train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
- batch_size=batch_size,
- shuffle=True,
- num_workers=1)
- test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
- batch_size=batch_size,
- shuffle=True,
- num_workers=1)
- class VGG16Lite(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, num_classes=4):
- super(VGG16Lite, self).__init__()
- self.features = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
- nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
- nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
- )
- self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(256 * 28 * 28, 4096),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.Dropout(),
- nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
- nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
- nn.Dropout(),
- nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
- )
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.features(x)
- x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
- x = self.classifier(x)
- return x
- device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
- print("Using {} device".format(device))
- model = VGG16Lite().to(device)
- print(model)
- import torch.optim as optim
- optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
- loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- epochs = 40
- train_loss = []
- train_acc = []
- test_loss = []
- test_acc = []
- best_acc = 0
- best_model = None
- for epoch in range(epochs):
- model.train()
- epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
- model.eval()
- epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
- if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
- best_acc = epoch_test_acc
- best_model = model.state_dict()
- train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
- train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
- test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
- test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
- lr = optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']
- template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
- print(template.format(epoch + 1, epoch_train_acc * 100, epoch_train_loss,
- epoch_test_acc * 100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
- PATH = './best_model_lite.pth'
- torch.save(best_model, PATH)
- print('Done')
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()

3.4 轻量化上述VGG16模型
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torchvision.transforms as transforms
- import torchvision
- from torchvision import transforms, datasets
- import os,PIL,pathlib,warnings
- warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
- def main():
- device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
- print(device)
- import os,PIL,random,pathlib
- data_dir = 'D:/P7/49-data/'
- data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
- data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
- classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[3] for path in data_paths]
- print(classeNames)
- image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*.png')))
- print("图片总数为:",image_count)
- train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
- transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
- # transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
- transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
- transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
- mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
- std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
- ])
- test_transform = transforms.Compose([
- transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
- transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
- transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
- mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
- std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
- ])
- total_data = datasets.ImageFolder("D:/P7/49-data",transform=train_transforms)
- print(total_data)
- print(total_data.class_to_idx)
- train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
- test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
- train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
- print(train_dataset, test_dataset)
- batch_size = 32
- train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
- batch_size=batch_size,
- shuffle=True,
- num_workers=1)
- test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
- batch_size=batch_size,
- shuffle=True,
- num_workers=1)
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- class vgg16(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(vgg16, self).__init__()
- # 卷积块1
- self.block1 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块2
- self.block2 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块3
- self.block3 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块4
- self.block4 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 卷积块5
- self.block5 = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
- )
- # 全连接网络层,用于分类
- self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(in_features=512*7*7, out_features=4096),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4)
- )
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.block1(x)
- x = self.block2(x)
- x = self.block3(x)
- x = self.block4(x)
- x = self.block5(x)
- x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
- x = self.classifier(x)
- return x
- device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
- print("Using {} device".format(device))
- model = vgg16().to(device)
- print(model)
- # 统计模型参数量以及其他指标
- import torchsummary as summary
- summary.summary(model, (3, 224, 224))
- # 训练循环
- def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
- size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
- num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
- train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
- for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
- X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
- # 计算预测误差
- pred = model(X) # 网络输出
- loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
- # 反向传播
- optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
- loss.backward() # 反向传播
- optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
- # 记录acc与loss
- train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
- train_loss += loss.item()
- train_acc /= size
- train_loss /= num_batches
- return train_acc, train_loss
- def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
- size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
- num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
- test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
- # 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
- with torch.no_grad():
- for imgs, target in dataloader:
- imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
- # 计算loss
- target_pred = model(imgs)
- loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
- test_loss += loss.item()
- test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
- test_acc /= size
- test_loss /= num_batches
- return test_acc, test_loss
- import copy
- optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr= 1e-4)
- loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
- epochs = 40
- train_loss = []
- train_acc = []
- test_loss = []
- test_acc = []
- best_acc = 0 # 设置一个最佳准确率,作为最佳模型的判别指标
- for epoch in range(epochs):
- model.train()
- epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
- model.eval()
- epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
- # 保存最佳模型到 best_model
- if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
- best_acc = epoch_test_acc
- best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
- train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
- train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
- test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
- test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
- # 获取当前的学习率
- lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
- template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
- print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss,
- epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
- # 保存最佳模型到文件中
- PATH = './best_model.pth' # 保存的参数文件名
- torch.save(model.state_dict(), PATH)
- print('Done')
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()

-
相关阅读:
R包的尽头是 C/C++
数据赋能(121)——体系:数据清洗——实施过程、应用特点
合肥工业大学计算机网络课设-在线留言板
多端统一开发框架Taro、UniApp和WeApp这三个应用各自在前端开发领域有着独特的定位和功能
Node.js 应用开发详解14 工具应用:使用 clinicj 工具实现通用性安全检查
轻量封装WebGPU渲染系统示例<1>-彩色三角形(源码)
第6章 Elasticsearch,分布式搜索引擎
【迁移ORACLE数据到MogDB/openGauss时的字符集问题】
树莓派 RaspBerryPi 网络配置相关与改造usb网络摄像头
基于ssm+vue的美食分享网站
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_60245590/article/details/133411047
