-
java面向对象(九)
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考一、abstract的应用举例
public abstract class Vehicle{ public abstract double calaFuelEfficiency(); //计算燃料效率的抽象方法 public abstract double clacTripDistance(); //计算行驶距离的抽象方法 } public class Truck extends Vehicle{ public double calaFuelEfficiency(){ //写出计算卡车的燃料效率的具体方法 } public double clacTripDistance(){ //写出计算卡车行驶距离的具体方法 } } public class RiverBarge extends Vehicle{ public double calaFuelEfficiency(){ //写出计算卡车的燃料效率的具体方法 } public double clacTripDistance(){ //写出计算卡车行驶距离的具体方法 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
二、接口的使用
1.概念
1.接口使用上也满足多态性
2.接口,实际上就是定义了一种规范
3.开发中,体会面向接口编程!2.代码案例
public clas USBTest{ main(){ Computer com = new Computer(); //1.创建了接口的非匿名实现类的非匿名对象 Flash flash = new Flash(); com.transferData(falsh); //2.创建了接口的非匿名实现类的匿名对象 com.transferData(new Printer()); //3.创建了接口的匿名实现类的非匿名对象 USB phone = new USB(){ public void start(){ sysout("手机开始工作"); } public void stop(){ sysout("手机结束工作"); } }; com.transferData(phone); //4.创建了接口的匿名实现类的匿名对象 com.transferData(new USB(){ public void start(){ sysout("mp3开始工作"); } public void stop(){ sysout("mp3结束工作"); } }); } } class Computer{ public void transferData(USB usb) { //USB usb = new Flash(); usb.start(); sysout("具体传输数据的细节"); usb.stop(); } } interface USB{ //常量,定义了长、宽、最大最小的传输速度等。 void start(); void stop(); } class Flash implements USB{ public void start(){ sysout("U盘开启工作"); } @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("U盘结束工作"); } } class Printer implements USB{ public void start(){ sysout("打印机开启工作"); } @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("打印机结束工作"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
三、try-catch-finally使用步骤
1.注意点
- finally是可选的。
- 使用try将可能出现异常代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会生成一个对应异常类的对象,根据此对象的类型,去catch中进行匹配
- 一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就进入catch中进行异常的处理。一旦处理完成,就跳出当前的try-catch结构 (在没有写finally的情况),继读执行其后的代码。
- catch中的异常类型如果没有子父类关系,则谁声明在上,谁声明在下无所谓。catch中的异常类型如果满足子父类关系,则要求子类一定声明在父类的上面。否则,报错。
- 常用的异常对象处理的方式: @ String getMessage() printStackTrace()
- 在try结构中声明的变量,再出了try结构以后,就不能再被调用
使用try-catch-finally处理编译时异常,使得程序在编译时就不再报错,但是运行时仍可能报错。
相当于我们使用try-catch-finally将一个编译时可能出现的异常延迟到运行时出现。
2.finally注意点
1.finally是可选的
2.finally中声明的是一定会被执行的代码。即使catch中又出现异常了,try中有return语句,catch中有return语句等情况。
3.像数据库连接、输入输出流、网络编程Socket等资源JVM是不能自动的回收的,我们需要自己手动的进行资源的释放。此时的资源释放,就需要声明在finally中。代码如下(示例):
public void test1() { try { int a = 10; int b = 0; System.out.println(a/b); }catch (ArithmeticException e) { //e.printStackTrace(); int [] arr = new int[10]; System.out.println(arr[10]); }catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //System.out.println("我好美呀哈哈哈~~~"); finally { System.out.println("我好美呀哈哈哈~~~"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
public void test2() { FileInputStream fis = null; try { File file = new File("hello.txt"); fis = new FileInputStream(file); int data = fis.read(); while(data != -1) { System.out.println((char)data); data = fis.read(); } }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { if(fis != null) fis.close(); }catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } @Test public void testMethod() { int num = method(); System.out.println(num); } public int method() { try { int [] arr = new int[10]; System.out.println(arr[10]); return 1; }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ e.printStackTrace(); return 2; }finally { System.out.println("我一定会被执行"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
四、异常处理的方式二:throws + 异常类型
1.如图所示:
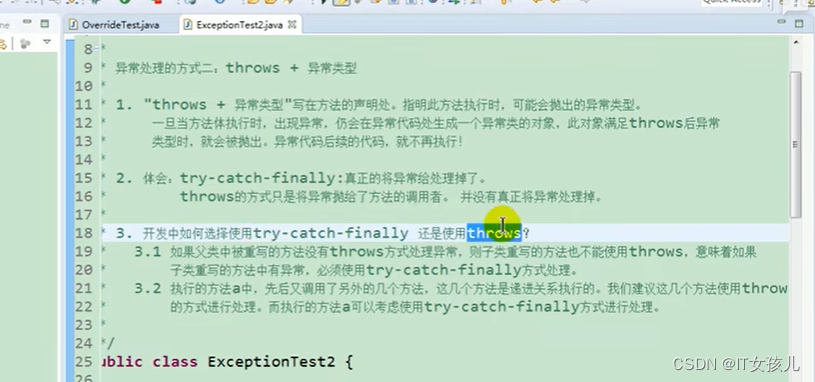
2.代码如下:
/** * @author YML * 异常处理的方式二:throws + 异常类型 * 1. "throws +异常类型" */ public class ExpectionTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { method2(); } catch(FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method3() { try { method2(); }catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method2() throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { method1(); } public static void method1() throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{ File file = new File("hello.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); int data = fis.read(); while(data != -1) { System.out.println((char)data); data = fis.read(); } fis.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
-
相关阅读:
企业电子文档管理系统哪个好?怎么选?
Nat. Med. | 基于遗传学原发部位未知癌症的分类和治疗反应预测
数一独有:多元函数积分的概念、计算及其应用
Linux 安装Harbor镜像仓库私服
FreeRtos-09事件组的使用
判断某点是否在三角形内(Python)
48种数据分析可视化图表
部署基于efk+logstash+kafka构建日志收集平台并对nginx日志进行分析【待执行】
Nacos中服务删除不了,怎么办?
HTML网页设计制作大作业(游戏主题)---电竞
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lalalalalab/article/details/133150764
