-
【springMvc】自定义注解的使用方式

🎬 艳艳耶✌️:个人主页
🔥 个人专栏 :《Spring与Mybatis集成整合》
⛺️ 生活的理想,为了不断更新自己 !

1.前言
1.1.什么是注解
Annontation是Java5开始引入的新特征,中文名称叫注解。
它提供了一种安全的类似注释的机制,用来将任何的信息或元数据(metadata)与程序元素(类、方法、成员变量等)进行关联。为程序的元素(类、方法、成员变量)加上更直观、更明了的说明,这些说明信息是与程序的业务逻辑无关,并且供指定的工具或框架使用。Annontation像一种修饰符一样,应用于包、类型、构造方法、方法、成员变量、参数及本地变量的声明语句中。
Java注解是附加在代码中的一些元信息,用于一些工具在编译、运行时进行解析和使用,起到说明、配置的功能。注解不会也不能影响代码的实际逻辑,仅仅起到辅助性的作用。
1.2.注解的用处
- 生成文档。这是最常见的,也是java 最早提供的注解。常用的有@param @return 等
- 跟踪代码依赖性,实现替代配置文件功能。比如Dagger 2 依赖注入,未来java 开发,将大量注解配置,具有很大用处;
- 在编译时进行格式检查。如@override 放在方法前,如果你这个方法并不是覆盖了超类方法,则编译时就能检查出。
1.3.注解的原理
注解本质是一个继承了Annotation 的特殊接口,其具体实现类是Java 运行时生成的动态代理类。而我们通过反射获取注解时,返回的是Java 运行时生成的动态代理对象$Proxy1。通过代理对象调用自定义注解(接口)的方法,会最终调用AnnotationInvocationHandler 的invoke 方法。该方法会从memberValues 这个Map 中索引出对应的值。而memberValues 的来源是Java 常量池。
2.注解的案列:
2.1 案例一(获取类与方法上的注解值)
定义一个类:
- package com.sy.annotation.pi;
- public enum TranscationModel {
- Read, Write, ReadWrite //定义三个实例,可以将它看作类
- }
写三个注解:
- package com.sy.annotation;
- import java.lang.annotation.*;
- /**
- * MyAnnotation1注解可以用在类、接口、属性、方法上
- * 注解运行期也保留
- * 不可继承
- */
- @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD})
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Documented
- public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
- String name();
- }
- package com.sy.annotation;
- import java.lang.annotation.*;
- /**
- * MyAnnotation2注解可以用在方法上
- * 注解运行期也保留
- * 不可继承
- */
- @Target(ElementType.METHOD)
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Documented
- public @interface MyAnnotation2 {
- TranscationModel model() default TranscationModel.ReadWrite;
- }
- package com.sy.annotation;
- import java.lang.annotation.*;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- *
- * MyAnnotation3注解可以用在方法上
- * 注解运行期也保留
- * 可继承
- */
- @Target(ElementType.METHOD)
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Inherited
- @Documented
- public @interface MyAnnotation3 {
- TranscationModel[] models() default TranscationModel.ReadWrite;
- }
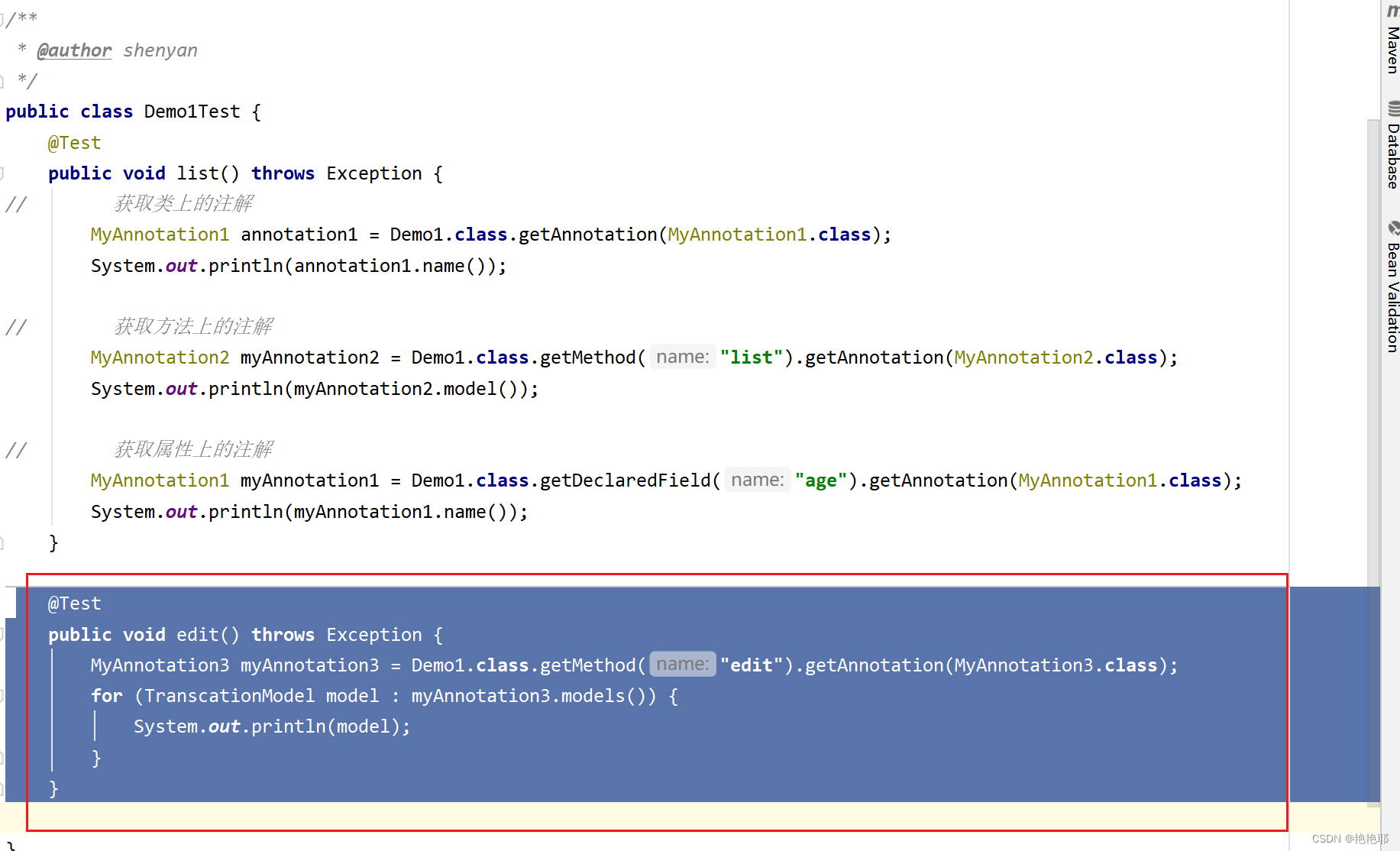
创建几个方法使用这些注解
- package com.sy.annotation.Demo1;
- import com.sy.annotation.MyAnnotation1;
- import com.sy.annotation.MyAnnotation2;
- import com.sy.annotation.MyAnnotation3;
- import com.sy.annotation.TranscationModel;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- *
- * 获取类与方法上的注解值
- */
- @MyAnnotation1(name = "艳艳耶")
- public class Demo1 {
- @MyAnnotation1(name = "csdn")
- private Integer age;
- @MyAnnotation2(model = TranscationModel.Read)
- public void list() {
- System.out.println("list");
- }
- @MyAnnotation3(models = {TranscationModel.Read, TranscationModel.Write})
- public void edit() {
- System.out.println("edit");
- }
- }
最后,进行测试
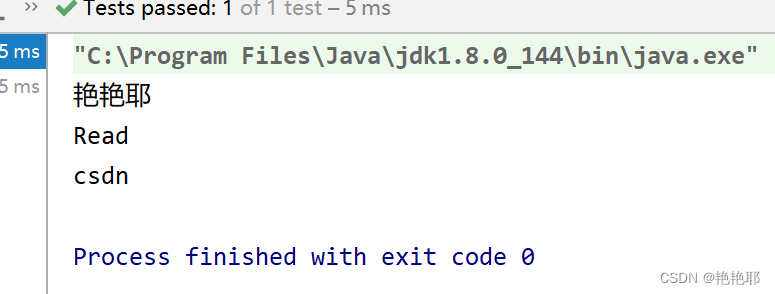
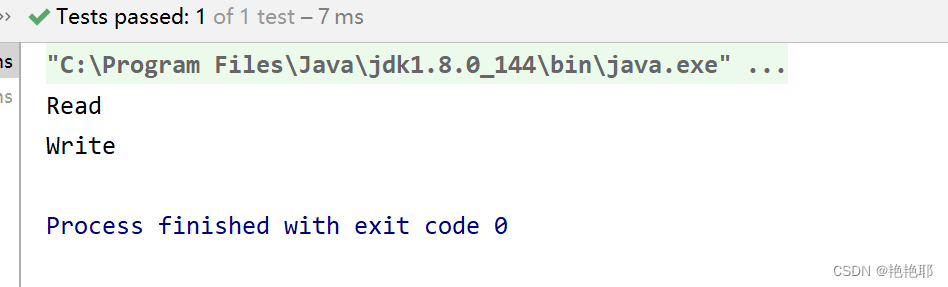
2.2 案例二(获取类属性上的注解属性值,默认值的赋予)
- package com.sy.annotation.Demo2;
- import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
- import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
- import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
- import java.lang.annotation.Target;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- * /
- //@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
- public @interface TestAnnotation {
- String value() default "默认value值";
- String what() default "这里是默认的what属性对应的值";
- }
建立类测试:
有些两个值都赋予了,有些只赋予了一个
- package com.sy.annotation.Demo2;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- *
- * 获取类属性上的注解属性值
- */
- public class Demo2 {
- @TestAnnotation(value = "这就是value对应的值_msg1", what = "这就是what对应的值_msg1")
- private static String msg1;
- @TestAnnotation("这就是value对应的值1")
- private static String msg2;
- @TestAnnotation(value = "这就是value对应的值2")
- private static String msg3;
- @TestAnnotation(what = "这就是what对应的值")
- private static String msg4;
- }
测试结果:

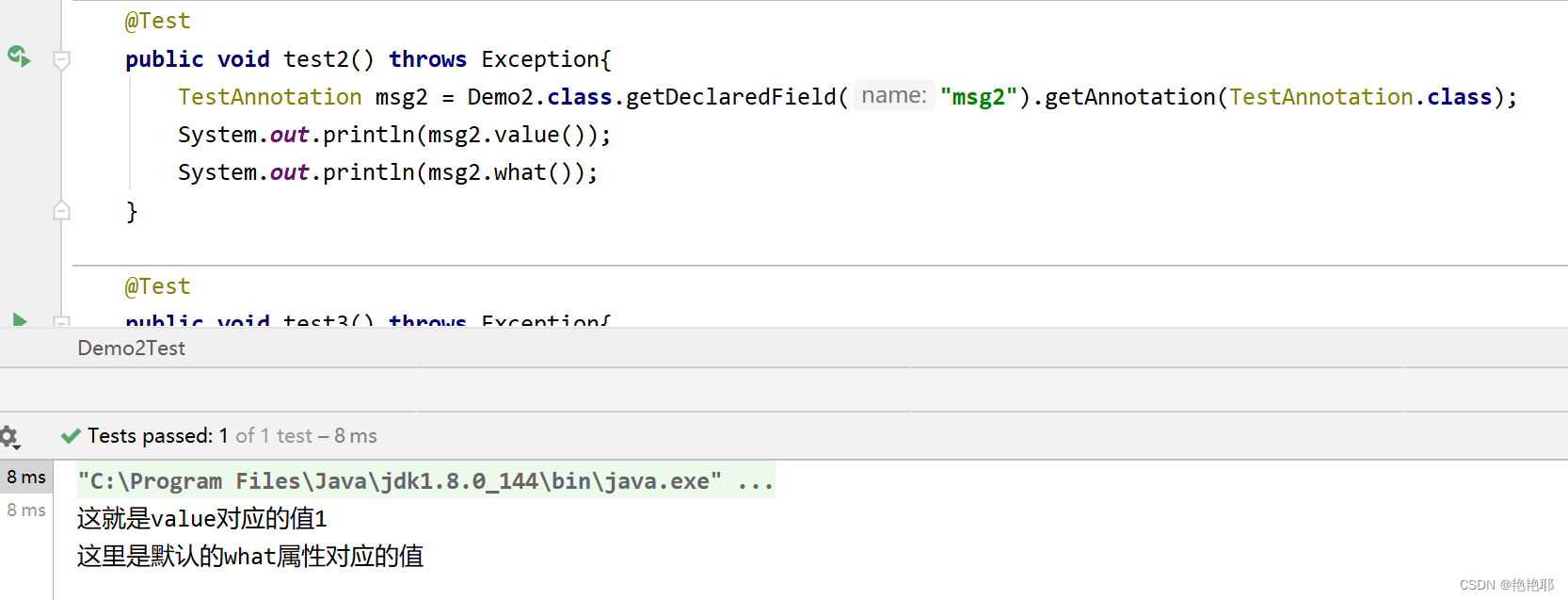
2.3 案例三(获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值,非空注解)
- package com.sy.annotation;
- import java.lang.annotation.*;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- *
- * 非空注解:使用在方法的参数上,false表示此参数可以为空,true不能为空
- */
- @Documented
- @Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- public @interface IsNotNull {
- boolean value() default false;
- }
建立方法,进行测试:
- package com.sy.annotation.Demo3;
- import com.sy.annotation.IsNotNull;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- *
- * 获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值
- */
- public class Demo3 {
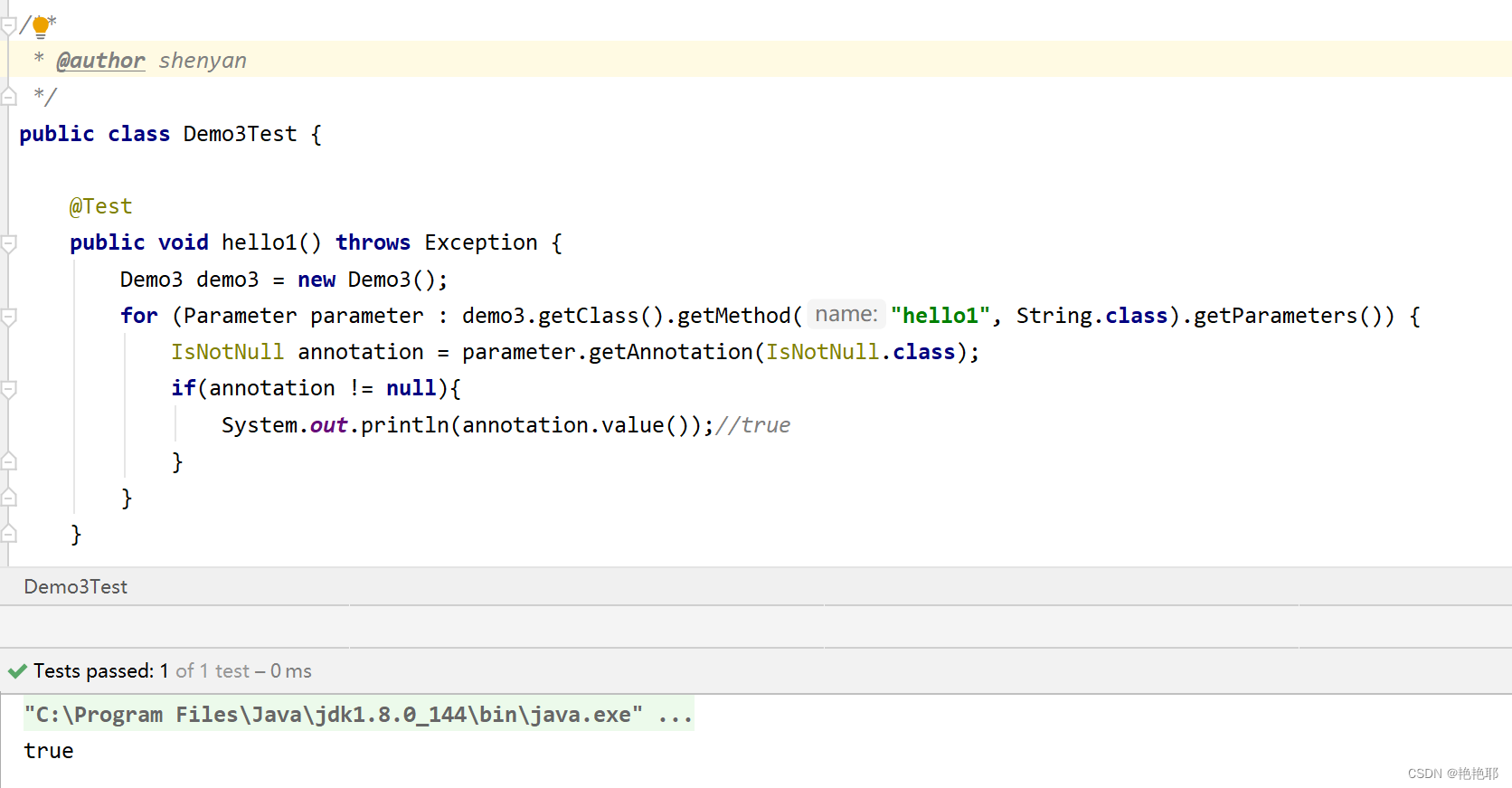
- public void hello1(@IsNotNull(true) String name) {
- System.out.println("hello:" + name);
- }
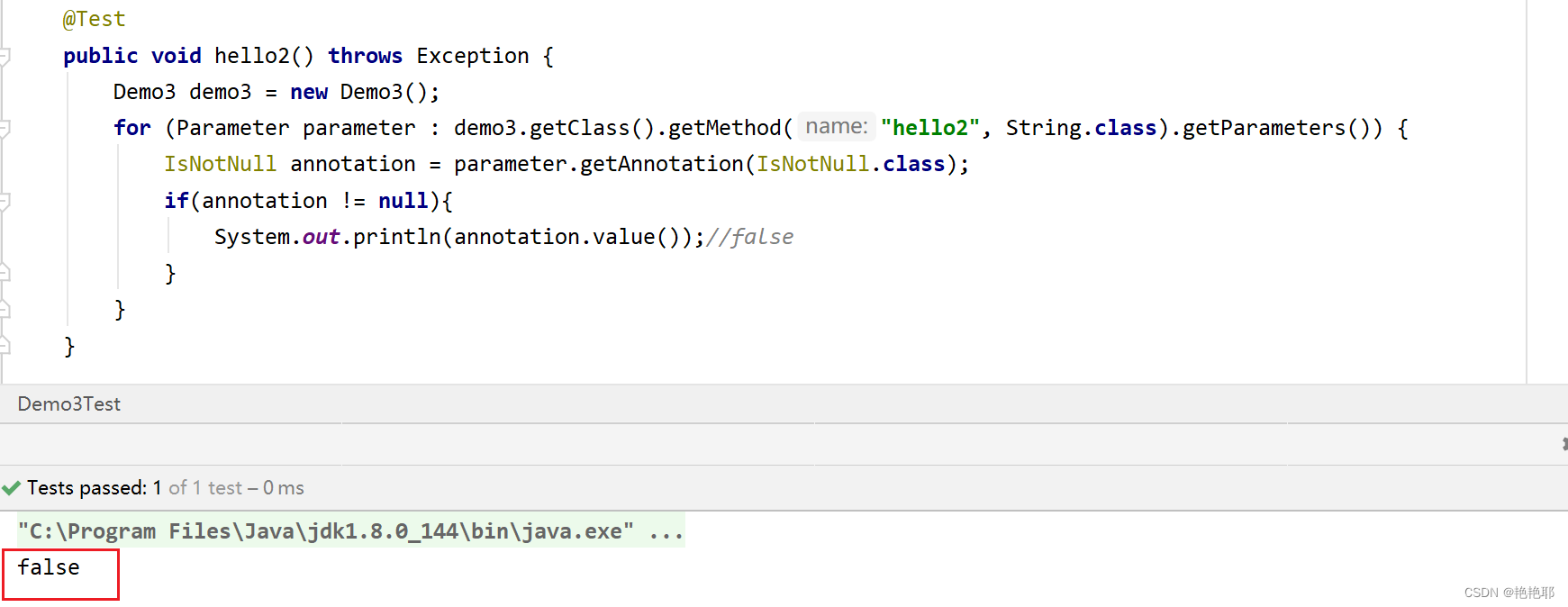
- public void hello2(@IsNotNull String name) {
- System.out.println("hello:" + name);
- }
- }
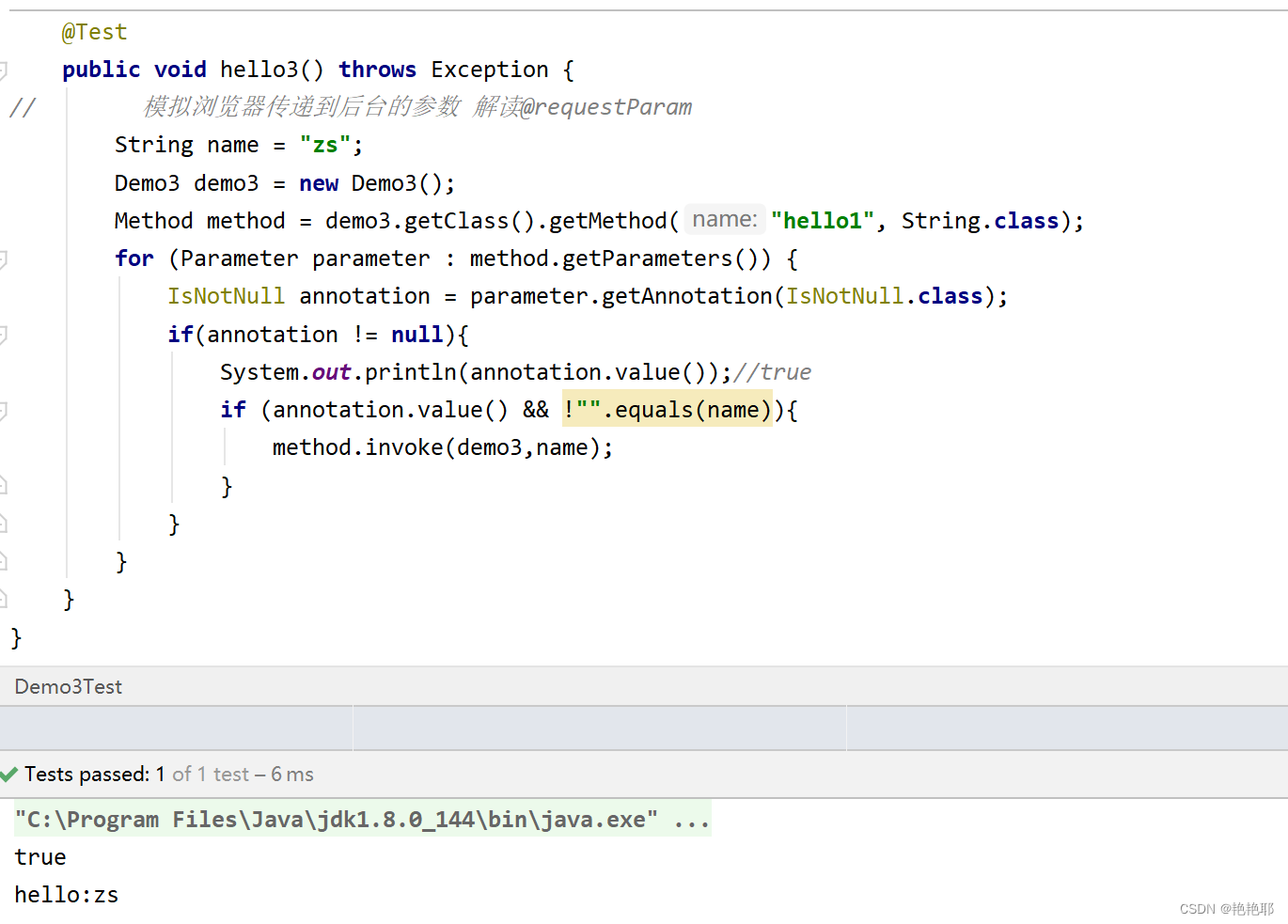
测试类:
方法1:
方法2:
方法3:
3.AOP结合自定义注解案例
配置相关AOP pom文件
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
- </dependency>
applicationContext.xml
- "1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
- xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
- <context:annotation-config/>
- <context:component-scan base-package="com.zking"/>
- <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
- beans>
定义一个标志日志的注解
- package com.sy.annotation;
- import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
- import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
- import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
- import java.lang.annotation.Target;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- */
- @Target(ElementType.METHOD)
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- public @interface MyLog {
- String desc();
- }
再创建一个切面类
LogAspect,用于实现日志记录的逻辑。- package com.sy.annotation.aop;
- import com.sy.annotation.MyLog;
- import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
- import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
- import org.slf4j.Logger;
- import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- */
- @Component
- @Aspect
- public class MyLogAspect {
- private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyLogAspect.class);
- /**
- * 只要用到了com.javaxl.p2.annotation.springAop.MyLog这个注解的,就是目标类
- */
- @Pointcut("@annotation(com.sy.annotation.MyLog)")
- private void MyValid() {
- }
- @Before("MyValid()")
- public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
- MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
- logger.debug("[" + signature.getName() + " : start.....]");
- System.out.println("[" + signature.getName() + " : start.....]");
- MyLog myLog = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(MyLog.class);
- logger.debug("【目标对象方法被调用时候产生的日志,记录到日志表中】:"+myLog.desc());
- System.out.println("【目标对象方法被调用时候产生的日志,记录到日志表中】:" + myLog.desc());
- }
- }
在方法上运用日志注解
- package com.sy.annotation.aop;
- import com.sy.annotation.MyLog;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- /**
- * @author shenyan
- */
- @Controller
- public class LogController {
- @RequestMapping("/myLog")
- @MyLog(desc = "这是结合spring aop知识,讲解自定义注解应用的一个案例")
- public void testLogAspect(){
- System.out.println("这里随便来点啥");
- }
- }
运行结果:

今日分享结束!

-
相关阅读:
前端基础(四十一):你不知道的JavaScript - 行为委托 及 类写法的实例应用
AI绘画工具介绍
<蓝桥杯软件赛>零基础备赛20周--第2周
基于微信小程序的英语互助小程序设计与实现(亮点:小组制打卡、模拟考试答题、错题本、学习论坛)
【ARFoundation学习笔记】平面检测
人工智能与神经网络BenchMark--MLPerf
Java项目:SSM农业信息管理系统
40.组合总和 II
前端面试话术集锦第 13 篇:高频考点(Vue常考进阶知识点)
Python实战——Selenium与iframe结合应用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_76988707/article/details/132900886
