-
知识储备--基础算法篇-链表
1.链表
链表在python中是可以自定义的,属性包括val和next。一般表示链表都是用头节点表示,得到下一个节点用next,都是地址,想要得到值用val。
1.1第160题-相交链表
简单来说,就是求两个链表交点节点的 指针。 这里要注意,交点不是数值相等,而是指针相等。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, x):
- # self.val = x
- # self.next = None
- class Solution(object):
- def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
- """
- :type head1, head1: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- # 用顺序遍历的方法
- p, q = headA, headB
- # 先得到两个链表的长度
- lenA = 0
- lenB = 0
- while p != None:
- p = p.next
- lenA += 1
- while q != None:
- q = q.next
- lenB += 1
- # 尾部对齐
- # 再次将pq对准链表头节点
- p, q = headA, headB
- if lenA < lenB:
- temp = lenB - lenA
- while temp != 0:
- q = q.next
- temp -= 1
- else:
- temp = lenA - lenB
- while temp != 0:
- p = p.next
- temp -= 1
- # 同时向后遍历
- len_min = min(lenA, lenB)
- for i in range(len_min):
- if p == q:
- return p
- else:
- p = p.next
- q = q.next
- return None

看了解析,自己用倒序法做做试试。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, x):
- # self.val = x
- # self.next = None
- class Solution(object):
- def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
- """
- :type head1, head1: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- # 用倒序遍历的方法
- # 用栈,先将地址顺序存进去,然后倒着遍历
- p, q = headA, headB
- # 先得到两个链表的长度
- lenA = 0
- lenB = 0
- listA = []
- listB = []
- while p != None:
- listA.append(p)
- p = p.next
- lenA += 1
- while q != None:
- listB.append(q)
- q = q.next
- lenB += 1
- len_min = min(lenA, lenB)
- result = None
- for i in range(len_min):
- if listA[lenA-1-i] == listB[lenB-1-i]:
- result = listA[lenA-1-i]
- else:
- return result
- return result

1.2第206题-反转链表
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。心得:若节点被引用,如p=head,这时改变head会使p也改变。所以需要提前存储节点。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def reverseList(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- # 值反转还是地址反转
- # 地址反转,因为读取链表的值需要一直遍历得到
- length = 0
- p = head
- q = head
- list_ = []
- while p != None:
- list_.append(p)
- length += 1
- q = p
- p = p.next
- p = head
- # 需要倒序遍历储存了节点地址的列表
- for i in reversed(range(length)):
- if i == 0:
- list_[i].next = None
- else:
- list_[i].next = list_[i-1]
- return q

一开始就想的这个方法,可惜不知道怎么实现。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def reverseList(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- pre = None
- cur = head
- while cur != None:
- nex = cur.next
- cur.next = pre
- pre = cur
- cur = nex
- return pre

1.3第234题-回文链表
第一时间想的就是把节点的值都存储到数组中,然后直接判断数组是否回文。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def isPalindrome(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: bool
- """
- p = head
- length = 0
- values = []
- while p != None:
- values.append(p.val)
- length += 1
- p = p.next
- for i in range(length/2):
- if values[i] == values[length-i-1]:
- continue
- else:
- return False
- return True

用快慢指针的方法能够节省很多空间
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def isPalindrome(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: bool
- """
- p = head
- # 用快慢指针
- fast = head
- slow = head
- # 1.找到前半部分尾节点
- while fast != None:
- if fast.next == None:
- break
- elif fast.next.next == None:
- break
- slow = slow.next
- fast = fast.next.next
- # 慢指针为前半部分的尾节点
- # 2.反转后半部分链表
- pre = None
- cur = slow
- while cur != None:
- nex = cur.next
- cur.next = pre
- pre = cur
- cur = nex
- # 3.判断是否回文
- while p != None:
- val1 = p.val
- val2 = pre.val
- if val1 != val2:
- return False
- p = p.next
- pre = pre.next
- # 4.恢复链表,和第二步一样操作
- # 5.返回结果
- return True

1.4第141题-环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点
head,判断链表中是否有环。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪
next指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。如果链表中存在环 ,则返回
true。 否则,返回false。心得:想到哈希表,虽然ac了,但时间跟空间都不行。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, x):
- # self.val = x
- # self.next = None
- class Solution(object):
- def hasCycle(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: bool
- """
- # 第一时间想到用字典,键值名是节点地址,键值是索引
- # 不需要返回环在第几个,可以用哈希表
- hash_table = set()
- p = head
- while p != None:
- if p in hash_table:
- return True
- else:
- hash_table.add(p)
- p = p.next
- return False

思考:环形链表有尾节点吗,有地址是None的情况吗。
答:没有尾节点,地址没有None的情况。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, x):
- # self.val = x
- # self.next = None
- class Solution(object):
- def hasCycle(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: bool
- """
- # 快慢指针?
- # 慢指针记录当前地址和前一个地址
- # 当快指针的地址与这两个相同时即存在环形链表
- if head == None:
- return False
- elif head.next == None:
- return False
- pre = None
- slow = head
- fast = head.next
- while slow != None:
- if fast == pre or fast == slow:
- return True
- if fast.next==None or fast.next.next==None:
- return False
- pre = slow
- slow = slow.next
- fast = fast.next.next
- return False

因为环形链表没有None,所以暴力解法。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, x):
- # self.val = x
- # self.next = None
- class Solution(object):
- def hasCycle(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: bool
- """
- # 因为环形链表没有None
- # 且数目最大是10**4
- p = head
- length = 0
- while 1:
- if p == None:
- return False
- else:
- length += 1
- p = p.next
- if length > 10000:
- return True

1.5第142题-环形链表2
给定一个链表的头节点
head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回null。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪
next指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果pos是-1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:

心得:还是先用哈希表做。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, x):
- # self.val = x
- # self.next = None
- class Solution(object):
- def detectCycle(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- # 用哈希表记录地址
- hash_table = set()
- p = head
- while p != None:
- if p not in hash_table:
- hash_table.add(p)
- else:
- return p
- p = p.next

看了题解,用快慢指针做,太复杂了,纯考数学啊。
1.6第21题-合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:

可以先创建一个val为-1的单链表,然后在其基础上拓展。思路还是挺简单的。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def mergeTwoLists(self, list1, list2):
- """
- :type list1: Optional[ListNode]
- :type list2: Optional[ListNode]
- :rtype: Optional[ListNode]
- """
- # 比较val的大小,然后决定next的地址
- # 头指针
- neww = ListNode(-1)
- # 移动指针
- new = neww
- while 1:
- if list1 == None:
- while list2 != None:
- new.next = list2
- new = new.next
- list2 = list2.next
- break
- elif list2 == None:
- while list1 != None:
- new.next = list1
- new = new.next
- list1 = list1.next
- break
- if list1.val <= list2.val:
- new.next = list1
- list1 = list1.next
- else:
- new.next = list2
- list2 = list2.next
- new = new.next
- return neww.next

1.7第2题-两数相加
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:

心得:逻辑挺简单的就是进位注意不要遗忘。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
- """
- :type l1: ListNode
- :type l2: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- neww = ListNode(-1)
- new = neww
- up = 0
- while l1 != None or l2 != None:
- if l1 != None and l2 != None:
- if l1.val + l2.val + up < 10:
- temp = ListNode(l1.val + l2.val + up)
- up = 0
- else:
- temp = ListNode((l1.val + l2.val + up)%10)
- up = 1
- l1 = l1.next
- l2 = l2.next
- elif l1 == None:
- if l2.val + up < 10:
- temp = ListNode(l2.val + up)
- up = 0
- else:
- temp = ListNode(0)
- up = 1
- l2 = l2.next
- elif l2 == None:
- if l1.val + up < 10:
- temp = ListNode(l1.val + up)
- up = 0
- else:
- temp = ListNode(0)
- up = 1
- l1 = l1.next
- new.next = temp
- new = new.next
- if up == 1:
- temp = ListNode(1)
- new.next = temp
- new = new.next
- return neww.next

1.8第19题-删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第
n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。示例 1:
先试试第三种方法
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :type n: int
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- # 几种方法
- # 1、先翻转,再删除第n个节点,再翻转
- # 2、计算长度,然后再遍历一遍,删掉节点
- # 3、计算长度并将地址存入数组,直接索引删除节点
- p = head
- index = []
- length = 0
- while p != None:
- length += 1
- index.append(p)
- p = p.next
- target = length - n
- if target == 0:
- return head.next
- if n == 1:
- index[target-1].next = None
- else:
- index[target-1].next = index[target+1]
- return head

再试试第二种
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :type n: int
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- # 几种方法
- # 1、先翻转,再删除第n个节点,再翻转
- # 2、计算长度,然后再遍历一遍,删掉节点
- # 3、计算长度并将地址存入数组,直接索引删除节点
- p = head
- length = 0
- while p != None:
- length += 1
- p = p.next
- target = length - n
- num = 0
- if target == 0:
- return head.next
- p = head
- while p != None:
- num += 1
- if num == target:
- p.next = p.next.next
- break
- p = p.next
- return head

第一种时间复杂度太高,就不试了。
看了解析,这种倒数第几个的方式应该要想到用栈来做,弹出的第n个节点就为需要删除的节点了。
哑节点的设置
dummy = ListNode(0, head)心得:看到一个双指针的方法,用两个指针,中间相差n,当一个指针到达尾部时,另一个就在目标位置,删除即可,没想到,可惜。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :type n: int
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- count = 0
- dummy_note = ListNode(0,head)
- fast = dummy_note
- slow = dummy_note
- while fast != None:
- if count > n:
- slow = slow.next
- count += 1
- fast = fast.next
- slow.next = slow.next.next
- return dummy_note.next
时间太长了吧。

1.9第24题-两两交换链表中的节点
心得:节点的地址永远不变,但表示地址的变量随时可以改变。要注意,要赋值的地址在上一两行不能改变,不然就混乱了,要合理安排赋值的顺序。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def swapPairs(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- # 1、把地址全存下来改
- # 2、遍历一遍并修改
- # 局部翻转链表
- # 两两交换需要三步
- if head == None:
- return head
- elif head.next == None:
- return head
- pre = ListNode(0,head)
- result = pre
- cur = head
- while cur:
- if cur.next == None:
- break
- back = cur.next
- cur.next = back.next
- back.next = cur
- pre.next = back
- pre = cur
- cur = cur.next
- return result.next

1.10第138题-复制带随机指针的链表
- """
- # Definition for a Node.
- class Node:
- def __init__(self, x, next=None, random=None):
- self.val = int(x)
- self.next = next
- self.random = random
- """
- class Solution(object):
- def copyRandomList(self, head):
- """
- :type head: Node
- :rtype: Node
- """
- if head == None:
- return None
- p = head
- q = head.next
- result = Node(p.val)
- cur = result
- i = result
- # 先生成单链表
- # 用双循环,当外层指针的random等于内层指针地址时,新链表的random也等于这个位置的地址
- while q:
- back = Node(q.val)
- cur.val = p.val
- cur.next = back
- cur = cur.next
- p = p.next
- q = q.next
- p = head
- k = result
- while p:
- i = result
- j = head
- while i:
- if p.random == None:
- k.random = None
- break
- if p.random == j:
- k.random = i
- i = i.next
- j = j.next
- p = p.next
- k = k.next
- return result

在题解评论中看到一个很巧妙的方法,试了一下确实很通俗易懂。
- """
- # Definition for a Node.
- class Node:
- def __init__(self, x, next=None, random=None):
- self.val = int(x)
- self.next = next
- self.random = random
- """
- class Solution(object):
- def copyRandomList(self, head):
- """
- :type head: Node
- :rtype: Node
- """
- if head == None:
- return None
- # 将新老节点地址储存在一起,遍历得到对应的next和random
- store = {}
- p = head
- while p:
- store[p] = Node(p.val)
- p = p.next
- p = head
- while p:
- if p.next == None:
- store[p].next = None
- else:
- store[p].next = store[p.next]
- if p.random == None:
- store[p].random = None
- else:
- store[p].random = store[p.random]
- p = p.next
- return store[head]

1.11第148题-排序链表
给你链表的头结点
head,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。示例 1:
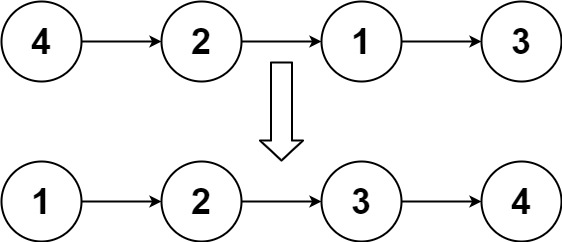
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
心得:想法是地址随着val排序,结果超时了。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def sortList(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- if head == None:
- return None
- # 把地址和对应的val存储起来
- # 先排序val,然后相应的地址也会改变
- p = head
- addrees = []
- length = 0
- while p:
- length += 1
- addrees.append(p)
- p = p.next
- for i in range(length):
- j = 0
- while j < length - i - 1:
- if addrees[j].val > addrees[j+1].val:
- temp_addrees = addrees[j]
- addrees[j] = addrees[j+1]
- addrees[j+1] = temp_addrees
- j += 1
- dummy = ListNode(0)
- head = addrees[0]
- dummy.next = head
- for i in range(1,length):
- head.next = addrees[i]
- head = head.next
- head.next = None
- return dummy.next
链表适合归并排序,冒泡、插入、归并都必须掌握。
- # Definition for singly-linked list.
- # class ListNode(object):
- # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
- # self.val = val
- # self.next = next
- class Solution(object):
- def sortList(self, head):
- """
- :type head: ListNode
- :rtype: ListNode
- """
- def sortFunc(head, tail):
- if not head:
- return head
- if head.next == tail:
- head.next = None
- return head
- slow = fast = head
- while fast != tail:
- slow = slow.next
- fast = fast.next
- if fast != tail:
- fast = fast.next
- mid = slow
- return merge(sortFunc(head, mid), sortFunc(mid, tail))
- def merge(head1, head2):
- dummyHead = ListNode(0)
- temp, temp1, temp2 = dummyHead, head1, head2
- while temp1 and temp2:
- if temp1.val <= temp2.val:
- temp.next = temp1
- temp1 = temp1.next
- else:
- temp.next = temp2
- temp2 = temp2.next
- temp = temp.next
- if temp1:
- temp.next = temp1
- elif temp2:
- temp.next = temp2
- return dummyHead.next
- return sortFunc(head, None)

-
相关阅读:
MySQL-大小写规范及sql_mode设置
U盘RAW格式无法格式化怎么办?
计算机毕业设计 基于SpringBoot的“漫画之家”系统的设计与实现 Java实战项目 附源码+文档+视频讲解
c++ - 模板(一)
宋浩概率论笔记(六)样本与统计量
java计算机毕业设计校园共享单车管理系统源码+系统+数据库+lw文档+mybatis+运行部署
zookeeper节点类型
基于JAVA商店管理系统计算机毕业设计源码+系统+mysql数据库+lw文档+部署
noip游记
盘点ERP开发的那点事-业务流和数据流
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Orange_sparkle/article/details/132766265