-
【算法】快速排序 详解
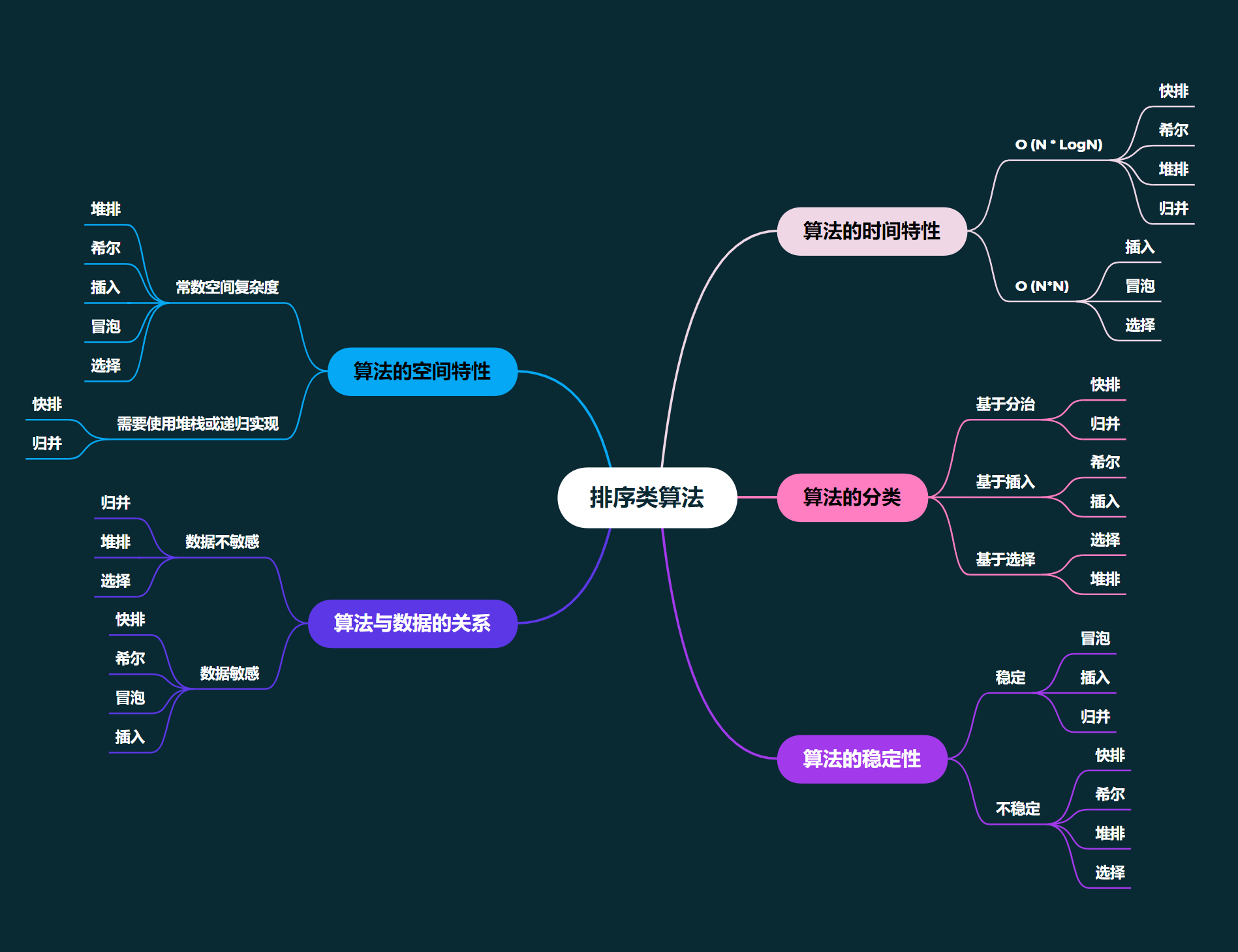
排序: 排序,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作。
稳定性: 假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具有相同的关键字的记录,若经过排序,这些记录的相对次序保持不变,即在原序列中, r[i] = r[j], 且 r[i] 在 r[j] 之前,而在排序后的序列中, r[i] 仍在 r[j] 之前,则称这种排序算法是稳定的;否则称为不稳定的。
(注意稳定排序可以实现为不稳定的形式, 而不稳定的排序实现不了稳定的形式)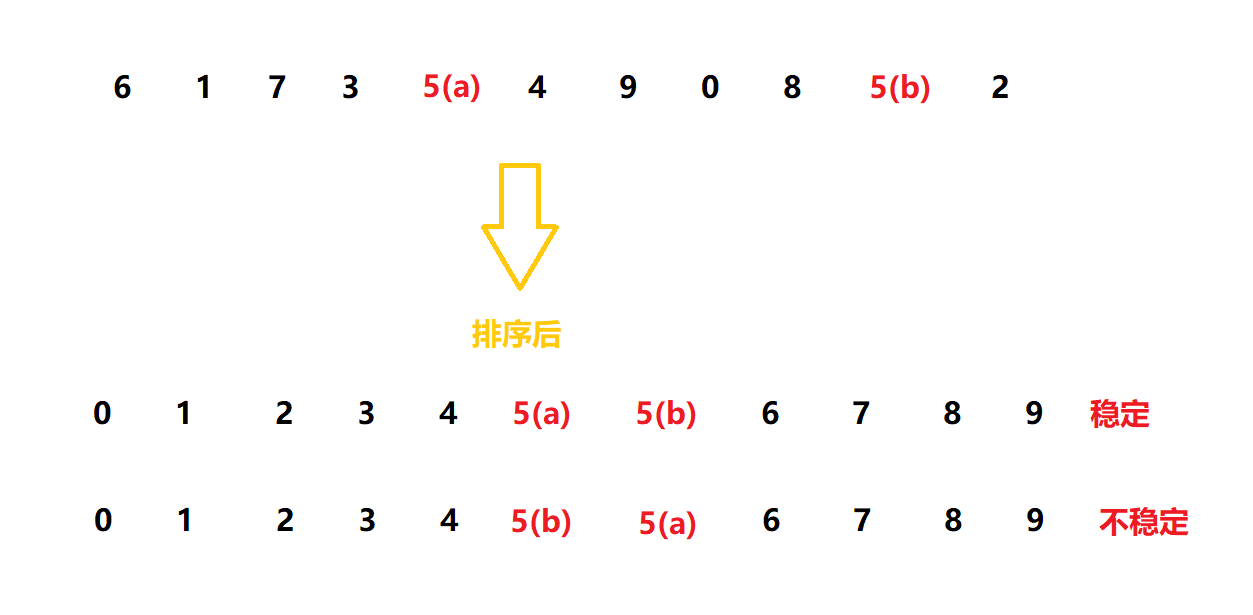
内部排序: 数据元素全部放在内存中的排序。
外部排序: 数据元素太多不能同时放在内存中,根据排序过程的要求不能在内外存之间移动数据的排序。
快速排序
快速排序是 Hoare 于 1962 年提出的一种二叉树结构的交换排序方法,其基本思想为:任取待排序元素序列中的某元素作为基准值,按照该排序码将待排序集合分割成两子序列,左子序列中所有元素均小于基准值,右子序列中所有元素均大于基准值,然后最左右子序列重复该过程,直到所有元素都排列在相应位置上为止。
1. 挖坑法
-
选择基准元素:从待排序的数组中选择一个元素作为基准(pivot)。通常情况下,可以选择第一个元素、最后一个元素、中间元素或者随机选择一个元素作为基准。
-
分割数组:从数组的两端开始,分别设置两个指针,一个从左边(low指针)开始,一个从右边(high指针)开始,分别向中间移动,直到它们相遇。在移动过程中,通过比较元素与基准的大小关系,找到一个大于基准的元素和一个小于基准的元素,并将它们互换位置。
-
继续分割:重复步骤2,直到low指针和high指针相遇。在此过程中,将小于基准的元素移到基准的左侧,将大于基准的元素移到基准的右侧,形成三个区域。
-
递归排序:对左侧小于基准的区域和右侧大于基准的区域,分别递归地应用快速排序算法。
public static void quickSort(int[] arr) { int len = arr.length; partition(arr, 0, len-1); } public static void partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return; } int pivot = left; int value = arr[left]; // 从两边开始遍历 int begin = left; int end = right; while (begin < end) { // 注意一定要带上 ==, 不然死循环 while (begin < end && arr[end] >= value) { end--; } // 右边找到小于 value 的值 arr[pivot] = arr[end]; // end 变为 坑 pivot = end; while (begin < end && arr[begin] <= value) { begin++; } // 左边找到大于 value 的值 arr[pivot] = arr[begin]; // begin 变为坑 pivot = begin; } // value 找到自己的正确位置 arr[pivot] = value; // 递归左边和右边 partition(arr, left, pivot-1); partition(arr, pivot+1, right); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
2. 左右指针法 (Hoare 法)
从两边开始, 左边找到比基准值大的, 右边找比基准值小的, 找到后, 两边交换, 一直到左右两个指针相遇, 相遇位置即为基准值的正确位置, 然后递归确定左右两边的区间元素的位置。
public static void quickSort(int[] arr) { int len = arr.length; partition(arr, 0, len-1); } public static void partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return; } int value = arr[left]; int begin = left; int end = right; while (begin < end) { // 注意一定要带上 ==, 不然死循环 while (begin < end && arr[end] >= value) { end--; } while (begin < end && arr[begin] <= value) { begin++; } swap(arr, begin, end); } swap(arr, left, begin); partition(arr, left, begin-1); partition(arr, begin+1, right); } public static void swap (int[] arr, int index1, int index2) { int temp = arr[index1]; arr[index1] = arr[index2]; arr[index2] = temp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
3. 前后指针法
后面的指针指向小于基准值的最后一个, 前面的指针一直往后找, 找到小于基准值的就与后面指针的下一个位置交换, 后面的指针 ++, 直到前面的指针遍历完, 最后后面的指针的位置, 就是基准值的正确位置。然后再递归确定左右区间的元素的位置。
public static void quickSort(int[] arr) { int len = arr.length; partition(arr, 0, len-1); } public static void partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return; } int value = arr[left]; // 前后指针 int end = left; int front = left + 1; while (front <= right) { if (arr[front] < value) { swap(arr, end+1, front); end++; } front++; } swap(arr, left, end); // 递归左边和右边 partition(arr, left, end-1); partition(arr, end+1, right); } public static void swap (int[] arr, int index1, int index2) { int temp = arr[index1]; arr[index1] = arr[index2]; arr[index2] = temp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
4. 快排非递归
使用栈记录要排序的区间
public static void quickSortNonR(int[] arr) { int len = arr.length; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(arr.length-1); stack.push(0); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { int left = stack.pop(); int right = stack.pop(); if (left >= right) { continue; } int pivot = left; int value = arr[left]; // 从两边开始遍历 int begin = left; int end = right; while (begin < end) { // 注意一定要带上 ==, 不然死循环 while (begin < end && arr[end] >= value) { end--; } // 右边找到小于 value 的值 arr[pivot] = arr[end]; // end 变为 坑 pivot = end; while (begin < end && arr[begin] <= value) { begin++; } // 左边找到大于 value 的值 arr[pivot] = arr[begin]; // begin 变为坑 pivot = begin; } // value 找到自己的正确位置 arr[pivot] = value; // 右区间 stack.push(right); stack.push(pivot+1); // 左区间 stack.push(pivot-1); stack.push(left); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
代码优化
优化一:
三数取中:
当我们找基准值时, 基准值越靠近是中位数,每次都近似于将一个大的区间分成两个相等的区间, 那么时间复杂度越低, 越靠近是 O(N*logN), 最坏的情况下, 每次确定一个元素, 即分成的两个区间其中一个只有一个元素, 那么如果每次都是这样的话, 最终的时间复杂度为 O(N*N), 所以选择基准值时, 越靠近中位数越好。这里面以前后指针为例使用了 三数取中
public static void quickSort(int[] arr) { int len = arr.length; partition(arr, 0, len-1); } /** * 前后指针 */ public static void partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return; } // 三数取中 int midIndex = getMidIndex(arr, left, right); swap(arr, left, midIndex); int value = arr[left]; // 前后指针 int end = left; int front = left + 1; while (front <= right) { if (arr[front] < value) { swap(arr, end+1, front); end++; } front++; } swap(arr, left, end); // 递归左边和右边 partition(arr, left, end-1); partition(arr, end+1, right); } public static int getMidIndex(int[] arr, int left, int right) { int midIndex = ((right - left) >> 1) + left; if (arr[left] <= arr[midIndex]) { if (arr[midIndex] <= arr[right]) { return midIndex; } else { if (arr[left] >= arr[right]) { return left; } else { return right; } } } else { if (arr[midIndex] >= arr[right]) { return midIndex; } else { if (arr[left] >= arr[right]) { return right; } else { return left; } } } } public static void swap (int[] arr, int index1, int index2) { int temp = arr[index1]; arr[index1] = arr[index2]; arr[index2] = temp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
优化二:
小区间优化, 当区间中元素数量比较少时,区间中元素本身就接近有序, 使用直接插入排序能提高效率 (直接插入排序)
假如说有 100W 个数据, 就会调用 100W 次 partition 函数, 但是光最后两层就会调用近 80W 次, 所以使用小区间优化提高效率。直接插入排序
public static void insertSort(int[] arr) { int len = arr.length; for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { // 从已经有序的位置从后往前开始比较 int key = arr[i]; int end = i-1; while (end >= 0 && arr[end] > key) { // 数据往后挪 arr[end+1] = arr[end]; end--; } // 找到了合适位置, 就插入进去 arr[end+1] = key; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
在快排中使用小区间优化
/** * 直接插入排序 */ public static void insertSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) { for (int i = left+1; i <= right; i++) { // 从已经有序的位置从后往前开始比较 int key = arr[i]; int end = i-1; while (end >= 0 && arr[end] > key) { // 数据往后挪 arr[end+1] = arr[end]; end--; } // 找到了合适位置, 就插入进去 arr[end+1] = key; } } public static void quickSort(int[] arr) { int len = arr.length; partition(arr, 0, len-1); } public static void partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) { return; } // 小区间优化, 当数组中元素个数 <= 100 个时使用直接插入排序 // 主要是减少了递归的次数 if (right - left + 1 <= 100) { insertSort(arr, left, right); return; } // 三数取中 int midIndex = getMidIndex(arr, left, right); swap(arr, left, midIndex); int value = arr[left]; // 前后指针 int end = left; int front = left + 1; while (front <= right) { if (arr[front] < value) { swap(arr, end+1, front); end++; } front++; } swap(arr, left, end); // 递归左边和右边 partition(arr, left, end-1); partition(arr, end+1, right); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
总结:
- 快速排序整体的综合性能和使用场景都是比较好的,所以才敢叫快速排序
- 时间复杂度: O (N*logN)
- 空间复杂度: O(logN)
- 是不稳定排序
- 对数据比较敏感: 当数据本身就是有序时, 情况最坏, 因为每次只能确定一个数据, 时间复杂度为 O(N*N)

好啦, 以上就是对快速排序的讲解, 希望能帮到你 !
评论区欢迎指正 ! -
-
相关阅读:
【原创】基于SSM的剧本杀预约管理系统(毕业设计源代码)
[附源码]java毕业设计基于的高校学生考勤管理系统
Learn Git Branching:在游戏中学会Git
python -opencv 边缘检测
JWT 简介与 C# 示例
Cordova插件的简单使用
11--Django-Ajax使用-前后端序列化、反序列化及layer组件
代码开源设计实现思路
matlab EL image绘制
OpenCV/C++ 图片锐化
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61832361/article/details/132642290
