-
【LeetCode题目详解】第九章 动态规划part08 139.单词拆分 (day46补)
本文章代码以c++为例!
一、力扣第139题:单词拆分
题目:
给你一个字符串
s和一个字符串列表wordDict作为字典。请你判断是否可以利用字典中出现的单词拼接出s。注意:不要求字典中出现的单词全部都使用,并且字典中的单词可以重复使用。
示例 1:
输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"] 输出: true 解释: 返回 true 因为 "leetcode" 可以由 "leet" 和 "code" 拼接成。
示例 2:
输入: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"] 输出: true 解释: 返回 true 因为
"applepenapple"可以由"apple" "pen" "apple" 拼接成。 注意,你可以重复使用字典中的单词。示例 3:
输入: s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats", "dog", "sand", "and", "cat"] 输出: false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 3001 <= wordDict.length <= 10001 <= wordDict[i].length <= 20s和wordDict[i]仅由小写英文字母组成wordDict中的所有字符串 互不相同
思路
看到这道题目的时候,大家应该回想起我们之前讲解回溯法专题的时候,讲过的一道题目回溯算法:分割回文串
(opens new window),就是枚举字符串的所有分割情况。
(opens new window):是枚举分割后的所有子串,判断是否回文。
本道是枚举分割所有字符串,判断是否在字典里出现过。
那么这里我也给出回溯法C++代码:
- class Solution {
- private:
- bool backtracking (const string& s, const unordered_set
& wordSet, int startIndex) { - if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
- return true;
- }
- for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
- string word = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
- if (wordSet.find(word) != wordSet.end() && backtracking(s, wordSet, i + 1)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- public:
- bool wordBreak(string s, vector
& wordDict) { - unordered_set
wordSet(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end()) ; - return backtracking(s, wordSet, 0);
- }
- };
- 时间复杂度:O(2^n),因为每一个单词都有两个状态,切割和不切割
- 空间复杂度:O(n),算法递归系统调用栈的空间
那么以上代码很明显要超时了,超时的数据如下:
- "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaab"
- ["a","aa","aaa","aaaa","aaaaa","aaaaaa","aaaaaaa","aaaaaaaa","aaaaaaaaa","aaaaaaaaaa"]
递归的过程中有很多重复计算,可以使用数组保存一下递归过程中计算的结果。
这个叫做记忆化递归,这种方法我们之前已经提过很多次了。
使用memory数组保存每次计算的以startIndex起始的计算结果,如果memory[startIndex]里已经被赋值了,直接用memory[startIndex]的结果。
C++代码如下:
- class Solution {
- private:
- bool backtracking (const string& s,
- const unordered_set
& wordSet, - vector<bool>& memory,
- int startIndex) {
- if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
- return true;
- }
- // 如果memory[startIndex]不是初始值了,直接使用memory[startIndex]的结果
- if (!memory[startIndex]) return memory[startIndex];
- for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
- string word = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
- if (wordSet.find(word) != wordSet.end() && backtracking(s, wordSet, memory, i + 1)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- memory[startIndex] = false; // 记录以startIndex开始的子串是不可以被拆分的
- return false;
- }
- public:
- bool wordBreak(string s, vector
& wordDict) { - unordered_set
wordSet(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end()) ; - vector<bool> memory(s.size(), 1); // -1 表示初始化状态
- return backtracking(s, wordSet, memory, 0);
- }
- };
这个时间复杂度其实也是:O(2^n)。只不过对于上面那个超时测试用例优化效果特别明显。
这个代码就可以AC了,当然回溯算法不是本题的主菜,背包才是!
# 背包问题
单词就是物品,字符串s就是背包,单词能否组成字符串s,就是问物品能不能把背包装满。
拆分时可以重复使用字典中的单词,说明就是一个完全背包!
动规五部曲分析如下:
- 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
dp[i] : 字符串长度为i的话,dp[i]为true,表示可以拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
- 确定递推公式
如果确定dp[j] 是true,且 [j, i] 这个区间的子串出现在字典里,那么dp[i]一定是true。(j < i )。
所以递推公式是 if([j, i] 这个区间的子串出现在字典里 && dp[j]是true) 那么 dp[i] = true。
- dp数组如何初始化
从递推公式中可以看出,dp[i] 的状态依靠 dp[j]是否为true,那么dp[0]就是递推的根基,dp[0]一定要为true,否则递推下去后面都都是false了。
那么dp[0]有没有意义呢?
dp[0]表示如果字符串为空的话,说明出现在字典里。
但题目中说了“给定一个非空字符串 s” 所以测试数据中不会出现i为0的情况,那么dp[0]初始为true完全就是为了推导公式。
下标非0的dp[i]初始化为false,只要没有被覆盖说明都是不可拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
- 确定遍历顺序
题目中说是拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词,所以这是完全背包。
还要讨论两层for循环的前后顺序。
如果求组合数就是外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包。
如果求排列数就是外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品。
我在这里做一个总结:
求组合数:动态规划:518.零钱兑换II
(opens new window) 求排列数:动态规划:377. 组合总和 Ⅳ (opens new window)、动态规划:70. 爬楼梯进阶版(完全背包) (opens new window) 求最小数:动态规划:322. 零钱兑换 (opens new window)、动态规划:279.完全平方数
而本题其实我们求的是排列数,为什么呢。 拿 s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"] 举例。
"apple", "pen" 是物品,那么我们要求 物品的组合一定是 "apple" + "pen" + "apple" 才能组成 "applepenapple"。
"apple" + "apple" + "pen" 或者 "pen" + "apple" + "apple" 是不可以的,那么我们就是强调物品之间顺序。
所以说,本题一定是 先遍历 背包,再遍历物品。
- 举例推导dp[i]
以输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"]为例,dp状态如图:

dp[s.size()]就是最终结果。
动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
- class Solution {
- public:
- bool wordBreak(string s, vector
& wordDict) { - unordered_set
wordSet(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end()) ; - vector<bool> dp(s.size() + 1, false);
- dp[0] = true;
- for (int i = 1; i <= s.size(); i++) { // 遍历背包
- for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { // 遍历物品
- string word = s.substr(j, i - j); //substr(起始位置,截取的个数)
- if (wordSet.find(word) != wordSet.end() && dp[j]) {
- dp[i] = true;
- }
- }
- }
- return dp[s.size()];
- }
- };
- 时间复杂度:O(n^3),因为substr返回子串的副本是O(n)的复杂度(这里的n是substring的长度)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
# 拓展
关于遍历顺序,再给大家讲一下为什么 先遍历物品再遍历背包不行。
这里可以给出先遍历物品再遍历背包的代码:
- class Solution {
- public:
- bool wordBreak(string s, vector
& wordDict) { - unordered_set
wordSet(wordDict.begin(), wordDict.end()) ; - vector<bool> dp(s.size() + 1, false);
- dp[0] = true;
- for (int j = 0; j < wordDict.size(); j++) { // 物品
- for (int i = wordDict[j].size(); i <= s.size(); i++) { // 背包
- string word = s.substr(i - wordDict[j].size(), wordDict[j].size());
- // cout << word << endl;
- if ( word == wordDict[j] && dp[i - wordDict[j].size()]) {
- dp[i] = true;
- }
- // for (int k = 0; k <= s.size(); k++) cout << dp[k] << " "; //这里打印 dp数组的情况
- // cout << endl;
- }
- }
- return dp[s.size()];
- }
- };
使用用例:s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple", "pen"],对应的dp数组状态如下:
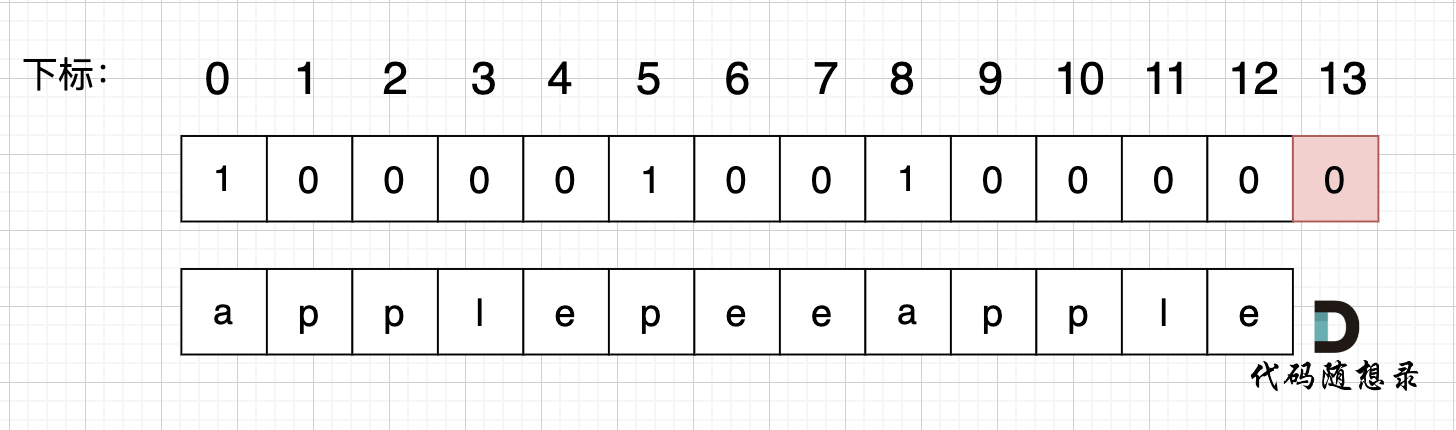
最后dp[s.size()] = 0 即 dp[13] = 0 ,而不是1,因为先用 "apple" 去遍历的时候,dp[8]并没有被赋值为1 (还没用"pen"),所以 dp[13]也不能变成1。
除非是先用 "apple" 遍历一遍,再用 "pen" 遍历,此时 dp[8]已经是1,最后再用 "apple" 去遍历,dp[13]才能是1。
如果大家对这里不理解,建议可以把我上面给的代码,拿去力扣上跑一跑,把dp数组打印出来,对着递推公式一步一步去看,思路就清晰了。
# 总结
本题和我们之前讲解回溯专题的回溯算法:分割回文串
(opens new window)非常像,所以我也给出了对应的回溯解法。
稍加分析,便可知道本题是完全背包,是求能否组成背包,而且这里要求物品是要有顺序的。
-
相关阅读:
详细了解一下股票量化交易接口股
SpringBoot整合阿里云短信服务
P3799 妖梦拼木棒——枚举+组合数学
Active Directory密码恢复:徒劳的行为
RabbitMQ初步到精通-第十一章-RabbitMQ之常见问题汇总
3步接入顺丰快递云打印电子面单接口API
甘肃教育杂志甘肃教育杂志社甘肃教育编辑部2022年第15期目录
React(二):Redux基本使用方法
Redis内存回收
跨环境同步数据的操作方式:使用mysqldump 远程执行备份与还原
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_67972246/article/details/132781277
