-
基于随机森林的otto商品分类
数据集介绍
Otto Group数据集来源于《Otto Group Product Classification Challenge》。Otto集团是世界上最大的电子商务公司之一,在20多个国家拥有子公司。我们每天在全球销售数百万种产品,在我们的产品线中添加了数千种产品。
我们公司对我们产品性能的一致性分析至关重要。然而,由于我们的全球基础设施不同,许多相同的产品被分类不同。因此,我们的产品分析的质量在很大程度上取决于对类似产品进行准确分类的能力。分类越好,我们对产品范围的了解就越多。
在这次竞争中,我们为超过200000种产品提供了一个具有93项功能的数据集。目的是建立一个预测模型,能够区分我们的主要产品类别。获奖模型将采用开源模式。
奥托集团产品分类数据集:
- Target:共9个商品类别
- Features:93个特征:整数型特征
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import os import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, OneHotEncoder from sklearn.metrics import log_loss from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV %matplotlib inline- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
读取数据
查看当前工作路径
os.path.abspath('.')- 1
读取数据
data = pd.read_csv("./otto-group-product-classification-challenge/train.csv") data.head()- 1
- 2
id feat_1 feat_2 feat_3 feat_4 feat_5 feat_6 feat_7 feat_8 feat_9 ... feat_85 feat_86 feat_87 feat_88 feat_89 feat_90 feat_91 feat_92 feat_93 target 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Class_1 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Class_1 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Class_1 3 4 1 0 0 1 6 1 5 0 0 ... 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 Class_1 4 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 Class_1 5 rows × 95 columns
# 数据维度 data.shape- 1
- 2
(61878, 95)- 1
数据特征分析
# 描述性统计 data.describe()- 1
- 2
id feat_1 feat_2 feat_3 feat_4 feat_5 feat_6 feat_7 feat_8 feat_9 ... feat_84 feat_85 feat_86 feat_87 feat_88 feat_89 feat_90 feat_91 feat_92 feat_93 count 61878.000000 61878.00000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 ... 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 61878.000000 mean 30939.500000 0.38668 0.263066 0.901467 0.779081 0.071043 0.025696 0.193704 0.662433 1.011296 ... 0.070752 0.532306 1.128576 0.393549 0.874915 0.457772 0.812421 0.264941 0.380119 0.126135 std 17862.784315 1.52533 1.252073 2.934818 2.788005 0.438902 0.215333 1.030102 2.255770 3.474822 ... 1.151460 1.900438 2.681554 1.575455 2.115466 1.527385 4.597804 2.045646 0.982385 1.201720 min 1.000000 0.00000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 ... 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 25% 15470.250000 0.00000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 ... 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 50% 30939.500000 0.00000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 ... 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 75% 46408.750000 0.00000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.000000 0.000000 ... 0.000000 0.000000 1.000000 0.000000 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 max 61878.000000 61.00000 51.000000 64.000000 70.000000 19.000000 10.000000 38.000000 76.000000 43.000000 ... 76.000000 55.000000 65.000000 67.000000 30.000000 61.000000 130.000000 52.000000 19.000000 87.000000 8 rows × 94 columns
# 查看数据分布 sns.countplot(x=data.target)- 1
- 2
- 1
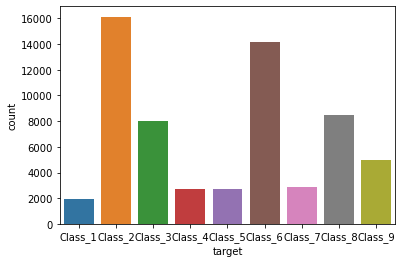
可以看出,数据类别不均衡
数据处理
# 特征值 x = data.drop(["id","target"], axis=1) # 目标值 y = data["target"]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
x.head()- 1
feat_1 feat_2 feat_3 feat_4 feat_5 feat_6 feat_7 feat_8 feat_9 feat_10 ... feat_84 feat_85 feat_86 feat_87 feat_88 feat_89 feat_90 feat_91 feat_92 feat_93 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 1 0 0 1 6 1 5 0 0 1 ... 22 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 5 rows × 93 columns
y.value_counts().sort_index()
# 由于数据集较大,同时样本类别分布不均衡,故通过欠采样缩小数据集规模 # from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler- 1
- 2
把标签值转换为数字
y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(y) y- 1
- 2
array([0, 0, 0, ..., 8, 8, 8])- 1
分割数据
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y, test_size=0.2) x_train.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape, x_test.shape- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
((49502, 93), (49502,), (12376,), (12376, 93))- 1
模型训练
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier rf_model = RandomForestClassifier(oob_score=True) rf_model.fit(x_train, y_train)- 1
- 2
- 3
RandomForestClassifier(oob_score=True)- 1
y_pred = rf_model.predict(x_test)- 1
模型评估
# 模型在训练集上的准确率 rf_model.score(x_train, y_train)- 1
- 2
0.9999797987960083- 1
# 模型在测试集上的准确率 rf_model.score(x_test, y_test)- 1
- 2
0.8089043309631545- 1
# 包外估计 rf_model.oob_score_- 1
- 2
0.7993818431578522- 1
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False) y_test = encoder.fit_transform(y_test.reshape(-1,1)) y_pred = encoder.fit_transform(y_pred.reshape(-1,1)) y_test,- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(array([[0., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 1., 0., 0.], ..., [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 1.], [0., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [1., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]]),)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
y_pred- 1
array([[0., 0., 1., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 1., 0.], ..., [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 1.], [0., 1., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
# logloss评估 log_loss(y_test, y_pred, eps=1e-15, normalize=True)- 1
- 2
6.600210582899472- 1
# 以概率形式输出 y_pred_proba = rf_model.predict_proba(x_test) y_pred_proba- 1
- 2
- 3
array([[0. , 0.2 , 0.77, ..., 0. , 0.02, 0. ], [0.02, 0.48, 0.16, ..., 0.06, 0. , 0. ], [0.03, 0.02, 0.03, ..., 0.3 , 0.32, 0.02], ..., [0.12, 0.01, 0.05, ..., 0.08, 0.11, 0.53], [0.01, 0.56, 0.32, ..., 0.01, 0.02, 0. ], [0.18, 0.09, 0.01, ..., 0.1 , 0.2 , 0.14]])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
rf_model.oob_score_- 1
0.7993818431578522- 1
log_loss(y_test, y_pred_proba, eps=1e-15, normalize=True)- 1
0.6232249914857839- 1
- 1
-
相关阅读:
接口自动化测试总结
如何使用递归,递归使用的技巧详解
统一身份认证实现,推广的可能性及优缺点?
【代码随想录】算法训练计划04
模式识别与图像处理课程实验二:基于UNet的目标检测网络
【C++基础】左值引用、右值引用、move、forward
人机验证reCAPTCHA v3使用完备说明
C#大作业——学生信息管理系统
使用自定义 PyTorch 运算符优化深度学习数据输入管道
Vue中的事件修饰符
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43276566/article/details/132576111