-
C语言实现“队列“

🎈个人主页:🎈 :✨✨✨初阶牛✨✨✨
🐻推荐专栏: 🍔🍟🌯C语言进阶
🔑个人信条: 🌵知行合一
🍉本篇简介:>:分享数据结构之C语言实现"队列".各个接口分别分析,讲解思路已经动图讲解.
金句分享:
✨书要好好读,喜欢的人也要好好争取!✨前言
一、队列
1.1 队列的介绍:
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表.
队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行"插入"操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行"删除"操作的一端称为队头
用顺序表还是用链表实现队列比较好呢?
结构 尾插 头插 顺序表 效率很高,不需要移动数据 效率极低,需要移动除首元素以外的所有数据 链表 效率较低,需要遍历链表找尾巴 效率高,改变头指针即可 - 对于链表的缺点,我们可以额外创建一个尾指针用于记录尾结点.这样效率就不是问题了,而顺序表的头插是硬伤.
- 链表不需要扩容,顺序表需要动态扩容/
综上,咱还是选择链表=实现队列吧!
typedef int QDatatype; typedef struct QueueNode { struct QueueNode* next; QDatatype data; }QNode; typedef struct Queue { QNode* head;//记录队首 QNode* tail;//记录队尾 int size;//记录长度 }Queue;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
图解:

1.2 "队列"的常见接口:
接口介绍:
//队列的初始化操作 void QueueInit(Queue* pq); //队列的销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq); //入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x); //出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq); //队列的长度 int QueueSize(Queue* pq); //队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); //取队头元素 QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq); //取队尾元素 QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
二、接口的具体实现:
2.1 "队列"的"初始化"操作(QueueInit)
队列的结构是由两个结点指针,加一个记录长度的
size变量组成.队列的初始状态:
头指针=尾指针,长度为0.代码:
//初始化"队列"操作 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL; int size = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.2 "入队"操作(QueuePush)
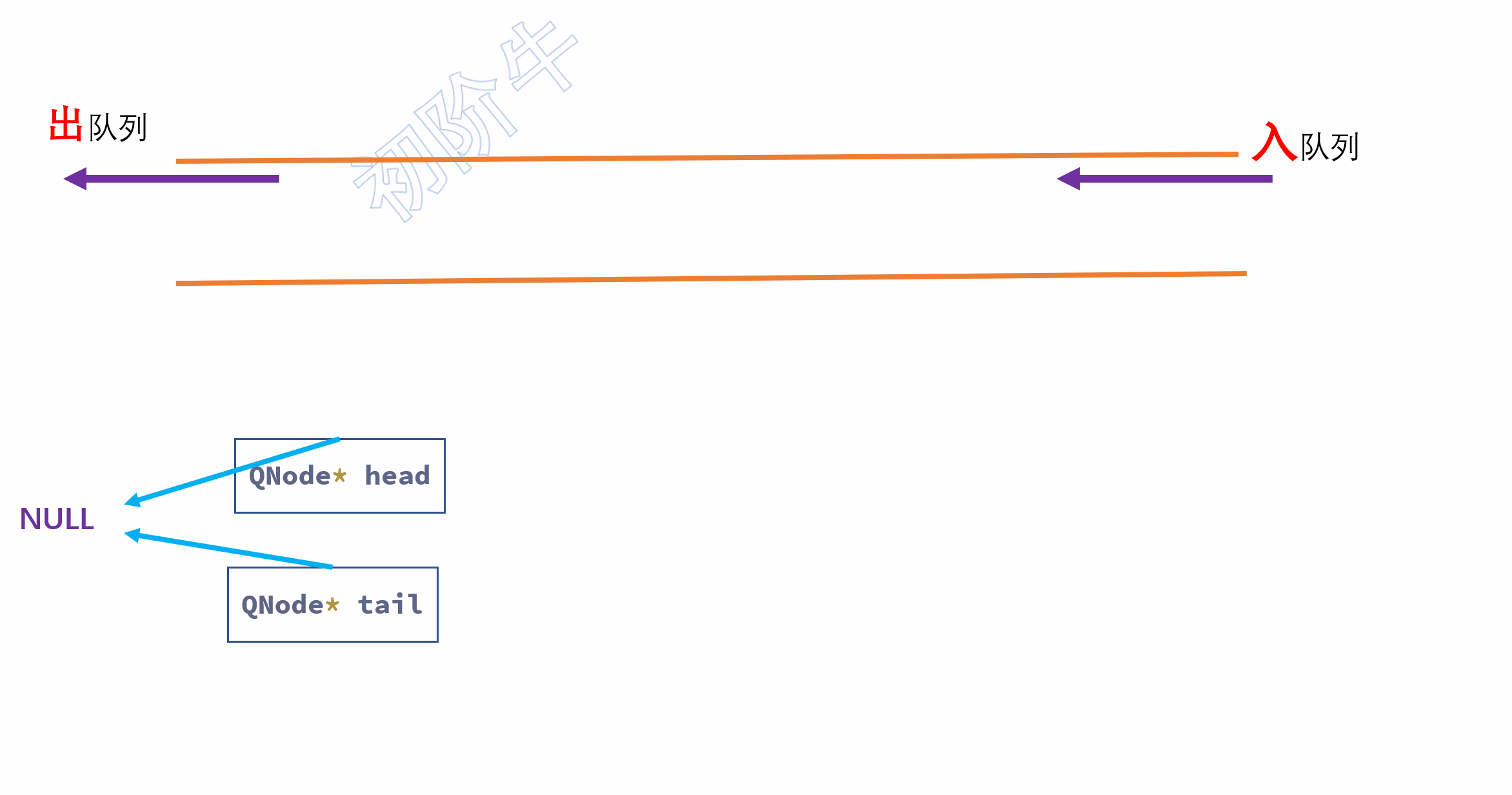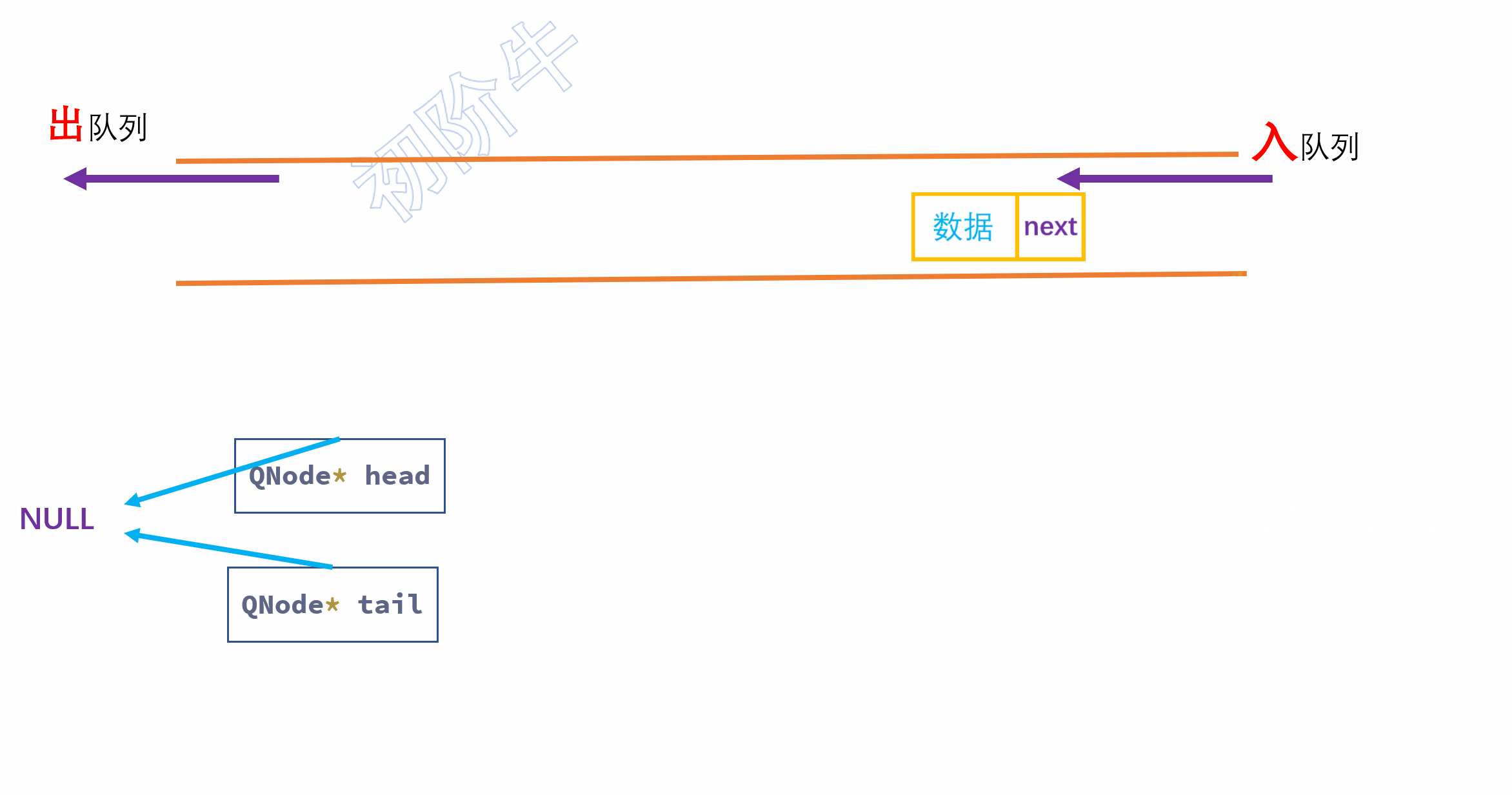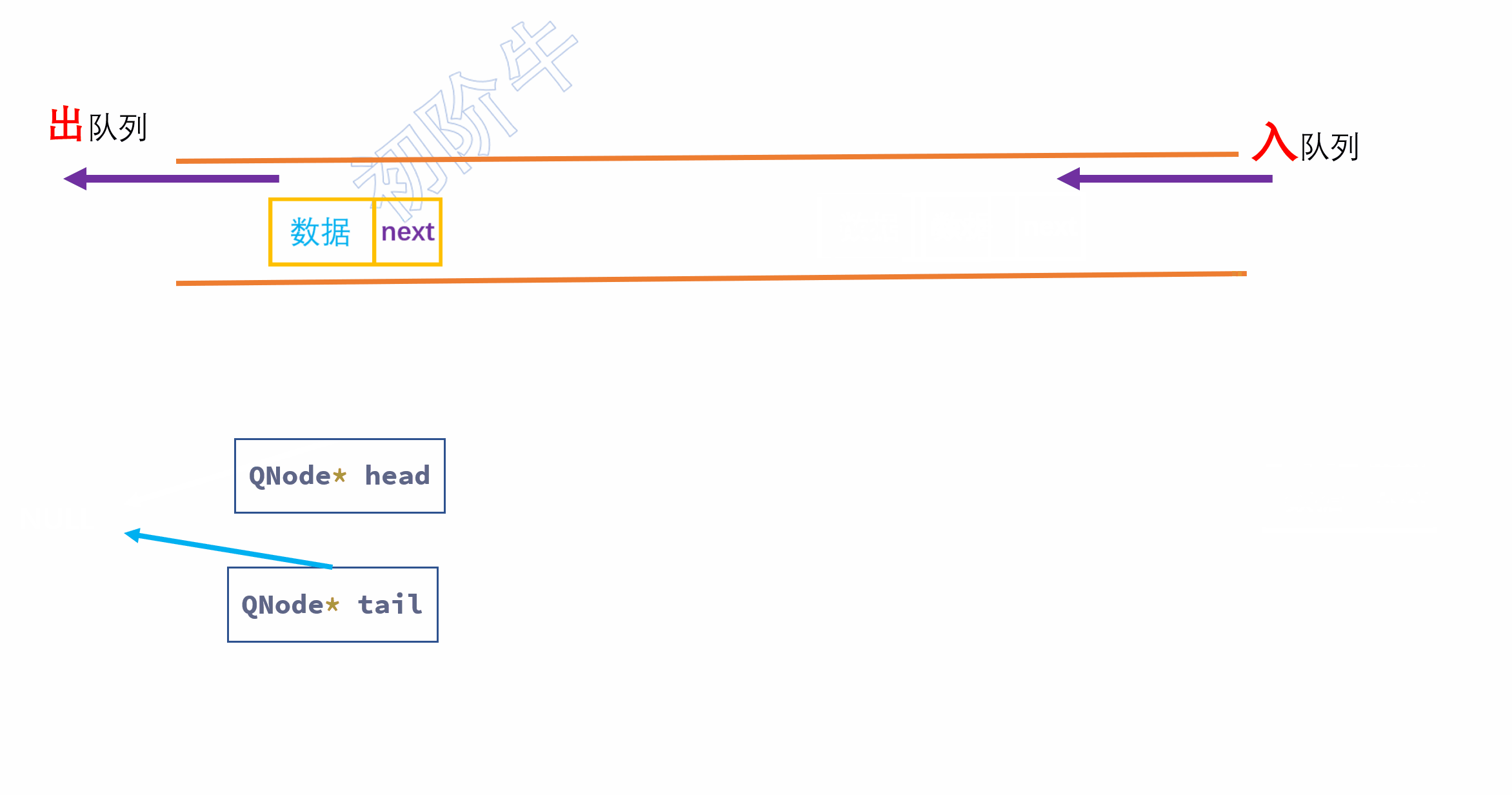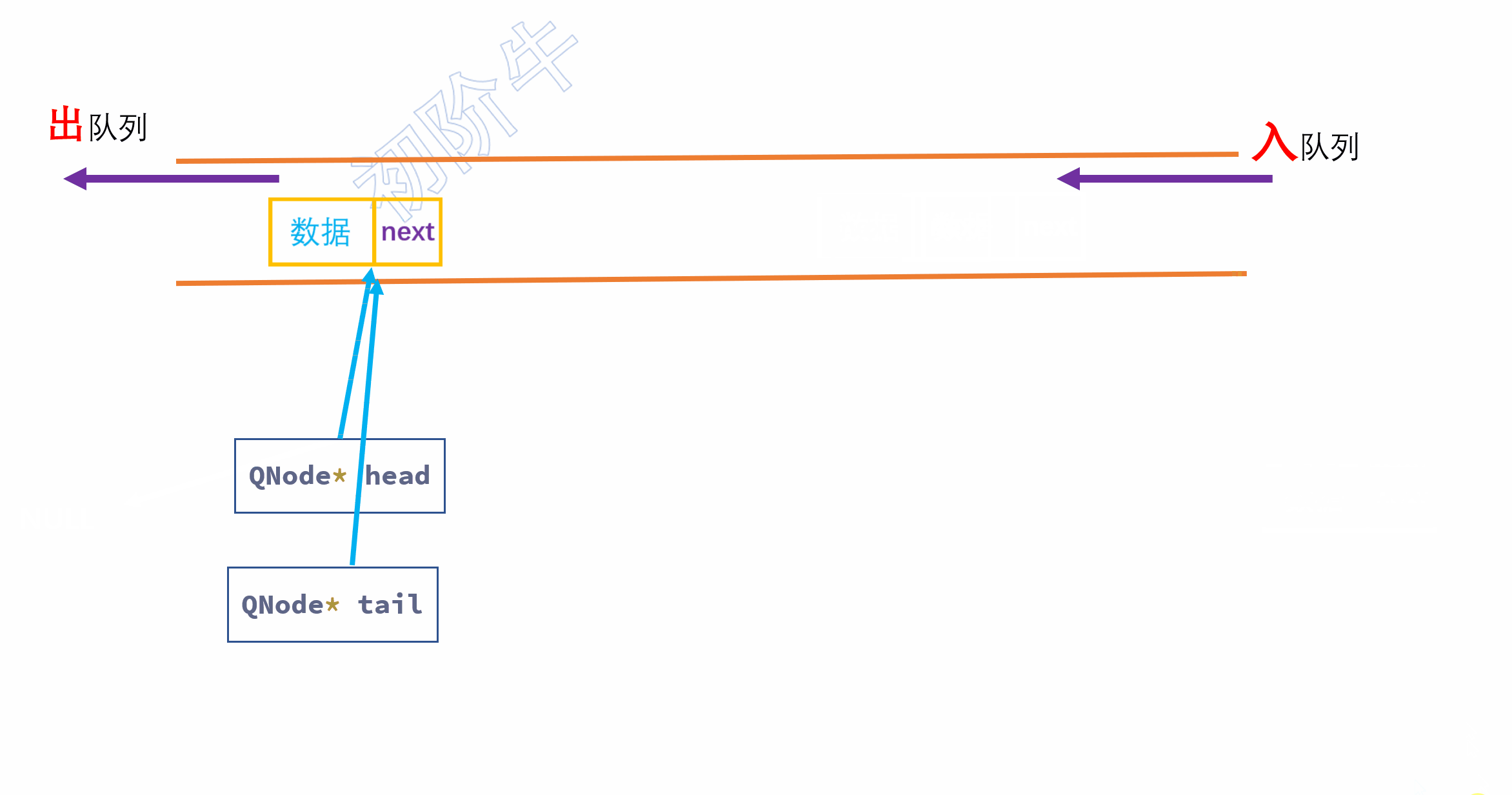
步骤:
- 申请一个结点,将
数据域赋值为x(目标值),指针域指向NULL; - 一般情况下,"入队"操作只影响
尾指针. - 链接:将
尾指针的指针域指向新节点. - 更新尾指针(令
尾指针本身指向新节点).
特殊情况:
第一个元素入队时,
头指针和尾指针都会收受到影响.需要将头指针和尾指针都指向新节点.
特殊情况:
代码:
//入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x) { assert(pq); QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->head == NULL)//第一个元素入队列时,会影响头指针 { pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;//将头指针和尾指针都指向新节点 } else { pq->tail->next = newnode; pq->tail = newnode;//更新队尾 } pq->size++; return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
2.3 "队列"判空(QueueEmpty)
如果头指针和尾指针都指向NULL则表示空队列
代码:
//队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); //如果头指针和尾指针都指向NULL则表示空队列 if (pq->head == pq->tail && pq->tail == NULL) { return true; } return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2.4 “出队”(QueuePop)
步骤:
- 对于删除元素的"出队"操作,我们首先要进行"判空"操作.空队列不允许删除.
- 创建一个结点指针(
Delete):用于记录待会要出队的原队首结点. - 将队首结点向后移动一步.(即将队首指针指向第二个元素).
- 释放
Delete结点. - 长度(size)减少1;

特殊情况:
剩下最后一个待出队元素时:
会影响头指针,需要将头指针和尾指针都置空NULL;这里就不画图了,相信聪明的友友们可以理解.
代码:
//出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); QNode* Delete = pq->head;//记录原队首 if (pq->head == pq->tail)//如果是最后一个元素出队列 { pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; } else pq->head = pq->head->next;//更新队头指针 free(Delete);//释放原队首 pq->size--; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
2.5 "队列"长度函数
这里采用了增加一个变量size用于记录队列的长度.所以直接返回
size即可.
如果没有size就需要遍历.//队列的长度 int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2.6 取"队头"和"队尾"元素
在创建队列时,我们已经分析了链式队列的结构,队首=和队尾元素我们可以直接通过队首指针(
head)和队尾指针(tail)访问其数据域即可.//取队头元素 QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->head); return pq->head->data; } //取队尾元素 QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->tail); return pq->tail->data; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2.7 "队列"的销毁:
与链表的销毁类似:
步骤:- 创建两个结点指针
(1):QNode* cur:从头指针开始,遍历整个队列
(2):QNode* next:用于记录下一个结点,方便cur被释放后,继续往下遍历.- 释放cur指针指向的结点.
- 更新cur指针和next指针.
- 将队首指针(
head)和队尾指针(tail)指向NULL. - 将size置为0;
代码:
//队列的销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->head; QNode* next = cur; while (next) { next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
三、结语:
"栈"和"队列"都是很重要的一种数据结构,在计算机中有很多应用,后续会更新==“循环队列”==,和OJ题:用栈模拟队列,用队列模拟栈等.
如果文章对大家有帮助的话,牛牛会很开心的.💗💗💗如果文章中有错误,或者不理解的地方,欢迎小伙伴们私信提意见和提问哦!互相交流学习.
最后,小伙伴们的点赞就是给牛牛最大的支持,能不能给牛牛来一个一键三连呢?谢谢支持。
四、总代码:
4.1 主测试区(test.c)
#include"Queue.h" int main() { Queue q; QueueInit(&q); QueuePush(&q, 1); QueuePush(&q, 2); QueuePush(&q, 3); QueuePush(&q, 4); printf("队头数据%d\n", QueueFront(&q)); printf("队头数据%d\n", QueueBack(&q)); while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) { printf("%d ", q.head->data); QueuePop(&q); } QueueDestroy(&q);; return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
4.2 接口实现区(Queue.c):
#include "Queue.h" //队列的初始化操作 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->head = NULL; pq->tail = NULL; int size = 0; } //入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x) { assert(pq); QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->head == NULL)//第一个元素入队列时,会影响头指针 { pq->head = pq->tail = newnode; } else { pq->tail->next = newnode; pq->tail = newnode;//更新队尾 } pq->size++; return 0; } //队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); if (pq->head == pq->tail && pq->tail == NULL) { return true; } return false; } //出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); QNode* Delete = pq->head;//记录原队首 if (pq->head == pq->tail)//如果是最后一个元素出队列 { pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; } else pq->head = pq->head->next;//更新队头指针 free(Delete);//释放原队首 pq->size--; } //队列的长度 int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; } //取队头元素 QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->head); return pq->head->data; } //取队尾元素 QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->tail); return pq->tail->data; } //队列的销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->head; QNode* next = cur; while (next) { next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
4.3 接口声明区(Queue.h):
#pragma once #include#include #include #include typedef int QDatatype; typedef struct QueueNode { struct QueueNode* next; QDatatype data; }QNode; typedef struct Queue { QNode* head; QNode* tail; int size; }Queue; //队列的初始化操作 void QueueInit(Queue* pq); //队列的销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq); //入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDatatype x); //出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq); //队列的长度 int QueueSize(Queue* pq); //队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); //取队头元素 QDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq); //取队尾元素 QDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
-
相关阅读:
HOWTO:在 Tomcat 中抑制服务器身份
JMeter-- token写入/读取csv文件+清除掉token的csv文件
用html做一个漂亮的网站【茶文化12页】期末网页制作 HTML+CSS网页设计实例 企业文化网站制作
通过 vue-cli 创建一个 vue3 的项目
vue二次封装-echarts
C++初始化列表使用与否的区别
Lintcode 642 · Moving Average from Data Stream
C# StringBuilder 的使用
Java_IO流
windows环境装MailHog
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_67276605/article/details/130791917