摘要:基于.NET Core 7.0WebApi后端架构实战【2-实现动态路由与Dynamic API】 2023/02/22, ASP.NET Core 7.0, VS2022
引言#
使用过ABP vNext和Furion框架的可能都会对它们的动态API感到好奇,不用手动的去定义,它会动态的去创建API控制器。后端代码
架构的复杂在核心代码,如果这些能封装的好提升的是小组整体的生产力。灵图图书的扉页都会有这样一句话:"站在巨人的肩膀上"。我在
这里大言不惭的说上一句我希望我也能成为"巨人"!
动态路由#
在.Net Core WebAPI程序中通过可全局或局部修改的自定义Route属性和URL映射组件匹配传入的HTTP请求替代默认路由即为动态路由
WebApplicationBuilder#
在3.1以及5.0的版本中,Configure方法中会自动添加UseRouting()与UseEndpoints()方法,但是在6.0以上版本已经没有了。其实在创建WebApplicationBuilder实例的时候默认已经添加进去了。请看源码:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);/// internal WebApplicationBuilder(WebApplicationOptions options, Action? configureDefaults = null)
{
Services = _services;
var args = options.Args;
// Run methods to configure both generic and web host defaults early to populate config from appsettings.json
// environment variables (both DOTNET_ and ASPNETCORE_ prefixed) and other possible default sources to prepopulate
// the correct defaults.
_bootstrapHostBuilder = new BootstrapHostBuilder(Services, _hostBuilder.Properties);
// Don't specify the args here since we want to apply them later so that args
// can override the defaults specified by ConfigureWebHostDefaults
_bootstrapHostBuilder.ConfigureDefaults(args: null);
// This is for testing purposes
configureDefaults?.Invoke(_bootstrapHostBuilder);
// We specify the command line here last since we skipped the one in the call to ConfigureDefaults.
// The args can contain both host and application settings so we want to make sure
// we order those configuration providers appropriately without duplicating them
if (args is { Length: > 0 })
{
_bootstrapHostBuilder.ConfigureAppConfiguration(config =>
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
});
}
_bootstrapHostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webHostBuilder =>
{
// Runs inline.
//看这里
webHostBuilder.Configure(ConfigureApplication);
// Attempt to set the application name from options
options.ApplyApplicationName(webHostBuilder);
});
// Apply the args to host configuration last since ConfigureWebHostDefaults overrides a host specific setting (the application n
_bootstrapHostBuilder.ConfigureHostConfiguration(config =>
{
if (args is { Length: > 0 })
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
// Apply the options after the args
options.ApplyHostConfiguration(config);
});
Configuration = new();
// This is chained as the first configuration source in Configuration so host config can be added later without overriding app c
Configuration.AddConfiguration(_hostConfigurationManager);
// Collect the hosted services separately since we want those to run after the user's hosted services
_services.TrackHostedServices = true;
// This is the application configuration
var (hostContext, hostConfiguration) = _bootstrapHostBuilder.RunDefaultCallbacks(Configuration, _hostBuilder);
// Stop tracking here
_services.TrackHostedServices = false;
// Capture the host configuration values here. We capture the values so that
// changes to the host configuration have no effect on the final application. The
// host configuration is immutable at this point.
_hostConfigurationValues = new(hostConfiguration.AsEnumerable());
// Grab the WebHostBuilderContext from the property bag to use in the ConfigureWebHostBuilder
var webHostContext = (WebHostBuilderContext)hostContext.Properties[typeof(WebHostBuilderContext)];
// Grab the IWebHostEnvironment from the webHostContext. This also matches the instance in the IServiceCollection.
Environment = webHostContext.HostingEnvironment;
Logging = new LoggingBuilder(Services);
Host = new ConfigureHostBuilder(hostContext, Configuration, Services);
WebHost = new ConfigureWebHostBuilder(webHostContext, Configuration, Services);
Services.AddSingleton(_ => Configuration);
}
private void ConfigureApplication(WebHostBuilderContext context, IApplicationBuilder app)
{
Debug.Assert(_builtApplication is not null);
// UseRouting called before WebApplication such as in a StartupFilter
// lets remove the property and reset it at the end so we don't mess with the routes in the filter
if (app.Properties.TryGetValue(EndpointRouteBuilderKey, out var priorRouteBuilder))
{
app.Properties.Remove(EndpointRouteBuilderKey);
}
if (context.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
// Wrap the entire destination pipeline in UseRouting() and UseEndpoints(), essentially:
// destination.UseRouting()
// destination.Run(source)
// destination.UseEndpoints()
// Set the route builder so that UseRouting will use the WebApplication as the IEndpointRouteBuilder for route matching
app.Properties.Add(WebApplication.GlobalEndpointRouteBuilderKey, _builtApplication);
// Only call UseRouting() if there are endpoints configured and UseRouting() wasn't called on the global route builder already
if (_builtApplication.DataSources.Count > 0)
{
// If this is set, someone called UseRouting() when a global route builder was already set
if (!_builtApplication.Properties.TryGetValue(EndpointRouteBuilderKey, out var localRouteBuilder))
{
//添加路由中间件
app.UseRouting();
}
else
{
// UseEndpoints will be looking for the RouteBuilder so make sure it's set
app.Properties[EndpointRouteBuilderKey] = localRouteBuilder;
}
}
// Wire the source pipeline to run in the destination pipeline
app.Use(next =>
{
_builtApplication.Run(next);
return _builtApplication.BuildRequestDelegate();
});
if (_builtApplication.DataSources.Count > 0)
{
// We don't know if user code called UseEndpoints(), so we will call it just in case, UseEndpoints() will ignore duplicate DataSources
//添加终结点中间件
app.UseEndpoints(_ => { });
}
// Copy the properties to the destination app builder
foreach (var item in _builtApplication.Properties)
{
app.Properties[item.Key] = item.Value;
}
// Remove the route builder to clean up the properties, we're done adding routes to the pipeline
app.Properties.Remove(WebApplication.GlobalEndpointRouteBuilderKey);
// reset route builder if it existed, this is needed for StartupFilters
if (priorRouteBuilder is not null)
{
app.Properties[EndpointRouteBuilderKey] = priorRouteBuilder;
}
}public IWebHostBuilder Configure(Action configure )
{
var startupAssemblyName = configure.GetMethodInfo().DeclaringType!.Assembly.GetName().Name!;
UseSetting(WebHostDefaults.ApplicationKey, startupAssemblyName);
// Clear the startup type
_startupObject = configure;
_builder.ConfigureServices((context, services) =>
{
if (object.ReferenceEquals(_startupObject, configure))
{
services.Configure(options =>
{
var webhostBuilderContext = GetWebHostBuilderContext(context);
options.ConfigureApplication = app => configure(webhostBuilderContext, app);
});
}
});
return this;
}
private static WebHostBuilderContext GetWebHostBuilderContext(HostBuilderContext context)
{
if (!context.Properties.TryGetValue(typeof(WebHostBuilderContext), out var contextVal))
{
var options = new WebHostOptions(context.Configuration, Assembly.GetEntryAssembly()?.GetName().Name ?? string.Empty);
var webHostBuilderContext = new WebHostBuilderContext
{
Configuration = context.Configuration,
HostingEnvironment = new HostingEnvironment(),
};
webHostBuilderContext.HostingEnvironment.Initialize(context.HostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath, options);
context.Properties[typeof(WebHostBuilderContext)] = webHostBuilderContext;
context.Properties[typeof(WebHostOptions)] = options;
return webHostBuilderContext;
}
// Refresh config, it's periodically updated/replaced
var webHostContext = (WebHostBuilderContext)contextVal;
webHostContext.Configuration = context.Configuration;
return webHostContext;
}
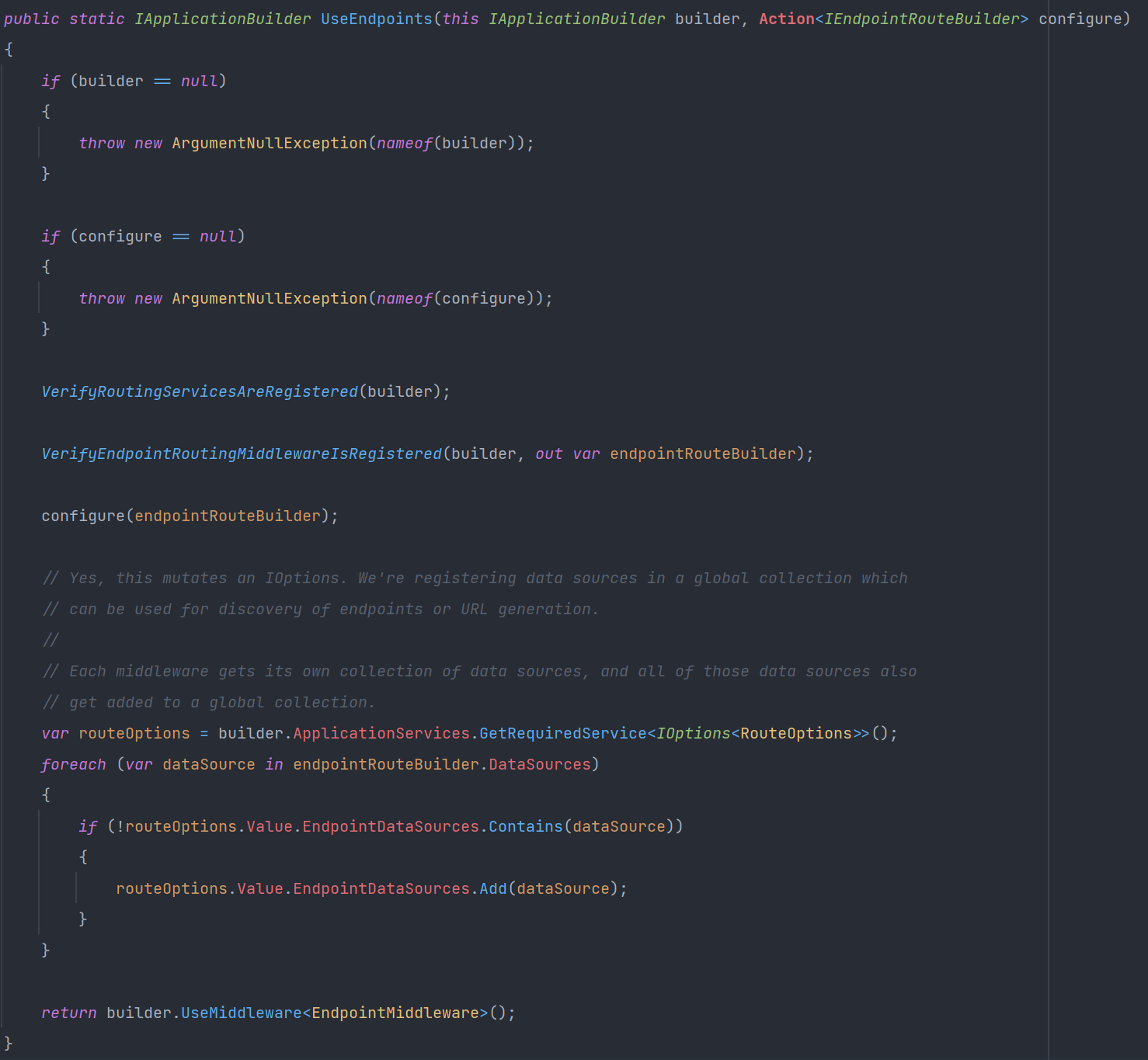
UseRouting#
源码如下图所示:
①erifyRoutingServicesAreRegistered用于验证路由服务是否已注册到容器内部
②判断在请求管道的共享数据字典的Properties中是否有GlobalEndpointRouteBuilderKey的键,如果没有则New一个新的终结点路由构建者对象,并将EndpointRouteBuilder添加到共享字典中。后面UseEndpoints(Action执行时,会将前面New的DefaultEndpointRouteBuilder 实例取出,并进一步配置它: configure(EndpointRouteBuilder实例)
③将EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件注册到管道中,该中间件根据请求和Url匹配最佳的Endpoint,然后将该终结点交由EndpointMiddleware 处理。
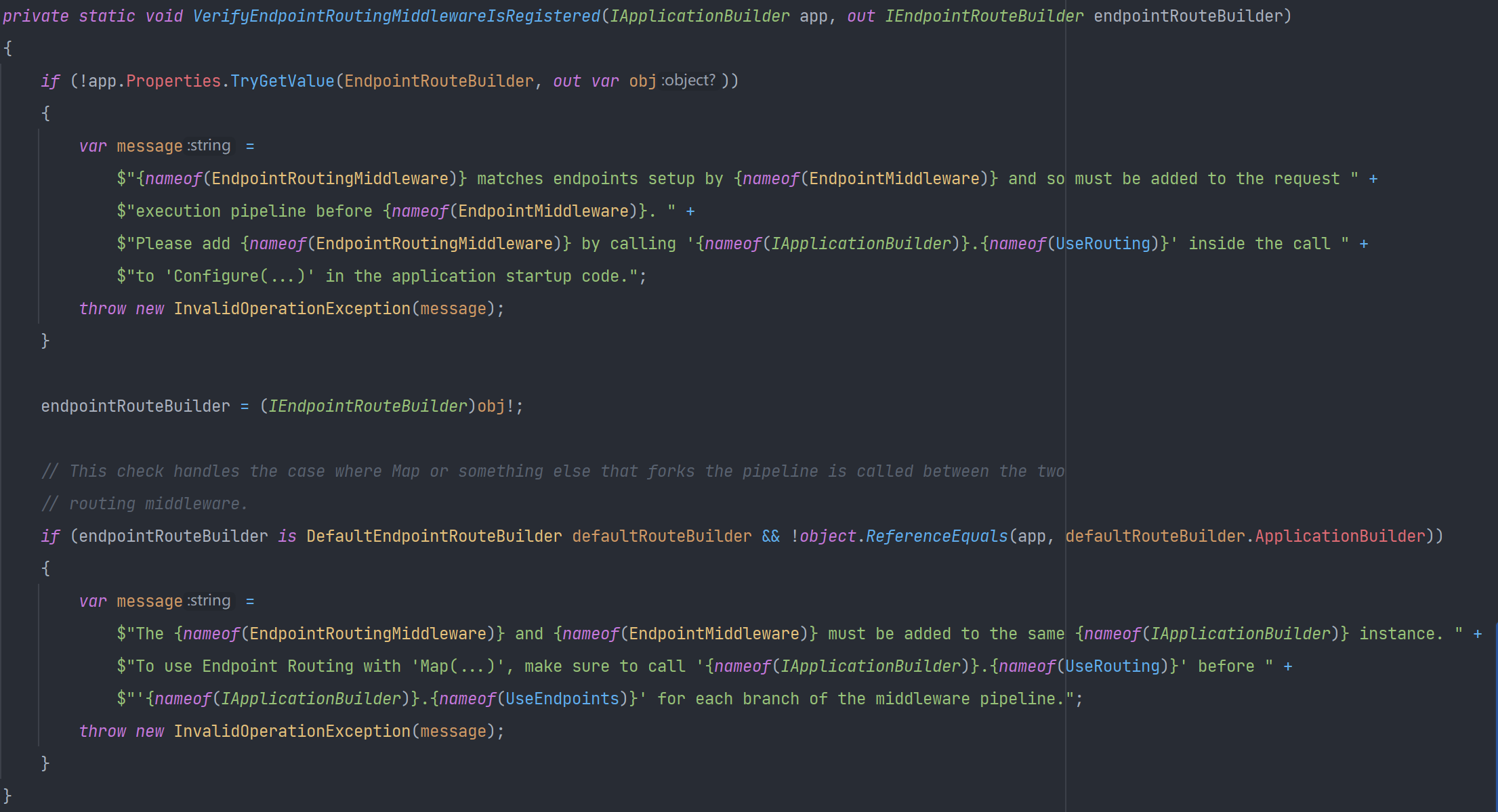
UseEndpoints#
源码如下图所示:
①VerifyEndpointRoutingMiddlewareIsRegistered方法将EndpointRouteBuilder从请求管道的共享字典中取出,如果没有则说明之前没有调用UseRouting(),所以调用UseEndpoints()之前要先调用UseRouting(),VerifyEndpointRoutingMiddlewareIsRegistered方法如下图所示:
②EndpointMiddleware主要是在EndpointRoutingMiddleware筛选出endpoint之后,调用该endpoint的endpoint.RequestDelegate(httpContext)进行请求处理。并且这个中间件会最终执行RequestDelegate委托来处理请求。请求的处理大部分功能在中间件EndpointRoutingMiddleware中,它有个重要的属性_endpointDataSource保存了上文中初始化阶段生成的MvcEndpointDataSource,而中间件EndpointMiddleware的功能比较简单,主要是在EndpointRoutingMiddleware筛选出endpoint之后,调用该endpoint.RequestDelegate(httpContext)方法进行请求处理。
看一下Endpoint类源码,Endpoint就是定义谁(Action)来执行请求的对象
public class Endpoint
{
///Metadata非常重要,是存放控制器还有Action的元数据,在应用程序启动的时候就将控制器和Action的关键信息给存入,例如路由、特性、HttpMethod等
RequestDelegate 用于将请求(HttpContext)交给资源(Action)执行
AddControllers#
我们来看下AddControllers()和AddMvcCore()及相关联的源码
MvcServiceCollectionExtensions文件中,AddControllersCore方法用于添加控制器的核心服务,它最主要的作用是主要作用就是扫描所有的有关程序集封装成ApplicationPart。
public static class MvcServiceCollectionExtensions
{
/// ());
}
return builder;
}
}
AddMvcCore方法用于添加MVC的核心服务,下面的GetApplicationPartManager方法先获取ApplicationPartManager对象,然后将当前程序集封装成了ApplicationPart放进ApplicationParts集合中。ConfigureDefaultFeatureProviders(partManager)主要作用是创建了一个新的ControllerFeatureProvider实例放进了partManager的FeatureProviders属性中,注意这个ControllerFeatureProvider对象在后面遍历ApplicationPart的时候负责找出里面的Controller。AddMvcCore()方法其后是添加Routing服务再接着添加Mvc核心服务然后构建一个MvcCoreBuilder实例并返回
///下面的PopulateDefaultParts()方法从当前程序集找到所有引用到了的程序集(包括[assembly:ApplicationPart(“demo”)]中标记的)把他们封装成ApplciationPart,然后把他们放在了ApplciationPartManager的ApplicationParts属性中,用于后面筛选Controller提供数据基础。
namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ApplicationParts
{
///
/// Manages the parts and features of an MVC application.
///
public class ApplicationPartManager
{
///
/// Gets the list of instances.
///
/// Instances in this collection are stored in precedence order. An that appears
/// earlier in the list has a higher precedence.
/// An may choose to use this an interface as a way to resolve conflicts when
/// multiple instances resolve equivalent feature values.
///
///
public IList ApplicationParts { get; } = new List();
internal void PopulateDefaultParts(string entryAssemblyName)
{
//获取相关联的程序集
var assemblies = GetApplicationPartAssemblies(entryAssemblyName);
var seenAssemblies = new HashSet();
foreach (var assembly in assemblies)
{
if (!seenAssemblies.Add(assembly))
{
// "assemblies" may contain duplicate values, but we want unique ApplicationPart instances.
// Note that we prefer using a HashSet over Distinct since the latter isn't
// guaranteed to preserve the original ordering.
continue;
}
var partFactory = ApplicationPartFactory.GetApplicationPartFactory(assembly);
foreach (var applicationPart in partFactory.GetApplicationParts(assembly))
{
ApplicationParts.Add(applicationPart);
}
}
}
private static IEnumerable GetApplicationPartAssemblies(string entryAssemblyName)
{
//加载当前主程序集
var entryAssembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(entryAssemblyName));
// Use ApplicationPartAttribute to get the closure of direct or transitive dependencies
// that reference MVC.
var assembliesFromAttributes = entryAssembly.GetCustomAttributes()
.Select(name => Assembly.Load(name.AssemblyName))
.OrderBy(assembly => assembly.FullName, StringComparer.Ordinal)
.SelectMany(GetAssemblyClosure);
// The SDK will not include the entry assembly as an application part. We'll explicitly list it
// and have it appear before all other assemblies \ ApplicationParts.
return GetAssemblyClosure(entryAssembly)
.Concat(assembliesFromAttributes);
}
private static IEnumerable GetAssemblyClosure(Assembly assembly)
{
yield return assembly;
var relatedAssemblies = RelatedAssemblyAttribute.GetRelatedAssemblies(assembly, throwOnError: false)
.OrderBy(assembly => assembly.FullName, StringComparer.Ordinal);
foreach (var relatedAssembly in relatedAssemblies)
{
yield return relatedAssembly;
}
}
}
}
MapControllers#
它的主要作用是将controllerl里面的action映射为我们的终结点。我们接下来看下Controller里的Action是怎样注册到路由模块的。MapControllers()方法执行时就会遍历遍历已经收集到的ApplicationPart进而将其中Controller里面的Action方法转换封装成一个个的EndPoint放到路由中间件的配置对象RouteOptions中然后交给Routing模块处理。前面提到EndpointMiddleware的一大核心代码主要是执行Endpoint 的RequestDelegate 委托,也即对Controller 中的Action 的执行。所有的Http请求都会走到EndpointMiddleware中间件中,然后去执行对应的Action。在应用程序启动的时候会把我们的所有的路由信息添加到一个EndpointSource的集合中去的,所以在MapController方法,其实就是在构建我们所有的路由请求的一个RequestDelegate,然后在每次请求的时候,在EndpointMiddleWare中间件去执行这个RequestDelegate,从而走到我们的接口中去。简而言之,这个方法就是将我们的所有路由信息添加到一个EndpointDataSource的抽象类的实现类中去,默认是ControllerActionEndpointDataSource这个类,在这个类中有一个基类ActionEndpointDataSourceBase,ControllerActionEndpointDataSource初始化的时候会订阅所有的Endpoint的集合的变化,每变化一次会向EndpointSource集合添加Endpoint,从而在请求的时候可以找到这个终结点去调用。
我们来看下MapControllers()的源码
public static class ControllerEndpointRouteBuilderExtensions
{
///
/// Adds endpoints for controller actions to the without specifying any routes.
///
///The .
/// An for endpoints associated with controller actions.
public static ControllerActionEndpointConventionBuilder MapControllers(this IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints)
{
if (endpoints == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(endpoints));
}
EnsureControllerServices(endpoints);
return GetOrCreateDataSource(endpoints).DefaultBuilder;
}
private static void EnsureControllerServices(IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints)
{
var marker = endpoints.ServiceProvider.GetService();
if (marker == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatUnableToFindServices(
nameof(IServiceCollection),
"AddControllers",
"ConfigureServices(...)"));
}
}
private static ControllerActionEndpointDataSource GetOrCreateDataSource(IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints)
{
var dataSource = endpoints.DataSources.OfType().FirstOrDefault();
if (dataSource == null)
{
var orderProvider = endpoints.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService();
var factory = endpoints.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService();
dataSource = factory.Create(orderProvider.GetOrCreateOrderedEndpointsSequenceProvider(endpoints));
endpoints.DataSources.Add(dataSource);
}
return dataSource;
}
}
首先EnsureControllerServices方法检查mvc服务是否注入了,GetOrCreateDataSource方法执行完就获取到了dateSource,dateSource中就是所有的Action信息。需要注意的是ControllerActionEndpointDataSource这个类,它里面的方法帮我们创建路由终结点。我们来看一下它的定义:
internal class ControllerActionEndpointDataSource : ActionEndpointDataSourceBase
{
private readonly ActionEndpointFactory _endpointFactory;
private readonly OrderedEndpointsSequenceProvider _orderSequence;
private readonly List _routes;
public ControllerActionEndpointDataSource(
ControllerActionEndpointDataSourceIdProvider dataSourceIdProvider,
IActionDescriptorCollectionProvider actions,
ActionEndpointFactory endpointFactory,
OrderedEndpointsSequenceProvider orderSequence)
: base(actions)
{
_endpointFactory = endpointFactory;
DataSourceId = dataSourceIdProvider.CreateId();
_orderSequence = orderSequence;
_routes = new List();
DefaultBuilder = new ControllerActionEndpointConventionBuilder(Lock, Conventions);
// IMPORTANT: this needs to be the last thing we do in the constructor.
// Change notifications can happen immediately!
Subscribe();
}
public int DataSourceId { get; }
public ControllerActionEndpointConventionBuilder DefaultBuilder { get; }
// Used to control whether we create 'inert' (non-routable) endpoints for use in dynamic
// selection. Set to true by builder methods that do dynamic/fallback selection.
public bool CreateInertEndpoints { get; set; }
public ControllerActionEndpointConventionBuilder AddRoute(
string routeName,
string pattern,
RouteValueDictionary? defaults,
IDictionary<string, object?>? constraints,
RouteValueDictionary? dataTokens)
{
lock (Lock)
{
var conventions = new List();
_routes.Add(new ConventionalRouteEntry(routeName, pattern, defaults, constraints, dataTokens, _orderSequence.GetNext(), conventions));
return new ControllerActionEndpointConventionBuilder(Lock, conventions);
}
}
protected override List CreateEndpoints(IReadOnlyList actions, IReadOnlyList conventions )
{
var endpoints = new List();
var keys = new HashSet(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
// MVC guarantees that when two of it's endpoints have the same route name they are equivalent.
//
// However, Endpoint Routing requires Endpoint Names to be unique.
var routeNames = new HashSet(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
// For each controller action - add the relevant endpoints.
//
// 1. If the action is attribute routed, we use that information verbatim
// 2. If the action is conventional routed
// a. Create a *matching only* endpoint for each action X route (if possible)
// b. Ignore link generation for now
for (var i = 0; i < actions.Count; i++)
{
if (actions[i] is ControllerActionDescriptor action)
{
_endpointFactory.AddEndpoints(endpoints, routeNames, action, _routes, conventions, CreateInertEndpoints);
if (_routes.Count > 0)
{
// If we have conventional routes, keep track of the keys so we can create
// the link generation routes later.
foreach (var kvp in action.RouteValues)
{
keys.Add(kvp.Key);
}
}
}
}
// Now create a *link generation only* endpoint for each route. This gives us a very
// compatible experience to previous versions.
for (var i = 0; i < _routes.Count; i++)
{
var route = _routes[i];
_endpointFactory.AddConventionalLinkGenerationRoute(endpoints, routeNames, keys, route, conventions);
}
return endpoints;
}
internal void AddDynamicControllerEndpoint(IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints, string pattern, Type transformerType, object? state, int? order = null)
{
CreateInertEndpoints = true;
lock (Lock)
{
order ??= _orderSequence.GetNext();
endpoints.Map(
pattern,
context =>
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("This endpoint is not expected to be executed directly.");
})
.Add(b =>
{
((RouteEndpointBuilder)b).Order = order.Value;
b.Metadata.Add(new DynamicControllerRouteValueTransformerMetadata(transformerType, state));
b.Metadata.Add(new ControllerEndpointDataSourceIdMetadata(DataSourceId));
});
}
}
}
在CreateEndpoints方法中会遍历每个ActionDescriptor对象,ActionDescriptor对象里面存储的是Action方法的元数据。然后创建一个个的Endpoint实例,Endpoint对象里面有一个RequestDelegate参数,当请求进入的时候会执行这个委托进入对应的Action。另外这其中还有一个DefaultBuilder属性,可以看到他返回的是ControllerActionEndpointConventionBuilder对象,这个对象是用来构建约定路由的。AddRoute方法也是用来添加约定路由的。我们再来看下构造函数中的Subscribe()方法,这个方法是调用父类ActionEndpointDataSourceBase中的。我们来看一下这个类:
internal abstract class ActionEndpointDataSourceBase : EndpointDataSource, IDisposable
{
private readonly IActionDescriptorCollectionProvider _actions;
// The following are protected by this lock for WRITES only. This pattern is similar
// to DefaultActionDescriptorChangeProvider - see comments there for details on
// all of the threading behaviors.
protected readonly object Lock = new object();
// Protected for READS and WRITES.
protected readonly List Conventions;
private List? _endpoints;
private CancellationTokenSource? _cancellationTokenSource;
private IChangeToken? _changeToken;
private IDisposable? _disposable;
public ActionEndpointDataSourceBase(IActionDescriptorCollectionProvider actions)
{
_actions = actions;
Conventions = new List();
}
public override IReadOnlyList Endpoints
{
get
{
Initialize();
Debug.Assert(_changeToken != null);
Debug.Assert(_endpoints != null);
return _endpoints;
}
}
// Will be called with the lock.
protected abstract List CreateEndpoints(IReadOnlyList actions, IReadOnlyList conventions
protected void Subscribe( )
{
// IMPORTANT: this needs to be called by the derived class to avoid the fragile base class
// problem. We can't call this in the base-class constuctor because it's too early.
//
// It's possible for someone to override the collection provider without providing
// change notifications. If that's the case we won't process changes.
if (_actions is ActionDescriptorCollectionProvider collectionProviderWithChangeToken)
{
_disposable = ChangeToken.OnChange(
() => collectionProviderWithChangeToken.GetChangeToken(),
UpdateEndpoints);
}
}
public override IChangeToken GetChangeToken()
{
Initialize();
Debug.Assert(_changeToken != null);
Debug.Assert(_endpoints != null);
return _changeToken;
}
public void Dispose()
{
// Once disposed we won't process updates anymore, but we still allow access to the endpoints.
_disposable?.Dispose();
_disposable = null;
}
private void Initialize()
{
if (_endpoints == null)
{
lock (Lock)
{
if (_endpoints == null)
{
UpdateEndpoints();
}
}
}
}
private void UpdateEndpoints()
{
lock (Lock)
{
var endpoints = CreateEndpoints(_actions.ActionDescriptors.Items, Conventions);
// See comments in DefaultActionDescriptorCollectionProvider. These steps are done
// in a specific order to ensure callers always see a consistent state.
// Step 1 - capture old token
var oldCancellationTokenSource = _cancellationTokenSource;
// Step 2 - update endpoints
_endpoints = endpoints;
// Step 3 - create new change token
_cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
_changeToken = new CancellationChangeToken(_cancellationTokenSource.Token);
// Step 4 - trigger old token
oldCancellationTokenSource?.Cancel();
}
}
}
_actions属性是注入进来的,这个对象是我们在services.AddMvcCore()中注入进来的:services.TryAddSingleton我们来说下ChangeToken.OnChange()方法,他里面有两个委托类型的参数,GetChangeToken()它的作用是用来感知ActionDescriptor数据源的变化,然后执行UpdateEndpoints方法中的具体的逻辑:
- 首先更新ActionDescriptors对象的具体元数据信息
- 获取旧的令牌
- 更新终结点
- 创建新的令牌
- 废弃旧的令牌
大家做的项目都有鉴权、授权的功能。而每一个角色可以访问的资源是不相同的,因此策略鉴权是非常关键的一步,它可以阻止非此菜单资源的角色用户访问此菜单的接口。一般来说有一个接口表(Module)、一个菜单表(Permission)、一个接口菜单关系表(ModulePermission),接口需要挂在菜单下面,假如一个项目几百个接口,那录起来可就麻烦了。按照我们上面说的,在管道构建时,程序就会扫描所有相关程序集中Controller的Action然后交给“路由”模块去管理。Action的这些元数据信息会存在我们上面说的IActionDescriptorCollectionProvider中的ActionDescriptorCollection对象的ActionDescriptor集合中,这样在http请求到来时“路由”模块才能寻找到正确的Endpoint,进而找到Action并调用执行。那么我们就可以读到项目中所有注册的路由,然后导入到数据库表中😊
private readonly IActionDescriptorCollectionProvider _actionDescriptorCollectionProvider;
public RouteController(IActionDescriptorCollectionProvider actionDescriptorCollectionProvider)
{
_actionDescriptorCollectionProvider = actionDescriptorCollectionProvider;
}
/// ().FirstOrDefault()?.HttpMethods.First(),
Template = x.AttributeRouteInfo.Template
}).ToList();
return Ok(routes);
} 上面我们聊了一些源码,接下来我们来看下如何实现动态路由
MvcOptions#
先说一下MvcOptions类,它为.Net Core 整个框架提供基础配置。这样说估计太抽象了,我举例一下哈。例如Action加上[FromBody],客户端传入的Body为null的话,接口会报400错误:A non-empty request body is required。可以使用模型验证AllowEmptyInputInBodyModelBinding参数配置null值可传入(.Net5之后可以根据需要按请求进行配置)。还有FilterCollection集合这个参数,从MVC时代沿用到现在的五种资源过滤器,其实他们都默认继承自IFilterMetadata空接口,而FilterCollection集合就是承载这些Filter的容器且继承自Collection,关于AOP和管道中间件这些我后面会单独抽源码来讲。好了我们这篇主要要说一下它里面的IList参数。
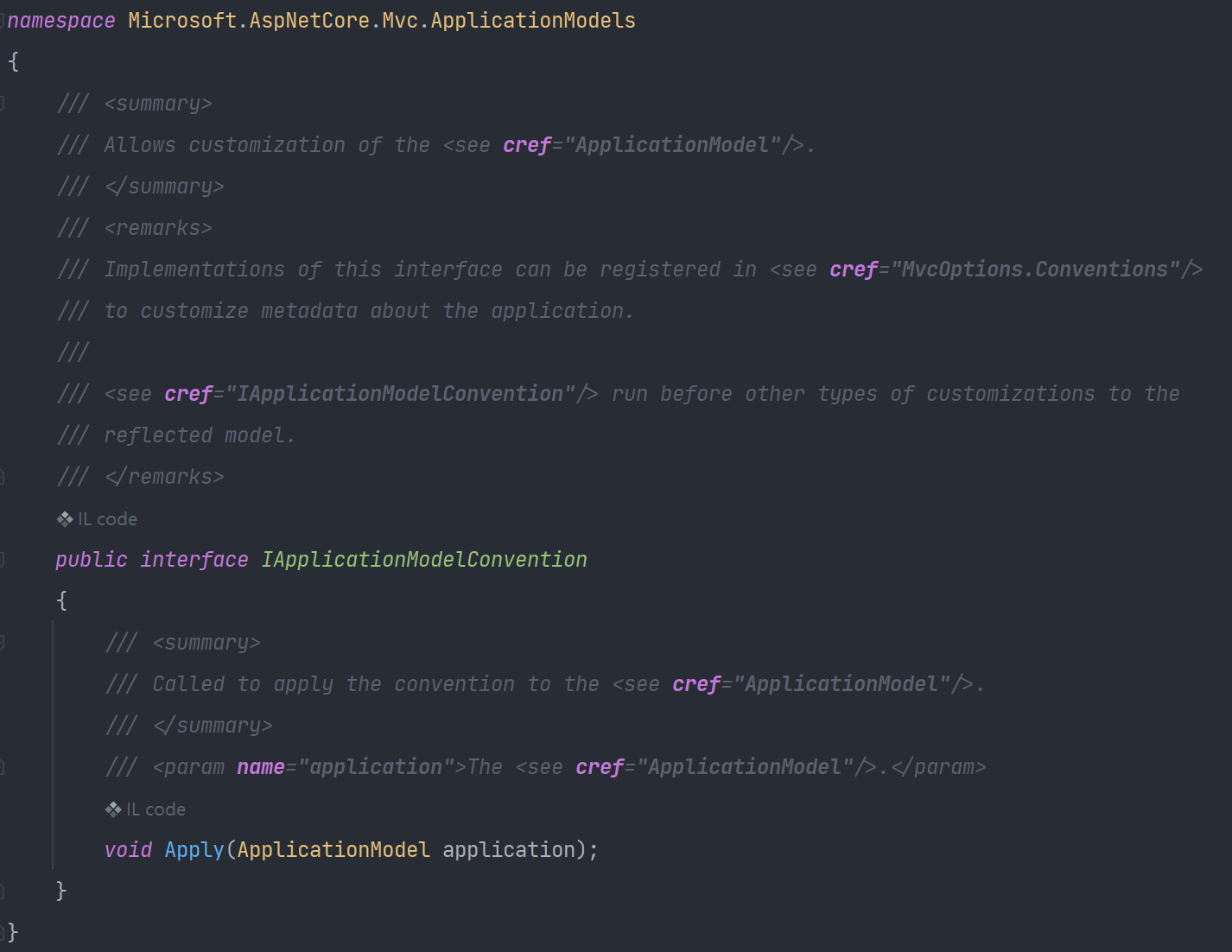
IApplicationModelConvention#
我们先看下它的源码:
我们可以写一个类继承它,实现它的Apply方法,修改.Net Core程序内部对路由、控制器的默认生成行为,然后将它添加到Convention集合中😊
通过Apply方法来进行自定义,可以修改的内容由ApplicationModel对象提供。特别是它里面的ControllerModel对象,有了它我们可以直接对控制器进行各种配置和操作。
看一下ApplicationModel对象的定义:
/// ();
Filters = new List();
Properties = new Dictionary<object, object?>();
}
/// Controllers { get; }
/// Filters { get; }
/// ①ApiExplorer可以用来配置控制器的组信息还有可见性
②Controllers可以获取Controller的相关信息,再借助IControllerModelConvention对其进行定制扩展
③Filters存放的都是空接口,起到标记作用,换句话说就是在请求管道构建的时候用于判断是否为Filter类
④Properties属于共享字典
给路由添加全局配置
services.AddControllers(options =>
{
options.UseCentralRoutePrefix(new RouteAttribute("core/v1/api/[controller]/[action]"));
});
添加我们自定义扩展方法
public static class MvcOptionsExtensions
{
/// 具体的实现类
/// POCO控制器#
在Java中有一个叫POJO的名词,即"Plain Old Java Object",直译就是简单的Java对象,其实它表示的是没有继承任何类,也没有实现任何接口的对象。在C#中也有一个相同含义的名词叫POCO(Plain Old C# Object),两者表示的含义是一样的。在.Net Core中有一个POCO Controller的特性,它不用继承Controller或ControllerBase,只需要在类名后加上Controller的后缀或标记[Controller]特性也能拥有Controller的功能。
下面简单演示一下:
public class TestController
{
[HttpGet]
public async Taskint>> Get()
{
Func<int, int> triple = m => m * 3;
var range = Enumerable.Range(1, 3);
return range.Select(triple);
}
}
[Controller]
public class TestOnce
{
[HttpGet]
public async Taskdynamic>> Index()
=> Enumerable.Range(1, 100).Select(triple => new { triple });
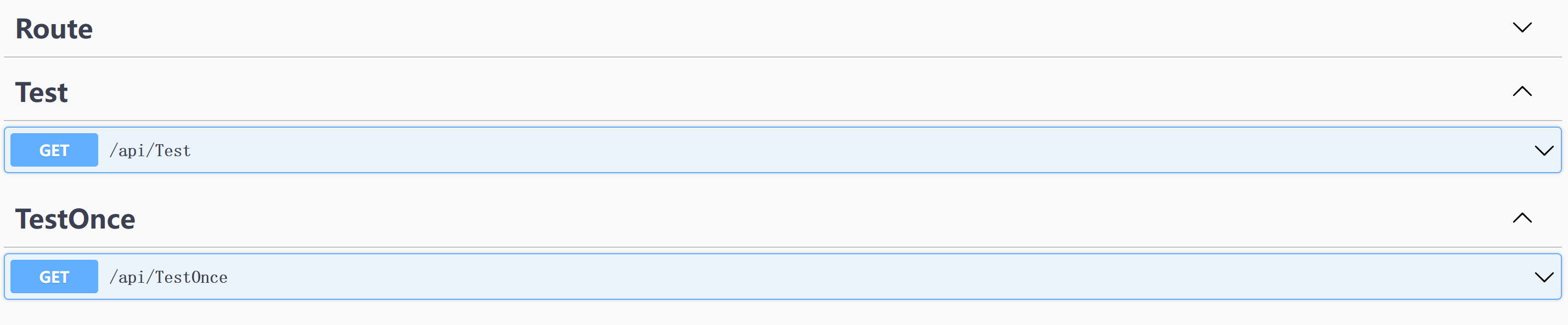
} 上面两个类中的Action会被正确扫描并添加到终结点中:
一个(控制器)类如果加上[NonController]就不会被注册到路由中😋。我们接下来还是看下源码:
// Licensed to the .NET Foundation under one or more agreements.
// The .NET Foundation licenses this file to you under the MIT license.
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.ApplicationParts;
namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Controllers;
/// parts,
ControllerFeature feature )
{
foreach (var part in parts.OfType())
{
foreach (var type in part.Types)
{
if (IsController(type) && !feature.Controllers.Contains(type))
{
feature.Controllers.Add(type);
}
}
}
}
/// 其实POCO控制器的核心就在于IApplicationFeatureProvider这个接口,ControllerFeatureProvider是其默认的实现类。
我们重新写一个类继承自ControllerFeatureProvider,把IsController方法进行重写加入我们的判断逻辑,其它我就不啰嗦了,上面的代码很清楚白了了😆
自定义控制器规则#
定义一个接口和一个特性使之成为我们的规则
public interface ICoreDynamicController { }
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class, Inherited = true)]
public class CoreDynamicControllerAttribute : Attribute { }继承ControllerFeatureProvider类并且实现IsController方法:
public class CoreDynamicExtendControlleFeatureProvider : ControllerFeatureProvider
{
protected override bool IsController(TypeInfo typeInfo)
{
var type = typeInfo.AsType();
if ((typeof(ICoreDynamicController).IsAssignableFrom(type) || //判断是否继承ICoreDynamicController接口
type.IsDefined(typeof(CoreDynamicControllerAttribute), true) || // 判断是否标记了ICoreDynamicController特性
type.BaseType == typeof(Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Controller)) && //判断基类型是否是Controller
(typeInfo.IsPublic && !typeInfo.IsAbstract && !typeInfo.IsGenericType && !typeInfo.IsInterface)) //必须是Public、不能是抽象类、必须是非泛型的
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
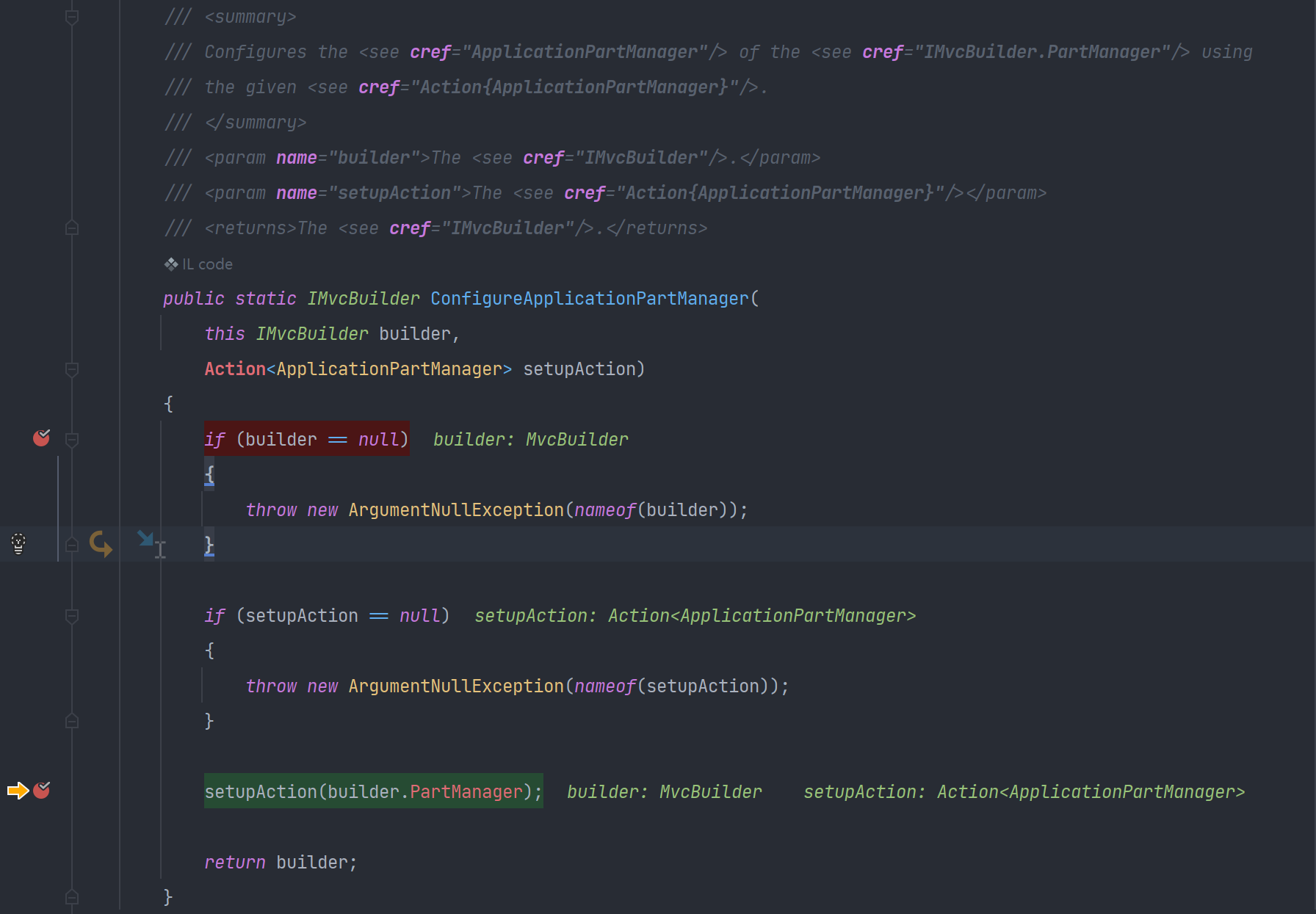
} 现在方法已经写好了,但是我们要把它配置到Mvc中才行。这里要说一下MvcCoreMvcBuilderExtensions类的IMvcBuilder的ConfigureApplicationPartManager方法,它的参数是一个委托,委托中的参数是ApplicationPartManager, ApplicationPartManager中有一个FeatureProviders的属性,它里面全是IApplicationFeatureProvider的实例。程序启动的时候会循环这些实例,我们把自己的自定义实现类添加进来,这样Core程序就能识别我们的控制器,并且赋予其控制器所有的功能。无图无真相,请看源码:
所以把我们自定义的识别类添加进来即可
services.AddControllers().ConfigureApplicationPartManager
(t => t.FeatureProviders.Add(new CoreDynamicExtendControlleFeatureProvider()));如下示例:
public class Test : ICoreDynamicController
{
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<int> Get(int value)
{
yield return value;
}
}Dynamic Api#
使用过ABP vNext框架的小伙伴都应该知道,如果一个类实现了IRemoteService或IApplicationService接口,那么它会被自动选择为API控制器。ABP vNext框架在动态API功能中遵从约定大于配置的原则,例如方法名称以GetList,GetAll或Get开头则请求的HttpMethod都为HttpGet
ABP vNext官方文档:API/Auto API Controllers | Documentation Center | ABP.IO
我们借助它的思想来实现我们的动态API
实现Apply方法#
在AspNetCore框架中给出了三个配置控制器、方法和参数的配置接口,分别是IControllerModelConvention、IActionModelConvention和IParameterModelConvention。在它们的Apply方法中,传入了一个 MVC 启动阶段扫描到的类型,对应的分别是ControllerModel、ActionModel和ParameterModel我们可以通过这三个Model加入我们的自定义配置。还是一样我们要继承IApplicationModelConvention接口筛选出符合条件的控制器,然后遍历其中的Action给其添加路由与HttpMethos(要根据Action的前缀进行判断)。本项目是根据下面列举的条件进行判断的(注意:得到ActionMethodName的时候要ToUpper或ToLower这样方便判断):
- Get:如果方法以
GET、QUERY开头 - Post:如果方法以
CREATE、SAVE、INSERT、ADD开头 - Put:如果方法以
UPDATE、EDIT开头 - Delete:如果方法以
Delete、REMOVE开头
"HttpMethodInfo": [
{
"MethodKey": "Get",
"MethodVal": [ "GET", "QUERY" ]
},
{
"MethodKey": "Post",
"MethodVal": [ "CREATE", "SAVE", "INSERT", "ADD" ]
},
{
"MethodKey": "Put",
"MethodVal": [ "UPDATE", "EDIT" ]
},
{
"MethodKey": "Delete",
"MethodVal": [ "Delete", "REMOVE" ]
}
]public class CoreDynamicControllerConvention : IApplicationModelConvention
{
private IConfiguration _configuration;
private List httpMethods = new();
public CoreDynamicControllerConvention(IConfiguration configuration)
{
_configuration = configuration;
httpMethods = (List)_configuration.GetSection("HttpMethodInfo").Get(typeof(List));
}
public void Apply(ApplicationModel application)
{
//循环每一个控制器信息
foreach (var controller in application.Controllers)
{
var controllerType = controller.ControllerType.AsType();
//是否继承ICoreDynamicController接口
if (typeof(ICoreDynamicController).IsAssignableFrom(controllerType))
{
foreach (var item in controller.Actions)
{
ConfigureSelector(controller.ControllerName, item);
}
}
}
}
private void ConfigureSelector(string controllerName, ActionModel action)
{
for (int i = 0; i < action.Selectors.Count; i++)
{
if (action.Selectors[i].AttributeRouteModel is null)
action.Selectors.Remove(action.Selectors[i]);
}
if (action.Selectors.Any())
{
foreach (var item in action.Selectors)
{
var routePath = string.Concat("api/", controllerName, action.ActionName).Replace("//", "/");
var routeModel = new AttributeRouteModel(new RouteAttribute(routePath));
//如果没有路由属性
if (item.AttributeRouteModel == null) item.AttributeRouteModel = routeModel;
}
}
else
{
action.Selectors.Add(CreateActionSelector(controllerName, action));
}
}
private SelectorModel CreateActionSelector(string controllerName, ActionModel action)
{
var selectorModel = new SelectorModel();
var actionName = action.ActionName;
string httpMethod = string.Empty;
//是否有HttpMethodAttribute
var routeAttributes = action.ActionMethod.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(HttpMethodAttribute), false);
//如果标记了HttpMethodAttribute
if (routeAttributes != null && routeAttributes.Any())
{
httpMethod = routeAttributes.SelectMany(m => (m as HttpMethodAttribute).HttpMethods).ToList().Distinct().FirstOrDefault();
}
else
{
var methodName = action.ActionMethod.Name.ToUpper();
foreach (var item in httpMethods)
{
if (item.MethodVal.Contains(methodName))
{
httpMethod = item.MethodKey;
break;
}
}
}
return ConfigureSelectorModel(selectorModel, action, controllerName, httpMethod);
}
public SelectorModel ConfigureSelectorModel(SelectorModel selectorModel, ActionModel action, string controllerName, string httpMethod)
{
var routePath = string.Concat("api/", controllerName, action.ActionName).Replace("//", "/");
//给此Action添加路由
selectorModel.AttributeRouteModel = new AttributeRouteModel(new RouteAttribute(routePath));
//添加HttpMethod
selectorModel.ActionConstraints.Add(new HttpMethodActionConstraint(new[] { httpMethod }));
return selectorModel;
}
}
控制器中就很简单了:
public class Test : IDynamicController { private readonly IHttpContextAccessor _httpAccessor; public Test(IHttpContextAccessor httpAccessor) => _httpAccessor = httpAccessor; public async Task SaveData() => _httpAccessor.HttpContext.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(new { _ = this.GetType() }); public async Task DeleteData() => _httpAccessor.HttpContext.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(new { _ = this.GetType() }); public async Task QueryData() => _httpAccessor.HttpContext.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(new { _ = this.GetType() }); public async Task UpdateData() => _httpAccessor.HttpContext.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(new { _ = this.GetType() }); }