-
spring-aop源码分析(2)_AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator后置处理器
本文将通过阅读AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator后置处理器的源码,分析其解析AOP通知、匹配切入点和创建AOP代理的流程。
入口
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是一个BeanPostProcessor实现,他在容器进行initializeBean的时候被调用:
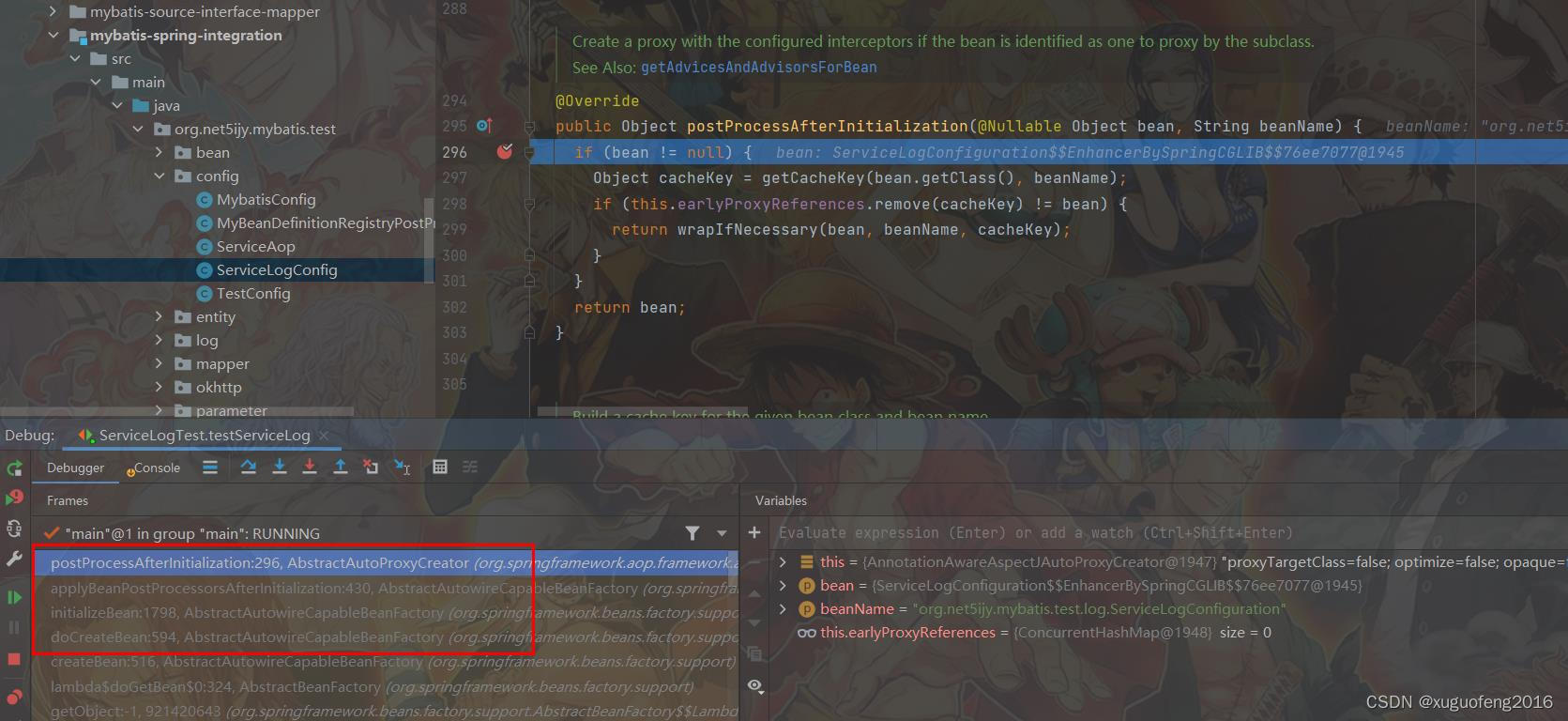
核心的BeanPostProcessor方法实现都在其父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator中实现。
wrapIfNecessary方法
在其父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization方法中。
核心功能:
- 查找AOP Advisor
- 创建AOP代理
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { // 最开始是一些是否需要AOP的判断,如果不需要或者已经创建代理,则直接返回了 // Create proxy if we have advice. // 查找AOP Advisor Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); // 创建AOP代理 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法
查找AOP Advisor
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) { List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); } // Find all eligible Advisors for auto-proxying this class. protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { // 此处分为两部分: // 1. 查找Spring容器里面注入的Advisor // 2. 解析所有的AspectJ AOP并创建Advisor // 实现逻辑在AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类中 List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); // Search the given candidate Advisors to find all Advisors that can apply to the specified bean. List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); // Add an ExposeInvocationInterceptor to the beginning of the advice chain. // This additional advice is needed when using AspectJ pointcut expressions and // when using AspectJ-style advice. extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; } // AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.findCandidateAdvisors protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() { // Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules. // 查找Spring容器里面注入的Advisor,代码就不再展开记录 List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors(); // Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory. // 解析所有的AspectJ AOP并创建Advisor if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) { advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()); } return advisors; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
过滤当前Bean可用Advisor
findAdvisorsThatCanApply方法用于过滤可用Advisor:
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply( List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName); try { return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass); } finally { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply方法:
// Determine the sublist of the candidateAdvisors list that is applicable to the given class. public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { // already processed continue; } if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; } public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass); } else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; // 使用pointcut判断 return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); } else { return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
排序
在查找Advisor集的过程中,有一步是Advisor集排序:
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { // 排序 eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; } protected List<Advisor> sortAdvisors(List<Advisor> advisors) { List<PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder> partiallyComparableAdvisors = new ArrayList<>(advisors.size()); for (Advisor advisor : advisors) { partiallyComparableAdvisors.add( new PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder(advisor, DEFAULT_PRECEDENCE_COMPARATOR)); } List<PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder> sorted = PartialOrder.sort(partiallyComparableAdvisors); if (sorted != null) { List<Advisor> result = new ArrayList<>(advisors.size()); for (PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder pcAdvisor : sorted) { result.add(pcAdvisor.getAdvisor()); } return result; } else { return super.sortAdvisors(advisors); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
核心的排序逻辑都在DEFAULT_PRECEDENCE_COMPARATOR中,他是一个Comparator实现:
public int compare(Advisor o1, Advisor o2) { int advisorPrecedence = this.advisorComparator.compare(o1, o2); // 如果advisorComparator比较结果相同,将使用AspectJ相关的方法排序,此部分不分析 if (advisorPrecedence == SAME_PRECEDENCE && declaredInSameAspect(o1, o2)) { advisorPrecedence = comparePrecedenceWithinAspect(o1, o2); } return advisorPrecedence; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
advisorComparator也是一个Comparator实现,他内部有一些从Ordered实现方法、Order注解获取顺序的逻辑,此处不展开分析,了解即可。
创建AOP代理
// 创建AOP代理 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));- 1
- 2
- 3
createProxy入口方法
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) { // Expose the given target class for the specified bean, if possible. if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils .exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this); if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); } else { evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } // 构建AOP通知 Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true); } // 创建代理 return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); } // 构建AOP通知 protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors) { Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames(); List<Object> allInterceptors = new ArrayList<>(); if (specificInterceptors != null) { allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(specificInterceptors)); if (commonInterceptors.length > 0) { // 不重要 } } Advisor[] advisors = new Advisor[allInterceptors.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < allInterceptors.size(); i++) { advisors[i] = this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(allInterceptors.get(i)); } return advisors; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
proxyFactory.getProxy方法里面判断使用Cglib还是JdkProxy创建代理:
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader); } public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { // throw exception } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
Cglib代理
从上面的代码可以看到,Cglib代理是使用ObjenesisCglibAopProxy实现类创建的。
继承关系是这样的:
AopProxy |-- CglibAopProxy |-- ObjenesisCglibAopProxy- 1
- 2
- 3
Spring Cglib示例
下面代码演示如何是Spring Cglib创建一个代理类对象:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { ClassLoader classLoader = CglibTest.class.getClassLoader(); Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer(); // 设置目标类型 enhancer.setSuperclass(LogService.class); enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader); enhancer.setUseCache(false); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader)); // callback集 Callback[] callbacks = new Callback[]{ new MyMethodInterceptor() }; Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length]; for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) { types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass(); } enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types); // 创建代理类并实例化 Class<?> proxyClass = enhancer.createClass(); Object proxyInstance = proxyClass.newInstance(); ((Factory) proxyInstance).setCallbacks(callbacks); LogService o = (LogService) proxyInstance; o.testServiceLog(); } protected static Enhancer createEnhancer() { return new Enhancer(); } private static class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { @Override public Object intercept( Object enhancedConfigInstance, Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs, MethodProxy cglibMethodProxy) throws Throwable { System.out.printf("MyMethodInterceptor %s args: %s\n", beanMethod.getName(), Arrays.toString(beanMethodArgs)); return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
CglibAopProxy.getProxy实现
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) { try { Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass(); Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass; if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) { proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass(); Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) { this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface); } } // Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary. validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader); // Configure CGLIB Enhancer... Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer(); if (classLoader != null) { enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader); if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) { enhancer.setUseCache(false); } } enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass); enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised)); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader)); // 通过advisor创建cglib代理callback Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass); Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length]; for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) { types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass(); } // fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above enhancer.setCallbackFilter( new ProxyCallbackFilter( this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset)); enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types); // Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance. // 生成代理对象并返回 return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks); } catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) { // throw new AopConfigException } catch (Throwable ex) { // throw new AopConfigException } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
getCallbacks
创建cglib callback对象,最核心的就是使用spring aop advisor创建了一个DynamicAdvisedInterceptor对象,让其作为代理对象的处理逻辑。
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor这个类会在后续解析AOP执行流程时再做介绍。
下图就是该方法封装DynamicAdvisedInterceptor对象的结构:
- target - 封装原始的Bean对象
- advisors - spring aop advisor集
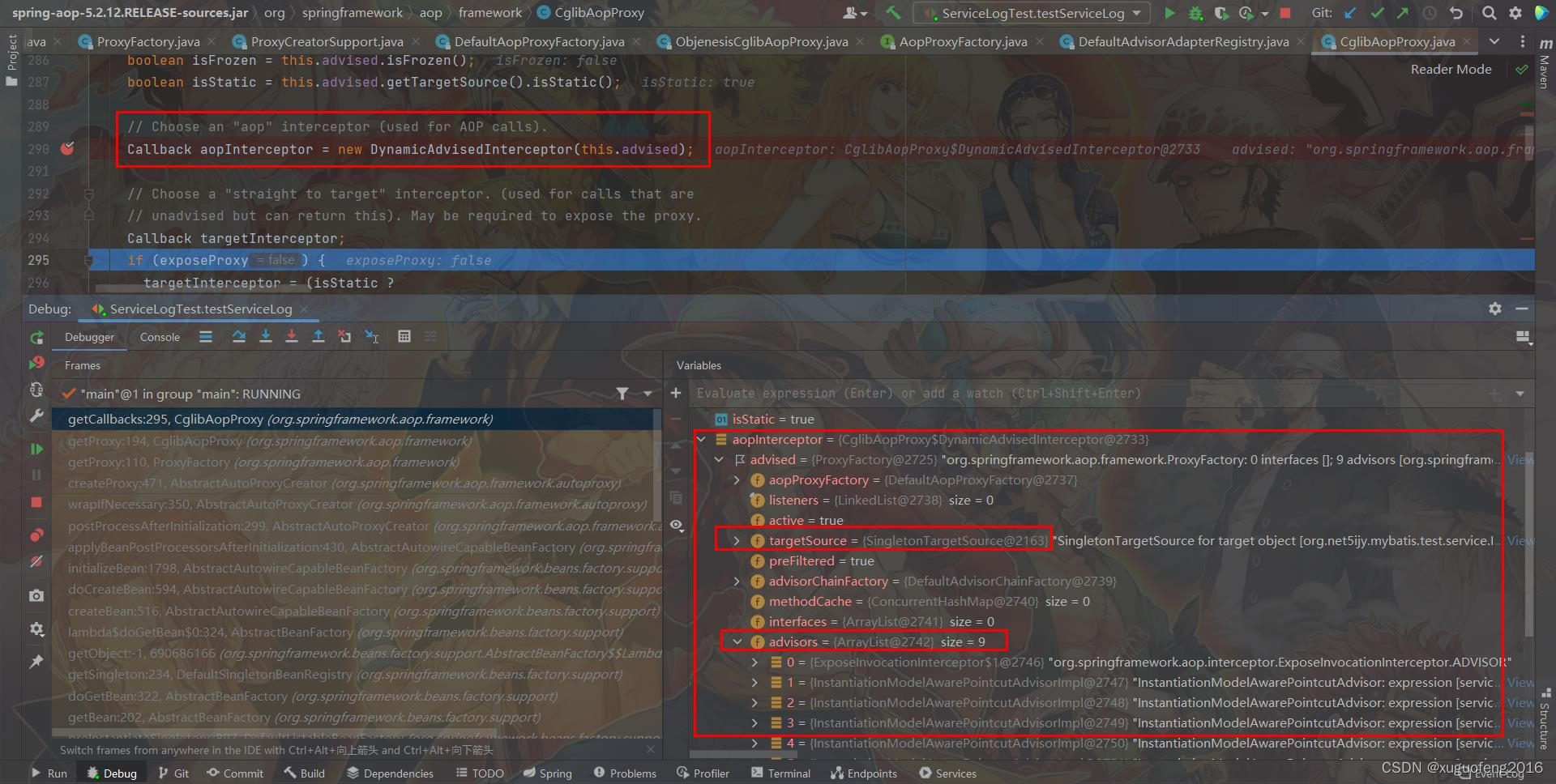
createProxyClassAndInstance
这个方法在ObjenesisCglibAopProxy类实现:
protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) { // Generate a new class if necessary and return it without creating a new instance. // This ignores any callbacks that have been set. // To create a new instance you will have to use reflection, // and methods called during the constructor will not be intercepted. // To avoid this problem, use the multi-arg create method. // 生成代理类 Class<?> proxyClass = enhancer.createClass(); Object proxyInstance = null; // 创建proxyInstance代理对象,实际上就是使用反射创建一个proxyClass的实例,代码省略 // 设置callback代理拦截 ((Factory) proxyInstance).setCallbacks(callbacks); return proxyInstance; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
Cglib生成代理类(暂时不分析)
不太懂,暂时不分析。
JDK代理
JDK代理示例
public static void main(String[] args) { LogService logService = new LogServiceImpl(); Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance( SpringJdkProxyDemo.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{LogService.class}, new MyInvocationHandler(logService)); LogService o = (LogService) proxyInstance; o.log(); } static class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { private final Object object; public MyInvocationHandler(Object object) { this.object = object; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.printf("MyInvocationHandler %s args: %s\n", method.getName(), Arrays.toString(args)); return method.invoke(this.object, args); } } interface LogService { void log(); } static class LogServiceImpl implements LogService { @Override public void log() { System.out.println("LogServiceImpl.log()"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
JdkDynamicAopProxy.getProxy
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) { Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
代码比较简单,就是使用java的Proxy创建代理对象,第三个参数传递的是this,因为JdkDynamicAopProxy实现了InvocationHandler接口。
小结
在本文中,我们了解到了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator后置处理器如何为Bean对象解析Advisor集、匹配可用Advisor集和创建代理对象的过程。
后续,我们将继续阅读CglibAopProxy和JdkDynamicAopProxy的代码,分析Spring AOP的执行流程。
-
相关阅读:
给运行中的docker容器挂载目录——筑梦之路
关于 Hypervisor的理解
解决方案中word中分页符的使用
(WebFlux)002、如何打印日志与链路ID
C# 集合(一) —— Array类
8086与8088
nvm管理(切换)node版本,方便vue2,vue3+ts开发
跨平台Android和IOS百度语音在线识别原生插件
代码随想录第四十三天|343. 整数拆分 ● 96.不同的二叉搜索树
【1. 操作系统—概述】
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/xuguofeng2016/article/details/128193774
