-
useState源码解读 及 手撕 useState 实现
useState源码解读 及 手撕 useState 实现
useState源码分析
逻辑图
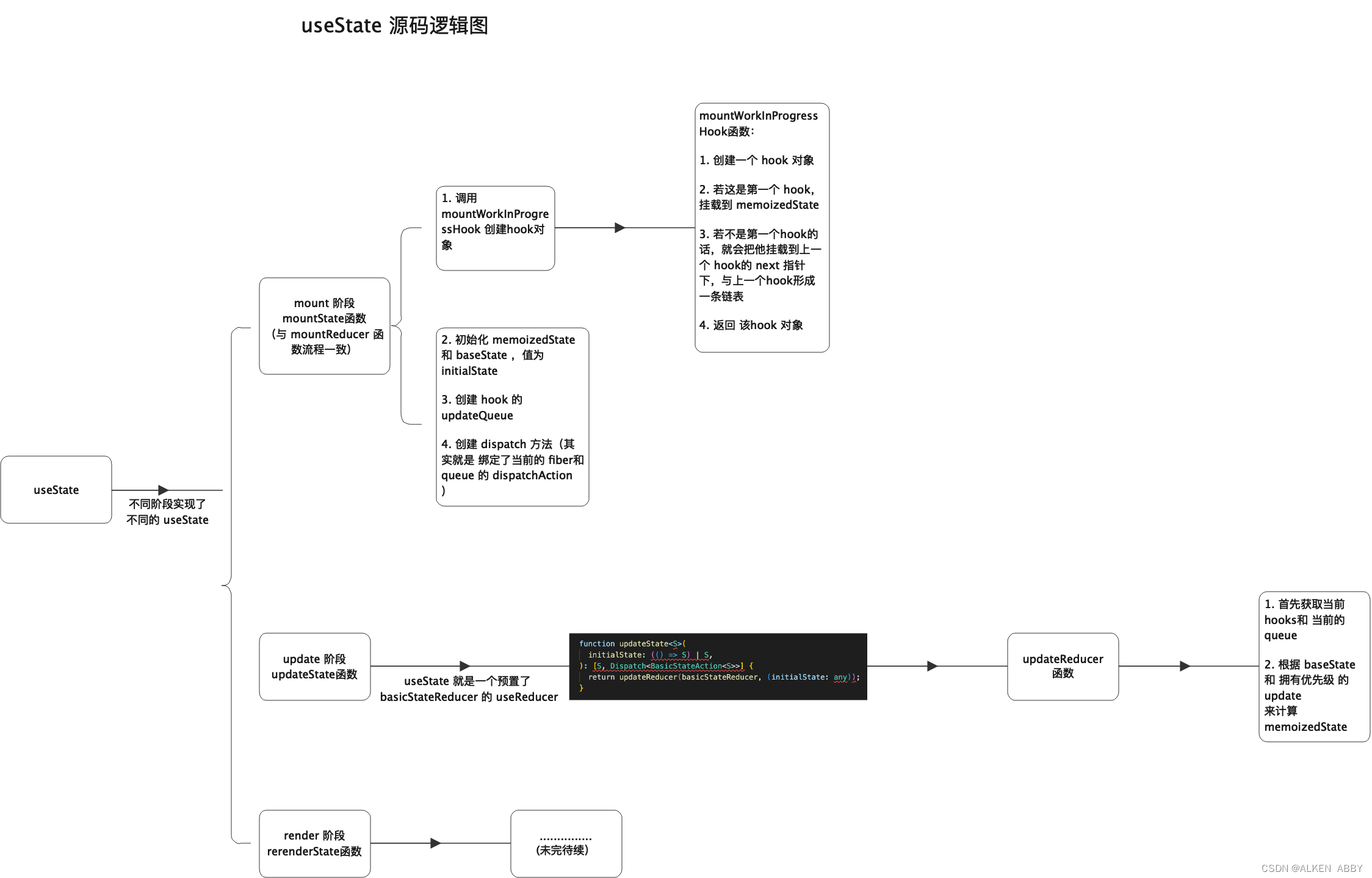
源码解读
hooks 保存在 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.old.js 文件中
有一个 dispatcher 的数据结构,是个对象,在不同的 dispatcher 中,都同样存在了 useState;
在不同的 dispatcher 中,useState 的实现对应的是不同的方法:
即 useState 在不同的上下文中对应的是不同的函数
所以:react 通过在不同的上下文使用不同的 dispatcher,来区分当前需要使用 hooks 的不同实现比如:
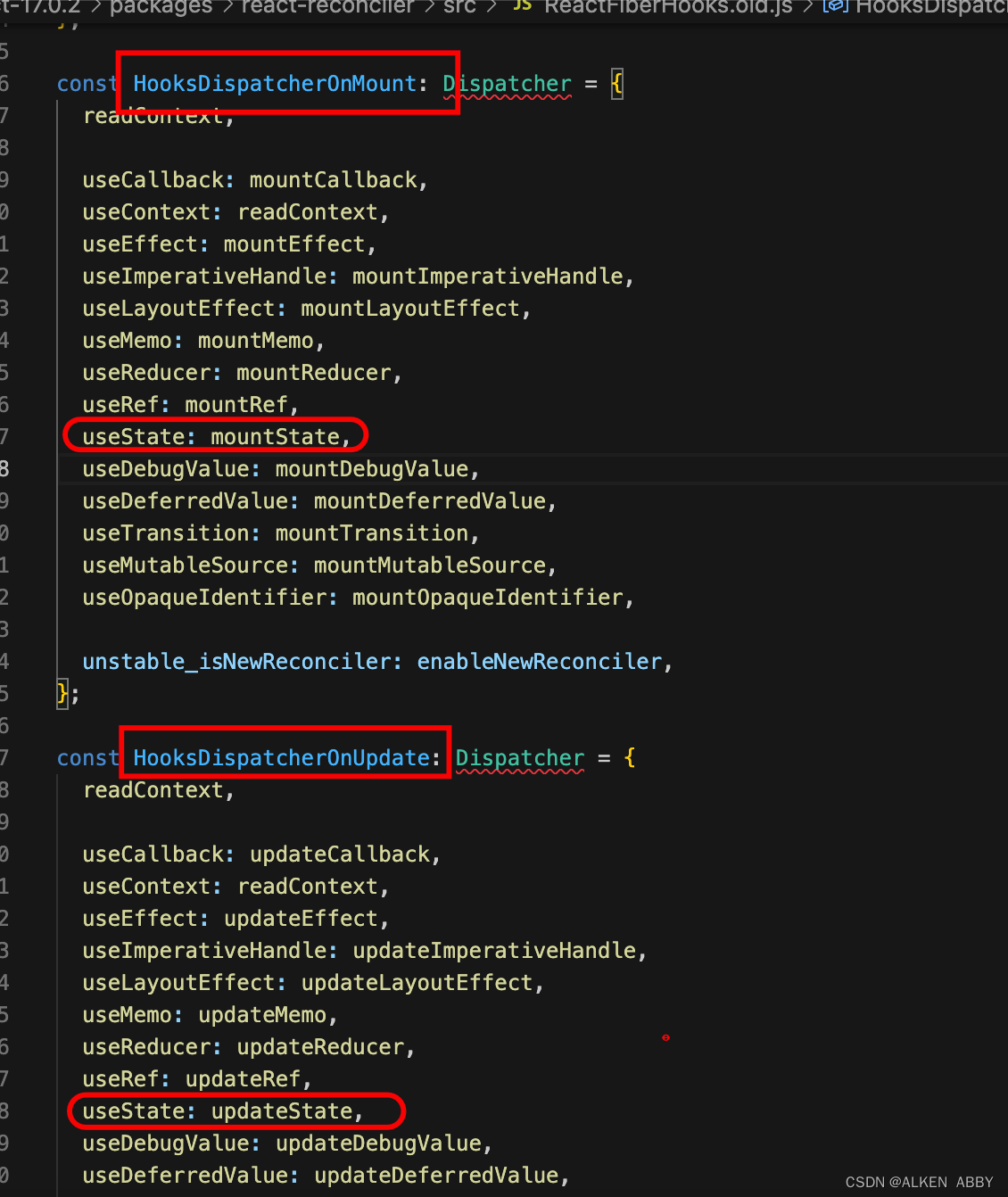
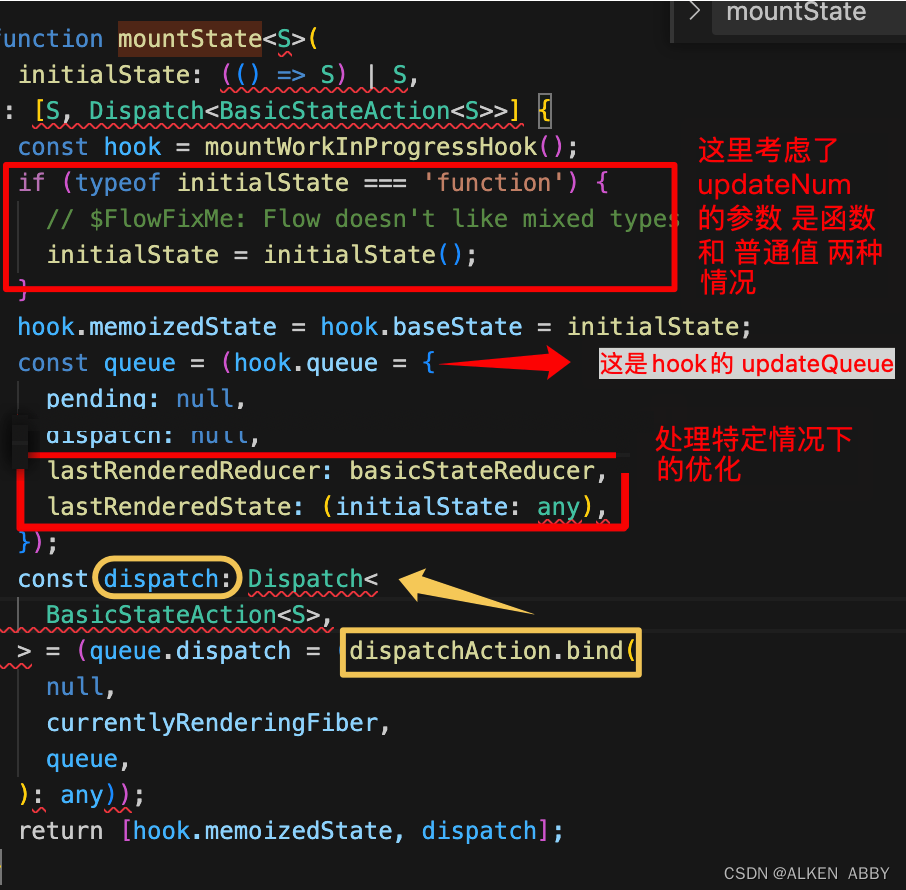
mountState
首先看 mountState 的实现:
- 调用 mountWorkInProgressHook 创建hook对象
- 初始化 memoizedState 和 baseState ,值为 initialState
- 创建 hook 的 updateQueue
- 创建 dispatch 方法(其实就是 绑定了当前的 fiber和 queue 的 dispatchAction )
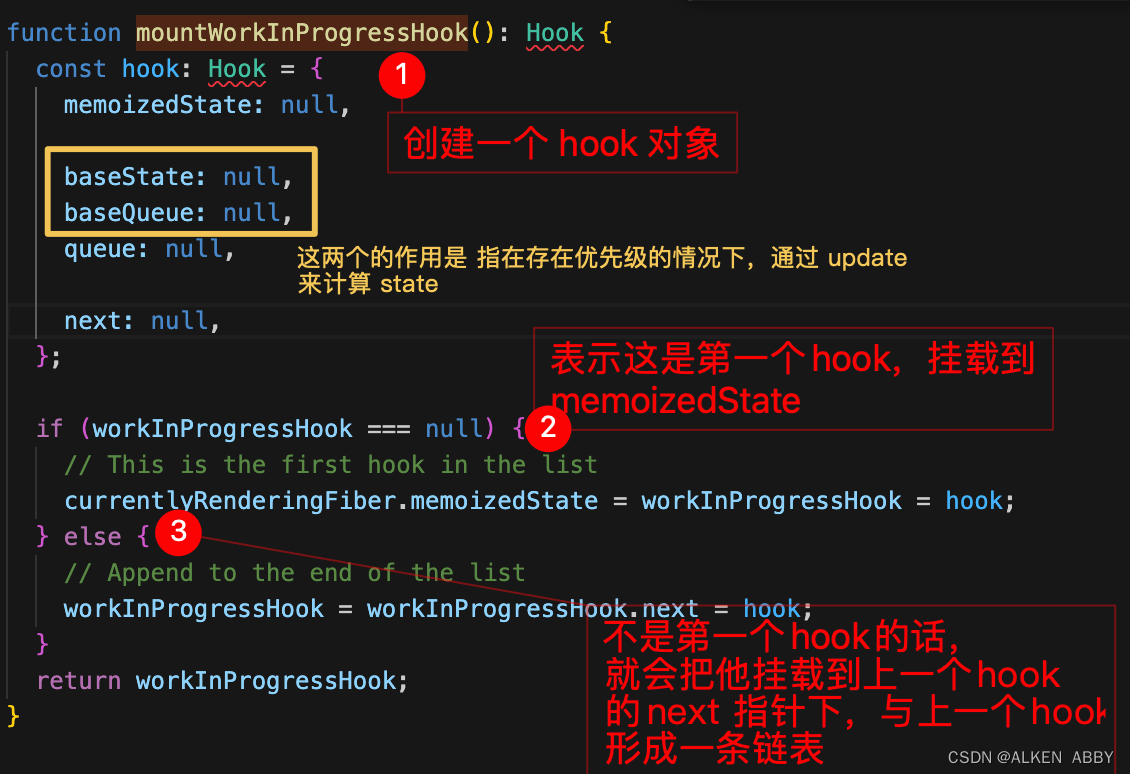
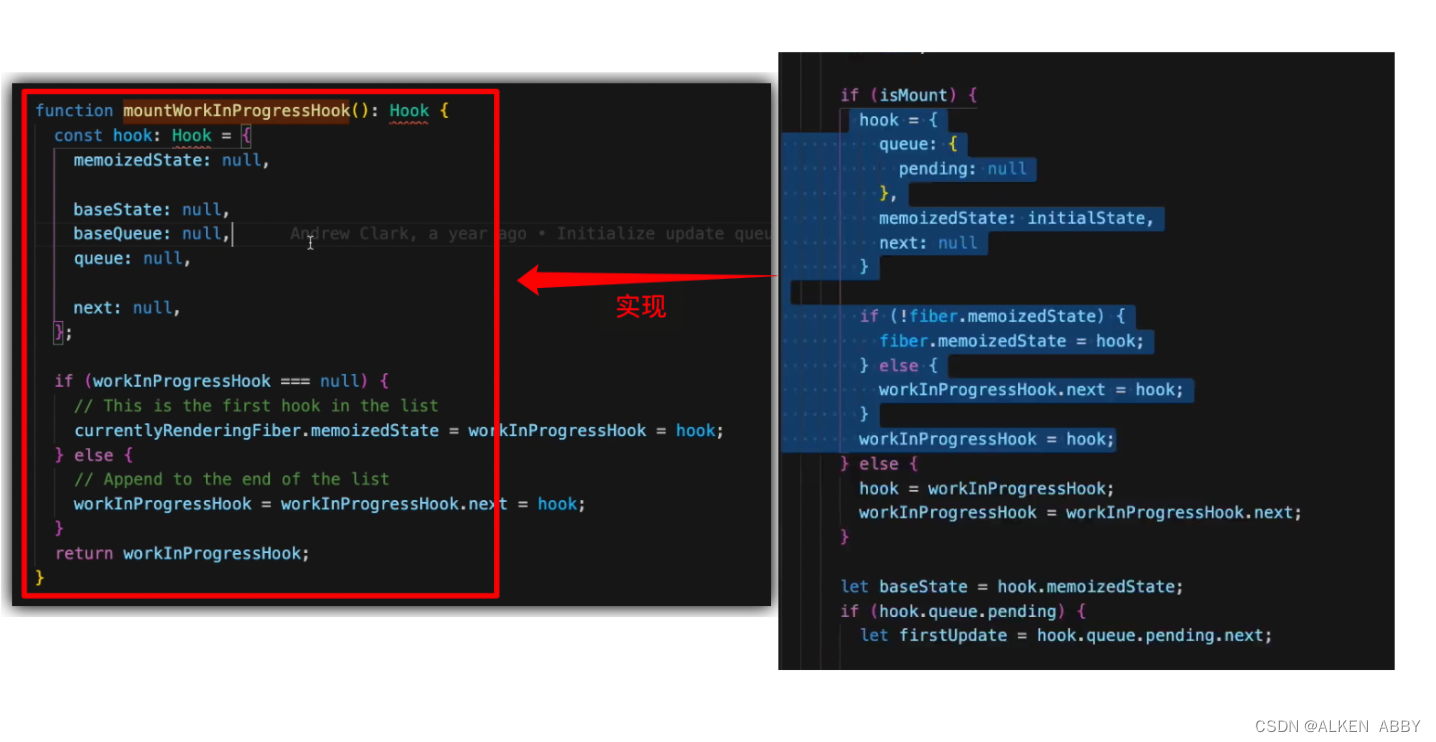
mountWorkInProgressHook 函数
- 创建一个 hook 对象
- 若这是第一个 hook,挂载到 memoizedState
- 若不是第一个hook的话,就会把他挂载到上一个 hook的 next 指针下,与上一个hook形成一条链表
- 返回 该hook 对象
updateState
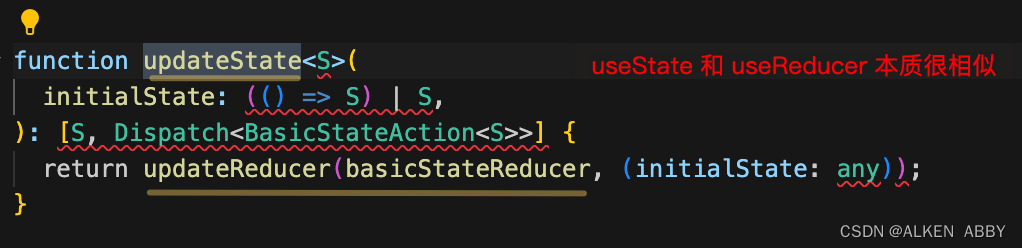
其实,useState 就是一个预置了 reducer 的 useReducer,预置的 reducer 就是 basicStateReducer

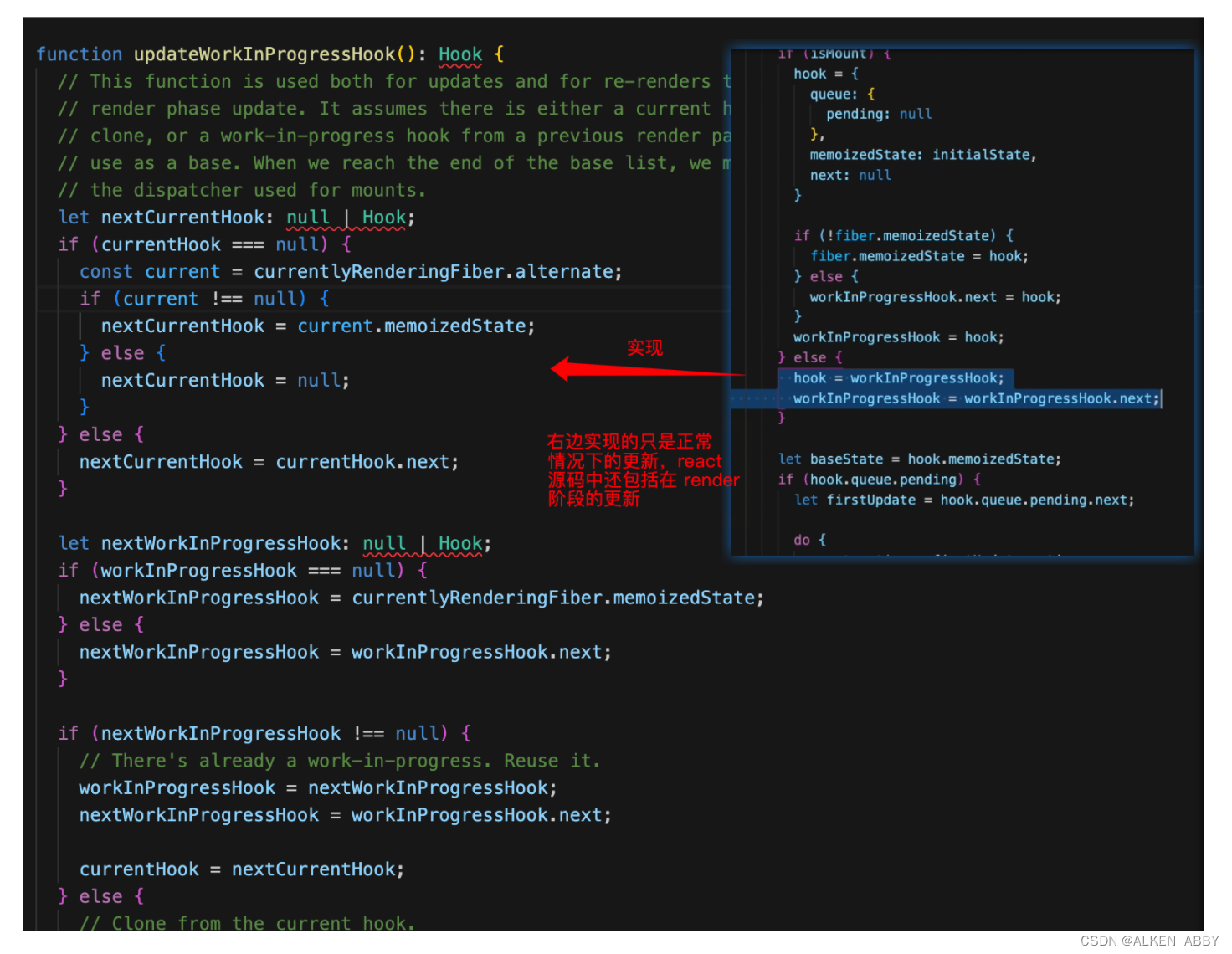
updateReducer 函数
总结:首先获取当前 hooks和 当前的 queue,之后就会 根据 baseState 和 拥有优先级 的 update来计算 memoizedState
具体代码在这:
function updateReducer<S, I, A>( reducer: (S, A) => S, initialArg: I, init?: I => S, ): [S, Dispatch<A>] { const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook(); const queue = hook.queue; invariant( queue !== null, 'Should have a queue. This is likely a bug in React. Please file an issue.', ); queue.lastRenderedReducer = reducer; const current: Hook = (currentHook: any); // The last rebase update that is NOT part of the base state. let baseQueue = current.baseQueue; // The last pending update that hasn't been processed yet. const pendingQueue = queue.pending; if (pendingQueue !== null) { // We have new updates that haven't been processed yet. // We'll add them to the base queue. if (baseQueue !== null) { // Merge the pending queue and the base queue. const baseFirst = baseQueue.next; const pendingFirst = pendingQueue.next; baseQueue.next = pendingFirst; pendingQueue.next = baseFirst; } if (__DEV__) { if (current.baseQueue !== baseQueue) { // Internal invariant that should never happen, but feasibly could in // the future if we implement resuming, or some form of that. console.error( 'Internal error: Expected work-in-progress queue to be a clone. ' + 'This is a bug in React.', ); } } current.baseQueue = baseQueue = pendingQueue; queue.pending = null; } if (baseQueue !== null) { // We have a queue to process. const first = baseQueue.next; let newState = current.baseState; let newBaseState = null; let newBaseQueueFirst = null; let newBaseQueueLast = null; let update = first; do { const updateLane = update.lane; if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) { // Priority is insufficient. Skip this update. If this is the first // skipped update, the previous update/state is the new base // update/state. const clone: Update<S, A> = { lane: updateLane, action: update.action, eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer, eagerState: update.eagerState, next: (null: any), }; if (newBaseQueueLast === null) { newBaseQueueFirst = newBaseQueueLast = clone; newBaseState = newState; } else { newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone; } // Update the remaining priority in the queue. // TODO: Don't need to accumulate this. Instead, we can remove // renderLanes from the original lanes. currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes = mergeLanes( currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes, updateLane, ); markSkippedUpdateLanes(updateLane); } else { // This update does have sufficient priority. if (newBaseQueueLast !== null) { const clone: Update<S, A> = { // This update is going to be committed so we never want uncommit // it. Using NoLane works because 0 is a subset of all bitmasks, so // this will never be skipped by the check above. lane: NoLane, action: update.action, eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer, eagerState: update.eagerState, next: (null: any), }; newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone; } // Process this update. if (update.eagerReducer === reducer) { // If this update was processed eagerly, and its reducer matches the // current reducer, we can use the eagerly computed state. newState = ((update.eagerState: any): S); } else { const action = update.action; newState = reducer(newState, action); } } update = update.next; } while (update !== null && update !== first); if (newBaseQueueLast === null) { newBaseState = newState; } else { newBaseQueueLast.next = (newBaseQueueFirst: any); } // Mark that the fiber performed work, but only if the new state is // different from the current state. if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) { markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate(); } hook.memoizedState = newState; hook.baseState = newBaseState; hook.baseQueue = newBaseQueueLast; queue.lastRenderedState = newState; } const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any); return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch]; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
查阅各种文档资料视频等,勉勉强强的弄懂了 useState 的实现原理,今天来简单实现一下 useState,思路都在 代码注释中:
实现
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Documenttitle> head> <body> <script> // 在 react 中,会通过判断 currentFiber 是否存在,来区别是 mount 还是 update // 在这个简易版本中,通过一个 全局变量来区分 let isMount = true; // workInProgressHook 指向当前正在执行的 hooks let workInProgressHook = null; // 模拟 schedule,render,commit 这个流程 function run() { //hooks 的初始化操作,初始化为第一个 hook workInProgressHook = fiber.memorizedState; // 模拟 render 阶段,render 阶段会触发 App 函数 const app = fiber.stateNode(); isMount = false; return app; } // 作用:创建 update,并将 update 连成一条环状链表 // 这样我们在调用 useState 中,才能从 hook.queue.pending 中取到这条环状链表 function dispatchAction(queue, action) { const update = { action, next: null }; if (queue.pending === null) { // 还不存在 update update.next = update; // 第一个 update 会与自己形成 环状链表 } else { // 环形链表操作 // 例子: 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 // 转变为 4 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 // update 代表当前的 update,queue.pending.next 代表 第一个, // 即实现 从 3 -> 0 变为 4 -> 0 update.next = queue.pending.next; // 实现 从 -> 3 变为 3 -> 4 queue.pending.next = update; } queue.pending = update; // queue.pending 指向的是最后一个 update run(); } // 函数组件有一个对应的 fiber const fiber = { /** * memorizedState 属性用于保存 hooks * 是使用的 链表的结构来保存的hooks */ memorizedState: null, stateNode: App // stateNode 保存了对应的 function } // 实现 useState function useState(initialState) { let hook; if (isMount) { // mount 阶段 // 创建 hooks 链表(和 update queue 是类似的) hook = { queue: { pending: null }, memorizedState: initialState, // 保存了 hooks 对应的state 的属性 next: null // next 指向下一个 hook } if (!fiber.memorizedState) { fiber.memorizedState = hook; // hooks 初始化 } else { workInProgressHook.next = hook; } workInProgressHook = hook; // 以上实现了将多个hook连接成一个单向链表 } else { // update 阶段 hook = workInProgressHook; workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next; } // 此时 hook 变量就是当前的 hook 对象 // 注意:这个版本中省略了 state 优先级的考虑,所以只需要实现 state 中的 baseState // 即 baseState 就是 memorizedState // 计算 state let baseState = hook.memorizedState; if (hook.queue.pending) { // 此时的hook有需要计算的 update /** * hooks 在 update 阶段中,在 updateQueue 中是以环状链表保存的 * * hook.queue.pending 保存了最后一个 update * 所以 hook.queue.pending.next 就指向了第一个 update */ let firstUpdate = hook.queue.pending.next; // 遍历链表 do { const action = firstUpdate.action; // action 表示 updateNum 传入的参数值(这里是函数 num => num + 1) baseState = action(baseState); firstUpdate = firstUpdate.next; } while (firstUpdate !== hook.queue.pending.next); hook.queue.pending = null; // update 计算完毕 } // 进行更新 hook.memorizedState = baseState; // 函数组件改变 update 的这个函数叫 dispatchAction return [baseState, dispatchAction.bind(null, hook.queue)] } function App() { const [num, updateNum] = useState(0); const [flag, updateFlag] = useState(false); console.log('isMount:', isMount); console.log('num', num); console.log('flag:', flag); return { onClick() { updateNum(num => num + 1); }, change() { updateFlag(flag => !flag); } } } window.app = run(); script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
对比图
实现效果
只声明一个 hook
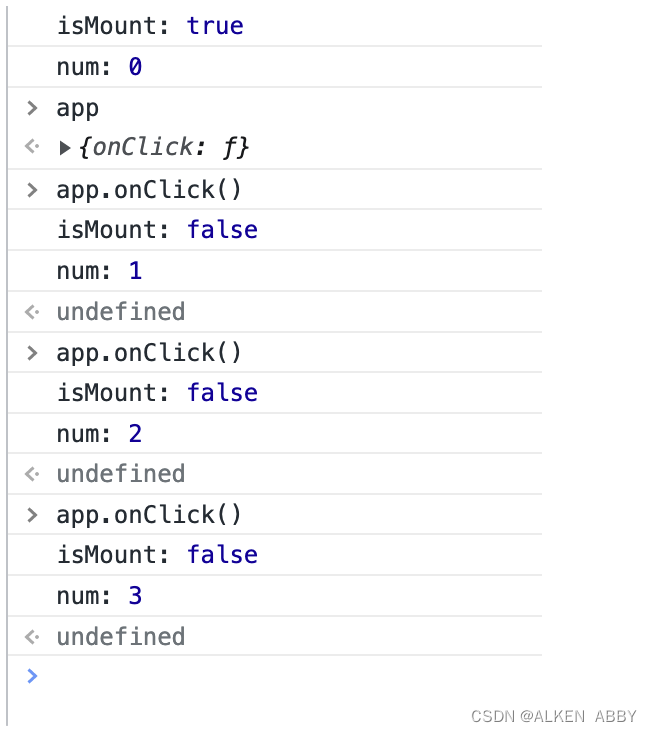
重复调用同一个 hook
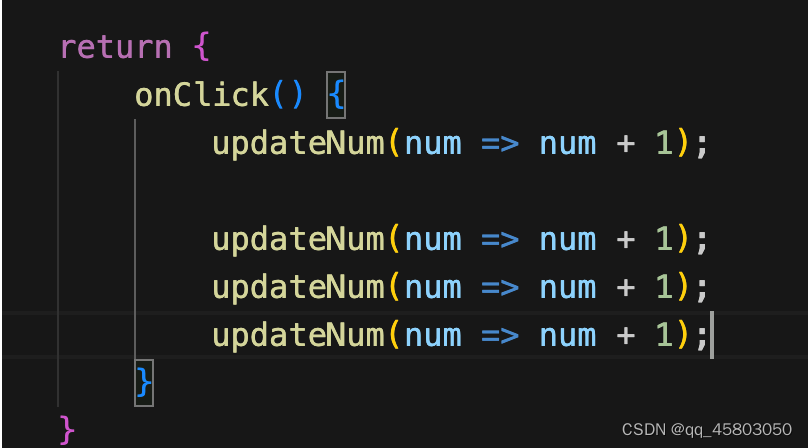
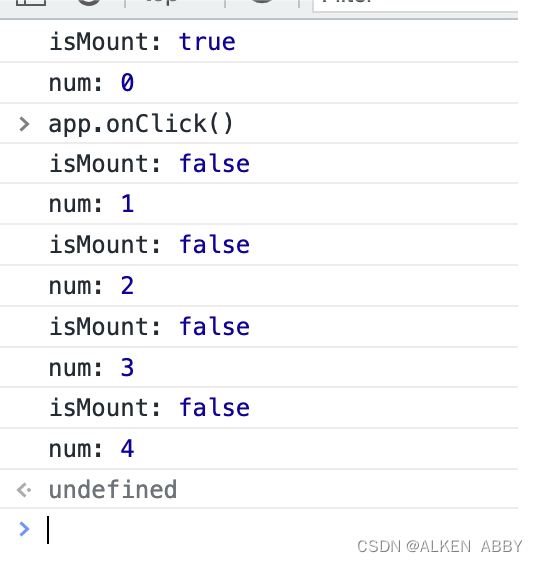
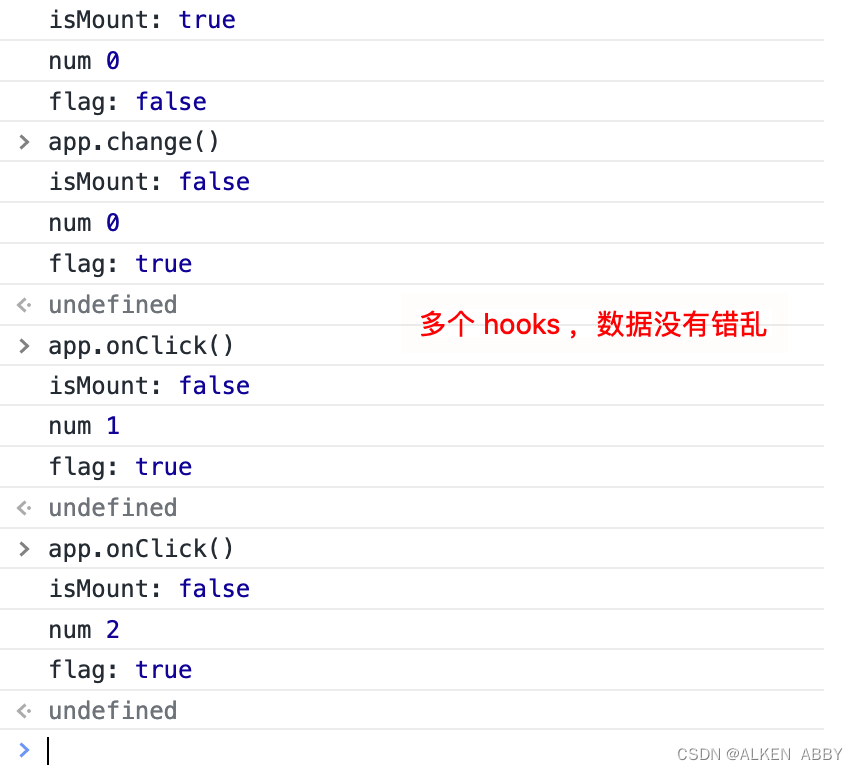
声明多个不同的 hooks
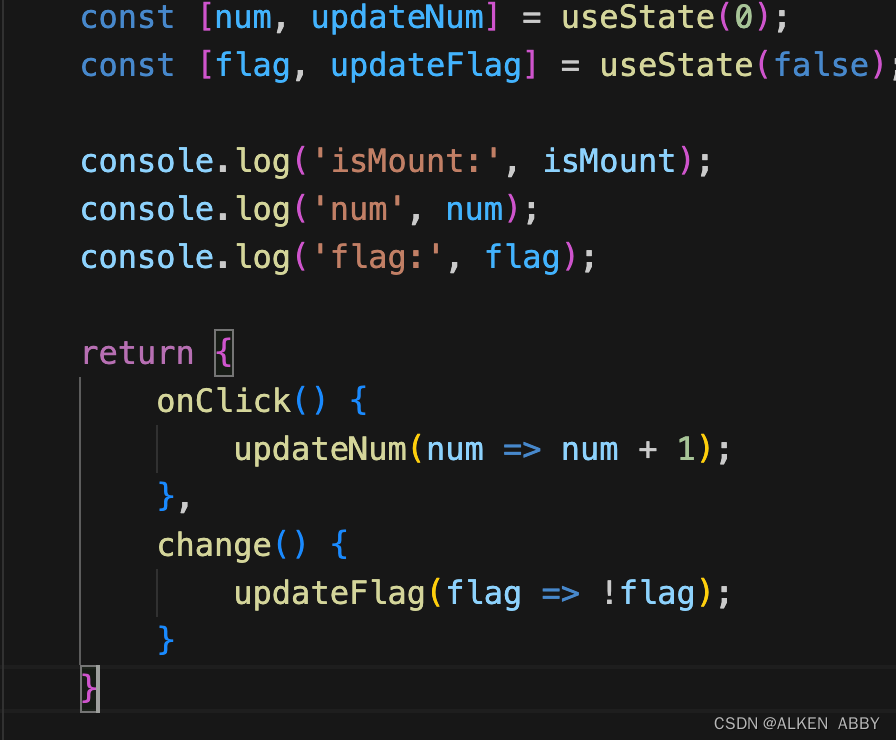
体验收获
源码确实很难,需要花很多时间,但是弄懂了之后,很有成就感,也觉得 react 没有那么神秘了,加油!
-
相关阅读:
Google Earth Engine APP——全球内陆水分布的APP展示
C++day5
AtCoder Beginner Contest 262 部分题解
Web3和低代码开发:下一代Web应用开发的合作与创新
gerrit本地代码关联到远程仓库
Zookeeper
用移动硬盘当系统盘,即插即用
HCIP实验(05)OSPF综合实验
Spring 补充@Component 和 注入技巧 问题
最简单的RNN预测股票收盘价
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45803050/article/details/128175152
