-
Service层代码单元测试以及单元测试如何Mock
一、背景
接着上一篇文章:单元测试入门篇,本篇文章作为单元测试的进阶篇,主要介绍如何对Springboot Service层代码做单元测试,以及单元测试中涉及外调服务时,如何通过Mock完成测试。
二、Springboot Service层代码单元测试
现在项目都流行前后端代码分离,后端使用springboot框架,在service层编写接口代码实现逻辑。假设现在前端不是你写的,你要对你自己写的后端springboot service层提供的接口方法做单元测试,以确保你写的代码是能正常工作的。
Service层代码单元测试:一个简单的service调mapper查询数据库replay_bug表数据量的接口功能
ReplayBugServiceImpl类代码:
@Service public class ReplayBugServiceImpl implements ReplayBugService { @Autowired ReplayBugMapper replayBugMapper; @Override public int queryBugTotalCount() { return replayBugMapper.queryBugTotalCount(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
replayBugMapper.queryBugTotalCount代码:
@Select("select count(1) from replay_bug") int queryBugTotalCount();- 1
- 2
单元测试ReplayBugServiceImplTest类代码:
import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ReplayBugServiceImplTest{ @Autowired ReplayBugServiceImpl replayBugService; @Test public void queryBugTotalCount() { int bugCount=replayBugService.queryBugTotalCount(); System.out.println("结果是:"+bugCount); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
代码很简单,调用这个接口服务,打印输出,测试是否能正确查出数据。其中关键的两个注解解释:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)注解:是一个测试启动器,可以加载SpringBoot测试注解。 让测试在Spring容器环境下执行。如测试类中无此注解,将导致service、dao等自动注入失败。 @SpringBootTest注解:目的是加载ApplicationContext,启动spring容器。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
测试结果如下:
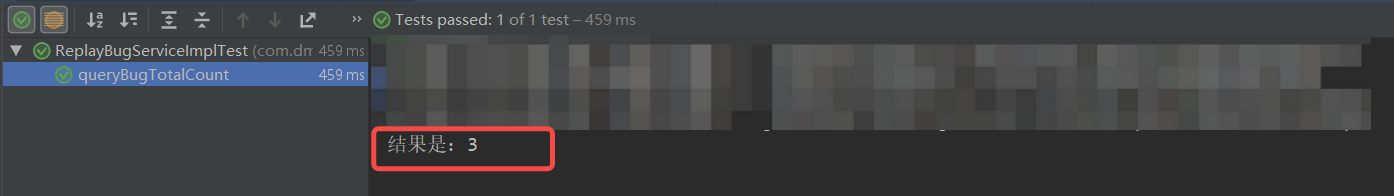
更进一步,测试带入参的service接口:新增接口单元测试
import com.test.service.BestTest; import com.test.domain.UrlWhiteListVO; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ReplayUrlWhiteListServiceImplTest{ @Autowired ReplayUrlWhiteListServiceImpl replayUrlWhiteListService; private UrlWhiteListVO urlWhiteListVO; @Before public void setup(){ urlWhiteListVO=new UrlWhiteListVO(); urlWhiteListVO.setAppId(78); urlWhiteListVO.setAppName("testAPP"); urlWhiteListVO.setUrlWhite("http://www.baidu.com"); urlWhiteListVO.setRemarks("测试一下"); } @Test public void save() { System.out.println("测试结果:"+replayUrlWhiteListService.save(urlWhiteListVO)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
比之前多了一个@Before注解,下面自行设置不同的参数值,测试是否在各种入参情况下接口代码都没有问题。
单元测试结果:
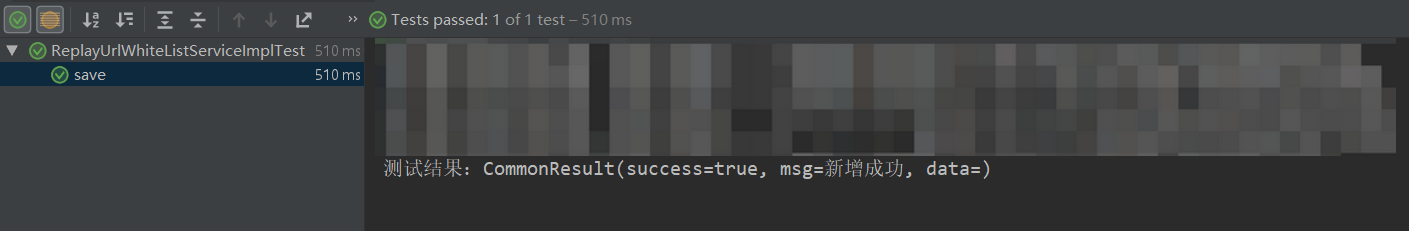
数据库检查数据插入成功:

三、单元测试使用Mockito完成Mock测试
实际业务代码中可能会调到其他第三方接口、会和数据库有交互,如果要测试跑通一个场景,准备数据会非常麻烦。而单元测试很多时候,我们只关心自己的代码逻辑是否有漏洞,这个使用就需要用到Mock, 不真实调用,而是将外调的接口、数据库层面都Mock返回自己想要的各类假数据。
因此再进一步,单元测试使用Mockito完成Mock测试:
import com.test.dao.ReplayBugMapper; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.mockito.InjectMocks; import org.mockito.Mock; import org.mockito.Mockito; import org.mockito.MockitoAnnotations; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ReplayBugServiceImplMockTest { /** * 使用@Autowired是让实例对象正常注入 * 使用@InjectMocks是为了向里面添加@Mock注入的对象 * */ @Autowired @InjectMocks ReplayBugServiceImpl replayBugService; @Mock ReplayBugMapper replayBugMapper; @Before public void setup() { //添加Mock注解初始化 MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); } @Test public void queryBugTotalCount() { int count=1; Mockito.when(replayBugMapper.queryBugTotalCount()).thenReturn(count); int bugCount=replayBugService.queryBugTotalCount(); System.out.println("Mock单元测试返回的结果是:"+bugCount); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
同样的接口,之前真实调用数据库的时候,我们看到返回的结果是3。本次Mock测试代码中我们定义了count为1,使用Mockito让数据库调用直接Mock返回我们定义的1,不再真实调用数据库。
测试结果:

Mockito介绍:Mockito是一款用于java开发的mock测试框架,用于快速创建和配置mock对象。通过创建外部依赖的 Mock 对象, 然后将此 Mock 对象注入到测试类中,简化有外部依赖的类的测试。
Mockito使用:在项目pom.xml中引入依赖spring-boot-starter-test,内部就依赖了Mockito
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
测试代码中用到Mockito的注解作用解释:
@InjectMocks:让@Mock(或@Spy)注解创建的mock将被注入到用该实例中。 @Mock:对函数的调用均执行mock,不执行真实调用。- 1
- 2
如果只想对某一些外调做mock,其他的外调都走真实调用:
比如Service ReplayServiceImpl中方法如下
public int addBug(ReplayVO replayVO) { if(replayManageMapper.addBug(replayVO.getId())==1){ //判断如果replay_bug表中已经有这条数据,不再重复添加。应对场景是用户多次点击标记记录为待解决bug。 if(replayBugService.existBugRecords(replayVO)>=1){ log.info("replay_bug表中数据已存在,不再重复插入数据"); return 1; }else{ log.info("向replay_bug表中插入数据"); return replayManageMapper.saveToReplayBug(replayVO.getAppId(),replayVO.getRequestId(),replayVO.getId(),replayVO.getAppName(),replayVO.getSysDomain(),replayVO.getSysUrl(),replayVO.getUserAccount(),replayVO.getParameters(),replayVO.getResponse(),replayVO.getReplayStatus(),CommonUtils.convertDateToTime(replayVO.getReplayTime())); } }else{ return 0; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
第一步先调用replayManageMapper.addBug对replay表中的这条数据更新状态,更新成功后返回1。
第二步再调用replayBugService.existBugRecords判断replay_bug表中是否存在该条记录,如果存在就不再重复插入。
第三步如果不存在,就再调用replayManageMapper.saveToReplayBug,向replay_bug表中插入该条记录。
现在的需求是单元测试时,对第二步外调的其他接口服务replayBugService做Mock处理,对数据库相关的操作不做Mock,真实调用。单元测试代码如下:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ReplayServiceImplTest { private ReplayVO replayVO; @Autowired @InjectMocks ReplayServiceImpl replayService; @Mock ReplayBugService replayBugService; @Before public void setUp() { //添加Mock注解初始化 MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); replayVO=new ReplayVO(); replayVO.setAppId(1); replayVO.setRequestId(2); replayVO.setId(111); replayVO.setAppName("testApp"); replayVO.setSysDomain("www.test.com"); replayVO.setSysUrl("http://www.test.com/queryList"); replayVO.setUserAccount("测试人员"); replayVO.setParameters("{\"userID\":\"123\"}"); replayVO.setResponse("{\"result\":\"成功\"}"); replayVO.setReplayStatus(5); Date date =new Date(); replayVO.setReplayTime(date); } @Test public void addBug() { Mockito.when(replayBugService.existBugRecords(replayVO)).thenReturn(5); System.out.println("返回值:"+replayService.addBug(replayVO)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
代码解释:
ReplayBugService做Mock处理,所以加了注解@Mock; ReplayServiceImpl中,由于需要部分外调服务Mock,部分外调服务不Mock,所以需要加上注解@Autowired和@InjectMocks: 使用@Autowired是让实例对象正常注入; 使用@InjectMocks是为了向里面添加@Mock注入的对象;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
当replayBugService.existBugRecords(replayVO), Mock返回5,测试结果为:

当replayBugService.existBugRecords(replayVO), Mock返回0,测试结果为:

数据库查看,数据成功插入:

顺带说一下Mockito的@Spy与@Mock区别:
@Spy修饰的外部类,必须是真实存在的,如果没有我们要自己生成创建
Mockito.doReturn(response).when(testService).save(Mockito.any());- 1
@Mock修饰的外部类,是完全模拟出来的,就算项目中没有这个类的实例,也能自己mock出来一个。
比如Spring项目中如果你引入了一个外部的Service:
- 如果在写单元测试时候,外部的Service能加载到的话就可以使用@Spy注解,因为Spring能为你从外部服务找到这个Service并生成实例注入。
- 但是如果外部的服务没有部署,那么Spring就不能为你创建实例,就会报错提示你在创建@Spy修饰服务必须要先实例,此时只要用@Mock注解替换@Spy就好了。
最后,如果有很多的类都需要做单元测试,每一个单元测试类的头上都加公共的注解:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
就显得比较麻烦,可以抽出来写成一个Base类,如果Springboot项目有一些公共的配置需要添加也可以放在这个Base类中:import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class BeseTest { @BeforeClass public static void init(){ System.setProperty("server.domain", "test.server.com"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
然后其他单元测试类使用时继承这个BaseTest类就OK了,不用再每个类都去加公共的注解、配置:
public class ReplayServiceImplTest extends BestTest- 1
================================================================================================
以上就是本次的全部内容,都看到这里了,如果对你有帮助,麻烦点个赞+收藏+关注,一键三连啦~欢迎下方扫码关注我的vx公众号:程序员杨叔,各类文章都会第一时间在上面发布,持续分享全栈测试知识干货,你的支持就是作者更新最大的动力~
-
相关阅读:
C语言入门Day_24 函数与指针
校园小情书微信小程序,社区小程序前后端开源,校园表白墙交友小程序
python 可变对象与不可变对象对变量赋值与引用的影响
Django4 -----深入模板
清理Mac磁盘空间时,这些最容易被忽视的“垃圾”你清理了吗?
为什么HashMap的键值可以为null,而ConcurrentHashMap不行?
PHP 中文匹配
如何实现Spring中服务关闭时对象销毁执行代码
CRM项目记录(一)
Twisted 框架简介
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_28340727/article/details/127890340
