-
springboot简述
一、SpringBoot简介
SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。使用了
Spring框架后已经简化了我们的开发。而SpringBoot又是对Spring开发进行简化的,可想而知SpringBoot使用的简单及广泛性。1、springboot快速入门
1、开发步骤
SpringBoot开发起来特别简单,分为如下几步:- 创建新模块,选择Spring初始化,并配置模块相关基础信息
- 选择当前模块需要使用的技术集
- 开发控制器类
- 运行自动生成的Application类
1.创建springboot入门项目


经过以上步骤后就创建了如下结构的模块,它会帮我们自动生成一个Application类,而该类一会在启动服务器时会用到,其实它就是服务器,springboot自身包含服务器,不需要我们导入服务器了。

== 注意:==
-
在创建好的工程中不需要创建配置类
-
创建好的项目会自动生成其他的一些文件,而这些文件目前对我们来说没有任何作用,所以可以将这些文件删除。
可以删除的目录和文件如下:
.mvn.gitignoreHELP.mdmvnwmvnw.cmd
2.创建controller
在
com.example.controller包下创建BookController,代码如下:@RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class BookController { @GetMapping("/{id}") public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("id==>"+id); return "hello,springboot!"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

3.启动服务器
运行
SpringBoot工程不需要使用本地的Tomcat和 插件,只运行项目com.example包下的Application类,我们就可以在控制台看出如下信息

4.测试
使用apifox工具进行测试


至此入门案例已经开发完成,我们写的只有controller层的一些内容,复杂的配置都省略了。
2、对比spring

-
坐标
Spring程序中的坐标需要自己编写,而且坐标非常多SpringBoot程序中的坐标是我们在创建工程时进行勾选自动生成的 -
web3.0配置类
Spring程序需要自己编写这个配置类。这个配置类大家之前编写过,肯定感觉很复杂SpringBoot程序不需要我们自己书写 -
配置类
Spring/SpringMVC程序的配置类需要自己书写。而SpringBoot程序则不需要书写。
注意:基于Idea的
Spring Initializr快速构建SpringBoot工程时需要联网。3、springboot工程快速启动
以后我们和前端开发人员协同开发,而前端开发人员需要测试前端程序就需要后端开启服务器,这就受制于后端开发人员。为了摆脱这个受制,前端开发人员尝试着在自己电脑上安装
Tomcat和Idea,在自己电脑上启动后端程序,这显然不现实。我们后端可以将
SpringBoot工程打成jar包,该jar包运行不依赖于Tomcat和Idea这些工具也可以正常运行,只是这个jar包在运行过程中连接和我们自己程序相同的Mysql数据库即可。这样就可以解决这个问题,如下图

在打包之前确认自己是否导入打包插件,在我们创建springboot工程时默认是给我们导入好的,这里只是提一下,如果没有这个插件,打包好的jar包是有问题的。<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId> <version>2.3.7.RELEASEversion> plugin>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5



输入命令java -jar springboot_01-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar启动工程,启动完成后我们依然可以通过apifox进行测试

4.切换web服务器
现在我们启动工程使用的是
tomcat服务器,那能不能不使用tomcat而使用jetty服务器,而要切换web服务器就需要将默认的tomcat服务器给排除掉,怎么排除呢?使用exclusion标签


这样服务器就切换成功了,测试方法不变。二、配置文件
1.配置文件格式
在这里以端口号的编写举例,主要有三种格式
-
application.propertiesserver.port=80- 1
-
application.ymlserver: port: 81- 1
- 2
-
application.yamlserver: port: 82- 1
- 2
注意:
SpringBoot程序的配置文件名必须是application,只是后缀名不同而已。2.properties配置文件
在这里简单配置了一下应用名称和端口号
# 应用名称 spring.application.name=springboot_01 # 应用服务 WEB 访问端口 server.port=8080- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.yaml格式配置文件
YAML(YAML Ain’t Markup Language),一种数据序列化格式。
最开始我们使用的是
xml,格式如下:<enterprise> <name>muname> <age>18age> <tel>111111tel> enterprise>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
properties类型的配置文件如下enterprise.name=mu enterprise.age=18 enterprise.tel=111111- 1
- 2
- 3
yaml类型的配置文件内容如下enterprise: name: mu age: 18 tel: 111111- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
优点:
-
容易阅读
yaml类型的配置文件比xml类型的配置文件更容易阅读,结构更加清晰 -
容易与脚本语言交互
-
以数据为核心,重数据轻格式
yaml更注重数据,而xml更注重格式
YAML 文件扩展名:
.yml(主流).yaml
上面两种后缀名都可以,以后使用更多的还是
yml的。1.语法规则
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不允许使用Tab键)
空格的个数并不重要,只要保证同层级的左侧对齐即可。 - 属性值前面添加空格(
属性名与属性值之间使用冒号+空格作为分隔)
核心规则:数据前面要加空格与冒号隔开
数组数据在数据书写位置的下方使用减号作为数据开始符号,每行书写一个数据,减号与数据间空格分隔,例如
enterprise: name: mu age: 18 tel: 111111 subject: - Java - 前端 - 大数据- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.yaml配置文件的数据读取
1.使用@value注解
注解中用于读取属性名引用方式是:
${一级属性名.二级属性名……}我们可以在
BookController中使用@Value注解读取配合文件数据,如下@RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class BookController { @Value("${server.port}") private Integer port; @Value("${enterprise.name}") private String name; @GetMapping("/{id}") public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println(port); System.out.println(name); return "hello,springboot!"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
我们创建一个
enterprise实体类来封装数据public class Enterprise { private String name; private int age; private String tel; private String[] subject; //setter and getter //toString }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写yaml配置文件
server: port: 81 enterprise: name: mu age: 18 tel: 11111 subject: - Java - 前端 - 大数据- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
测试


2.使用Environment对象
上面方式读取到的数据特别零散,
SpringBoot还可以使用@Autowired注解注入Environment对象的方式读取数据。这种方式SpringBoot会将配置文件中所有的数据封装到Environment对象中,如果需要使用哪个数据只需要通过调用Environment对象的getProperty(String name)方法获取。具体代码如下:@RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class BookController { @Autowired private Environment env; @GetMapping("/{id}") public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id) { System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.port")); System.out.println(env.getProperty("enterprise.name")); return "hello,springboot!"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
注意:这种方式,框架内容大量数据,而在开发中我们很少使用。
3.自定义对象
SpringBoot还提供了将配置文件中的数据封装到我们自定义的实体类对象中的方式。具体操作如下:-
将实体类
bean的创建交给Spring管理。在类上添加
@Component注解 -
使用
@ConfigurationProperties注解表示加载配置文件在该注解中也可以使用
prefix属性指定只加载指定前缀的数据 -
在
BookController中进行注入
Enterprise实体类内容如下:@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "enterprise") public class Enterprise { private String name; private int age; private String tel; private String[] subject; //setter and getter //toString }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
BookController内容如下:@RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class BookController { @Autowired private Enterprise ent; @GetMapping("/{id}") public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id) { System.out.println(ent.getName()); System.out.println(ent.getSubject()[0]); return "hello,springboot!"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
注意:
使用第三种方式,在实体类上有如下警告提示

这个警告提示解决是在
pom.xml中添加如下依赖即可<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行测试


三、springboot整合junit
步骤:
- 在测试类上添加
SpringBootTest注解 - 使用
@Autowired注入要测试的资源 - 定义测试方法进行测试
创建一个全新springboot项目,创建时导入junit测试依赖


在
com.example.service下创建BookService接口,内容如下public interface BookService { public void save(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
在
com.example.service.impl包写创建一个BookServiceImpl类,使其实现BookService接口,内容如下@Service public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService { public void save() { System.out.println("book service is running ..."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
编写测试类
@SpringBootTest class SpringbootJunitApplicationTests { @Autowired private BookService bookService; @Test void save() { bookService.save(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
运行服务器
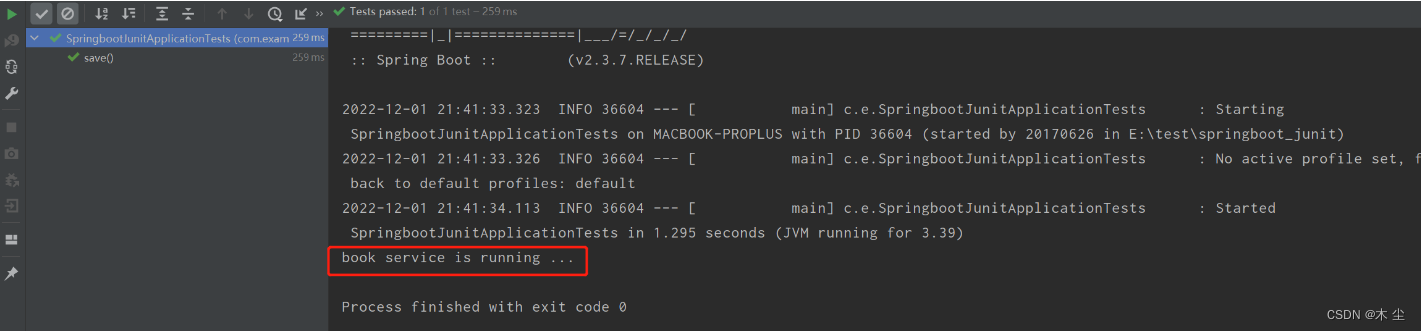
==注意:==这里的引导类所在包必须是测试类所在包及其子包。例如:
- 引导类所在包是
com.example - 测试类所在包是
com.example - 一定要在实现类上加上@service使其能够被spring加载为bean管理,否则会报错
如果不满足这个要求的话,就需要在使用
@SpringBootTest注解时,使用classes属性指定引导类的字节码对象。如@SpringBootTest(classes = Springboot07TestApplication.class)四、springboot整合mybatis
1.回顾一下spring整合mybatis
Spring整合Mybatis需要定义很多配置类-
SpringConfig配置类-
导入
JdbcConfig配置类 -
导入
MybatisConfig配置类@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.example") @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") @Import({JdbcConfig.class,MyBatisConfig.class}) public class SpringConfig { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
-
JdbcConfig配置类-
定义数据源(加载properties配置项:driver、url、username、password)
public class JdbcConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String userName; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource getDataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(driver); ds.setUrl(url); ds.setUsername(userName); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
-
-
MybatisConfig配置类-
定义
SqlSessionFactoryBean -
定义映射配置
@Bean public MapperScannerConfigurer getMapperScannerConfigurer(){ MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer(); msc.setBasePackage("com.example.dao"); return msc; } @Bean public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource){ SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.example.domain"); ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource); return ssfb; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
-
2.springboot整合mybatis
1.创建一个全新的模块导入相关依赖


2.定义实体类
在
com.example.domain包下定义实体类User,内容如下public class User { private Integer id; private String name; //setter and getter //toString }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.定义dao接口
@Mapper public interface UserDao { @Select("select * from tbl_user where id = #{id}") public User getById(Integer id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
4.定义测试类
@SpringBootTest class SpringbootMybatisApplicationTests { @Autowired private UserDao userDao; @Test void testGetById() { User user = userDao.getById(3); System.out.println(user); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
5.编写配置
我们代码中并没有指定连接哪儿个数据库,用户名是什么,密码是什么。所以这部分需要在
SpringBoot的配置文件中进行配合。使用druid数据源
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibabagroupId> <artifactId>druidartifactId> <version>1.1.16version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
这里我使用的是创建springboot项目后自带的properties配置文件,个人感觉还挺好用的,我们对里面的一些配置进行修改
# 应用名称 spring.application.name=springboot_mybatis #下面这些内容是为了让MyBatis映射 #指定Mybatis的Mapper文件 mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mappers/*xml #指定Mybatis的实体目录 mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.example.mybatis.entity # 数据库驱动: spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 数据源名称 spring.datasource.name=defaultDataSource # 数据库连接地址 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisplus_db?serverTimezone=UTC # 数据库用户名&密码: spring.datasource.username=**** spring.datasource.password=****- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
6.注意
Mybatis会扫描接口并创建接口的代码对象交给Spring管理,但是现在并没有告诉Mybatis哪个是dao接口。而我们要解决这个问题需要在BookDao接口上使用@Mapper注意:
SpringBoot版本低于2.4.3(不含),Mysql驱动版本大于8.0时,需要在url连接串中配置时区jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blue?serverTimezone=UTC,或在MySQL数据库端配置时区解决此问题7.运行测试类


至此springboot整合mybatis完成,主要就是在创建springboot工程时导入依赖,然后编写接口,在测试类中注入接口,在接口上使用**@mapper注解让其被spring管理**并加载为一个bean
五、结语
感谢各位大佬的浏览,有什么问题大家可以指出,私信或者评论都是可以的,互相学习~
-
相关阅读:
【云原生】k8s中volumeMounts.subPath的巧妙用法
python常用库之数据库orm框架之SQLAlchemy
模块化打包工具-Webpack插件与其他功能
电脑如何下载视频号的视频?电脑微信视频号使用的方法!
BFT问题思考
如何优雅的使用 IDEA Debug 进行调试
C++ -- 学习系列 std::deque 的原理与使用
一个由硬链接引发的问题
SpringBoot的配置 和 日志文件
前端网站分享
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51470901/article/details/128140410