-
【计算机网络】以太网供电PoE - Power over Ethernet
原理介绍
PoE was firstly introduced by Cisco in 2000s for their IP phones, and it was called Cisco Inline Power at that time. (POE最初由思科在2000年代为自家的IP电话供电发明,期初叫做Cisco Inline Power)
重要名词缩写:
PD: Powered Device 指被供电设备,如IP电话、AP、照明灯等
PSE: Power Sourcing Equipment 指提供电力的设备,如路由器、交换机等
LLDP: Link Layer Discovery Protocol 数据链路层发现协议
MDI: Media Dependent Interface
TLV: Type-Length-Value
MED: Media Endpoint Discovery known as LLDP-MED
CDP: Cisco Discovery Protocol 思科发现协议
以太网(Ethernet Network),不同于同步光纤网(SONET: Synchronous Optical Network)和无线局域网(WLAN: Wireless Local Area Network),在通信的两端之间存在能够导电的物理介质,俗称网线,因此在传输网络信号的同时能够轻松的提供电力传输。
现在的PoE标准已经不是简单的将8根网线中没有用到的4根用来做供电线了。首先,在百兆网络中,1 2线为发送差分对,3 6线为接收差分对,因此有4 5 7 8这四根线闲置,可以用作电源线。而在千兆网络中,所有8根线都需要传输数据,1 2和3 6两对差分线用于发送数据,4 5和7 8两对差分线接收数据,没有空闲的线可以作为电源线,怎么办呢?
这里用到两个个概念:1、信号隔离。网卡的MAC芯片将数据通过MII接口发送给PHY芯片之后,PHY芯片没有直接将电信号传输到网线上,而是会通过一个网络变压器(Ethernet Magnetics)将电信号转换之后才发送到网线上去,这时候PHY芯片出来的电信号和网络变压器出来的信号之间是隔离的,不共地,不存在压差。


2、差分信号。由于Magnetics的存在,网线上走的信号都是差分信号。发送端Magnetics的PHY侧产生变化的电信号,在Magnetics的cable侧感应出电信号,通过网线将信号传输到接收端的cable侧,继而在Magnetics的PHY侧感应出网络信号。Ethernet使用的信号调制解调方式复杂这里不说,下图是10BASE-T的信号波形:

基于上诉的两个概念,我们使用收发端的网络变压器的cable侧的感应线圈的中间抽头作为电源线,如下图:

这样由于供电信号和网络信号之间不存在压差,网络信号不会被电源信号破坏。另外由于电源线是从Magnetics的感应线圈的中间抽头接出,假设这个线圈接出的两根差分线的布线阻抗完全相同,那么从中间抽头到线圈两端抽头的电流是一样大小的,且产生的电磁信号是反向的,相互抵消了,不会产生干扰信号。假如一对差分线的布线阻抗不同,那么在电源供电电流变化的过程中,会在接收端Magnetics感应出干扰信号,因此PoE对网线有一定要求,尤其是电阻不平衡问题。
此外,PoE系统中的供电设备PSE也不是简单的给一个固定电压的电源给手电设备PD,这中间存在协商negotiation,类似于现在的手机快充协议一样。PSE会通过阻抗检测和电流检测以及LLDP协议来判断对端是否存在PD以及确定PD的所需要的电源功率。
PoE标准
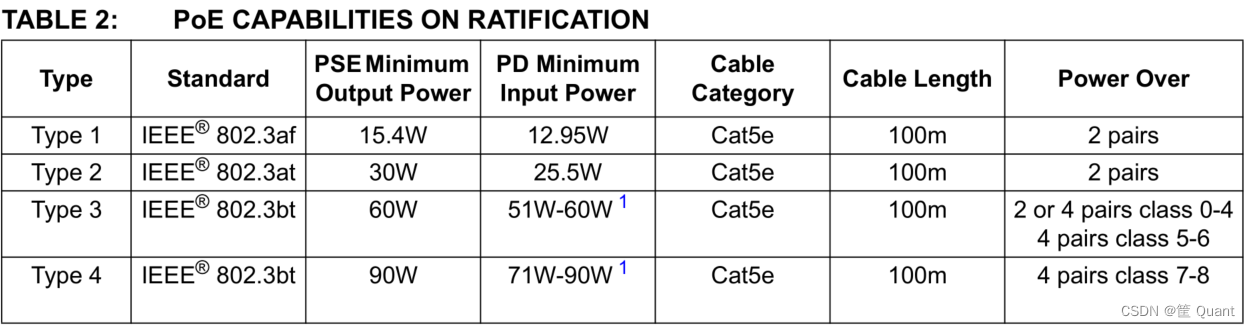
PSE向PD供电的最大功率大小由PD所属的Class等级而定。PoE的三个标准定义了Class分类:
IEEE 802.3af-2003 standard is commonly known as "PoE". It defines PoE Classes 0-3, with maximum power at PD being 12.95W.
IEEE 802.3at-2009 standard is commonly known as "PoE+" or "PoE Plus" and it is the later update to the IEEE 802.3af-2003 "PoE" standard. It defines PoE Classes 0-4, where Classes 0-3 are incorporated from the older 802.3af "PoE" standard under "Type 1", and "Type 2" only includes Class 4 with maximum power at PD being 25.5W.
IEEE 802.3bt-2018 is named "4PPoE". It incorporated Classes 0-4 from the earlier standards and adds "Type 3" (Classes 5-6) and "Type 4" (Classes 7-8) with maximum power at PD being 71.3W.

PSE和PD端不同Type和Class之间的对应关系:

不同Type的PSE和PD供电能力以及所需要的差分对数量:
电源接口 Power Interface
An important concept in the standard is the Power Interface, or PI. The PI is the physical point
where the cabling connects to the PSE or to the PD. In essence it is where the two modular
connectors touch. All specifications in the standard apply at the PI, anything inside the PSE or
PD is considered “implementation specific”.
The PI consists of 8 individual contacts, that correspond to the 8 conductors in a communication
cable. Two conductors form a pair (a twisted pair in the cable), both always at the same nominal
voltage. There are four pairs. A pairset consists of a positive and a negative pair. There are two pairsets, which are called Alternative A (ALT-A) and Alternative B (ALT-B) for the PSE, and Mode A and Mode B for the PD. The relations between these concepts is shown in Figure 2.
Alternative A模式和Alternative B模式。这两种模式只使用两个pairset中的一个pairset:Alternative A或Alternative B进行供电,最大供电功率有限。Alternative A模式:PSE设备利用两对数据线1、2,3、6进行供电。

Alternative B模式:PSE设备利用两对空闲线4、5,7、8进行供电。

基于LTPoE++芯片的802.3bt 4对8线制连线示意图:

Detection and Classification
Classification terminologies from WP_EA_Overview8023bt_V2p1_FINAL.pdf


Detection phase:

Classification phase:




SINGLE-SIGNATURE 和 DUAL-SIGNATURE
An IEEE 802.3bt PSE will identify the PD type and set the power accordingly. According to the application nature, Single-Signature PD or Dual-Signature PD can be implemented. Supporting both architectures is ideal, as it allows more applications to be powered by PoE. Dual-Signature PDs allow supporting two independent loads, each with different power class; e.g. in a surveillance camera built with Dual-Signature PD, one pair may be connected to the camera and the other pair may be connected to the heater.
Dual-signature means a PD allows PSE to perform detection and classification separately on both pairset, so two signature processes will proceed, that's why it is called Dual-signature. e.g. Class3D PDs request the power of Class3 on both pairset, so the total power request is 27.4W which is twice the value of Class3.


对于IEEE 802.3bt标准中的type3和type4中的4个Class PD而言,由于功率较高,2个pairset都需要用于供电,这就产生了两种signature方式:single-signature和dual-signature:

Single-signature waveform (from Si3470A datasheet, just ignore the Class Probe phase):

Dual-signature waveform:

LLDP
如果使用LLDP进行协商,PD需要先使用Hardware Based Negotiation将自己classify成class 3的设备,以获取到13W的电源以驱动PD的CPU,从而完成后续的LLDP数据报文交换。
LTPoE++ Extends PoE to 90W with Reliable and Easy-to-Use Standard | Analog Devices:While Type 2 PSEs may optionally implement LLDP, fully IEEE-compliant Type 2 PDs must implement both physical classification and LLDP power negotiation capabilities. First, this places the burden of LLDP software development on all Type 2 PDs. In addition, designs are complicated by the dual power requirements inferred by the LLDP requirement. Specifically, the PD-side processor must be fully functional at the 13W power level and then have the ability to negotiate, via LLDP, for the delivery of additional power. Clearly this requirement can increase development and system costs and complexity.
以太网电源分离器 PoE Spliter
PoE Spliter is used to separate network signals and power from a PoE cable for PDs that do not have intergrated PoE function. For example, the image below is a PoE spliter that converts voltage on the cable which usually is 54V to 12V for IP cameras or lights to use.

以太网电源供电器 PoE Injector
PoE Injector, on the other hand, is a device that can turn an RJ45 port that doesn't have the PoE capability to an RJ45 port that does by so called injecting power. Below is a PoE injector by TP-LINK:

参考链接:
Power over Ethernet (PoE) - Biamp Cornerstone ☆☆☆
拆解报告:TP-LINK普联标准PoE供电器TL-POE170S_其他数码配件_什么值得买
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GxeC1vVOcw4
如有错误,欢迎指正。
-
相关阅读:
【Python】time模块以及应用
网页前端知识汇总(三)——网页前端利用二维码插件qrcode生成在线二维码
力扣 240.搜素矩阵II
高防IP是什么,高防IP有什么作用?
【题解】二叉树的镜像、判断是不是二叉搜索树
【Java基础】数据结构与算法
git报错The project you were looking for could not be found 解决方式
刷题之莲子的软件工程学和机械动力学以及物理热力学
HCNP Routing&Switching之MAC安全
数据结构 - 链表详解一 - 链表的介绍
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/tq384998430/article/details/128007070