-
Mybatis 源码分析
mybatis 的一些总结
XMLConfigBuilder
mybatis 的配置文件解析的能力是交给了XMLCconfigBuilder 去解析的
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { try { XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
创建一个 configuration 对象
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) { super(new Configuration()); ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration"); this.configuration.setVariables(props); this.parsed = false; this.environment = environment; this.parser = parser; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
baseBuilder 中 ,类型注册器 和 别名注册器等,其实都是Configuration 的成员变量
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) { this.configuration = configuration; this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry(); this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
typeAliasRegistry 别名注册器
Configuration 在构造的之后会默认添加一些类的别名到别名注册器中
public Configuration() { typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class); typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class); languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class); languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
xmlconfigbuilder 的成员变量 及继承关系

configuration 的成员变量
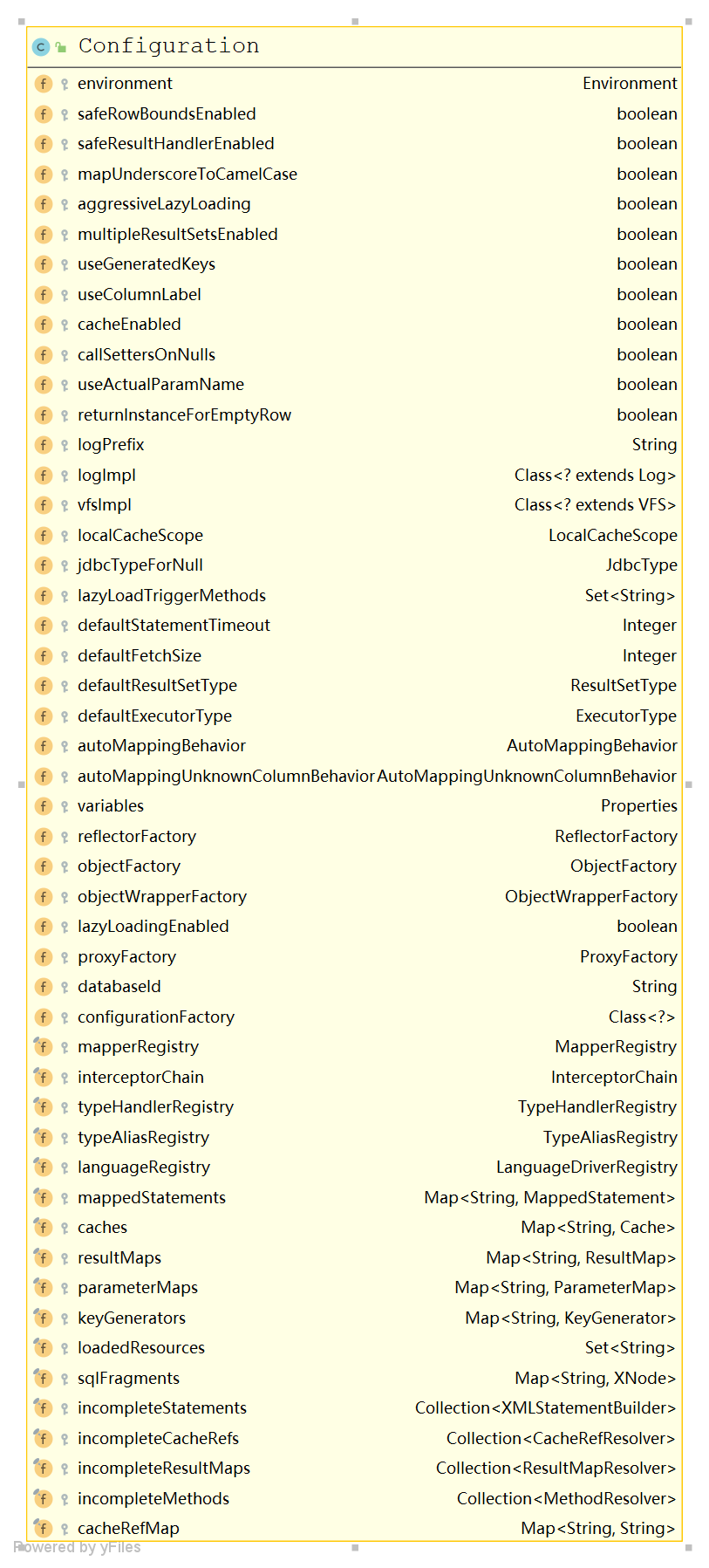
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); loadCustomVfs(settings); loadCustomLogImpl(settings); typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
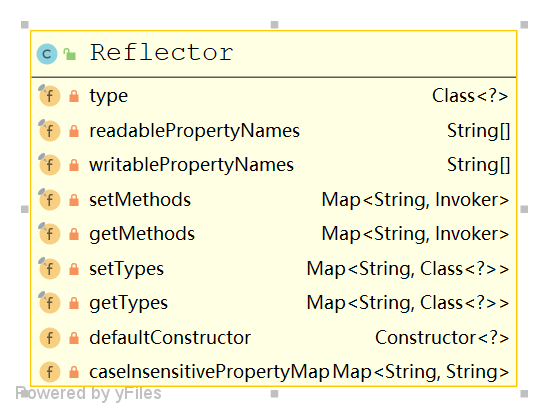
MetaClass 及 reflector
关于 settingAsProperties 的一些解释,MetaClass 通过 reflector 的反射能力,来提供 时候有set get方法的监测机制
private Properties settingsAsProperties(XNode context) { if (context == null) { return new Properties(); } Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); // 获取 MetaClass MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory); for (Object key : props.keySet()) { if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) { throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive)."); } } return props; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
reflector的构造方法,并挑addGetMethods 方法来看
public Reflector(Class<?> clazz) { type = clazz; addDefaultConstructor(clazz); addGetMethods(clazz); addSetMethods(clazz); addFields(clazz); readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]); writablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]); for (String propName : readablePropertyNames) { caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName); } for (String propName : writablePropertyNames) { caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
private void addGetMethods(Class<?> clazz) { Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters = new HashMap<>(); //获取该类的所有方法,包括 interface 和 superClass 方法 Method[] methods = getClassMethods(clazz); Arrays.stream(methods).filter(m -> m.getParameterTypes().length == 0 && PropertyNamer.isGetter(m.getName())) .forEach(m -> addMethodConflict(conflictingGetters, PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(m.getName()), m)); //解决冲突的方法 resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
//以后我们是不是也会了呢 private Method[] getClassMethods(Class<?> clazz) { Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods = new HashMap<>(); Class<?> currentClass = clazz; while (currentClass != null && currentClass != Object.class) { addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, currentClass.getDeclaredMethods()); // we also need to look for interface methods - // because the class may be abstract Class<?>[] interfaces = currentClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) { addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, anInterface.getMethods()); } currentClass = currentClass.getSuperclass(); } Collection<Method> methods = uniqueMethods.values(); return methods.toArray(new Method[0]); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21

typeHandler 类型处理器
关于 typeHandler 的一些说明
@mappedType @mappedJdbcType 而 typeHandlerMap 是通过配置文件加载的,其 key 值有一下区别,如果没有解析到javatype 就是null,如果 jdbc 没有解析到 值,也就是null 。
//存储 从 jdbc 到 TypeHandler 的映射关系 是在初始化 registry 的时候创建的 private final Map<JdbcType, TypeHandler<?>> jdbcTypeHandlerMap = new EnumMap<>(JdbcType.class); //解析 handler 并进行注册 private final Map<Type, Map<JdbcType, TypeHandler<?>>> typeHandlerMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public TypeHandlerRegistry() { register(JdbcType.BOOLEAN, new BooleanTypeHandler()); register(JdbcType.BIT, new BooleanTypeHandler()); register(JdbcType.TINYINT, new ByteTypeHandler()); register(JdbcType.SMALLINT, new ShortTypeHandler());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
private void typeHandlerElement(XNode parent) { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String typeHandlerPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerPackage); } else { String javaTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("javaType"); String jdbcTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("jdbcType"); String handlerTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("handler"); Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaTypeName); JdbcType jdbcType = resolveJdbcType(jdbcTypeName); Class<?> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(handlerTypeName); if (javaTypeClass != null) { if (jdbcType == null) { typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass); } else { typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, jdbcType, typeHandlerClass); } } else { typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerClass); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26

XMLMapperBuilder
public void parse() { if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { //解析 mapper节点 configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper")); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); //绑定 java 接口 bindMapperForNamespace(); } parsePendingResultMaps(); parsePendingCacheRefs(); parsePendingStatements(); } private void bindMapperForNamespace() { String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(); if (namespace != null) { Class<?> boundType = null; try { boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { } if (boundType != null) { if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) { configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace); //进行mapper 的绑定 configuration.addMapper(boundType); } } } } public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { if (type.isInterface()) { if (hasMapper(type)) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { //将 接口 替换为 MapperProxyFactory 对象 存放在 knowMappers 中 knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { knownMappers.remove(type); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54

MapperBuidlerAssistant
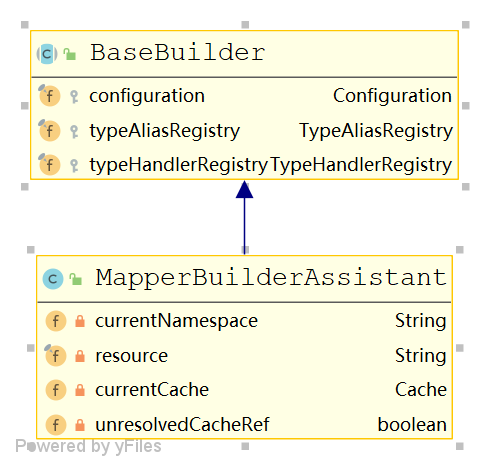
ResultMap

ResultMapping

而sql节点的解析 直接将节点放入到 configuration 中
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) { for (XNode context : list) { String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId"); String id = context.getStringAttribute("id"); id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false); if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) { sqlFragments.put(id, context); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName()); xmlParser.parse();- 1
- 2
XMLStatementBuilder
创建 SqlSource 解析生成 mappedStatement
public void parseStatementNode() { String id = context.getStringAttribute("id"); String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId"); if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) { return; } String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName(); SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)); boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT; boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect); boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect); boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false); // Include Fragments before parsing XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant); includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode()); String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType"); Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType); String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang"); LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang); // Parse selectKey after includes and remove them. processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver); // Parse the SQL (pre:and KeyGenerator keyGenerator; String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX; keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true); if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) { keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId); } else { keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys", configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType)) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; } SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass); StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString())); Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize"); Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout"); String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap"); String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType"); Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType); String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap"); String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType"); ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType); if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) { resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType(); } String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty"); String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn"); String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets"); builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass, resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets); }were parsed and removed) - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
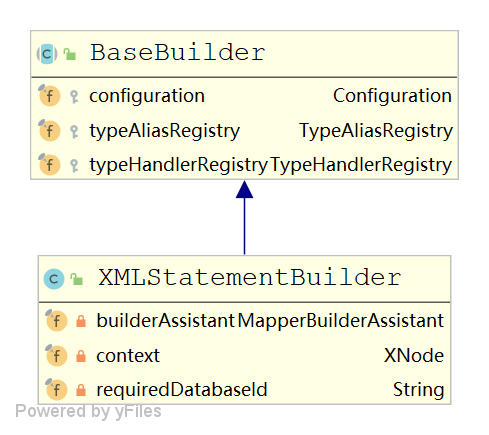
XMLScriptBuilder
public class XMLScriptBuilder extends BaseBuilder { private void initNodeHandlerMap() { nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler()); nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler()); } public SqlSource parseScriptNode() { MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context); SqlSource sqlSource; if (isDynamic) { sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode); } else { sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType); } return sqlSource; } protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) { List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>(); NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) { handler.handleNode(child, contents); isDynamic = true; } return new MixedSqlNode(contents); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
SqlNode


SqlSource
sqlSource 的创建
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) { XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType); return builder.parseScriptNode(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
sqlSource 里面实际存储的是所有的 sqlNode 和 configuration

MappedStatement
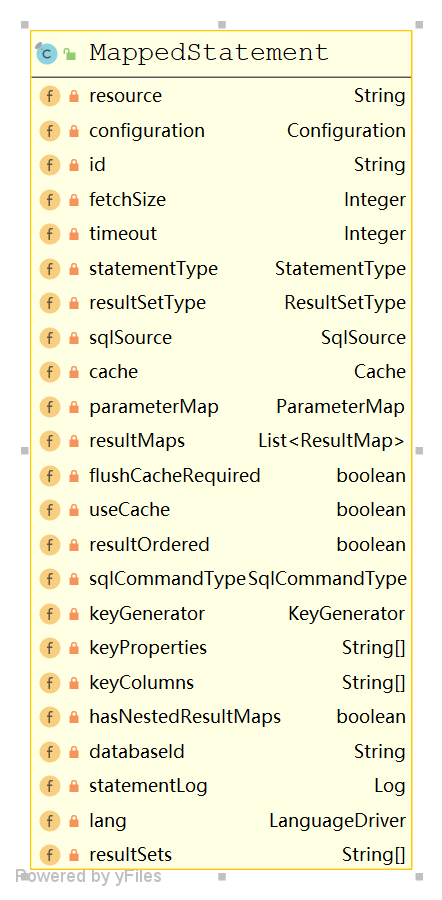
SqlSession

MapperProxyFactory
sqlSession 最终会调用 configuration 中的mapperRegistry 获取 MapperProxyFacroty 进行代理的创建
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession { public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { return configuration.getMapper(type, this); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public class Configuration { public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public class MapperRegistry { public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { //代理的实例化 final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
MapperProxy
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //调用MapperMethod 的 execute final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
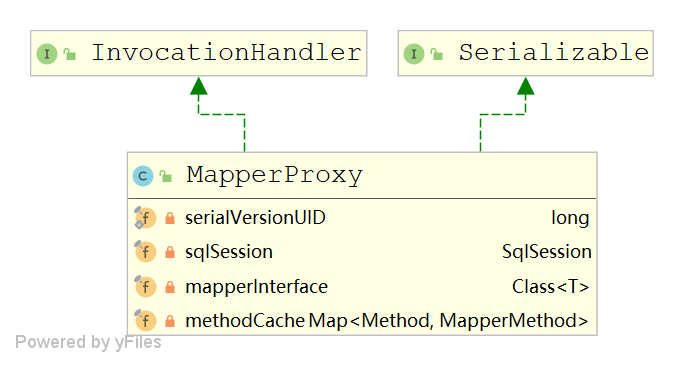
MapperMethod
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; switch (command.getType()) { //最后解析参数,调用 sqlSession Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); return result; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
public static class MethodSignature { public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) { return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

SqlCommand
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-906JmIQP-1669173513901)(C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\SqlCommand.png)]
MethodSignature

ParamNameResolver
map 存储 index -> name
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) { final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations(); final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>(); int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length; // get names from @Param annotations for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) { if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) { // skip special parameters continue; } String name = null; for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) { if (annotation instanceof Param) { hasParamAnnotation = true; name = ((Param) annotation).value(); break; } } if (name == null) { // @Param was not specified. if (config.isUseActualParamName()) { name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex); } if (name == null) { // use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...) // gcode issue #71 name = String.valueOf(map.size()); } } map.put(paramIndex, name); } names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34

最终会调用 DefaultSqlSession
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
我们看一下 Boundsql 是个啥,是如何创建的,最终会调用SqlSource去创建
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource { private final Configuration configuration; private final SqlNode rootSqlNode; @Override public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject); rootSqlNode.apply(context); //到此为止,除了 #{} 其他的都已经解析完毕并追加到 sql中 SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration); Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass(); SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings()); BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject); context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter); return boundSql; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
DynamicContext
bindings 存储 我们的参数,sqlBuilder 存储我们的sql
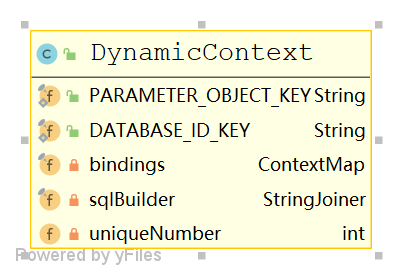
那 ${} 举例
public class TextSqlNode implements SqlNode { //替换字符通过GenericTokenParser 实现,具体替换为什么的逻辑交给BindingTokenParser去实现 @Override public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) { GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter)); context.appendSql(parser.parse(text)); return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
GenericTokenParser
public class GenericTokenParser { private final TokenHandler handler; public String parse(String text) { builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString())); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
TokenHandler
class BindingTokenParser implements TokenHandler { @Override public String handleToken(String content) { Object parameter = context.getBindings().get("_parameter"); if (parameter == null) { context.getBindings().put("value", null); } else if (SimpleTypeRegistry.isSimpleType(parameter.getClass())) { context.getBindings().put("value", parameter); } Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(content, context.getBindings()); String srtValue = value == null ? "" : String.valueOf(value); // issue #274 return "" instead of "null" checkInjection(srtValue); return srtValue; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
BoundSql
最终 通过 SqlSourceBuilder 解析为 StaticSqlSource
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) { ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters); GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler); String sql = parser.parse(originalSql); return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

然后调用 getBoundSql 获取BoundSql

有了 BoundSql
就可以直接到executor 中的方法去分析了
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); //创建 Statement stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); //设置参数 handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
StatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); // 应用插件到 StatementHandler 上 statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { switch (ms.getStatementType()) { case STATEMENT: delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case PREPARED: delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case CALLABLE: delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; default: throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
最终会创建为 StatementHandler,我们看一看 PreparedStatementHandler

public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); Statement statement = null; try { statement = instantiateStatement(connection); setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout); setFetchSize(statement); return statement; } catch (SQLException e) { closeStatement(statement); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { closeStatement(statement); throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); } } protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { //最终 使用sql 创建Statement String sql = boundSql.getSql(); if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) { String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns(); if (keyColumnNames == null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames); } } else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
public class DefaultParameterHandler implements ParameterHandler { public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) { ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); if (parameterMappings != null) { for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null) { value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else { MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType(); if (value == null && jdbcType == null) { jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull(); } try { //最终会调用解析器 设置参数 typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType); } catch (TypeException | SQLException e) { throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e); } } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36

然后执行 query 方法查询参数,并将结果集交给 resultSetHandler 处理
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.execute(); return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
ResultSetHandler
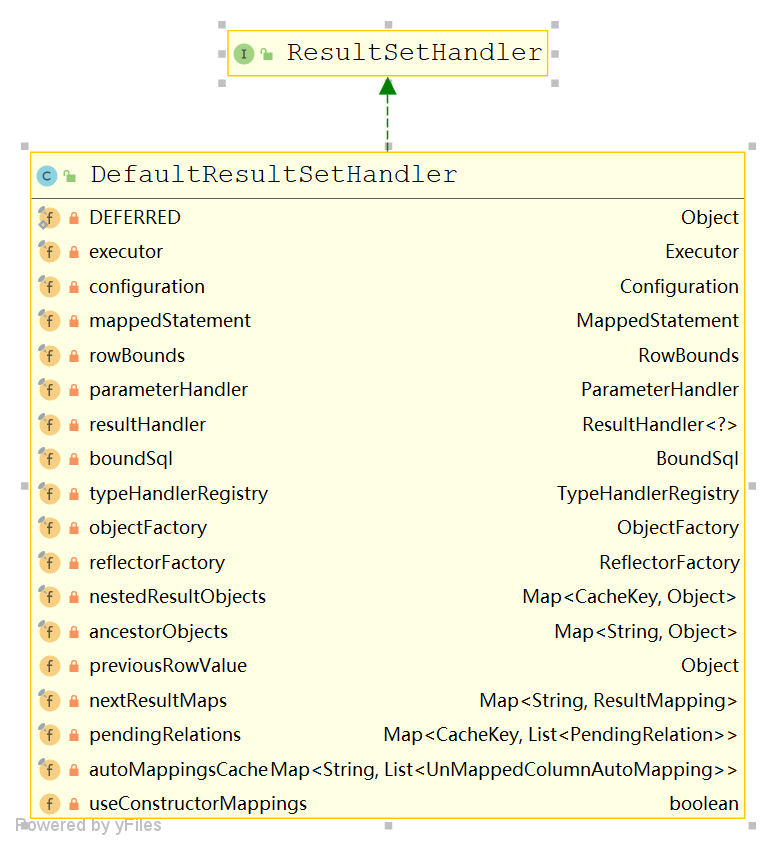
到此 mybatis 的大部分类都已经总结到了。.
插件
MyBatis 允许你在映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用。默认情况下,MyBatis 允许使用插件来拦截的方法调用包括:
- Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
- ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
- ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
- StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
这些类中方法的细节可以通过查看每个方法的签名来发现,或者直接查看 MyBatis 发行包中的源代码。 如果你想做的不仅仅是监控方法的调用,那么你最好相当了解要重写的方法的行为。 因为在试图修改或重写已有方法的行为时,很可能会破坏 MyBatis 的核心模块。 这些都是更底层的类和方法,所以使用插件的时候要特别当心。
插件的原理,拿Executor 举例。其调用 interceptorChain.pluginAll() 方法代理 executor。
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public class InterceptorChain { private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>(); public Object pluginAll(Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { target = interceptor.plugin(target); } return target; } public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { interceptors.add(interceptor); } public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() { return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
看到其会调用interceptor.plugin() 方法。
下面这是插件创建代理的通用逻辑。
Interceptor
public interface Interceptor { Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable; default Object plugin(Object target) { return Plugin.wrap(target, this); } default void setProperties(Properties properties) { // NOP } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) { Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor); Class<?> type = target.getClass(); Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap); if (interfaces.length > 0) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance( type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)); } return target; } //解析注解要拦截的方法 private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) { Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class); // issue #251 if (interceptsAnnotation == null) { throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName()); } Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value(); Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<>(); for (Signature sig : sigs) { Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.computeIfAbsent(sig.type(), k -> new HashSet<>()); try { Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args()); methods.add(method); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e); } } return signatureMap; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
@Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.TYPE) public @interface Intercepts { Signature[] value(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
@Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({}) public @interface Signature { Class<?> type(); String method(); Class<?>[] args(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
示例:
@Intercepts( { @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}), @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class}), } ) public class PageInterceptor implements Interceptor { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
那么 就会抽象出一个通用的 拦截逻辑,就是 Plugin
Plugin
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) { //调用拦截逻辑 return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args)); } return method.invoke(target, args); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

Invocation
当然Invocation 不是plugin 特有的。

分页插件简述
分别有dialect.beforeCount dialect.afterCount dialect.beforePage dialect.afterPage
@Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { try { //调用方法判断是否需要进行分页,如果不需要,直接返回结果 if (!dialect.skip(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) { //判断是否需要进行 count 查询 if (dialect.beforeCount(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) { count = executeAutoCount(executor, countMs, parameter, boundSql, rowBounds, resultHandler); //处理查询总数 //返回 true 时继续分页查询,false 时直接返回 if (!dialect.afterCount(count, parameter, rowBounds)) { //当查询总数为 0 时,直接返回空的结果 return dialect.afterPage(new ArrayList(), parameter, rowBounds); } } //判断是否需要进行分页查询 if (dialect.beforePage(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) { //生成分页的缓存 key CacheKey pageKey = cacheKey; //处理参数对象 parameter = dialect.processParameterObject(ms, parameter, boundSql, pageKey); //调用方言获取分页 sql String pageSql = dialect.getPageSql(ms, boundSql, parameter, rowBounds, pageKey); BoundSql pageBoundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, pageSql, boundSql.getParameterMappings(), parameter); //执行分页查询 resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, pageKey, pageBoundSql); } } return dialect.afterPage(resultList, parameter, rowBounds); } finally { dialect.afterAll(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
-
相关阅读:
yarn通过日志聚合将作业日志存储在HDFS中
Servlet
什么是模糊理论,基础,流程
Java Web实现用户登录功能
10.DesignForSymbols\ExportPadstack
代理IP应该怎么选?如何选择合适的代理IP
力扣 272. 最接近的二叉搜索树值 II 递归
代驾APP_第一章_项目环境搭建_第二节
set_seed(args)
隐私计算FATE-离线预测
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/c1523456/article/details/127996963
