-
块级格式化上下文BFC
BFC是前端日常开发中离不开的知识点,“块级格式化上下文”是格式化上下文中最常用的一种,格式化上下文是指页面中的一块渲染区域 拥有一套自己的渲染规则。 近两天又系统的学习了一遍BFC的知识,也从本站上看了许多其他人讲解BFC的文章。受益匪浅的同时,也决定从我自己的认知角度写 一篇关于BFC的学习文章。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
创建格式化上下文
1、文档的根元素html
2、 使用float使其浮动的元素
3、设置position: absolute;或者position:fixed的元素
4、设置display:inline-block的元素
5、表格单元格或者使用display:table-cell(包括使用display:table-*)属性的所有表格单元格
6、表格标题或者使用display:table-caption的元素
7、overflow属性不为visible的块级元素
8、设置display:flow-root或者display:flow-root list-item的元素
9、设置contain:layout,content,strict的元素
10、弹性盒子的一级子元素
11、网格布局元素
12、multicol containers
13、设置column-span为all的元素BFC有哪些特性?
前端网页有多种布局方式,比如盒子模型的display属性、文档流的三种布局手段:标准流、浮动流、定位流等。我们在使用这些布局时,元素之间经常会出现互相影响的情况,比如块级元素的高度塌陷问题、浮动元素覆盖标准流元素问题等。这个时候,我们就可以用BFC的特性来解决布局中出现的这些问题。
特性一
BFC包含内部所有元素的行为。
特性二
不同BFC之间元素互不影响。
特性三
BFC中的元素按照正常流程遵循块和内联布局规则进行布局。
特性四
BFC特性所影响的元素只包括这个BFC容器的一级子元素,并不能影响元素本身节点和其子元素的子元素。
总结以上几点可以得出一个结论,BFC就相当于一个包含在根元素中的一个小的独立的根元素布局,而且这个BFC中的元素完全不会影响到BFC之外的其他元素。
BFC的特性可以解决哪些问题?
高度塌陷
高度塌陷问题一般是由于元素浮动引起的,当一个元素本身没有设置高度,其高度完全由子元素撑开,而子元素被设置为浮动元素后,由于子元素脱离了标准文档流,因此父元素就没有了高度。
高度塌陷前:- 1
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; } .bg_red { background-color: red; } .bg_yellow { background-color: yellow; } style> head> <body> <div class="bg_yellow"> <p>123p> <div class="box bg_red">div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27

高度塌陷后:- 1
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; } .bg_red { background-color: red; } .bg_yellow { background-color: yellow; } .float { float: left; } style> head> <body> <div class="bg_yellow"> <p>123p> <div class="box bg_red float">div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
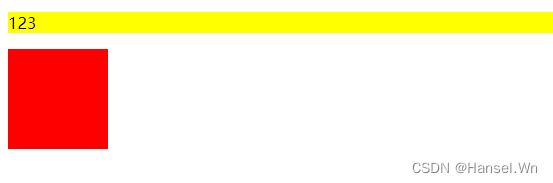
因为BFC包含其内部的所有元素,所以这时候可以将父元素设置BFC:DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; } .bg_red { background-color: red; } .bg_yellow { background-color: yellow; } .float { float: left; } .bfc { overflow: hidden; } style> head> <body> <div class="bg_yellow bfc"> <p>123p> <div class="box bg_red float">div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36

margin塌陷
在标准文档流中,两个垂直排布的元素,其相邻的margin-top和margin-bottom会重叠,因此这两个元素之间的margin之和并不是想象中的两个外边距相加,而是取两个margin中较大的值。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>BFCtitle> <style> .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; margin: 50px; } .bg_red { background-color: red; } .bg_blue { background-color: blue; } style> head> <body> <div class="box bg_red">div> <div class="box bg_blue">div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
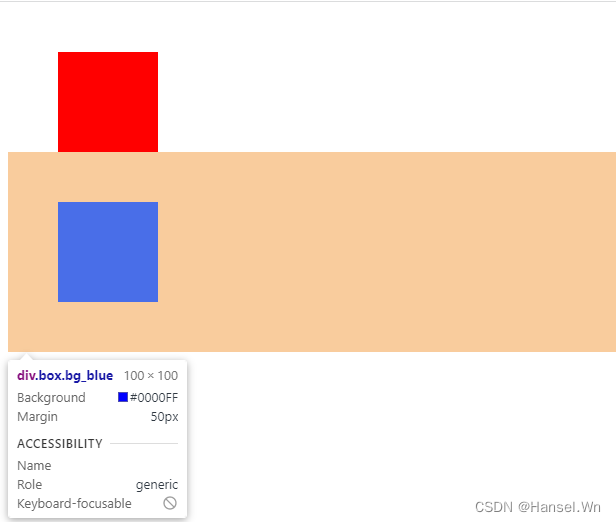
因为不同BFC之间元素不会互相影响,所以我们可以给其中一个元素分别包裹上一层BFC:DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; margin: 50px; } .bg_red { background-color: red; } .bg_blue { background-color: blue; } .bfc { overflow: hidden; } style> head> <body> <div class="box bg_red">div> <div class="bfc"> <div class="box bg_blue">div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33

包含塌陷
直接上代码:
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .big_box { width: 300px; height: 400px; } .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; margin: 50px; } .bg_blue { background-color: blue; } .bg_yellow { background-color: yellow; } style> head> <body> <div class="big_box bg_yellow"> <div class="box bg_blue">div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32

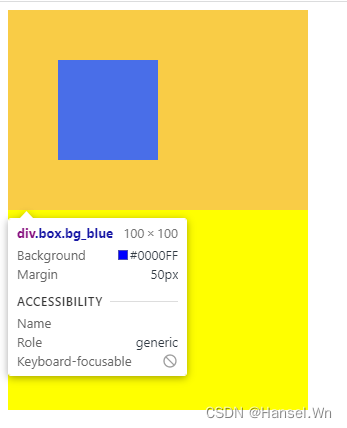
在下面的例子中,由于给内部蓝色的div设置了一个margin,导致外部div也有了一个相同的margin,这时候,可以将外部div设置为BFC,就可以解决问题:DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <style> .big_box { width: 300px; height: 400px; } .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; margin: 50px; } .bg_blue { background-color: blue; } .bg_yellow { background-color: yellow; } .bfc { overflow: hidden; } style> head> <body> <div class="big_box bg_yellow bfc"> <div class="box bg_blue">div> div> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
-
相关阅读:
Substance Painter导出透明背景贴图
一文搞懂数据仓库分层模型
算法拾遗十五补链表相关面试题
使用IDEA创建SpringCloud项目
以太坊合并后,区块链生态将发生什么改变?
尚医通 (十七) --------- 数据字典开发
MatrixOne 支持多样化生态工具,持续提升开发者体验
flutter开发实战-inappwebview实现flutter与Javascript方法调用
【前端精进之路】JS篇:第1期 数据类型总结
进入大厂的我是如何通过面试官的问题,拿到满意的Offer?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Dominic_W/article/details/127972172
