-
JDBC:PreparedStatement 插入BLOB类型的数据,PreparedStatement 批量处理,Connection 事务处理
JDBC:PreparedStatement 插入BLOB类型的数据,PreparedStatement 批量处理,Connection 事务处理

每博一文案
村上春树说: 你要做一个不动声色的大人了,不准情绪化,不准偷偷想念,不准回头看自己, 你要听话,不是所有的鱼都会生活在同一片海里。曾几十起,我们在不经意间练成了,按时清空记忆的本领。 朋友圈设置成三天,可见或者一年只发两三条动态,不是我们退去了,生活的激动,只是习惯了有些心事, 一个人消化,不是没人倾诉,只是不想说。 有时即便说出来了,也未必有人懂,因为不是所有的事,别人都能感同身受,哪些所谓的哀伤忧愁, 也自然显得不再那么重要了,知道了这个世间所有关系,凡觉辛苦,皆是强求,渐渐的便也不会更新自己的朋友圈了。 正如百年孤独中写道: 孤独是一个陪伴,人一生的朋友,是一个既定事实,与其否认与,与其抗争,与其无谓的逃避,不如接受它,拥挤的人群里,让它保护你回家,周六的上午,让他陪你吃早餐。 整理阳光,人行天地间,忽如远客,我们本就是一个人来,一个人走,与其在热闹中无所适从,不如关注自身, 做好自己。 —————— 一禅心灵庙语- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
文章目录
1. PreparedStatement 向数据库中 插入BLOB类型的数据
1.1 MySQL BLOB类型
- MySQL 中,BLOB 是一个二进制大型对象,是一个可以存储大量数据的容器,它能容纳不同大小的数据。
- 在Java向数据库插入 BLOB 类型的数据必须使用 PreparedStatement ,不可以使用 Statement ,因为对于BLOB 类型的数据是无法使用字符串拼接 写的。
- 在 MySQL 中有如下 四种 BLOB 类型: (注意: 他们四个类型之间除了在可存储的最大信息量上不同外,其他的所有都是等同的 )。
类型 大小(单位: 字节) TinyBlob 最大: 255 Blob 最大:65K MediumBlob 最大: 16M LongBlob 最大:4G - 我们在实际的开发使用中根据需要存入的数据大小,来决定不同的 BLOB 类型
- 需要注意的是:如果存储的文件过大,对于数据库中的性能就会有所下降 。
- 如果在指定了相关的 BLOB 类型以后,还报错 xxx too large ,那么我们需要进行一定的配置,在Mysql的安装目录下,找
my.ini文件加上 ,如下的配置参数:max_allowed_packet=16M。因为我们修改了Mysql中的配置文件my.ini的信息,所以我们需要重启 MySQL 服务器,重新读取 my.ini 中的配置信息 。 这一般是在 MySQL5.0以下 才需要的,而MySQL8.0以上 的版本是不需要的。
1.2 PreparedStatement向数据表中插入大数据类型(MediumBlob 图片信息)
这里我们演示 使用PreparedStatement向 customers 数据表中插入大数据类型 。
如下是有关 customers 数据表的 定义的结构类型 。

如下是有关 customers 数据表中的存储的信息

我们向 customers 数据表中插入一条这样的记录
22,李华,lihua@125.com,2022-11-14,图片,插入如下这张图片到该数据表中:
具体代码实现如下:
注意:对于大型的二进制类型的数据文件,我们不可以单纯的使用像基本数据类型一样简单的将数据插入了,我们需要通过使用
I/O流的方式。将二进制大型数据文件插入其中。package Blogs.blogs03; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; public class InsertBlob { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; // 扩大作用域,用于关闭资源 try { // 1.注册数据库驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接注册的驱动中的数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // 3. 获取到操作数据库的对象(预编译sql语句对象) String sql = "insert into customers(id,name,email,birth,photo) values(?,?,?,?,?)"; // 占位符不要加单引号(不然就成字符串) preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅是编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充是在预编译sql语句之后的,不然可能就存在SQL注入的问题了 preparedStatement.setInt(1,22); // jdbc占位符的起始下标是 1, preparedStatement.setString(2,"李华"); preparedStatement.setString(3,"lihua@126.com"); preparedStatement.setString(4,"2022-11-14"); // 通过I/O流导入图片 FileInputStream photo = new FileInputStream(new File("blodTest.png")); preparedStatement.setBlob(5,photo); // 4. 执行sql语句 int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 返回影响数据库的行数 System.out.println(count > 0 ? "成功" : "失败"); // 5. 处理select 查询显示的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭/释放资源 // !=null:连接/使用了资源需要关闭资源,==null:没有连接/使用资源不需要关闭资源 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try{ preparedStatement.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
运行结果:


1.3 PreparedStatement 修改数据表中的Blob类型字段
这里我们演示将 customers 数据表中有关 Blob 类型的信息修改:
我们将
id为 22 的中 name 名为 李华的信息中的刚刚我们插入的图片信息修改为如下这张图片:
具体代码实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; public class InsertBlob { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; // 扩大作用域,用于关闭资源 try { // 1.注册数据库驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接注册的驱动中的数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // 3. 获取到操作数据库的对象(预编译sql语句对象) String sql = "update customers set photo = ? where id = ?"; // 占位符不要加单引号(不然就成字符串) preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅是编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 FileInputStream photo = new FileInputStream(new File("test.jpg")); preparedStatement.setBlob(1,photo); // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充是在预编译sql语句之后的,不然可能就存在SQL注入的问题了 // 通过I/O流导入图片 preparedStatement.setInt(2,22); // jdbc占位符的起始下标是 1, // 4. 执行sql语句 int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 返回影响数据库的行数 System.out.println(count > 0 ? "成功" : "失败"); // 5. 处理select 查询显示的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭/释放资源 // !=null:连接/使用了资源需要关闭资源,==null:没有连接/使用资源不需要关闭资源 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try{ preparedStatement.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70


1.4 查询数据表大数据类型(BLOB)信息并存储到本地文件中去
读取数据表中大数据类型 BLOB 的数据内容。读取到保留到本地文件中,存储起来。
同理对于大数据的二进制数据类型,我们不能像基本数据类型那样,直接定义类型变量存储起来。这样是不行的,我们需要像数据库插入大型二进制数据类型的方式,通过
I/O的方式,查询数据库数据表的信息并获取到其中的BLoB类似的大型二进制。存储到本地文件当中去。这里我们演示: 将数据表 customers : id 为 16 ,name 名为 朱茵 中的 photo 数据类型为
mediumblob的图片信息查询到,并读取存储到本地文件当中存储起来: 如下:
具体代码实现如下:
public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; InputStream io = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; // 扩大作用域,用于关闭资源 try { // 1.注册数据库驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接注册的驱动中的数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // 3. 获取到操作数据库的对象(预编译sql语句对象) String sql = "select id,name,email,birth,photo from customers where id = ?"; // 占位符不要加单引号(不然就成字符串) preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅是编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 填充占位符 preparedStatement.setInt(1,16); // 4 执行sql语句 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); // 5.处理select查询显示的结果集信息 /* 获取查询的结果集的方式一:通过对应字段的下标索引到指定的列中,起始下标是从 1 开始的 if(resultSet.next()) { // next:指向select查询显示的记录(行),并判断其是否含有记录,有true,并移动向下移动指针,没有false int id = resultSet.getInt(1); // jdbc 起始下标是 1 String name = resultSet.getString(2); String email = resultSet.getString(3); Date birth = resultSet.getDate(4); }*/ // 获取查询的结果集的信息的方式二: 通过对应字段名(别名)的方式,锁定对应字段的内容并获取到该字段的信息 if(resultSet.next()) { int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String name = resultSet.getString("name"); String email = resultSet.getString("email"); Date birth = resultSet.getDate("birth"); // 将大型二进制数据类型(BLOB)的信息下载下来,以文件的形式存储到本地文件当中 Blob photo = resultSet.getBlob("photo"); io = photo.getBinaryStream(); fos = new FileOutputStream("zhuyin.jpg"); // 设定存储到本地的文件名 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = io.read(buffer)) != -1) { fos.write(buffer,0,len); } System.out.println(id+"->"+name+"->"+email+"->"+birth); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先释放 // !=null:连接/使用了资源需要关闭资源,==null:没有连接/使用资源不需要关闭资源 if(fos != null) { // 防止null引用报错 try{ fos.close(); } catch(IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行时异常抛出 } } if(io !=null ) { // 防止null引用报错 try{ io.close(); } catch(IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(resultSet != null) { try{ resultSet.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try{ preparedStatement.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107

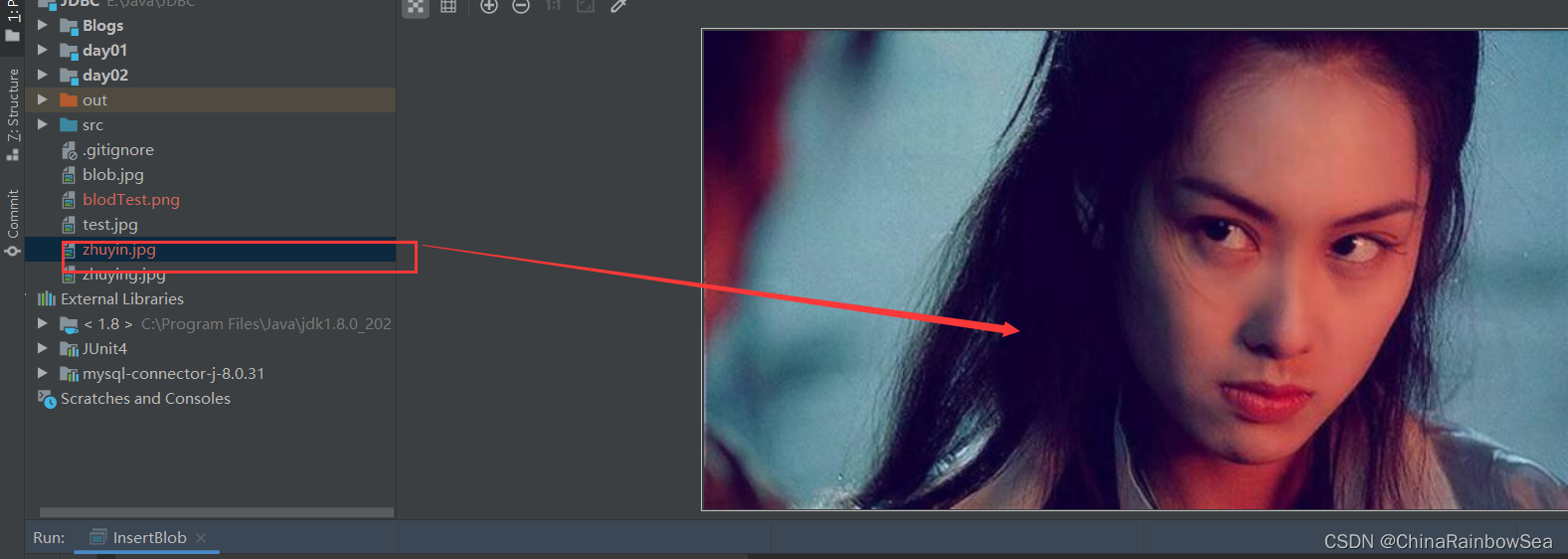
读取下载到本地文件成功。
1.5 删除数据表中BLOB大数据类型的记录
删除数据表中的 BLOB 大数据类型的文件记录和删除基本数据类型的方式是一样的。
演示这里将数据表 customers 中 id 为 22 ,name 为李华的该条记录删除了
public class InsertBlob { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; // 扩大作用域,用于关闭资源 try { // 1.注册数据库驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接注册的驱动中的数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // 3. 获取到操作数据库的对象(预编译sql语句对象) String sql = "delete from customers where id = ?"; // 占位符不要加单引号(不然就成字符串) preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅是编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充是在预编译sql语句之后的,不然可能就存在SQL注入的问题了 preparedStatement.setInt(1,22); // 4. 执行sql语句 int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 返回影响数据库的行数 System.out.println(count > 0 ? "成功" : "失败"); // 5. 处理select 查询显示的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭/释放资源 // !=null:连接/使用了资源需要关闭资源,==null:没有连接/使用资源不需要关闭资源 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try{ preparedStatement.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52


2. PreparedStatement批量处理
当许哟成批插入或者更新记录时,可以采用Java的批量 更新 机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。无论是在 Mysql 还是Java当中的 update 和 delete 操作本身就具有批量操作的效果。 我们这里所说的批量处理指的 批量插入数据信息 的操作。
在JDBC 中的批量处理语句包括下面的三个方法:
- PreparedStatement.addBatch() :将需要执行的SQL语句暂存到缓存区中。
- PreparedStatement.executeBatch() : 执行存放在缓存区中的 SQL语句 。
- PreparedStatement.clearBatch() : 清空缓存区中已经被执行过的SQL语句(就是清空暂存区中的数据信息)。
通常我们会遇到两种批量执行SQL语句的情况:
- 多条SQL语句的批量处理;
- 一个SQL语句的批量传参;
2.1 批量执行SQL语句
准备工作 : 1. 首先创建好一个数据表,用于实验 批量 插入数据信息,如下:
CREATE TABLE tests( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, NAME VARCHAR(25) ); SELECT COUNT(*) FROM tests;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

2.2 方式一: 使用Statement批量处理
方式一: 使用 Statement 接口中的方法,通过 Java 中的循环代码,将 20000(2W) 条记录插入到 我们刚刚创建的 tests 数据表中。 并通过System.currentTimeMillis() 方法,计算出插入完这 2W 条记录所消耗的时间:
具体代码实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; /** * CREATE TABLE tests( * id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, * NAME VARCHAR(25) * ); * * SELECT COUNT(*) * FROM tests; */ public class BatchTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; Statement statement = null; // 扩大作用域,用于关闭资源 try { // 1.注册数据库驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接驱动中的数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // 3. 获取到操作数据库的对象 statement = connection.createStatement(); // 获取到执行sql插入 2W 记录时的时间点 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 4. 执行sql语句 for(int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { String sql = "insert into tests(`name`) values('i')"; int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql); // 执行sql语句 } // 获取到执行完 2W 条记录的时间点: long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 执行完批量2W记录的插入所消耗的时间 = 执行结束 - 执行开始的时间 System.out.println("执行2W记录插入所消耗的时间: "+(end-begin)); // 5.处理select 查询的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭; //!=null 连接/使用的资源释放空间,==null,没有连接使用的资源不用关闭释放空间 if(statement != null) { // 防止null引用 try{ statement.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行时异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77


2.3 方式二:使用PreparedStatement 批量处理
DBServer 会对预编译语句,提供性能优化,因为预编译语句有可能被重复调用,所以语句在被DBServer 的编译器编译后的执行代码,被
缓存下来, 那么下次调用时只要是相同的预编译语句,就不需要编译,只要将参数直接传入编译过的 SQl语句,执行代码中就会得到执行。在Statement 语句中,即便是相同的操作,但因为数据内容不一样,所以整个语句本身不能匹配,没有缓存语句的意义,事实是没有数据库会对普通语句编译后的执行代码缓存。这样每执行一次都要对传入的语句编译一次。
而**PreparedStatement ** 通过预编译的机制,可以做到相同的SQL语句,一次编译,多次执行。
这里我们使用 PreparedStatement 对 tests数据表,控制变量的方式(同样是插入2W条记录),比较方式一使用:Steament,与这里的方式二: 使用 PreparedStatement 的所消耗的时间:
首先执行如下 SQL语句,清空 tests数据表中的数据
TRUNCATE TABLE tests; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM tests;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

具体代码实现如下:
public class BatchTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { // 1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2.连接驱动上的数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // 3.获取到操作数据库的对象(预编译sql对象) String sql = "insert into tests(name) values(?)"; // 占位符不要加上单引号,不然就成字符串了,失去了占位符的作用的 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 计算执行sql语句前的时间点 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 单位毫秒 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充要在预编译sql语句的后面,不然会 sql注入 for(int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { preparedStatement.setString(1,"name_"+i); // 4. 执行sql语句 int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 注意是无参数的,因为上面我们已经预编译过了 } // 执行完2W记录的插入后的时间点: long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 计算执行批量处理2W条记录的所消耗的时间点: System.out.println("2W条记录插入所花费的时间: "+(end-begin)); // 5.处理select 查询显示的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭; //!=null 连接/使用的资源释放空间,==null,没有连接使用的资源不用关闭释放空间 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62


从运行结果上看,与第一种方式插入 2W 条记录,所消耗的时间并没有太大的区别,是因为这里我们没有使用上 PreparedStatement ** 批量处理的相关方法配置。下面的方式三** 就使用了相关的批量处理的方法 Batch 。
2.4 方式三:使用PreparedStatement 配合使用 addBatch() / executeBatch() / clearBatch() 批量处理
我们使用上**PreparedStatement ** 中批量处理的方法:
- PreparedStatement.addBatch() : 将预执行的SQL语句存入到暂存区/缓存区当中
- PreparedStatement.executeBatch() : 执行暂存区/缓存区当中的 SQL语句
- PreparedStatement.clearBatch() : 清空暂存区当中已经执行完的SQL语句的内容
主要的思想: 就是先将一定量的sql语句先存储起来,等到了一定的数量以后在,一次性全部交给数据库Mysql执行,这样大大减少了对磁盘的读取,以及对数据库的操作信息,原本的 2w 条记录,需要和数据库交互 2W 次,现在通过暂存的方式,将预执行的sql语句暂存到一定数量后,再交给数据库执行,现在 2W 条记录就只需要和数据库交互 41 次了,从 2W次节省到 41次,这其中的节省了多少与数据库交互的时间了。速度自然要快了。
注意: mysql服务器默认是关闭批处理的,我们需要通过一个参数,让mysql开启批处理的支持,如在
url的后面添加上?rewriteBatchedStatements=true这个参数就可以了,表示开始mysql的批处理?rewriteBatchedStatements=true- 1



同样我们控制变量,比较方式一,方式二,方式三,批处理插入2W条记录所消耗的时间。
首先我们先清空 tests 数据表中的记录
TRUNCATE TABLE tests; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM tests;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

具体代码实现如下:
public class BatchTest { /** * 批处理方式三: 使用PreparedStatement中的Batch()批处理方法 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { // 1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2.连接驱动上的数据库,在url中添加上启动批处理:?rewriteBatchedStatements=true参数 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6?rewriteBatchedStatements=true","root","MySQL123"); // 3.获取到操作数据库的对象(预编译sql对象) String sql = "insert into tests(name) values(?)"; // 占位符不要加上单引号,不然就成字符串了,失去了占位符的作用的 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 计算执行sql语句前的时间点 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 单位毫秒 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充要在预编译sql语句的后面,不然会 sql注入 for(int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { // 填充占位符; preparedStatement.setString(1,"name_"+i); // 1. “攒” sql:将预执行的sql语句暂存到缓存区当中去 preparedStatement.addBatch(); // 是无参数的 // 暂存区/缓存区当中每存储到 500 条sql语句就执行,执行完并清空暂存区/缓存区 if( i % 500 == 0) { // 2. 执行暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句 preparedStatement.executeBatch(); // 3. 执行完后,清空暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句,方便后面的继续存储sql语句 preparedStatement.clearBatch(); // 清空暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句内容 } // 注意最后一次, 没有被 % 500 尽的sql语句也要执行 if(i == 19999) { preparedStatement.executeBatch(); // 执行暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句 preparedStatement.clearBatch(); // 清空暂存区/缓存区当中的存储的数据 } } // 执行完2W记录的插入后的时间点: long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 计算执行批量处理2W条记录的所消耗的时间点: System.out.println("2W条记录插入所花费的时间: "+(end-begin)); // 5.处理select 查询显示的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭; //!=null 连接/使用的资源释放空间,==null,没有连接使用的资源不用关闭释放空间 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82


从运行结果上看,2W条记录方式三:仅仅只用了 274 毫秒的时间,比方式一,方式二快了 100 倍的速度。
主要的思想: 就是先将一定量的sql语句先存储起来,等到了一定的数量以后在,一次性全部交给数据库Mysql执行,这样大大减少了对磁盘的读取,以及对数据库的操作信息,原本的 2w 条记录,需要和数据库交互 2W 次,现在通过暂存的方式,将预执行的sql语句暂存到一定数量后,再交给数据库执行,现在 2W 条记录就只需要和数据库交互 41 次了,从 2W次节省到 41次,这其中的节省了多少与数据库交互的时间了。速度自然要快了。
2.5 方式四:使用PreparedStatement (加上)+ addBatch() / executeBatch() / clearBatch() +(再加上) 使用Connection 的 setAutoCommit(false) / commit() 进行批量处理
最后的终极批处理最优的方法:在第三种方式的基础上 +(加上)
setAutoCommit(false)(关闭自动提交数据) / commit()手动提交数据在MySQL当中只要执行任意的 DML 语句,则会自动 commit 将修改的数据信息提交给数据库。这是jdbc 默认的事务行为。
主要的优化思路: 我们可以通过
setAutoCommit(false)取消掉自动提交数据,在方式三的基础上,更进一步的减少对数据库的访问的交互行为,等到最后执行完所有的批处理操作,再手动commit()将插入的数据记录提交给数据库。同时也减少了对网络访问的次数,以及占用网络通道。同样先清空 tests 数据表中的数据信息,执行如下SQL语句。
TRUNCATE TABLE tests; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM tests;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

这里我们把插入的记录扩大一点,改为插入 100W条记录,因为太快了,比较不明显,所以我们扩大批处理的数量,看看所消耗的时间的是多少 ???
具体代码实现如下:
public class BatchTest { /** * 批处理方式四: 在方式三的基础上加上: connection.setAutoCommit(false);取消自动提交数据 * connection.commit();手动提交数据 * * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { // 1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2.连接驱动上的数据库,在url中添加上启动批处理:?rewriteBatchedStatements=true参数 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6?rewriteBatchedStatements=true","root","MySQL123"); // 设置取消自动提交数据 connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 3.获取到操作数据库的对象(预编译sql对象) String sql = "insert into tests(name) values(?)"; // 占位符不要加上单引号,不然就成字符串了,失去了占位符的作用的 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 计算执行sql语句前的时间点 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 单位毫秒 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充要在预编译sql语句的后面,不然会 sql注入 for(int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) { // 填充占位符; preparedStatement.setString(1,"name_"+i); // 1. “攒” sql:将预执行的sql语句暂存到缓存区当中去 preparedStatement.addBatch(); // 是无参数的 // 暂存区/缓存区当中每存储到 5000 条sql语句就执行,执行完并清空暂存区/缓存区 if( i % 5000 == 0) { // 2. 执行暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句 preparedStatement.executeBatch(); // 3. 执行完后,清空暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句,方便后面的继续存储sql语句 preparedStatement.clearBatch(); // 清空暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句内容 } // 注意最后一次, 没有被 % 5000 尽的sql语句也要执行 if(i == 999999) { preparedStatement.executeBatch(); // 执行暂存区/缓存区当中的sql语句 preparedStatement.clearBatch(); // 清空暂存区/缓存区当中的存储的数据 } } // 执行完所有的100W记录,手动提交数据 connection.commit(); // 执行完100W记录的插入后的时间点: long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 计算执行批量处理2W条记录的所消耗的时间点: System.out.println("100W条记录插入所花费的时间: "+(end-begin)); // 5.处理select 查询显示的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭; //!=null 连接/使用的资源释放空间,==null,没有连接使用的资源不用关闭释放空间 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92


我们从结果上我们可以看到 100W 条记录的插入,我们仅仅使用了 6秒,够不够快,哈哈六不六。这里就是我们的批处理的最终优化的版本。
3. 数据库事务
3.1 数据库事务介绍
- 事务:一组逻辑操作单元,使数据从一种状态变换到另一种状态。
- 事务处理(事务操作) :为了保证所有的事务都作为一个工作单元来执行,即使出现了故障,都不能改变这种执行方式。当在一个事务中执行多个操作时,要么所有的事务被正常执行被提交(commit) ,那么这些修改就永久地保存下来;要么数据库管理系统将放弃所作的所有修改,这个事务回滚)(rollback) 到最初的状态。
- 为确保数据库中数据的一致性 ,数据的操纵应当是离散的,成组的逻辑单元:当它全部完成时,数据的一致性可以保持,而当这个单元的一部分操作失败,这个事务应全部视为错误,所有从起始点以后的操作应全部回退到开始状态。
3.2 JDBC事务处理
JDBC 中的事务是自动提交的,什么是自动提交 ???,提交了又会怎么样
只要执行了任意一条DML语句,则会自动提交一次,这是JDBL默认的事务行为。而一旦数据提交了,就无法回滚了 。
在实际的业务当中,通常都是 N条DML语句共同联合才能完成的,必须保证他们这些 DML语句在同一个事务中同时成功或者同时失败。
需要注意的是: 当一个连接对象被创建时,默认情况下是自动提交事务的。 每次执行一个SQL语句,如果执行成功,就会向数据库自动提交,而不能回滚了。
哪些操作会导致数据自动提交 ???
- DDL(创建表,删除表,定义表) 操作一旦执行,就会自动提交数据。
- DML(表数据的增删改) 默认情况下,一旦执行,就会自动提交数据
- 默认关闭数据库连接,数据也会自动提交。
JDBC 程序中为了让多个 SQL语句作为一个事务执行:
- 调用 Connection 对象的
setAutoCommit(false)的方法,取消掉自动提交数据的事务操作 - 在所有的SQL语句都执行成功,没有异常中断,就可以使用 Connection 对象中的
commit(); 的方法手动提交数据操作事务 - 如果在执行SQL语句当中出现了异常,发生了中断,则可以调用 Connection 对象中的
rollback()方法进行回滚事务,回滚到最后一次提交事务的开始位置的数据保存的样子,前面的发生异常中断的操作修改的数据无效。 - 注意事项: 若此时数据库中自动提交设置关闭了,是会重复使用的,则需要恢复其自动提交状态
setAutoCommit(true)尤其是在使用数据库连接池技术时,执行 close()方法前,建议恢复自动提交状态。
若此时 Connection 没有被关闭,还可能被重复使用,则需要恢复其自动提交状态 setAutoCommit(true)。尤其是在使用数据库连接池技术时,执行close()方法前,建议恢复自动提交状态。
有关的 setAutoCommit() 方法的文档如下:

下面是有关 commit() 方法的文档 如下:

下面是有关 rollback() 方法的文档如下:

3.2.1 Connection事务处理
案例:用户AA 向用户 BB转账 1000 元
首先我们创建相关的数据表信息,创建一个名为 t_user 的数据表,分别为 name 字段,balance 余额信息。
执行如下代码:
CREATE TABLE t_user ( `name` VARCHAR(25), balance DOUBLE(7,2) ); INSERT INTO t_user(`name`,balance) VALUES('AA',10000), ('BB',10000); SELECT * FROM t_user;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13

首先我们先演示没有进行事务处理,实现用户 AA 向用户 BB 转账的操作,看看存在一个怎样的问题
具体代码实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * 博客事务演示转账操作 */ public class AffairTest { /** * 没有进行事务处理的转账演示操作 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { // 1. 注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接驱动中是数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // AA用户的转账 1000 元,update 减少 1000 元 // 3. 获取操作数据库对象(预编译sql语句的对象) String sqlAA = "update t_user set balance = balance - 1000 where `name` = ?"; // 占位符不要加单引号(不然就成了字符串了, // 失去了占位符的作用了 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sqlAA); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充在预编译 sql语句之后,不然可以存在sql注入的问题 preparedStatement.setString(1,"AA"); // 占位符的填充的起始下标是 1 // 4. 执行sql语句 int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // BB 用户的接受AA用户的转账金额, updata 增加 1000 元 String sqlBB = "update t_user set balance = balance + 1000 where `name` = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sqlBB); // 填充占位符 preparedStatement.setString(1,"BB"); // 执行sql语句 count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println( count > 0 ? "成功" : "失败" ); // 处理查询select 的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先释放空间 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用报错 try{ preparedStatement.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81


这里我们没有模拟网络出现异常的情况,结果上没有问题,但是我们附加上 一个异常
5/0一个简单的算术异常,来模拟网络上发生异常的中断。在运行如下代码,查看结果。首先我们先执行如下sql语句,恢复到起始状态
UPDATE t_user SET balance = 10000 WHERE `name` = 'AA'; UPDATE t_user SET balance = 10000 WHERE `name` = 'BB';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

再执行如下,含有一个 5/0 的算数异常模拟网络中出现的问题:

package Blogs.blogs03; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * 博客事务演示转账操作 */ public class AffairTest { /** * 没有进行事务处理的转账演示操作 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { // 1. 注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接驱动中是数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // AA用户的转账 1000 元,update 减少 1000 元 // 3. 获取操作数据库对象(预编译sql语句的对象) String sqlAA = "update t_user set balance = balance - 1000 where `name` = ?"; // 占位符不要加单引号(不然就成了字符串了, // 失去了占位符的作用了 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sqlAA); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充在预编译 sql语句之后,不然可以存在sql注入的问题 preparedStatement.setString(1,"AA"); // 占位符的填充的起始下标是 1 // 4. 执行sql语句 int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 创建一个算术异常模拟网络中断异常问题 int num = 5 / 0 ; // 分母是不可以为 0 的. // BB 用户的接受AA用户的转账金额, updata 增加 1000 元 String sqlBB = "update t_user set balance = balance + 1000 where `name` = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sqlBB); // 填充占位符 preparedStatement.setString(1,"BB"); // 执行sql语句 count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println( count > 0 ? "成功" : "失败" ); // 处理查询select 的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先释放空间 if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用报错 try{ preparedStatement.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
运行看看,第一步可以看到报出 ”0不可以为分母的异常“中断了程序往后面的执行

但是前面 用户AA 减少 1000 元的操作是,在异常中断之前执行的,所以执行了。发生了结果如下:

这样我们的用户AA的 1000 元钱就被丢失在了网络当中去了。这是不可以的,你想想当你转账的时候,转账了减少了 1000 元,但是你转账的用户却无法接受到你的转账金额,而你少了 1000 元。你受得了吗 ???
所以我们需要进行一定的 事务的处理 防止这种事情的发生。
下面是进行了事务处理的过后的转账
同样我们先执行如下SQL语句代码,恢复到起始金额
UPDATE t_user SET balance = 10000 WHERE `name` = 'AA'; UPDATE t_user SET balance = 10000 WHERE `name` = 'BB';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

具体代码实现如下:
public class AffairTest { /** * 考虑上事务的问题 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { // 1. 注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接驱动中是数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6", "root", "MySQL123"); // 1. 事务处理:取消自动commit 提交数据操作 connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 默认是true 开启自动提交数据信息的 // AA用户的转账 1000 元,update 减少 1000 元 // 3. 获取操作数据库对象(预编译sql语句的对象) String sqlAA = "update t_user set balance = balance - 1000 where `name` = ?"; // 占位符不要加单引号(不然就成了字符串了, // 失去了占位符的作用了 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sqlAA); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充在预编译 sql语句之后,不然可以存在sql注入的问题 preparedStatement.setString(1, "AA"); // 占位符的填充的起始下标是 1 // 4. 执行sql语句 int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); /* // 创建一个算术异常模拟网络中断异常问题 int num = 5 / 0; // 分母是不可以为 0 的.*/ // BB 用户的接受AA用户的转账金额, updata 增加 1000 元 String sqlBB = "update t_user set balance = balance + 1000 where `name` = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sqlBB); // 填充占位符 preparedStatement.setString(1, "BB"); // 执行sql语句 count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(count > 0 ? "成功" : "失败"); // 执行到这,说明没有异常,手动commit 提交数据信息 connection.commit(); // 处理查询select 的结果集 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // 发生了异常,事务回滚,不执行上述中断的转账操作 if (connection != null) { try { connection.rollback(); // 事务回滚 } catch (SQLException e2) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { // 发生了异常,事务回滚,不执行上述中断的转账操作 if (connection != null) { try { connection.rollback(); // 事务回滚 } catch (SQLException e2) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先释放空间 if (preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用报错 try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } // 这里我们不要关闭数据库连接,因为默认关闭连接是会提交commit 数据的 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83



从运行结果上看并没有问题,无论是转账方AA,还是接受方BB都成功交互了。
下面我们开启异常,看看是效果是:



这就是经过了事务处理的效果:这里主要是使用了 ,如下三个操作,进行了一个简单的事务处理。
connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 取消自动commit 提交数据 connection.commit(); // 手动提交数据信息 connection.rollback(); // 当发生异常时,回滚到最近的一次提交commit事务的位置。- 1
- 2
- 3
4. 事务的ACID属性
- 原子性(Atomicity)
原子性:是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。不可以存在中间情况:一半事务发生了,另一半事务没有发生。
- 一致性(Consistency)
事务必须使数据库从一个一致性状态变换到另外一个一致性状态。不可以存在中间情况
- 隔离性(Isolation)
事务的隔离性是指一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰,即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能相互干扰。
- 持久性(Durability)
持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就是永久性的,接下来的其他操作和数据库故障不应该对其有任何影响。
4.1 数据库的并发问题
对于同时运行的多个事务,当这些事务访问数据库中相同的数据时,如果没有采取必要的隔离机制,就会导致各种并发问题:
- 脏读 : 对于两个事务T1,T2 ,T1 读取了已经被 T2 更新但还 没有被提交 的字段。之后,若 T2 进行了回滚操作,那么T1 所读取到的内容就是临时且是无效的,因为所更新的数据已经被回滚了 。简单的说就是:会读取到未
commit给数据库的信息 。这个行为在实际的开发中是要避免的,因为所读取的数据是无效的。 - 不可重复读: 对于两个事务 T1,T2,T1 读取了一个字段的信息,然后 T2更新 了该字段信息内容,之后,T1 再次读取该字段的值。这时候T1 读取到的就是T2 更新之后的信息了。T1两次读取到的同一个字段的信息值是不同的,因为发生了更新。简单的说就是会读取到所及时更新的数据信息 。这个行为在实际开发中是比较常用的,一般是不会去避免它,如我们在网购的时候,一个商品的价格一开始是 100,后面突然就降价变成了 70。
- 幻读 : 对于两个事务 T1,T2,T1 从一个表中读取了一个字段,然后T2 在该表中 插入 了一些新的行。之后,T1 再次读取同一个表时,就会读取到 由T2 新插入的新数据信息,多出几行数据。简单的说就是可以读取到新插入的记录信息 。这个行为在实际开发中也是,经常使用的,一般都不会去避免它。例如:我们在双十一时刻,一个商品原本只剩下 10 件了,突然厂商又加货了,变成了 100件了。
一个事务与其他事务隔离的程度称为 隔离级别 。数据库规定了多种事务的隔离级别,不同隔离级别对应不同的干扰程度,其中隔离级别越高,数据一致性就越好,但并发性就越弱。
4.2 四种隔离级别
MySQL数据库提供的4种事务隔离级别:
隔离级别 描述 READ UNCOMMITTED(读未提交的数据) 允许事务读取未被其他事务提交的变更,脏读,不可重复读,幻读的问题都出现 。(就是上述三种事务并发问题都不解决)。 READ COMMITED (读已提交数据) 只允许事务中读取已经被其他事务提交的变更,可以避免脏读 问题,但不可重复读和幻读的问题依然存在。 REPEATABLE READ(可重复读) 确保事务可以多次从一个字段中读取相同的值,在这个事务持续期间,禁止其他事务对这个字段进行更新,可以避免脏读和不可重复读 的问题,但幻读的问题依然存在。 SERIALIZABLE (串行化) 确保事务可以从一个表中读取相同的行,在这个事务持续期间,禁止其他事务对该表执行插入,更新和删除操作,避免了脏读和不可重复读以及幻读 的问题。所有的事务并发问题都解决了,但性能却变差了。 READ COMMITTED(读已提交) 隔离级别下:一个事务在每次执行 SELECT 操作时都会生成一个 ReadView ,这个ReadView 的存在本身就保证了事务不可以读取到未提交的是事务所更改的记录,即避免了脏读的情况。
REPEATABLE READ(可重复读) 隔离级别下:一个事务只有在第一次执行 SELECT 操作才会生成一个 ReadView ,之后的SELECT 操作都是复用这个 ReadVieW ,这样也就避免了不可重复读和幻读的情况。
Oracle 支持 2 中事务的隔离级别 : READ COMMITED(读已提交数据),SERIALIZABLE(串行化) 。Oracle默认的事务的隔离级别为 : READ COMMITED .
MySQL 支持 4 种事务隔离级别。MySQL 默认的事务隔离基本为 :REPATABLE READ(读未提交数据)。在实际开发中主要使用的是如下2 种隔离级别: READ COMMITED(读已提交数据),REPEATALE READ(可重复读,避免脏读) 。
4.3 在MySql中设置隔离级别
- 每启动一个mysql程序,就会获得一个单独的数据库连接,每个数据库连接都有一个全局变量
@@tx_isolation表示当前的事务的隔离级别. - 查看当前的隔离级别:
SELECT @@tx_isolation;- 1
- 设置当前 mySQL 连接的隔离级别:
set transaction isolation level read committed;- 1
- 设置数据库系统的全局的隔离级别:
set global transaction isolation level read committed;- 1
补充操作:
-
创建mysql数据库用户:
create user tom identified by 'abc123';- 1
-
授予权限
#授予通过网络方式登录的tom用户,对所有库所有表的全部权限,密码设为abc123. grant all privileges on *.* to tom@'%' identified by 'abc123'; #给tom用户使用本地命令行方式,授予atguigudb这个库下的所有表的插删改查的权限。 grant select,insert,delete,update on atguigudb.* to tom@localhost identified by 'abc123';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
5. DAO及相关实现类 (实例演示)
- DAO: Data Access Object 访问数信息的类和接口,包括了对数据的 CRUD(Create,Retrival,Update) ,而不包含任何业务相关的信息,有时也称作:BaseDAO
- 作用: 为了实现功能的模块化,更有利于代码的维护和升级
下面是
user_table数据表的结构和内容信息

下面是一个关于user_table 数据表的一个 DAO使用的体现:
-
User 类 对user_table 数据表的一个 ORM 映射:
一个数据表对应Java中的一个类
一个数据表中的一行记录对应Java中的一个类对象
一行记录中的字段对应Java中的一个类属性
-
BaseDAO abstract(抽象类) 无法new 对象
功能:实现对通用数据表的增,删,改,查,并考虑上事务问题的封装实现
-
UserDAO interface(接口) 无法new 对象
功能:实现专门对 user_table 数据表的增,删,改,查操作的抽象方法的封装
-
UserDaoImpl class 类
public class UserDaoImpl extends BaseDAO implements UserDAO该类实现了 UserDAO的所有抽象方法:通过继承BaseDAO(抽象类)调用其中父类的方法,实现对应UserDAO接口中的抽象方法 -
class UserDaoImplTest 测试其UserDaoImpl class 类的方法功能实现是否存在错误
-
层次结构: 如下所示:

user class类具体代码的实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; public class User { private String user; private String password; private int balance; public User() { // 无参构造器,就算不使用也定义创建,提高代码的复用性 } public User(String user,String password,int balance) { this.user = user; this.password = password; this.balance = balance; } public void setUser(String user) { this.user = user; } public String getUser() { return this.user; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public int getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(int balance) { this.balance = balance; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "user='" + user + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", balance=" + balance + '}'; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
abstract class BaseDAO 抽象类的具体实现代码如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.sql.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 对通用数据表增,删,改,查 考虑上事务问题.进行处理. */ public abstract class BaseDAO { // 抽象方法是不可以 new 的 /** * 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭资源/释放资源, * 注意因为这里我们考虑上了事务的问题,Connection 连接不要关闭: * 因为当数据库连接一旦关闭了,就会自动 commit 提交数据,导致无法回滚信息. * @param resultSet * @param preparedStatement */ public void close(ResultSet resultSet, PreparedStatement preparedStatement) { // !=null 连接/使用了资源需要关闭资源,==null 没有连接/使用的资源是不需要关闭的 if(resultSet != null) { // 防止null引用的问题 try{ resultSet.close(); // 关闭select 查询对象的资源 } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用报错 try { preparedStatement.close(); // 关闭操作数据库对象资源 } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } /** * 通用的查询特殊信息内容,如:count个数 * @param connection * @param sql * @param args * @param* @return public <E> E getValues(Connection connection,String sql,Object...args) { PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意是在预编译sql语句之后 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } // 执行sql语句 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); if (resultSet.next()) { return (E) resultSet.getObject(1); // 直接获取到第一条记录就可以了,因为就只是查看一条记录而已 // 需要强制转换为 E 类型返回 } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 释放资源,最晚使用的最先释放资源 close(resultSet,preparedStatement); } return null; } /** * 通用查询处理操作,处理多条记录的结果集 * @param connection * @param clazz * @param sql * @param args * @paramE */ * @return public <T> List<T> getForList(Connection connection,Class<T> clazz,String sql,Object...args) { PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 预编译sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充在预编译之后,防止sql注入问题 for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,args[i]); } resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); // 执行sql语句 // 获取到select查询的结果集的元数据对象 ResultSetMetaData resultSetMetaData = preparedStatement.getMetaData(); // 通过元数据对象,获取到select 查询显示的一行记录中的所有总列数 int columnCount = resultSetMetaData.getColumnCount(); ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(); // 创建集合对象,存放数据 // 处理select 查询显示的结果集 while(resultSet.next()) { T t = clazz.newInstance(); // 创建orm对象存放select查询读取到的数据信息 // 处理一行的记录 for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { String columnLabel = resultSetMetaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); // 获取到select 查询显示的字段名/别名 Object columnValues = resultSet.getObject(i+1); // 给 t 对象指定的columnLabel属性,赋值为 columnValue,通过反射的方式 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel); // columnLabel列名要与orm映射的类中的属性名一致 field.setAccessible(true); field.set(t,columnValues); // 赋值 } list.add(t); // 将查询select 获取的信息存储到集合链表当中 } return list; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭 close(resultSet,preparedStatement); } return null; } /** * 对通用数据表查询,返回一条记录的封装,考虑上事务的问题(查询没有简单的回滚事务) * @param connection * @param clazz * @param sql * @param args * @paramList */ * @return public <T> T getInstance(Connection connection,Class<T> clazz,String sql,Object...args) { PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅是预编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意在预编译之后填充占位符,防止sql注入问题 for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,args[i]); // 占位符的填充的起始下标是从 1 开始的,而可变参数数组是从 0 开始的 } resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); // 执行sql语句,注意是没有参数的方法,因为上面我们已经预编译过了 // 处理select 查询的返回的结果集 // 1. 获取到select 查询显示的结果集的元数据对象 ResultSetMetaData resultSetMetaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); // 2. 通过获取到的元数据对象获取到select 查询显示的一行记录中(所有列/字段)的个数 int columnCount = resultSetMetaData.getColumnCount(); if(resultSet.next()) { // next指向当前select查询显示的行记录(判断是否有数据true,并向下移动指针,没有数据false,) T t = clazz.newInstance(); // 创建orm映射的数据表的对象的类,用于存储获取到select查询获取到的数据 // 处理select 查询显示的一行数据 for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { // 通过元数据对象获取到指定下标的位置的列名/别名 String columnLabel = resultSetMetaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //该方法可以获取到select查询的别名 // 通过对应字段名/别名/对应下标获取到其字段的内容的值 Object columnValues = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); // 通过 t 对象指定的 columnLabel 名对应orm映射的属性,赋值为 columnValue,通过反射 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel); // 变量名对应select查询显示的字段名/别名,不然无法赋值 field.setAccessible(true); field.set(t,columnValues); // 赋值 } return t; // 返回存储对象 } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先释放空间 close(resultSet,preparedStatement); } return null; } /** * 通用数据表的增删改,进行了事务处理 * @param connection * @param sql * @param args * @return int */ public int update(Connection connection,String sql,Object...args) { /* 可变参数位于参数的最后(不然无法识别区分), 只有一个,可以不传参数,但不要传null,防止null引用报错 可变参数和旧数组类似 * */ PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句,并没有执行sql语句 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充在预编译之后,防止SQL注入问题 for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,args[i]); // 注意jdbc的起始下标是 1,而数组的起始下标是 0 } return preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 执行sql语句,返回影响数据库的行数 } catch (SQLException e) { /*if(connection != null) { try { connection.rollback(); // 发生异常事务回滚 } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } }*/ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭资源 close(null,preparedStatement); } return 0; } }T */ - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
interface UserDAO 接口具体代码实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.util.List; /** * 对user_table表的增删改,查的工具类的封装的接口, * 接口不能实例化 */ public interface UserDAO { /** * 将对对象user 的属性值,添加到数据库中 * @param connection * @param user * @return int */ int insert(Connection connection,User user); /** * 针对指定的user,删除user_table表中的一条记录 * @param connection * @param user * @return int */ int deleteByUser(Connection connection,String user); /** * 针对内存中的users 对象,去修改user_table数据表中指定的记录 * @param connection * @param user * @return int */ int update(Connection connection,User user); /** * 针对指定的user查询得到对应的 User对象 * @param connection * @return User */ User getUser(Connection connection,String user); /** * 查询user_table 数据表中的所有数据信息 * @param connection * @return List*/ List<User> getAll(Connection connection); /** * 查询user_table 数据表中数据的条目数 * @param connection * @return long */ long getCount(Connection connection); /** * 查询user_table 表中的 balance 的最大值 * @param connection * @return int */ int getMaxBalance(Connection connection); /** * 关闭资源 * @param preparedStatement */ void close(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, ResultSet resultSet); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
class UserDaoImpl extends BaseDAO implements UserDAO 具体代码实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.util.List; /** * UserDaoImpl 实现对 user_table数据表的增,删,改,查的操作, * 通过继承 BaseDAO封装的工具类,实现UserDAO接口中的抽象方法 */ public class UserDaoImpl extends BaseDAO implements UserDAO{ /** * * @param connection * @param user * @return int 影响数据库的行数 */ @Override public int insert(Connection connection, User user) { String sql = "insert into user_table(`user`,`password`,balance) values(?,?,?)"; // 占位符不要加单引号不然就成字符串了 return super.update(connection,sql,user.getUser(),user.getPassword(),user.getBalance()); } /** * 根据user字段名的值,删除user_table数据表中的记录/行 * @param connection * @param user 影响数据库的行数 */ @Override public int deleteByUser(Connection connection, String user) { String sql = "delete from user_table where user = ?"; return super.update(connection,sql,user); } /** * 通过User对象中的属性值修改更新数user_table 数据表信息 * @param connection * @param user */ @Override public int update(Connection connection, User user) { String sql = "update user_table set user = ? ,password = ?, balance = ? where user = ?"; return super.update(connection,sql,user.getUser(),user.getPassword(),user.getBalance(),user.getUser()); } /** * 查询指定user_table 数据表中指定的 user的值 * @param connection * @return User */ @Override public User getUser(Connection connection,String user) { String sql = "select user,password,balance from user_table where user = ?"; return super.getInstance(connection,User.class,sql,user); } /** * 查询user_table 数据表中的所有记录构成集合信息返回 * @param connection * @return List*/ @Override public List<User> getAll(Connection connection) { String sql = "select user,password,balance from user_table"; return super.getForList(connection,User.class,sql); } /** * 查询user_table 数据表中记录总个数 * @param connection * @return long */ @Override public long getCount(Connection connection) { String sql = "select count(*) from user_table"; return super.getValues(connection,sql); } /** * 查询user_table表中 balance 的最大值 * @param connection * @return int */ @Override public int getMaxBalance(Connection connection) { String sql = "select max(balance) from user_table"; return super.getValues(connection,sql); } /** * 关闭资源,最晚使用的最先关闭 * @param preparedStatement */ @Override public void close(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, ResultSet resultSet) { super.close(resultSet,preparedStatement); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
class UserDaoImplTest 测试的具体代码实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; /** * 测试对应UserDaoImp的封装的工具类DAO */ public class UserDaoImplTest { private static UserDaoImpl userDao = new UserDaoImpl(); // 注意静态方法访问非静态方法 /** * 封装对 dbtest6 数据库的连接 * @return Connection */ public static Connection userConnection() { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root", "MySQL123"); return connection; } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } /** * 关闭Connection连接的数据库 * @param connection */ private static void closeConnection(Connection connection) { if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } } /** * 测试通过user字段名的值,删除user_table数据表中的记录/行 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 注册驱动,2. 连接驱动 Connection connection = userConnection(); try { // 考虑事务性,取消自动提交数据commit connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 默认是 true int count = userDao.deleteByUser(connection, "1"); // 模拟网络异常情况,事务的回滚操作 // int num = 5 / 0; if(count > 0) { // 执行成功,没有异常,手动commit 提交数据 System.out.println("成功"); if(connection != null) { connection.commit(); } } else { System.out.println("失败,回滚"); if(connection != null) { connection.rollback(); } } } catch (SQLException e) { // 发生异常中断,回滚数据 if(connection != null) { try { connection.rollback(); // 回滚事务 } catch(SQLException e2) { throw new RuntimeException(e2); } } e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭连接 closeConnection(connection); } } /** * 测试插入一条记录信息 * @param args */ public static void main6(String[] args) { // 1. 注册驱动,2. 连接驱动 Connection connection = userConnection(); try { // 考虑事务性,取消自动提交数据commit connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 默认是 true User user = new User("QQ","987",20000); int count = userDao.insert(connection, user); // 模拟网络异常情况,事务的回滚操作 // int num = 5 / 0; if(count > 0) { // 执行成功,没有异常,手动commit 提交数据 System.out.println("成功"); if(connection != null) { connection.commit(); } } else { System.out.println("失败,回滚"); if(connection != null) { connection.rollback(); } } } catch (SQLException e) { // 发生异常中断,回滚数据 if(connection != null) { try { connection.rollback(); // 回滚事务 } catch(SQLException e2) { throw new RuntimeException(e2); } } e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭连接 closeConnection(connection); } } /** * 测试通过User对象中的属性修改更新user_table 数据表信息 * @param args */ public static void main5(String[] args) { // 1. 注册驱动,2. 连接驱动 Connection connection = userConnection(); try { // 考虑事务性,取消自动提交数据commit connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 默认是 true User user = new User("KK","987",25000); int count = userDao.update(connection, user); // 模拟网络异常情况,事务的回滚操作 int num = 5 / 0; if(count > 0) { // 执行成功,没有异常,手动commit 提交数据 System.out.println("成功"); if(connection != null) { connection.commit(); } } else { System.out.println("失败,回滚"); if(connection != null) { connection.rollback(); } } } catch (SQLException e) { // 发生异常中断,回滚数据 if(connection != null) { try { connection.rollback(); // 回滚事务 } catch(SQLException e2) { throw new RuntimeException(e2); } } e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭连接 closeConnection(connection); } } /** * 测试: 查询user_table 数据表中指定的user的值 * @param args */ public static void main4(String[] args) { // 1.注册驱动,2.连接驱动 Connection connection = userConnection(); User user = userDao.getUser(connection, "KK"); System.out.println(user); // 关闭连接 closeConnection(connection); } /** * 测试查询user_table 数据表中所有的记录构成集合 * @param args */ public static void main3(String[] args) { // 1.注册驱动,2.连接驱动 Connection connection = userConnection(); List<User> userList = userDao.getAll(connection); userList.forEach(System.out::println); // 关闭资源连接 closeConnection(connection); } /** * 测试查询user_table数据表中记录总个数 * @param args */ public static void main2(String[] args) { // 1.注册驱动,2.连接驱动 Connection connection = userConnection(); System.out.println(userDao.getCount(connection)); // 关闭连接 closeConnection(connection); } /** * 查询user_table 表中的 balance 的最大值 * @param args */ public static void main1(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; // 1.注册驱动,2.连接驱动 connection = userConnection(); // this.userDao.getMaxBalance(); this无法在静态方法引用,因为this本身就是代表非静态的引用 int maxBalance = userDao.getMaxBalance(connection); System.out.println(maxBalance); // 关闭连接 closeConnection(connection); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
6. 补充Java当中使用模糊查询
在Java当中 模糊查询 该怎么写
下面我们以查询 depts 数据表中以 depts 数据表中字段 departement_name 以 A 开头的值的信息。

下面这种方式是错误的,使用模糊查询
// 3.获取操作数据库的对象(预编译sql语句对象) String sql = "select department_name as name from depts where department_name like '?%'"; // 错误的 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句并不执行 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充,在预编译sql语句之后,填充防止sql注入的问题 preparedStatement.setString(1,"A");- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

占位符(
?) 是不可以被单引号括起来的,一旦括起来了,就变成字符串了,就不再是占位符的意义了,失去了占位符的作用了。方法就无法识别到占位符的存在了,也就无法进行一个占位符填充的操作了正确的方法应该是: 不要将
?占位符用单引号括起来,使用模糊查询的时,通过填充占位符的方式,进行一个格式上的模糊查询如下:// 3.获取操作数据库的对象(预编译sql语句对象) String sql = "select department_name as name from depts where department_name like ?"; // 错误的 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句并不执行 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充,在预编译sql语句之后,填充防止sql注入的问题 preparedStatement.setString(1,"A%");- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

具体代码实现如下:
package Blogs.blogs03; import java.sql.*; public class JdbcLike { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; // 扩大作用域,用于释放资源 try { // 1. 注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // 2. 连接数据库 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest6","root","MySQL123"); // 3.获取操作数据库的对象(预编译sql语句对象) String sql = "select department_name as name from depts where department_name like ?"; // 错误的 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 仅仅只是预编译sql语句并不执行 // 填充占位符,注意占位符的填充,在预编译sql语句之后,填充防止sql注入的问题 preparedStatement.setString(1,"A%"); // 4. 执行sql语句 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); // 没有参数因为前面已经预编译过了 // 5. 处理select 查询显示的结果集 while(resultSet.next()) { // 有数据true,并向下移动指针,没有数据false String name = resultSet.getString("name"); // 获取对应字段名/别名的数据值, // getString 无论从数据库获取到的是什么类型的数据都以字符串的形式赋值到 变量中,同理的还有 getInt,getDouble System.out.println(name); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6. 关闭资源,最晚使用的资源最先释放空间 // !=null 连接/使用的资源释放,==null没有连接使用的资源不用关闭 if(resultSet != null) { // 防止null引用报错 try{ resultSet.close(); // 关闭select 结果集对象 } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(preparedStatement != null) { // 防止null引用 try { preparedStatement.close(); // 关闭操作数据库对象 } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } if(connection != null) { try{ connection.close(); // 关闭连接数据库 } catch(SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); // 将编译异常转换为运行异常抛出 } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70

SELECT department_name AS `name` FROM depts WHERE department_name LIKE 'A%';- 1
- 2
- 3

7. 总结:
- 插入BLOB 这种大型二进制数据内容到数据库中,不可以像基本数据类型一样的方式,
定义变量将值插入到数据库中这是行不通的。需要通过
I/O流的方式将完整的数据信息插入到数据库中。同理对于获取/读取数据库中保存的 BLOB 大型二进制数据内容,也是同样
I/O流的方式将文件的内容存储到本地文件当中-
批量处理数据的四种方式:其中使用PreparedStatement (加上)+ addBatch() / executeBatch() / clearBatch() +(再加上) 使用Connection 的 setAutoCommit(false) / commit() 进行批量处理PreparedStatement.addBatch() : 将预执行的SQL语句存入到暂存区/缓存区当中PreparedStatement.executeBatch() : 执行暂存区/缓存区当中的 SQL语句PreparedStatement.clearBatch() : 清空暂存区当中已经执行完的SQL语句的内容
主要的思路就是通过减少对数据库交互操作是次数,进行一定的数量的分组将交给数据库统一执行。以及减少磁盘的读取访问,以及网络通道的占用的多种方式减少不必要的时间上的消耗。
-
事务处理:自动提交commit 的数据的几种方式:*
- DDL(创建表,删除表,定义表) 操作一旦执行,就会自动提交数据。
- DML(表数据的增删改) 默认情况下,一旦执行,就会自动提交数据
- 默认关闭数据库连接,数据也会自动提交
-
数据库三种并发问题(脏读,不可重复读,幻读),以及解决方式设置隔离级别
-
DAO: Data Access Object 访问数信息的类和接口,包括了对数据的 CRUD(Create,Retrival,Update) ,而不包含任何业务相关的信息,有时也称作:BaseDAO
-
Java的当中模糊查询的注意事项: 不要使用单引号将
?占位符括起来,括起来了就变成字符串了,就失去了占位符的作用的,不再是占位符了,是无法识别到占位符的。
8. 最后:
限于自身水平,其中存在的错误,希望大家给予指教,韩信点兵——多多益善,谢谢大家,后会有期,江湖再见 !!!。有缘人,请留下你来过的证明。

-
相关阅读:
springboot中学成绩管理毕业设计源码100854
R和Python机器学习:广义线性回归glm,样条glm,梯度增强,随机森林和深度学习模型分析
mysql 常见操作指令
vue3中引入全局的less 和配置代理
JavaScript-操作BOM对象
Python_操作记录
面试中关于 SpringCloud 都需要了解哪些基础?
数据治理-元数据度量指标
领导提拔项目经理,看的从来不是努力
MyBatis注解开发
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_61635597/article/details/127880642
