-
SpringBoot ApplicationContext分析
ApplicationContext简述
ApplicationContext代表IOC容器,在SpringIOC容器中读取Bean配置创建Bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化,只有在容器实例化后才可以从IOC容器里获取Bean实例并使用。
Spring IOC容器实现方式
Spring 提供了两种类型的IOC容器实现:
- BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现。
- ApplicationContext:提供了更多的高级特性,是BeanFactory的子接口。
两种方式比较:
- BeanFactory:BeanFactory是Spring框架的基础设施,面向Spring本身:
- ApplicationContext : 面向使用Spring框架的开发者,**几乎所有的应用场合都直接使用ApplicationContext而非底层的BeanFactory。**无论使用何种方式,配置文件是相同的。
ApplicationContext接口梳理
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; if (contextClass == null) { try { switch (this.webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; case REACTIVE: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; default: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); } } return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
根据不同的环境创建不同的ApplicationContext实现
这里看一个基础的实现AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
类图分析
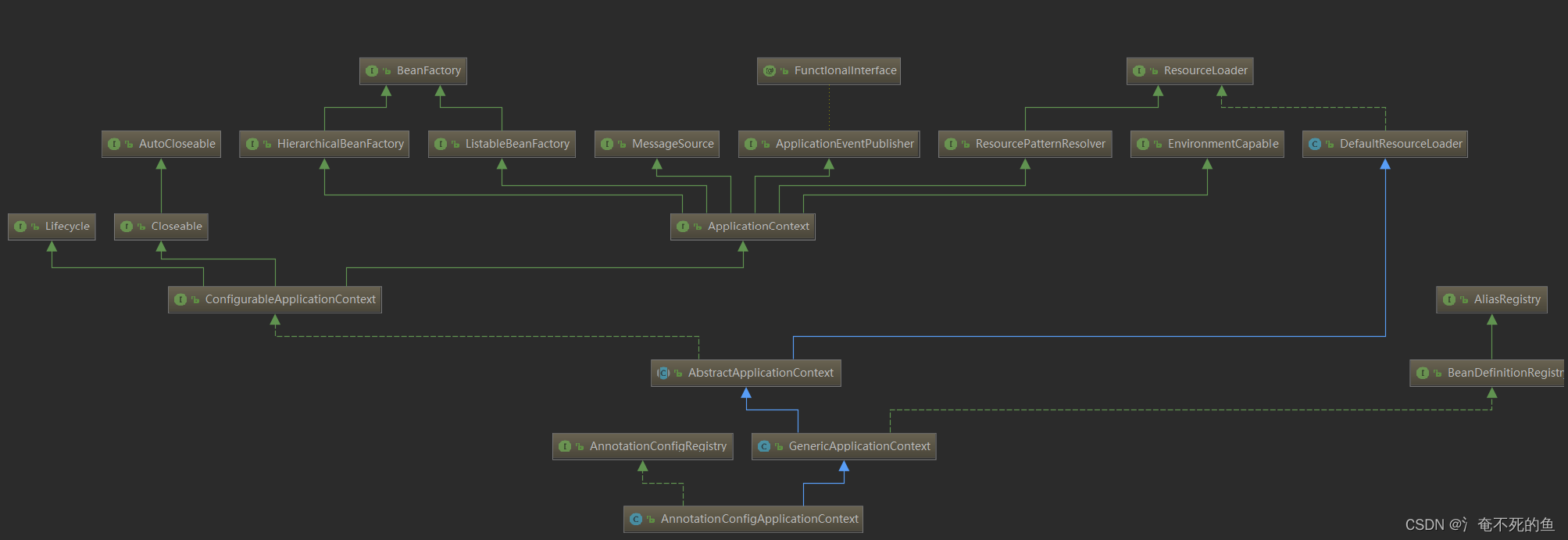
根据类图看,ApplicationContext也是一个bean工厂的实现,继承自ResourceLoader也说明其具备加载文件,扫描bean的能力。ApplicationEventPublisher事件发布的能力
- BeanFactory:Spring 管理 Bean 的顶层接口,ApplicationContext 继承了 BeanFactory 的两个子类:HierarchicalBeanFactory 和 ListableBeanFactory。HierarchicalBeanFactory 是一个具有层级关系的 BeanFactory,拥有属性 parentBeanFactory。 ListableBeanFactory 实现了枚举方法可以列举出当前 BeanFactory 中所有的 bean 对象而不必根据 name 一个一个的获取。
- ApplicationEventPublisher:用于封装事件发布功能的接口,向事件监听器(Listener)发送事件消息。
- ResourceLoader:Spring 加载资源的顶层接口,用于加载资源文件。ApplicationContext 继承 ResourceLoader 的子类 ResourcePatternResolver,该接口是将 location 解析为 Resource 对象的策略接口。
- MessageSource :解析 message 的策略接口,用于支撑国际化等功能。
- EnvironmentCapable :用于获取 Environment 的接口。
下面就这些接口来一一分析
MessageSource
MessageSource 定义了获取 message 的策略方法 getMessage(),在 ApplicationContext 体系中,该方法 AbstractApplicationContext 实现,在 AbstractApplicationContext 中,它持有一个 MessageSource 实例,将 getMessage() 的实现给该实例来实现,如下:
private MessageSource messageSource; public String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException { return this.getMessageSource().getMessage(resolvable, locale); } private MessageSource getMessageSource() throws IllegalStateException { if (this.messageSource == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("MessageSource not initialized - call 'refresh' before accessing messages via the context: " + this); } else { return this.messageSource; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
此外还有一个 initMessageSource()方法,在 refresh()中被调用,用来初始化一些国际化的属性。
protected void initMessageSource() { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.getBeanFactory(); if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean("messageSource")) { this.messageSource = (MessageSource)beanFactory.getBean("messageSource", MessageSource.class); if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) { HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource)this.messageSource; if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) { hms.setParentMessageSource(this.getInternalParentMessageSource()); } } if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]"); } } else { DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource(); dms.setParentMessageSource(this.getInternalParentMessageSource()); this.messageSource = dms; beanFactory.registerSingleton("messageSource", this.messageSource); if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace("No 'messageSource' bean, using [" + this.messageSource + "]"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
什么是国际化?
当我们web项目涉及到国外部署或者国外用户使用时,需要展示不同语言信息,所以就需要国际化支持,下面将讲解Springboot国际化支持操作
例如抛异常,我门希望在不同的环境能够显示不同的报错修改Springboot application.yml配置
spring: messages: basename: i18n/messages #配置国际化资源文件路径- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
创建国际化资源文件

messages.properties不带后缀为默认语言资源
简体中文 messages_zh_CN.propertiesunknown.exception=未知异常,请联系管理员! user.login.notExists={0} 用户不存在!- 1
- 2
- 3
英文 messages_en_US.properties
unknown.exception=Unknown error,Please contact the administrator! user.login.notExists={0} user not exists!- 1
- 2
- 3
messages.properties文件内容就和简体中文文件一致,如果未设置Locale参数,默认就为该文件内容,此文件也可不用
unknown.exception=未知异常,请联系管理员! user.login.notExists={0} 用户不存在!- 1
- 2
- 3
获取错误信息通过messageSource获取
public class MessageUtils { /** * 根据消息键和参数 获取消息 委托给spring messageSource * @param code 消息键 * @param args 参数 * @return 获取国际化翻译值 */ public static String message(String code, Object... args) { MessageSource messageSource = SpringUtils.getBean(MessageSource.class); return messageSource.getMessage(code, args, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
ApplicationEventPublisher
用于封装事件发布功能的接口,向事件监听器(Listener)发送事件消息。
该接口提供了一个 publishEvent() 用于通知在此应用程序中注册的所有的监听器。该方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 中实现。public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { this.publishEvent(event, (ResolvableType)null); } public void publishEvent(Object event) { this.publishEvent(event, (ResolvableType)null); } protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null"); Object applicationEvent; if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) { applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent)event; } else { applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent(this, event); if (eventType == null) { eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent)applicationEvent).getResolvableType(); } } if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) { this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent); } else { this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent((ApplicationEvent)applicationEvent, eventType); } if (this.parent != null) { if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { ((AbstractApplicationContext)this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType); } else { this.parent.publishEvent(event); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
根据不同的事件类型触发对应的监听器,并且会触发父容器的发布发布事件
ResourcePatternResolver
ResourcePatternResolver 接口继承 ResourceLoader 接口,为将 location 解析为 Resource 对象的策略接口。它提供的 getResources() 在 AbstractApplicationContext 中实现,在 AbstractApplicationContext 中它持有一个 ResourcePatternResolver 的实例对象。 其定义如下:
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { return this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(locationPattern); }- 1
- 2
- 3
该方法的具体实现在 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolve
ResourcePatternResolver 在 ResourceLoader 的基础上增加了 getResources(String locationPattern),以支持根据路径匹配模式返回多个 Resource 实例,同时也新增了一种新的协议前缀 classpath*:,该协议前缀由其子类负责实现。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 为 ResourcePatternResolver 最常用的子类,它除了支持 ResourceLoader 和 ResourcePatternResolver 新增的 classpath*: 前缀外,还支持 Ant 风格的路径匹配模式(类似于 **/*.xml)。EnvironmentCapable
提供当前系统环境 Environment 组件。提供了一个 getEnvironment() 用于返回 Environment 实例对象,该方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 实现。
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() { if (this.environment == null) { this.environment = this.createEnvironment(); } return this.environment; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
如果持有的 environment 实例对象为空,则调用 createEnvironment() 创建一个。
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() { return new StandardEnvironment(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
StandardEnvironment 是一个适用于非 WEB 应用的 Environment。
Lifecycle
一个用于管理声明周期的接口。
在 AbstractApplicationContext 中存在一个 LifecycleProcessor 类型的实例对象 lifecycleProcessor,AbstractApplicationContext 中关于 Lifecycle 接口的实现都是委托给 lifecycleProcessor 实现的。如下:public void start() { this.getLifecycleProcessor().start(); this.publishEvent((ApplicationEvent)(new ContextStartedEvent(this))); } public void stop() { this.getLifecycleProcessor().stop(); this.publishEvent((ApplicationEvent)(new ContextStoppedEvent(this))); } public boolean isRunning() { return this.lifecycleProcessor != null && this.lifecycleProcessor.isRunning(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
在启动、停止的时候会分别发布 ContextStartedEvent 和 ContextStoppedEvent 事件。
Closeable
Closeable 接口用于关闭和释放资源,提供了 close() 以释放对象所持有的资源。在 ApplicationContext 体系中由AbstractApplicationContext 实现,用于关闭 ApplicationContext 销毁所有 bean ,此外如果注册有 JVM shutdown hook,同样要将其移除。如下:
public void close() { synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) { this.doClose(); if (this.shutdownHook != null) { try { Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook); } catch (IllegalStateException var4) { } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
调用 doClose() 发布 ContextClosedEvent 事件,销毁所有 bean(单例),关闭 BeanFactory 。如下:
protected void doClose() { if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) { if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Closing " + this); } LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this); try { this.publishEvent((ApplicationEvent)(new ContextClosedEvent(this))); } catch (Throwable var3) { this.logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", var3); } if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) { try { this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose(); } catch (Throwable var2) { this.logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", var2); } } this.destroyBeans(); this.closeBeanFactory(); this.onClose(); if (this.earlyApplicationListeners != null) { this.applicationListeners.clear(); this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners); } this.active.set(false); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
BeanFactory
applicationContext对beanFactory的实现实际上基本上都是通过成员变量来实现的DefaultListableBeanFactory
在applicationContext的实现GenericApplicationContext中
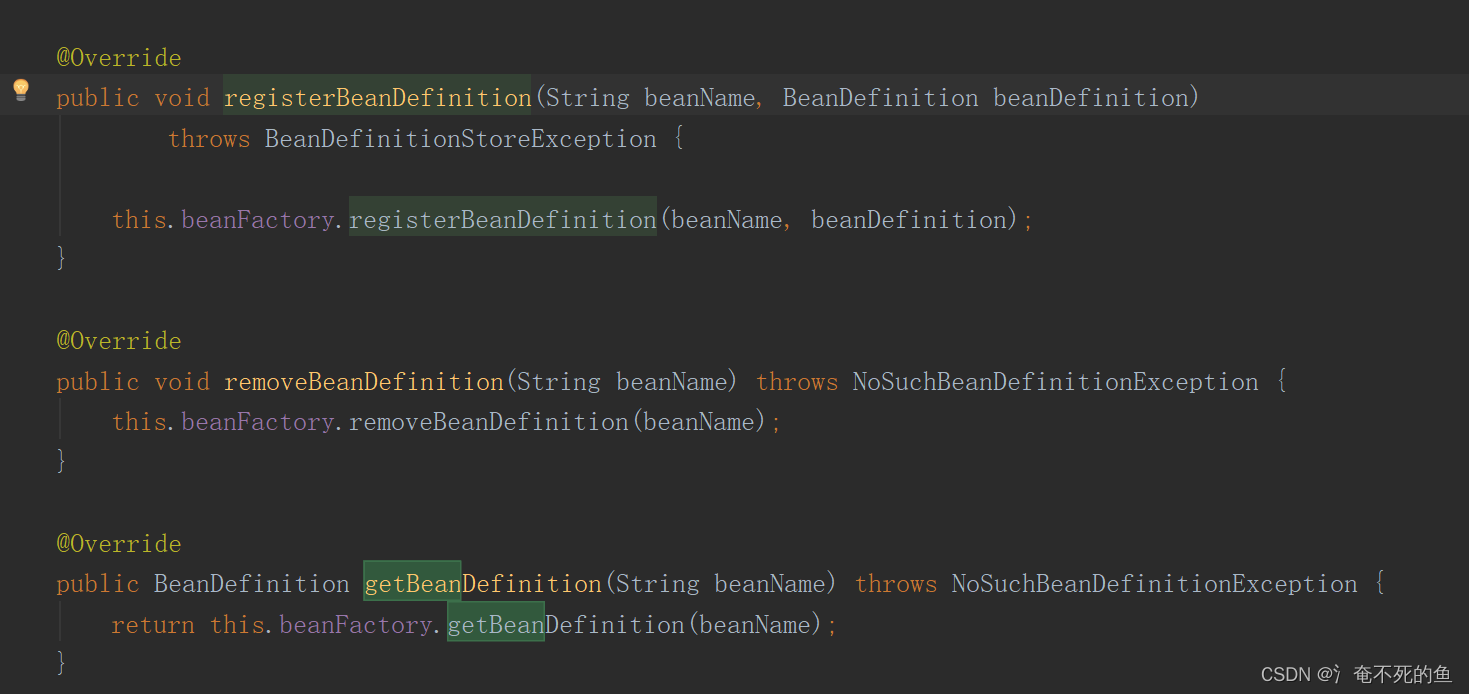
总结 ApplicationContext集大成者
在实现对应接口功能时都是使用对应的实现类去做,而不是自己实现,这点在ApplicationContext上十分常见,继承自功能接口,这样很容易看出ApplicationContext具备的功能,但是自身并不实现,而调用对应的实现类。继承了很多的功能。
ApplicaionContext创建
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; if (contextClass == null) { try { switch (this.webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; case REACTIVE: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; default: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); } } return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
springBoot会创建一个ConfigurableApplicationContext
通过webApplicationType判断创建什么类型的Context,如果是SERVLET那么实例化
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,利用反射调用无参构造器进行实例化。
webApplicationType推断方法static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() { if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) { return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; } for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) { if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { return WebApplicationType.NONE; } } return WebApplicationType.SERVLET; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
根据classPath下是对对应的类,来判断类型
根据webApplicationType加载对应的类
调用其构造函数进行初始化我这里看AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的构造过程
接下来通过构造方法看ApplicationContext的创建的过程AbstractApplicationContext
public AbstractApplicationContext() { this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver(); } protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() { return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 为 ResourcePatternResolver 最常用的子类,它除了支持 ResourceLoader 和 ResourcePatternResolver 新增的 classpath*: 前缀外,还支持 Ant 风格的路径匹配模式(类似于 **/*.xml)。用于扫描类路径下的类
GenericApplicationContext
public GenericApplicationContext() { this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
创建bean工厂,初始化一个空的bean工厂,后续注册获取bean都依靠这个bean工厂进行实现
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() { this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
构造函数中创建了AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader和 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader是一个根据指定类注册BeanDefinnation的功能,同时能根据Condition跳过未达到条件的Bean
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScannery
BeanDeifination扫描类
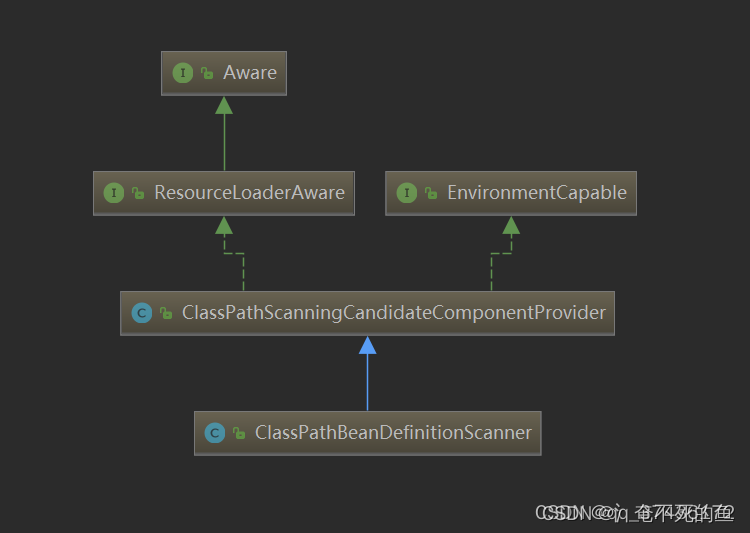
继承自RespourceAware和EnviromentCapable
设置environmentprivate static Environment getOrCreateEnvironment(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null"); if (registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) { return ((EnvironmentCapable) registry).getEnvironment(); } return new StandardEnvironment(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
设置资源加载器resourceLoader通过资源加载,和环境完成bean的扫描
@Override public void setResourceLoader(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { this.resourcePatternResolver = ResourcePatternUtils.getResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader); this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resourceLoader); this.componentsIndex = CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.loadIndex(this.resourcePatternResolver.getClassLoader()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
相关阅读:
fork()写时复制原理
从0开始搭建vue2管理后台基础模板
docker常见命令
零基础HTML入门教程(15)——合并单元格
docker部署excalidraw画图工具(银角大王课堂使用的画图软件搭建)
volatile的用途和说明
栈的运行算法
Leetcode2918. 数组的最小相等和
张量 Tensor
配置Eureka时Status显示的是电脑名而不是localhost及ipAddr显示为本机ip的问题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37436172/article/details/127759107
