-
WPF(七) Prism框架基本特性
参考文档:
- Prism 官方文档 Prism Library
- Prism GitHub 地址 GitHub - PrismLibrary/Prism
- 大佬博客 Prism合集 - 随笔分类 - 痕迹g - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
- 大佬博客 Prism框架系列笔记
一.Prism框架基本特性
1.BindableBase
在之前的文章中,为了能在MVVM框架中为前端View提供逻辑/数据绑定支持,使得后端数据具备通知UI数据变更的能力,我们手动实现了INotifyPropertyChanged 接口并将其封装为 ViewModelBase 基类。
在Prism框架中,Prism扩充了WPF的绑定通知功能。提供了已经实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口并封装好的基类 BindableBase 。并使用 CallerMemberName 特性自动获取属性名称,解决了属性改变事件调用繁琐的问题,同时在方法内部还是对相等值进行了过滤等操作,其源码如下:namespace Prism.Mvvm { ////// Implementation of to simplify models. /// public abstract class BindableBase : INotifyPropertyChanged { /// /// Occurs when a property value changes. /// public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; /// /// Checks if a property already matches a desired value. Sets the property and /// notifies listeners only when necessary. /// /// Type of the property. /// Reference to a property with both getter and setter. /// Desired value for the property. /// Name of the property used to notify listeners. This /// value is optional and can be provided automatically when invoked from compilers that /// support CallerMemberName. ///True if the value was changed, false if the existing value matched the /// desired value. protected virtual bool SetProperty<T>(ref T storage, T value, [CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null) { if (EqualityComparer<T>.Default.Equals(storage, value)) return false; storage = value; RaisePropertyChanged(propertyName); return true; } ////// Checks if a property already matches a desired value. Sets the property and /// notifies listeners only when necessary. /// /// Type of the property. /// Reference to a property with both getter and setter. /// Desired value for the property. /// Name of the property used to notify listeners. This /// value is optional and can be provided automatically when invoked from compilers that /// support CallerMemberName. /// Action that is called after the property value has been changed. ///True if the value was changed, false if the existing value matched the /// desired value. protected virtual bool SetProperty<T>(ref T storage, T value, Action onChanged, [CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null) { if (EqualityComparer<T>.Default.Equals(storage, value)) return false; storage = value; onChanged?.Invoke(); RaisePropertyChanged(propertyName); return true; } ////// Raises this object's PropertyChanged event. /// /// Name of the property used to notify listeners. This /// value is optional and can be provided automatically when invoked from compilers /// that support . protected void RaisePropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null) { OnPropertyChanged(new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } /// /// Raises this object's PropertyChanged event. /// /// The PropertyChangedEventArgs protected virtual void OnPropertyChanged(PropertyChangedEventArgs args) { PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, args); } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
在需要对数据做绑定通知时,我们只需要直接继承该 BindableBase 类即可。其属性更新通知方式有如下两种:
- SetProperty
private string _fieldName; public string PropertyName { get { return _fieldName; } set { SetProperty(ref _fieldName, value); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- RaisePropertyChanged
private string _fieldName; public string PropertyName { get { return _fieldName; } set { if(_fileName != value) { _fieldName = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
2.DelegateCommand
在之前的文章中,为了能在MVVM框架中实现前后端的逻辑分离,我们手动实现了 ICommand 接口并将自定义命令封装为 RelayCommand< T > ,用于在前后端之间传递逻辑/行为。在Prism框架中,Prism提供了已经实现 ICommand 接口并封装好的命令基类 DelegateCommandBase 及其子类 DelegateCommand,其不仅包含了我们手动实现命令类的所有基本功能,还拓展出了一些新的特性,大大简化了命令调用方式。
2.1 DelegateCommand 源码
DelegateCommand 这个类中的其它的定义和我们之前常规封装的ICommand的实现没有什么太大区别,重点是这个里面增加了ObservesProperty和ObservesCanExecute这两个带Expression参数的方法,这两个方法其内部都调用了一个叫做ObservesPropertyInternal的方法。那么这两个方法有什么作用呢?在之前的文章 WPF(六) Command 命令模型源码分析 中,我们分析了ICommand的命令模型:自定义命令要想实现命令状态的实时刷新,就必须手动触发 CanExecuteChanged 事件或者使用CommandManager代理的方式;而在 DelegateCommand 中,则使用了一种更加灵活的方式,通过封装 ObservesProperty 和 ObservesCanExecute 两个方法来监控目标属性值的变化,自动触发 CanExecuteChanged 事件,刷新命令状态。
//1.不带泛型的 DelegateCommand namespace Prism.Commands { ////// An whose delegates do not take any parameters for and . /// /// /// public class DelegateCommand : DelegateCommandBase { //命令所需执行的委托 Action _executeMethod; //判断命令是否可用所执行的委托 Func<bool> _canExecuteMethod; /// /// Creates a new instance of with the to invoke on execution. /// /// The to invoke when is called. public DelegateCommand(Action executeMethod) : this(executeMethod, () => true) { } /// /// Creates a new instance of with the to invoke on execution /// and a to query for determining if the command can execute. /// /// The to invoke when is called. /// The to invoke when is called public DelegateCommand(Action executeMethod, Func<bool> canExecuteMethod) : base() { if (executeMethod == null || canExecuteMethod == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(executeMethod), Resources.DelegateCommandDelegatesCannotBeNull); _executeMethod = executeMethod; _canExecuteMethod = canExecuteMethod; } /// /// Executes the command. /// public void Execute() { _executeMethod(); } /// /// Determines if the command can be executed. /// /// Returns public bool CanExecute() { return _canExecuteMethod(); } ///if the command can execute,otherwise returns . /// Handle the internal invocation of /// /// Command Parameter protected override void Execute(object parameter) { Execute(); } /// /// Handle the internal invocation of /// /// /// if the Command Can Execute, otherwise /// Observes a property that implements INotifyPropertyChanged, and automatically calls DelegateCommandBase.RaiseCanExecuteChanged on property changed notifications. /// /// The object type containing the property specified in the expression. /// The property expression. Example: ObservesProperty(() => PropertyName). ///The current instance of DelegateCommand public DelegateCommand ObservesProperty<T>(Expression<Func<T>> propertyExpression) { ObservesPropertyInternal(propertyExpression); return this; } ////// Observes a property that is used to determine if this command can execute, and if it implements INotifyPropertyChanged it will automatically call DelegateCommandBase.RaiseCanExecuteChanged on property changed notifications. /// /// The property expression. Example: ObservesCanExecute(() => PropertyName). /// The current instance of DelegateCommand public DelegateCommand ObservesCanExecute(Expression<Func<bool>> canExecuteExpression) { _canExecuteMethod = canExecuteExpression.Compile(); ObservesPropertyInternal(canExecuteExpression); return this; } } } //2.带泛型的 DelegateCommand namespace Prism.Commands { public class DelegateCommand<T> : DelegateCommandBase { public DelegateCommand(Action<T> executeMethod); public DelegateCommand(Action<T> executeMethod, Func<T, bool> canExecuteMethod); public bool CanExecute(T parameter); public void Execute(T parameter); public DelegateCommand<T> ObservesCanExecute(Expression<Func<bool>> canExecuteExpression); public DelegateCommand<T> ObservesProperty<TType>(Expression<Func<TType>> propertyExpression); protected override bool CanExecute(object parameter); protected override void Execute(object parameter); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
ObservesPropertyInternal 这个方法的内部会将当前的Expression参数传入一个类型为HashSet的_observedPropertiesExpressions的局部变量里面,如果当前集合中存在该变量就抛出异常避免重复添加,如果没有添加过就添加到当前集合中进行维护。接着,添加到集合中以后又调用了一个新的的方法,这个PropertyObserver.Observes方法会将当前的DelegateCommandBase 中的RaiseCanExecuteChanged方法作为参数传入到PropertyObserver类中的Observes方法中去,顾名思义PropertyObserver就是一个用来监控Propery属性变化的类。
通过Expression,内部调用PropertyObserver.Observes()方法并将RaiseCanExecuteChaned方法作为委托传入,在PropertyObserver将Expression保存在一个链表,并每个节点都订阅OnPropertyChanged事件。这样在属性Expression发生变化的时候就能够调用当前的RaiseCanExecuteChanged委托,从而最终触发命令的CanExecuteChanged事件从而达到刷新命令状态的目的。
namespace Prism.Commands { ////// An whose delegates can be attached for and . /// public abstract class DelegateCommandBase : ICommand, IActiveAware { private SynchronizationContext _synchronizationContext; private readonly HashSet<string> _observedPropertiesExpressions = new HashSet<string>(); /// /// Creates a new instance of a , specifying both the execute action and the can execute function. /// protected DelegateCommandBase() { _synchronizationContext = SynchronizationContext.Current; } /// /// Occurs when changes occur that affect whether or not the command should execute. /// public virtual event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged; /// /// Raises so every /// command invoker can requery . /// protected virtual void OnCanExecuteChanged() { var handler = CanExecuteChanged; if (handler != null) { if (_synchronizationContext != null && _synchronizationContext != SynchronizationContext.Current) _synchronizationContext.Post((o) => handler.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty), null); else handler.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty); } } /// /// Raises so every command invoker /// can requery to check if the command can execute. /// /// Note that this will trigger the execution of [SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Design", "CA1030:UseEventsWhereAppropriate")] public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged() { OnCanExecuteChanged(); } ///once for each invoker. /// Observes a property that implements INotifyPropertyChanged, and automatically calls DelegateCommandBase.RaiseCanExecuteChanged on property changed notifications. /// /// The object type containing the property specified in the expression. /// The property expression. Example: ObservesProperty(() => PropertyName). protected internal void ObservesPropertyInternal<T>(Expression<Func<T>> propertyExpression) { if (_observedPropertiesExpressions.Contains(propertyExpression.ToString())) { throw new ArgumentException($"{propertyExpression.ToString()} is already being observed.", nameof(propertyExpression)); } else { _observedPropertiesExpressions.Add(propertyExpression.ToString()); PropertyObserver.Observes(propertyExpression, RaiseCanExecuteChanged); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
2.2 DelegateCommand 使用
(1)基本使用
namespace CommandTest.ViewModels { public class MainViewModel : BindableBase { //1.委托不带参数 public DelegateCommand InitializeCommand { get; private set; } //2.委托带参数(泛型DelegateCommand) public DelegateCommand<Object> InitializeParamsCommand { get; private set; } //3.构造函数-初始化 public MainViewModel() { InitializeCommand = new DelegateCommand(Execute1); InitializeParamsCommand = new DelegateCommand<Object>(Execute2); } //4.委托方法 private void Execute1() { //do something... ... } private void Execute2(Object obj) { //do something... ... } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
(2)可执行检查
- RaiseCanExecuteChanged 手动刷新
在属性值改变时,手动通过RaiseCanExecuteChanged的调用触发 CanExecuteChanged 事件,更新CanExecute状态
namespace CommandTest.ViewModels { public class MainViewModel : BindableBase { //1.DelegateCommand属性声明 public DelegateCommand InitializeCommand { get; private set; } //2.构造函数-初始化 public MainViewModel() { InitializeCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoExecute,CanExecute); } //3.命令委托 private void DoSave() { //执行逻辑 } private bool CanExecute() { //能否执行的逻辑 return Param < 200; } private int _param = 100; public int Param { get{ return _param;} set { SetProperty(ref _param, value); InitializeCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();//手动触发 } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- ObservesProperty 属性监听
ObservesProperty 用于监听目标属性值的变化。当监听目标属性值发生变化时,就会自动进行状态检查,执行 RaiseCanExecuteChanged 方法,触发 CanExecuteChanged 事件,执行ICommand的 CanExecute 委托,更新CanExecute状态。ObservesProperty 也支持多条件检查。
namespace CommandTest.ViewModels { public class MainViewModel : BindableBase { //1.DelegateCommand属性声明 public DelegateCommand InitializeCommand { get; private set; } //2.构造函数-初始化 public MainViewModel() { //ObservesProperty 监听Param1和Param2 InitializeCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoExecute,CanExecute) .ObservesProperty(()=>Param1) .ObservesProperty(()=>Param2); } //3.命令委托 private void DoSave() { //执行逻辑 } private bool CanExecute() { //能否执行的逻辑(多条件) return Param1 < 200 && Param2 != String.Empty; } //4.属性值声明 private int _param1; public int Param1 { get{ return _param1;} set { SetProperty(ref _param1, value); } } private string _param2; public string Param2 { get{ return _param2;} set { SetProperty(ref _param2, value); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- ObservesCanExecute 监听
ObservesCanExecute 也是用于监听目标属性。不过与 ObservesProperty 不同的是,ObservesCanExecute 无需指定 CheckExecute 委托检查方法,而直接将命令的可用状态与目标属性值绑定,若目标属性值变为true则命令可用否则将不可用,且 ObservesCanExecute 绑定目标属性必须为 bool 类型。
namespace CommandTest.ViewModels { public class MainViewModel : BindableBase { //1.DelegateCommand属性声明 public DelegateCommand InitializeCommand { get; private set; } //2.构造函数-初始化 public MainViewModel() { InitializeCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoExecute) .ObservesCanExecute(() => DoCondition); } //3.命令委托 private void DoExecute() { //执行逻辑 } //4.属性值声明 public bool DoCondition { get{ return Age < 200 && string.IsNullOrEmpty(Name);} } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
3.容器与依赖注入
类似于Spring,Prism框架的核心组件也是容器与依赖注入。即通过一个容器去管理整个框架中所有类的对象及其生命周期,并且在引用的时候只需要通过注入接口框架就能够自动根据接口类型找到特定的实例,这样就会帮我们省掉大量创建对象的new操作,将程序不稳定的地方统一隔离在一个地方管理,而且在在软件设计过程中通过IOC容器实现依赖注入能够最大程度上实现最终的控制反转,从而保证软件设计的时候巨大灵活性和扩展性。PrismApplication 部分源码如下:
namespace Prism { ////// Base application class that provides a basic initialization sequence /// /// /// This class must be overridden to provide application specific configuration. /// public abstract class PrismApplicationBase : Application { IContainerExtension _containerExtension; IModuleCatalog _moduleCatalog; /// /// The dependency injection container used to resolve objects /// public IContainerProvider Container => _containerExtension; /// /// Raises the System.Windows.Application.Startup event. /// /// A System.Windows.StartupEventArgs that contains the event data. protected override void OnStartup(StartupEventArgs e) { base.OnStartup(e); InitializeInternal(); } /// /// Run the initialization process. /// void InitializeInternal() { ConfigureViewModelLocator(); Initialize(); OnInitialized(); } /// /// Runs the initialization sequence to configure the Prism application. /// protected virtual void Initialize() { ContainerLocator.SetContainerExtension(CreateContainerExtension); //获取并初始化全局静态的容器 _containerExtension = ContainerLocator.Current; //初始化模块 _moduleCatalog = CreateModuleCatalog(); //注册初始化服务 RegisterRequiredTypes(_containerExtension); RegisterTypes(_containerExtension); _containerExtension.FinalizeExtension(); ConfigureModuleCatalog(_moduleCatalog); var regionAdapterMappings = _containerExtension.Resolve<RegionAdapterMappings>(); ConfigureRegionAdapterMappings(regionAdapterMappings); var defaultRegionBehaviors = _containerExtension.Resolve<IRegionBehaviorFactory>(); ConfigureDefaultRegionBehaviors(defaultRegionBehaviors); RegisterFrameworkExceptionTypes(); var shell = CreateShell(); if (shell != null) { MvvmHelpers.AutowireViewModel(shell); RegionManager.SetRegionManager(shell, _containerExtension.Resolve<IRegionManager>()); RegionManager.UpdateRegions(); InitializeShell(shell); } InitializeModules(); } //... ... } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
3.1 接口分析
在Prism.Core中定义了Prism IOC容器相关的一些基础接口,他们的类图结构如下:
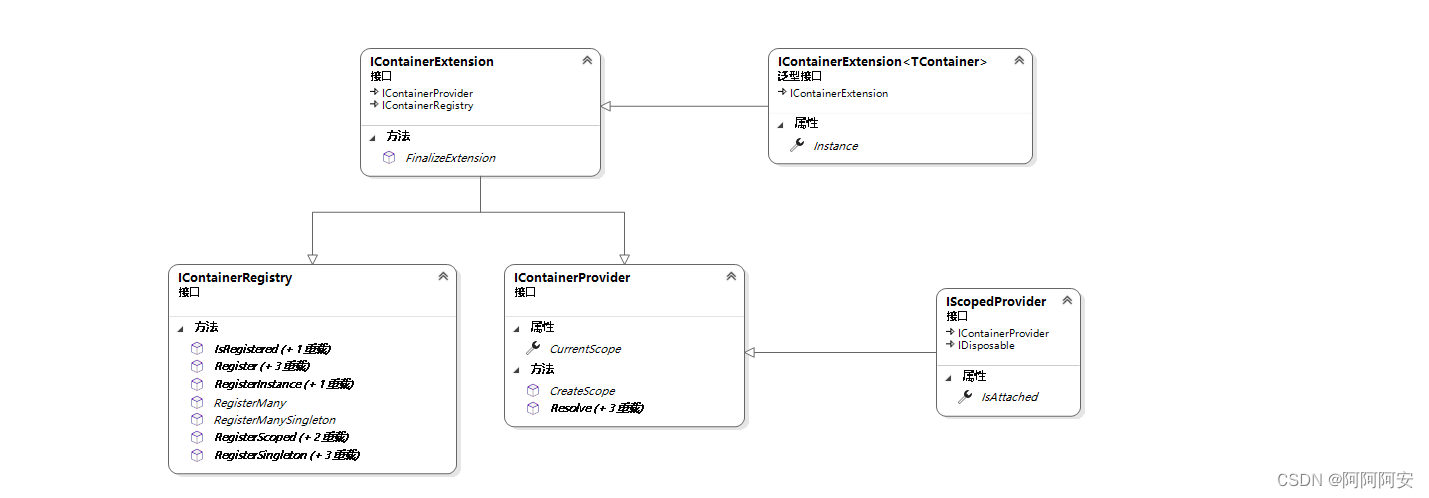
- IContainerRegistry接口 :这个接口的作用主要是将一系列的类型和对应的实体注入到容器里面(包括不同的生命周期类型),另外这个接口中还定义了IsRegistered方法用来判断某个对象是否已经进行过注册。
- IContainerProvider接口 :这个接口和IContainerRegistry接口的作用刚好相反,主要是通过类型或名称从容器中获取之前注册/管理的对象。
- ContainerLocator :ContainerLocator 是在Prism.Core中定义的一个静态类,用于定义/维护一个全局唯一的IContainerExtension对象。
- IContainerExtension :这个接口同时继承IContainerRegistry和IContainerProvider的两个接口,表示继承的对象同时拥有注册类型对象和解析类型对象的两种能力,另外还定义了一个FinalizeExtension方法用于做一些容器终结的操作。
3.2 自定义服务注册与注入
对于我们自定义的服务/组件,我们可以在 App.xaml.cs 中重写所继承 PrismApplicationBase 类的 RegisterTypes 方法,并通过 IContainerRegistry.Register 系列方法将组件注册到容器中。对于不同的生命周期类型,IContainerRegistry 提供了多种不同的基本注册方式即 Transient Registering 、 Singleton Registering 等
(1)Transient Registering
Transient Registering 每次注册都会创建一个新的实例,即多例模式。其使用方式如下:
namespace PrismDemo { ////// App.xaml 的交互逻辑 /// public partial class App : PrismApplication { protected override Window CreateShell() { return Container.Resolve<HomeView>(); } protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry) { // Where it will be appropriate to use FooService as a concrete type //具体类型注入 containerRegistry.Register<FooService>(); //接口类型注入(IBarService接口 -> 实现子类 BarService) containerRegistry.Register<IBarService, BarService>(); } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
(2)Singleton Registering
Singleton Registering 在整个应用程序生命周期以内只创建一个实例,即单例模式,只有在用到的时候该实例才会被创建出来。其使用方式如下:
namespace PrismDemo { ////// App.xaml 的交互逻辑 /// public partial class App : PrismApplication { protected override Window CreateShell() { return Container.Resolve<HomeView>(); } protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry) { // Where it will be appropriate to use FooService as a concrete type //具体类型注入 containerRegistry.RegisterSingleton<FooService>(); //接口类型注入(IBarService接口 -> 实现子类 BarService) containerRegistry.RegisterSingleton<IBarService, BarService>(); } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
(3)注入与使用
有了上述这些内容,我们就可以在窗体里通过构造函数直接注入对象即可,注入方式如下:
- 构造函数类型注入
private readonly MD5Provider _provider1; private readonly MD5Provider _provider2; public IndexViewModel(MD5Provider provider1, MD5Provider provider2) { _provider1 = provider1; _provider2 = provider2; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 容器解析对象注入
private readonly MD5Provider _provider1; private readonly MD5Provider _provider2; private readonly IContainerExtension _container; public IndexViewModel(IContainerExtension container) { _container = container; _provider1 = container.Resolve<MD5Provider>(); _provider2 = container.Resolve<MD5Provider>(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.ViewModelLocator
4.1 传统View-ViewModel关联
在经典的WPF中,我们通常使用DataContext来为View指定其绑定的ViewModel,从而建立数据连接,常见的指定方式有如下两种。这种指定方式虽然可以建立View-ViewModel关系,但是这种方式把View与ViewModel的关系编码方式固定了下来,在一定程度上提高了代码的耦合性,使得后期维护变得困难,打破了我们的开发原则。
- XAML配置
<Window x:Class="WPF_MVVM.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WPF_MVVM" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" xmlns:vm="clr-namespace:WPF_MVVM.ViewModel" Title="MainWindow" Width="300" Height="150" DataContext="{x:Static vm:MainWindowViewModel.Instance}" mc:Ignorable="d"> Window>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 代码配置
namespace WPF_Demo { public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); //声明本Window的上下文DataContext this.DataContext = null; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
4.2 Prism ViewModelLocator 关联
ViewModelLocator 是 Prism 框架提供的一种“视图模型定位器”。ViewModelLocator 可以根据我们指定的标准命名关联规则,在项目程序初始化时自动通过DataContext建立对应的View-ViewModel关系,而不需要我们手动指定。这样做一方面减少了我们代码开发的复杂度;另一方面不再显式的去绑定DataContext,从而降低了代码耦合。其使用步骤如下:
- 在View中,声明允许当前View自动装配ViewModel,即设置 ViewModelLocator.AutoWireViewModel = True
<Window x:Class="Demo.Views.MainWindow" ... xmlns:prism="http://prismlibrary.com/" prism:ViewModelLocator.AutoWireViewModel="True">- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 按照命名关联规则,放置和命名我们的View和ViewModel
在Prism初始化时,当 View 的AutoWireViewModel 设置为 True 时,ViewModelLocationProvider 类会自动调用 AutoWireViewModelChanged 方法,按照我们制定的规则去搜索和解析其对应的ViewModel,并建立DataContext关联关系。其解析顺序如下:
- 先解析用户通过 ViewModelLocationProvider.Register 方法手动注册的 ViewModel
- 如果第一步解析失败,则继续通过基本约定规则(默认规则、自定义规则)进行搜索和解析ViewModel
(1)默认命名规则
Prism ViewModelLocator 的默认命名规则如下:
-
View 和 ViewModel 位于同一个程序集中
-
View 放置在对应 .Views 子命名空间中,ViewModel 放置在对应 .ViewModels 子命名空间中(比如a.b.Views 对应 a.b.ViewModels),注意上级空间也必须一致
-
ViewModel 的类名称与 View 的名称必须对应,并且以 “ViewModel” 结尾(比如 ViewA -> ViewAViewModel,MainView -> MainViewModel)
注意: a.Views+a.ViewModels 与 b.c.Views+b.c.ViewModels是可以共存不冲突的,只要能在对应程序集包下找到对应命名的ViewModel即可,每个View视图在初始化时会根据默认命名规则去解析对应包下的ViewModel。
(2)自定义命名规则
如果不想遵循 ViewModelLocator 默认的命名约定,则我们可以自定义命名约定覆盖,ViewModelLocator 会根据自定义的约定将 View 关联到 ViewModel。
ViewModelLocationProvider类提供了一个静态方法SetDefaultViewTypeToViewModelTypeResolver,可以用来设置自己的命名关联规则。我们需要在App.xaml.cs中覆盖所继承 PrismApplication 类中的ConfigureViewModelLocator方法,然后在ViewModelLocationProvider.SetDefaultViewTypeToViewModelTypeResolver方法中提供自定义命名约定逻辑。protected override void ConfigureViewModelLocator() { base.ConfigureViewModelLocator(); //自定义命名规则 ViewModelLocationProvider.SetDefaultViewTypeToViewModelTypeResolver((viewType) => { var viewName = viewType.FullName.Replace(".Views.", ".CustomNamespace."); //视图View全限定名称:viewType.FullName = PrismDemo.Views.HomePage //自定义Model存放前缀:Replace = PrismDemo.CustomNamespace.HomePage var viewAssemblyName = viewType.GetTypeInfo().Assembly.FullName; //程序集名称:PrismDemo, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null var viewModelName = $"{viewName}ViewModel, {viewAssemblyName}"; //自定义Model映射:PrismDemo.CustomNamespace.HomePageViewModel, PrismDemo, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null return Type.GetType(viewModelName); //返回当前视图View的映射关系 }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
在每个View页初始化时,若当前View设置了
prism:ViewModelLocator.AutoWireViewModel="True",则会对每个初始化的View调用重写的ConfigureViewModelLocator方法,根据上述我们自定义的映射规则去解析对应的ViewModel位置并做关联。(3)自定义注册
如果在项目开发中我们大部分情况下是遵循
ViewModelLocator默认的命名约定,但有少数情况存在一些不符合默认约定的View-ViewModel关联。这时我们可以使用ViewModelLocationProvider.Register方法直接将ViewModel的映射注册到特定视图中。此时Prism初始化时会先解析用户通过 ViewModelLocationProvider.Register 方法手动注册的 ViewModel,找不到再去默认规则下进行解析。手动指定 View-ViewModel 映射的方式更快,效率更高。protected override void ConfigureViewModelLocator() { base.ConfigureViewModelLocator(); // Type / Type ViewModelLocationProvider.Register(typeof(MainWindow).ToString(), typeof(CustomViewModel)); // Type / Factory ViewModelLocationProvider.Register(typeof(MainWindow).ToString(), () => Container.Resolve<CustomViewModel>()); // 通用工厂 ViewModelLocationProvider.Register<MainWindow>(() => Container.Resolve<CustomViewModel>()); // 通用类型 ViewModelLocationProvider.Register<MainWindow, CustomViewModel>(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
-
相关阅读:
焦炉加热系统简述
第二十三章 STL-常用容器
解决SQL错误(208):对象名‘string_split‘无效的正确方法,亲测有效!!!
46:第四章:开发文件服务:7:在【files】文件服务中,整合阿里OSS;
Leetcode---361周赛
Git Cherry Pick命令
记录内网Docker启动Stable-Diffusion遇到的几个坑
振弦采集模块的信号检测与分析计算
JVM:类加载的双亲委派机制
网站页面禁止复制内容 JS代码
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40772692/article/details/127576247
