-
深入浅出Spring(24)
问题
什么是父子容器?
为什么需要用父子容器?
父子容器如何使用?
案例演示
d1包
@Component public class Service1 { public String m1() { return "我是module1中的Servce1中的m1方法"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
@Component public class Service2 { @Autowired private Service1 service1; public String m1() { //@2 return this.service1.m1(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
@ComponentScan public class Config { }- 1
- 2
- 3
d2包
@Component public class Service1 { public String m2() { return "我是module2中的Servce1中的m2方法"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
@Component public class Service3 { @Autowired private com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d2.Service1 service1; @Autowired private com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Service2 service2; public String m1() { return this.service2.m1(); } public String m2() { return this.service1.m2(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
@ComponentScan public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义容器 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); //注册bean context.register(com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Config.class, Client.class); //启动容器 context.refresh(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
关系梳理,d1包下有三个类,第一个Service1,第二个Service2注入了Service1,配置类扫描包下组件。
d2包下有三个类,第一个Service1不同包同类,第二个Service3,注入了二包的Service1和一包的Service2,第三个是启动类。输出截图
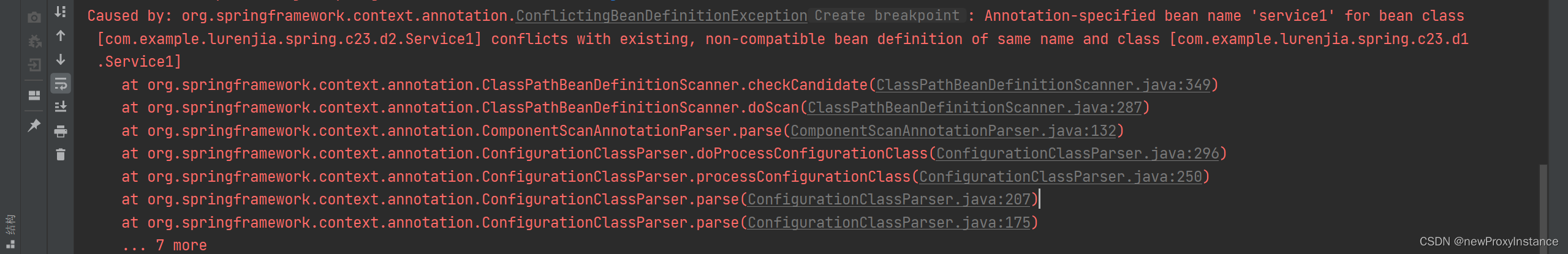
当容器中存在两个同类型的bean而且我们还不能修改名称的时候就可以考虑使用父子容器。如何设置父子容器 ?
childContext.setParent(parentContext); //点进去看实现 @Override public void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { super.setParent(parent); this.beanFactory.setParentBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
测试实例
@ComponentScan public class Client2 { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext parentContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); parentContext.register(com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Config.class); parentContext.refresh(); AnnotationConfigApplicationContext childContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); childContext.register(Client2.class); childContext.setParent(parentContext); childContext.refresh(); Service3 service3 = childContext.getBean(Service3.class); System.out.println(service3.m1()); System.out.println(service3.m2()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
我是module1中的Servce1中的m1方法 我是module2中的Servce1中的m2方法- 1
- 2
父子容器的特征
父子容器中的bean
String[] bdn = parentContext.getBeanDefinitionNames(); String[] bdn2 = childContext.getBeanDefinitionNames(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bdn)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bdn2));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
输出
[org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor, org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor, org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor, org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor, org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory, config, service1, service2] [org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor, org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor, org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor, org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor, org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory, client2, service1, service3]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
去掉公共部分可以看到 parentContext 有 config, service1, service2,childContext有 client2, service1, service3。
尝试在父容器获取service3,子容器获取service2。
Service1 bean5 = childContext.getBean(Service1.class); System.out.println(bean5); com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Service1 bean6 = parentContext.getBean(com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Service1.class); System.out.println(bean6); Service2 bean = childContext.getBean(Service2.class); System.out.println(bean); Service2 bean2 = parentContext.getBean(Service2.class); System.out.println(bean2); Service3 bean3 = childContext.getBean(Service3.class); System.out.println(bean3); Service3 bean4 = parentContext.getBean(Service3.class); System.out.println(bean4);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
输出
com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d2.Service1@5ea434c8 com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Service1@3bbc39f8 com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Service2@4ae3c1cd com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d1.Service2@4ae3c1cd com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d2.Service3@29f69090 Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d2.Service3' available at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:351) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:342) at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1177) at com.example.lurenjia.spring.c23.d2.Client2.main(Client2.java:54) 进程已结束,退出代码为 1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
总结:
- 使用父子容器后可以解决上述容器中存在两个类型名相同的bean。
- 子容器可以获取到父容器的bean,反之则不可以。
父子容器使用注意点
有的接口方法不支持向上查找,也就是子容器没有的bean不会查找父容器。
例如 getBeanNamesForType
public class Client3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建父容器parentFactory DefaultListableBeanFactory parentFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); //向父容器parentFactory注册一个bean[userName->"路人甲Java"] parentFactory.registerBeanDefinition("userName", BeanDefinitionBuilder. genericBeanDefinition(String.class). addConstructorArgValue("路人甲Java"). getBeanDefinition()); //创建一个子容器childFactory DefaultListableBeanFactory childFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); //调用setParentBeanFactory指定父容器 childFactory.setParentBeanFactory(parentFactory); //向子容器parentFactory注册一个bean[address->"上海"] childFactory.registerBeanDefinition("address", BeanDefinitionBuilder. genericBeanDefinition(String.class). addConstructorArgValue("上海"). getBeanDefinition()); System.out.println("获取bean【userName】:" + childFactory.getBean("userName")); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(childFactory.getBeanNamesForType(String.class))); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
那么有办法解决这个问题么,使用 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors 等带Ancestors这个的方法。
String[] beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(childFactory, String.class); System.out.println(Arrays.asList(beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors)); Map<String, String> beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(childFactory, String.class); System.out.println(Arrays.asList(beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
为什么有的方法会查找父容器有的不会查找父容器?
常见问题
问题1:springmvc中只使用一个容器是否可以?
只使用一个容器是可以正常运行的。
问题2:那么springmvc中为什么需要用到父子容器?
通常我们使用springmvc的时候,采用3层结构,controller层,service层,dao层;父容器中会包含dao层和service层,而子容器中包含的只有controller层;这2个容器组成了父子容器的关系,controller层通常会注入service层的bean。
采用父子容器可以避免有些人在service层去注入controller层的bean,导致整个依赖层次是比较混乱的。
父容器和子容器的需求也是不一样的,比如父容器中需要有事务的支持,会注入一些支持事务的扩展组件,而子容器中controller完全用不到这些,对这些并不关心,子容器中需要注入一下springmvc相关的bean,而这些bean父容器中同样是不会用到的,也是不关心一些东西,将这些相互不关心的东西隔开,可以有效的避免一些不必要的错误,而父子容器加载的速度也会快一些。
-
相关阅读:
AI 已经在污染互联网了。。赛博喂屎成为现实
JavaWeb三大组件【Servlet】【Filter】【Listener】学习笔记
数据结构篇——哈希表
IT新人如何在职场弯道超车?强推荐考取当下最有价值的云计算认证证书!
对于云原生时代的后端业务开发和项目系统学习,选Go Or Java?
pcl--第十节 点云曲面重建
第三篇------Virtual I/O Device (VIRTIO) Version 1.1
Spring Cloud微服务治理框架深度解析
【工具】Git-码农“吃饭的碗”要拿好
SQLSERVER 临时表和表变量到底有什么区别?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37151886/article/details/127569731
