-
js中的类class class源码
class
js中类的类型也是function
class Person {} console.log(typeof Person);- 1
- 2
- 3

constructor 构造器
构造器中实例化的属性配置 是 私有属性class Person { constructor(name = 'zhangsan', age = '18') { this.name = name; this.age = age; } } console.log(typeof Person);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
原型上的方法 是公有方法 直接写在类中
class Person { constructor(name = 'zhangsan', age = '18') { this.name = name; this.age = age; } say() { console.log(`my name is ${this.name} and age is ${this.age}`); } } console.log(new Person());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

类内部的方法是不可枚举的class Person { constructor(name = 'zhangsan', age = '18') { this.name = name; this.age = age; } say() { console.log(`my name is ${this.name} and age is ${this.age}`); } drink() { console.log('I can drink'); } eat() { console.log('I can eat'); } } console.log(Object.keys(Person.prototype));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

当我们什么都不指定 只有一个空的class new出来也不会报错 会自动加一个constructor在原型上class Person {} console.log(new Person());- 1
- 2
- 3

js中的类与函数非常相似function Person() {} console.log(new Person() instanceof Person);- 1
- 2
- 3

class Person {} console.log(new Person() instanceof Person);- 1
- 2
- 3

class Person { constructor() { return Object.create(null); } } console.log(new Person() instanceof Person);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

当我们创建一个函数时 如果把它赋值给一个变量 那么函数名就无意义了此时test1是可以省略的
let test = function test1() {}; let test = function () {};- 1
- 2
- 3
那对于类有没有这种特殊情况的
let Person = class Person1 { say() { console.log(1); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
我们尝试省略Person1
发现是可以的let Person = class { say() { console.log(1); } }; console.log(new Person().say());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

必须通过new 的方式执行 class这个样子是会报错的
let Person = class { say() { console.log(1); } }(); console.log(Person.say());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

let person = new (class { say() { console.log(1); } })(); console.log(person.say());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

let person = new (class { constructor(name = 'zhangsan', age = '18') { this.name = name; this.age = age; } say() { console.log(1); } })('lisi', '19'); console.log(person);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

类不能提升
不存在暂时性死区(TDZ)console.log(new Person()); class Person {}- 1
- 2
- 3

没有公有属性公有函数私有化
方式一 symbolconst eat = Symbol(); class Person { constructor(name, age) { this.age = age; this.name = name; } say() { console.log(1); } [eat]() { console.log(2); } } console.log(new Person().say()); console.log(new Person().eat());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
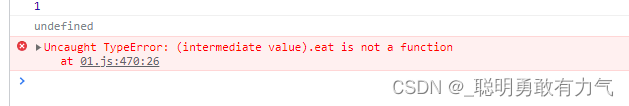
方式二class Person { constructor(name, age) { this.age = age; this.name = name; } say(baz) { children.call(this, baz); } } function children(baz) { return (this.baz = baz); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
static定义静态属性与静态方法
通过当前的类调用 不通过实例调用class Person { static a = 1; static foo() { return 2; } } console.log(Person.a); console.log(Person.foo());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

对象的get set 与类的get set
对象的get set 直接使用.运算符使用var obj = { get a() { console.log(1); }, set a(value) { console.log(value); }, }; console.log(obj.a); obj.a = 3;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

类的get 与set需要new 实例化后使用class Person { get a() { console.log(1); } set a(value) { console.log(value); } } let person = new Person(); console.log(person.a); person.a = 2;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

extends
继承
继承的是父级共有属性的默认值class Parent { constructor(name = 'zhangsan') { this.name = name; } } class Child extends Parent {} console.log(new Child());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
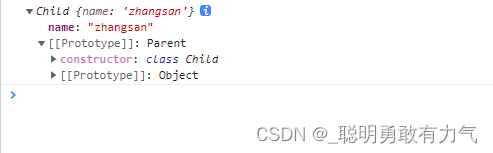
静态属性不继承class Parent { constructor(name = 'zhangsan') { this.name = name; } say() { console.log(1); } static a() { console.log(2); } } class Child extends Parent {} console.log(new Child().a());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

派生类
必须在派生类中this前 使用super改变this指向
如果不用就会报错class Parent { constructor(name = 'zhangsan') { this.name = name; } say() { console.log(1); } static a() { console.log(2); } } class Child extends Parent { constructor(age = '19') { this.age = age; } } console.log(new Child().age);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19

class Parent { constructor(name = 'zhangsan') { this.name = name; } say() { console.log(1); } static a() { console.log(2); } } class Child extends Parent { constructor(name = 'lisi', age = '19') { super(name); this.type = 'child'; this.age = age; } } console.log(new Child());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21

let proto = { y: 20, z: 40, }; let obj = { x: 10, foo() { console.log(super.y); }, }; Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, proto); obj.foo();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

super
1.在对象当中 指代对象的原型
2.在静态方法中 指向自己的父类class源码
类的写法
class Person { constructor(name = 'zhangsan', age = '18') { this.name = name; this.age = age; } say() { console.log('hello word'); } drink() { console.log('drink'); } static eat() { console.log('eat'); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
源码转为es5
'use strict'; var _createClass = (function () { function defineProperties(target, props) { for (var i = 0; i < props.length; i++) { var descriptor = props[i]; descriptor.enumerable = descriptor.enumerable || false; descriptor.configurable = true; if ('value' in descriptor) descriptor.writable = true; Object.defineProperty(target, descriptor.key, descriptor); } } return function (Constructor, protoProps, staticProps) { if (protoProps) defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps); if (staticProps) defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps); return Constructor; }; })(); function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) { if (!(instance instanceof Constructor)) { throw new TypeError('Cannot call a class as a function'); } } var Person = (function () { function Person() { var name = arguments.length > 0 && arguments[0] !== undefined ? arguments[0] : 'zhangsan'; var age = arguments.length > 1 && arguments[1] !== undefined ? arguments[1] : '18'; _classCallCheck(this, Person); this.name = name; this.age = age; } _createClass( Person, [ { key: 'say', value: function say() { console.log('hello word'); }, }, { key: 'drink', value: function drink() { console.log('drink'); }, }, ], [ { key: 'eat', value: function eat() { console.log('eat'); }, }, ] ); return Person; })();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
-
相关阅读:
高新技术企业认定的重要指标
JAVA 身份证号码的验证
校园网络设计环境分析
美团组件化事件总线方案改进:ModularEventBus
一文读懂Embedding
从功能测试到自动化测试你都知道他们的有缺点吗?
Debian11.5设置静态IP 221021记录
Linux:mongodb数据逻辑备份与恢复(3.4.5版本)
【Selenium4自动化测试(1)】Selenium4简介
k8s-集群里的三种IP(NodeIP、PodIP、ClusterIP)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_65402230/article/details/127443372
