-
java详解队列

一、队列是什么?
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)


队列是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在表的前端进行删除操作,而在表的后端进行插入操作。
LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。二、模拟实现队列
队列中既然可以存储元素,那底层肯定要有能够保存元素的空间,通过前面线性表的学习了解到常见的空间类型有两种:顺序结构 和 链式结构。同学们思考下:队列的实现使用顺序结构还是链式结构好?
因为队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,顺序表要想达到此目的,删除和取数据时间复杂度达到了O(n),那我们可不可以用单链表而且时间复杂度是O(1)呢?public class MyQueue { static class ListNode { public int value; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int value) { this.value = value; } } public ListNode head; public ListNode tail; //入队列 public void offer(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if(head == null) { head = node; tail = node; return; } tail.next = node; tail = node; } //出队列 public int poll() { if(isEmpty()) { return -1; } int ret = head.value; head = head.next; if(head == null) { tail = null; } return ret; } //查看队列第一个元素 public int peek() { if(isEmpty()) { return -1; } int ret = head.value; return ret; } //判断队列是否为空 public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; } //获取队列大小 public int size() { ListNode cur = head; int count = 0; while (cur != null) { cur = cur.next; count++; } return count; } }
三、模拟实现循环队列
循环队列是把顺序队列首尾相连,把存储队列元素的表从逻辑上看成一个环,成为循环队列。
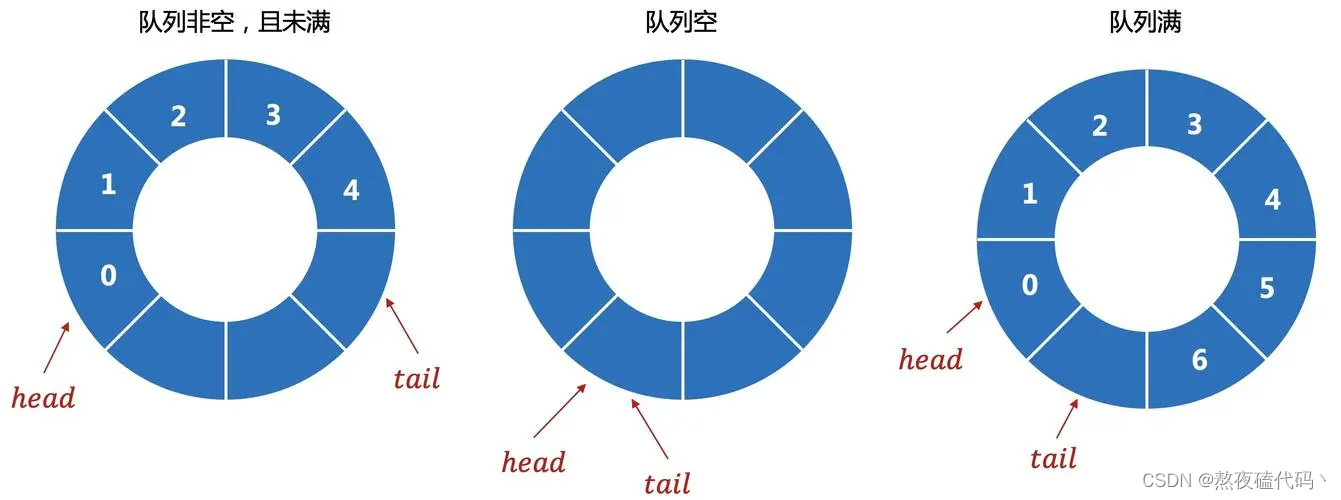
在实现循环队列时,我们主要面临的问题是,什么情况下队列为空,什么情况下队列为满,在判断满时:我们有两种方案,定义一个size变量,如果等于0为空,等于队列容量为满,这种过于简单,我们采用浪费一个空间的办法,如果head == tail队列为空,如果tail的下一个位置为head为满。class MyCircularQueue { public int[] arr; public MyCircularQueue(int k) { arr = new int[k+1]; } public int front; public int rear; public boolean enQueue(int value) { if(isFull()) { return false; } arr[rear] = value; rear = (rear + 1) % arr.length; return true; } public boolean deQueue() { if(isEmpty()) { return false; } front = (front + 1) % arr.length; return true; } public int Front() { if(!isEmpty()) { return arr[front]; } return -1; } public int Rear() { if(!isEmpty()) { int ret = rear == 0 ? arr.length - 1 : rear - 1; return arr[ret]; } return -1; } public boolean isEmpty() { return front == rear; } public boolean isFull() { return (rear + 1) % arr.length == front; } }四、用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。

import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; class MyStack { public Queue<Integer> qu1; public Queue<Integer> qu2; public MyStack() { qu1 = new LinkedList<>(); qu2 = new LinkedList<>(); } public void push(int x) { if(empty()) { qu1.offer(x); return; } if(qu1.isEmpty()) { qu2.offer(x); }else { qu1.offer(x); } } public int pop() { if(empty()) { return -1; } if(qu1.isEmpty()) { int x = qu2.size(); for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) { qu1.offer(qu2.poll()); } return qu2.poll(); }else { int x = qu1.size(); for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) { qu2.offer(qu1.poll()); } return qu1.poll(); } } public int top() { if(empty()) { return -1; } if(qu1.isEmpty()) { int x = qu2.size(); for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) { qu1.offer(qu2.poll()); } int ret = qu2.poll(); qu1.offer(ret); return ret; }else { int x = qu1.size(); for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) { qu2.offer(qu1.poll()); } int ret = qu1.poll(); qu2.offer(ret); return ret; } } public boolean empty() { return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty(); } }五、用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false

import java.util.Stack; class MyQueue{ public Stack<Integer> s1; public Stack<Integer> s2; public MyQueue() { s1 = new Stack<>(); s2 = new Stack<>(); } public void push(int x) { s1.push(x); } public int pop() { if(empty()) { return -1; } if(!s2.empty()) { return s2.pop(); }else { while(!s1.empty()) { s2.push(s1.pop()); } return s2.pop(); } } public int peek() { if(empty()) { return -1; } if(!s2.empty()) { return s2.peek(); }else { while(!s1.empty()) { s2.push(s1.pop()); } return s2.peek(); } } public boolean empty() { return s1.empty() && s2.empty(); } } -
相关阅读:
6_显示登录信息以及上传图片
python数字
万物皆可集成系列:低代码释放用友U8+深度价值(2)—数据拓展应用
长度最小的子数组(滑动窗口)
两篇论文的分享
读操作系统导论记录linux下锁的历史发展
Apollo安装全攻略
Redis五种数据结构-常用命令
相见恨晚的电脑软件,早知道早享福
云耀服务器L实例部署Discuz!Q论坛|华为云云耀云服务器L实例评测使用体验
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/buhuisuanfa/article/details/127021483