-
SpringSecurity入门和项目中使用
背景
spring家族的安全框架,两大核心: 认证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization) 。
通俗说:认证—你是谁?
授权----你有什么权限?
在认证和授权这两个核心功能之外,SpringSecurity还提供了很多安全管理的“周边功能”,这也是一个非常重要的特色,在开发中,即便我们不了解很多网络攻击,只要用了SpringSecurity它会帮助我们自动防御很多网络攻击,例如CSRF攻击,会话固定攻击等,同时还提供了HTTP防火墙来拦截大量的非法请求。
认证
认证规则有很多,有:
- 表单认证
- OAuth2.0认证
- SAML2.0认证
- CAS认证
- RememberMe自动认证
- JAAS认证
- OpenID认证
- Pre-Authentication Scenarios认证
- X509认证
- HTTP Basic认证
- HTTP Digest认证
- 自定义认证等等
看一下 Authentication 认证接口:
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable { //用来获取用户的权限 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(); //用来获取用户凭证,一般来说是密码 Object getCredentials(); //用来获取用户携带的详细信息,可能是当前请求之类等 Object getDetails(); //用来获取当前用户,例如是一个用户或一个用户对象 Object getPrincipal(); //当前用户是否认证成功。 boolean isAuthenticated(); void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
管理认证的接口 AuthenticationManager :
/** AuthenticationManager接口只有一个authenticate方法可以用来做认证,该方法有三个不同的返回值: 返回Authentication : 表示认证成功 抛出AuthenticationException异常:表示用户输入了无效的凭证. 返回null,表示不能断定 */ public interface AuthenticationManager { Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
实现认证管理的类 ProviderManager :
/** AuthenticationManager最主要的实现类是ProviderManager,ProviderManager管理了众多的AuthenticationProvider实例,AuthenticationProvider有点类似于AuthenticationManager,但是它多了一个supports方法用来短评是否指出给定的Authenticaion类型。 */ public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager{ private List<AuthenticationProvider> providers = Collections.emptyList(); private AuthenticationManager parent; @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { ... } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
具体管理某个认证的接口 AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider类似于AuthenticationManager ,只不过其只针对一个认证
/** 由于Authentication拥有众多不同的实现类,这些不同的实现类又由不能的AuthenticationProvider来处理,所以AuthenticationProvider会有一个supports方法,来判断当前的AuthenticationProvider是否支持对应的Authentication */ public interface AuthenticationProvider { Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException; boolean supports(Class<?> authentication); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
授权
- 基于URL的请求授权
- 支持方法的访问授权
- 支持SpEL访问控制
- 支持域对象安全
- 同时也支持动态权限配置
- 支持RBAC权限模型等
认证相关接口:
投票 接口AccessDecisionVoter
public interface AccessDecisionVoter<S> { int ACCESS_GRANTED = 1; int ACCESS_ABSTAIN = 0; int ACCESS_DENIED = -1; boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute); boolean supports(Class<?> clazz); int vote(Authentication authentication, S object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
管理投票接口 AccessDecisionManager
AccessDecisionVoter和AccessDecisionManager都有众多的实现类,在AccessDecisionManager中会挨个遍历AccessDecisionVoter,进而决定是否允许用户访问
public interface AccessDecisionManager { void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute); boolean supports(Class<?> clazz); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
过滤器
我们所见到SpringSecurity提供的功能,都是通过这些过滤器来实现的,这些过滤器按照既定的优先级排列,最终行程一个过滤器链。我们也可以自定义过滤器,并通过@Order来调整自定义过滤器在过滤链中的位置。
需要注意的是,默认过滤器并不是直接放在Web项目的原生过滤器链中,而是通过一个FilterChainProxy来统一管理。SpringSecurity中的过滤链通过FilterChainProxy嵌入到Web项目的原生过滤器链中,如下:
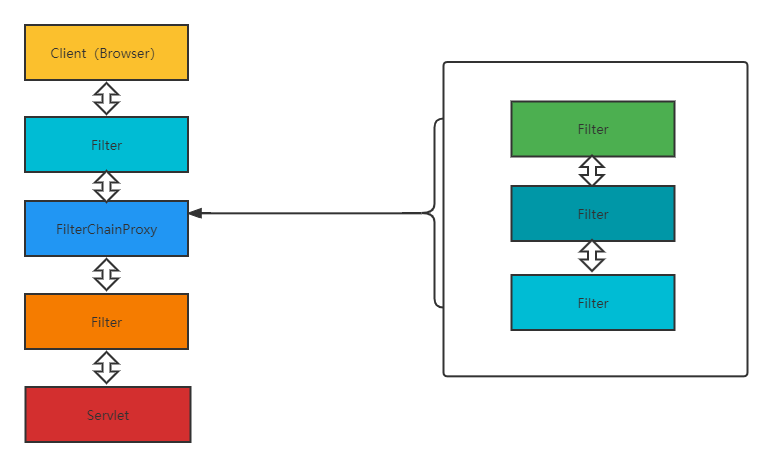
具体案例
springsecurity安全额配置类
/** * Spring security web security config. * */ @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig { public static final String API_PATTERN = "/api/**"; /** 无需认证的API patterns */ public static String[] PUBLIC_API_PATTERNS = new String[] { "/api/users/login", .... }; /** 需要认证的API patterns */ public static String[] PRIVATE_API_PATTERNS = new String[] {API_PATTERN, "/api2/**"}; /**X-Frame-Options设置 deny:表示该页面不允许在 frame 中展示,即便是在相同域名的页面中嵌套也不允许。 sameorigin:表示该页面可以在相同域名页面的 frame 中展示。 allow-from: 这是一个被弃用的指令,不再适用于现代浏览器;意思是只能被嵌入到指定域名的框架中 **/ public static final String X_FRAME_OPT_DENY = "deny"; public static final String X_FRAME_OPT_SAME_ORIGIN = "sameorigin"; public static final String X_FRAME_OPT_ALLOW_FROM_PREFIX = "allow-from "; @Setter(onMethod_ = {@Autowired}) private AccessTokenAuthenticationProvider accessTokenAuthProvider; @Setter(onMethod_ = {@Autowired}) private SettingService settingService; @Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // 设置认证 AccessTokenAuthenticationFilter accessTokenAuthenticationFilter = new AccessTokenAuthenticationFilter(); http.authorizeRequests() // 公共API无需认证 .antMatchers(PUBLIC_API_PATTERNS) .permitAll() .antMatchers(PRIVATE_API_PATTERNS) .authenticated() .and() // 提取令牌 .addFilterBefore(accessTokenAuthenticationFilter, BasicAuthenticationFilter.class) // 验证令牌 .authenticationProvider(this.accessTokenAuthProvider) .exceptionHandling() // 对于认证失败的返回401错误,而不是默认的403错误,请见:https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/api/org/springframework/security/config/annotation/web/configurers/ExceptionHandlingConfigurer.html#authenticationEntryPoint(org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint)。 .authenticationEntryPoint(new HttpStatusEntryPoint(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)) .and() .headers() // 设置X-Frame-Options响应头 //避免自己的网页被嵌入到别的站点 .frameOptions( options -> { String opt = 数据库或配置文件读取设置; if (StringUtils.isBlank(opt)) { options.disable(); } else if (X_FRAME_OPT_SAME_ORIGIN.equalsIgnoreCase(opt)) { options.sameOrigin(); } else if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(opt, X_FRAME_OPT_ALLOW_FROM_PREFIX)) { options .disable() .addHeaderWriter( new StaticHeadersWriter( XFrameOptionsHeaderWriter.XFRAME_OPTIONS_HEADER, opt)); } else { // Default policy. options.deny(); } }); // CSRF设置,将token存在cookie中,前端需要把cookie中的token读出来放到请求header里,必须要httpOnly的cookie才能被js读取 boolean csrfCheckEnabled = 数据库或者配置文查找是否支持跨域; List<String> csrfCheckHttpMethods = settingService.getStringList(SettingItem.WEB_CSRF_CHECK_HTTP_METHODS); List<String> csrfCheckExcludePaths = settingService.getStringList(SettingItem.WEB_CSRF_CHECK_EXCLUDE_PATHS); if (csrfCheckEnabled) { http.csrf() .requireCsrfProtectionMatcher( request -> { AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher(); String path = request.getRequestURI(); String method = request.getMethod(); // 检查白名单 if (Seq.seq(csrfCheckExcludePaths) .anyMatch(exclude -> antPathMatcher.match(exclude, path))) { return false; } // 仅仅对API启用csrf if (!antPathMatcher.match(API_PATTERN, path)) { return false; } if (Seq.seq(csrfCheckHttpMethods) .noneMatch(checkMethod -> checkMethod.equalsIgnoreCase(method))) { return false; } return true; }) .csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse()); } else { http.csrf().disable(); } return http.build(); } /** 提取令牌 */ public static class AccessTokenAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { @Override protected void doFilterInternal( @NotNull HttpServletRequest request, @NotNull HttpServletResponse response, @NotNull FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException { AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher(); String path = request.getRequestURI(); // 公共API无需认证,非私用API无需认证 boolean skipAuth = Seq.of(PUBLIC_API_PATTERNS).anyMatch(pattern -> antPathMatcher.match(pattern, path)) || Seq.of(PRIVATE_API_PATTERNS) .noneMatch(pattern -> antPathMatcher.match(pattern, path)); if (skipAuth) { // 如果无需认证但是Authentication却被设置了,需要清空,否则还是会进行认证,这可能发生在SecurityContextPersistenceFilter从 // session中恢复出了一个session的认证信息时。 if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() instanceof AccessTokenAuthentication) { SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null); } } else { Optional<String> userNameOpt = UserService.getAuthUserName(request); Optional<String> tokenOpt = UserService.getAuthToken(request); String clientIp = WebServerUtils.getClientIp(request); AccessTokenAuthentication auth = new AccessTokenAuthentication( tokenOpt.orElse(null), userNameOpt.orElse(null), clientIp); // 将authentication设置到(*****)SecurityContext(******),下面会取出来放到userContext方便随时读取用户信息 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(auth); } // 返回这个链式调用 chain.doFilter(request, response); } } //设置authentication中包含的信息 public static class AccessTokenAuthentication extends AbstractAuthenticationToken { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7495641216462496304L; private final String accessToken; private final String userName; private final String clientIp; public AccessTokenAuthentication(String accessToken, String userName, String clientIp) { super(null); this.accessToken = accessToken; this.userName = userName; this.clientIp = clientIp; setAuthenticated(false); } public String getAccessToken() { return this.accessToken; } public String getUserName() { return this.userName; } public String getClientIp() { return this.clientIp; } @Override public Object getCredentials() { return null; } @Override public Object getPrincipal() { return null; } } /** 验证令牌 */ @Component @AllArgsConstructor(onConstructor_ = {@Autowired}) public static class AccessTokenAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider { private final UserService userService; @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { AccessTokenAuthentication tokenAuth = (AccessTokenAuthentication) authentication; //其实就是从缓存中取用户的登录信息 userService.authenticate(tokenAuth.userName, tokenAuth.accessToken, tokenAuth.clientIp); authentication.setAuthenticated(true); return authentication; } @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) { return AccessTokenAuthentication.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication); } } @Bean public HttpFirewall httpFirewall() { // APT的客户端会发出路径包含"/./"的请求,默认的StrictHttpFirewall认为这是非法的url,会拒绝请求,换用DefaultHttpFirewall允许这种请求。 return new DefaultHttpFirewall(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
csrf:

配置登录缓存和全局信息
@Configuration public class UserConfig { /** 用户登录成功后将一些登录信息放入里面(比如用户名:登录信息【ip、token、权限】) loginCache.put(userName, new LoginInfo(clientIp, token, authPerms)) */ @Bean public Cache<String, LoginInfo> loginCache() { return Caffeine.newBuilder() .expireAfterWrite(从数据库或者配置文件中读取过期时间) .build(); } //将用户的登录信息 @Bean @RequestScope public UserContext userContext( HttpServletRequest request, Cache<String, LoginInfo> loginCache, PreferenceService prefService) { UserContext context = new UserContext(); Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication(); if (auth instanceof WebSecurityConfig.AccessTokenAuthentication) { // 带有令牌 WebSecurityConfig.AccessTokenAuthentication tokenAuth = (WebSecurityConfig.AccessTokenAuthentication) auth; context.setIpAddr(tokenAuth.getClientIp()); context.setUserName(tokenAuth.getUserName()); } else { // 没有令牌 context.setIpAddr(WebServerUtils.getClientIp(request)); context.setUserName(""); } LoginInfo loginInfo = loginCache.getIfPresent(context.getUserName()); if (loginInfo != null) { // Request from logged in user. context.setPerms(loginInfo.getPerms()); } context.setLocale(I18nService.detectLocale(request)); return context; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
方法级的授权
当我们想要开启spring方法级安全时,只需要在任何 @Configuration实例上使用 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 注解就能达到此目的。同时这个注解为我们提供了prePostEnabled 、securedEnabled 和 jsr250Enabled 三种不同的机制来实现同一种功能。
prePostEnabled
prePostEnabled = true 会解锁 @PreAuthorize / @PostAuthorize/ @PreFilter/@PostFilter
-
字就可以看出@PreAuthorize 注解会在方法执行前进行验证
-
@PostAuthorize 注解会在方法执行后进行验证。
-
@PreFilter: 对集合类型的参数执行过滤,移除结果为false的元素。
-
@PostFilter 基于返回值相关的表达式,对返回值进行过滤
Secured
@Secured注解是用来定义业务方法的安全配置。在需要安全[角色/权限等]的方法上指定 @Secured,并且只有那些角色/权限的用户才可以调用该方法。 但是其不支持springrl表达式。
jsr250E
启用 JSR-250 安全控制注解,这属于 JavaEE 的安全规范(现为 jakarta 项目)。一共有五个安全注解。如果你在 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 设置 jsr250Enabled 为 true ,就开启了 JavaEE 安全注解中的以下三个
- @DenyAll: 拒绝所有访问
- @RolesAllowed({“USER”, “ADMIN”}): 该方法只要具有"USER", "ADMIN"任意一种权限就可以访问。这里可以省略前缀ROLE_,实际的权限可能是ROLE_ADMIN
- @PermitAll: 允许所有访问
/** * Spring security method security config. */ @Configuration @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true, jsr250Enabled = true) public class MethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration { private CustomPermissionEvaluator customPermissionEvaluator; @Autowired @Lazy public void setCustomPermissionEvaluator(CustomPermissionEvaluator customPermissionEvaluator) { this.customPermissionEvaluator = customPermissionEvaluator; } @Override protected MethodSecurityExpressionHandler createExpressionHandler() { DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler handler = new DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler(); handler.setPermissionEvaluator(this.customPermissionEvaluator); return handler; } @Component @AllArgsConstructor(onConstructor_ = {@Autowired}) public static class CustomPermissionEvaluator implements PermissionEvaluator { /** * Return true if the user has permission to access the target, false otherwise. */ @Override public boolean hasPermission( Authentication authentication, Object targetDomainObject, Object permission) { return false; } /** * Return true if the user has permission to access the target, false otherwise. */ @Override @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes"}) public boolean hasPermission( Authentication authentication, Serializable targetId, String targetType, Object permission) { //将所需的权限 放在set中 Set<Access> accesses = new HashSet<>(); if (targetId instanceof Collection) { for (Object singleId : (Collection) targetId) { accesses.add(toAccess((Long) singleId, targetType, permission)); } } else { accesses.add(toAccess((Long) targetId, targetType, permission)); } //和用户自身的权限比对 查看是否有权限 return hasPermission(accesses); } private Access toAccess(Long id, String targetType, Object permission) { return new Access( new Access.Target(Access.TargetType.valueOf(targetType), id), Access.Action.valueOf((String) permission)); } private boolean hasPermission(Set<Access> accesses) { Set<AuthPerm> required = new HashSet<>(); for (Access access : accesses) { switch (access.getTarget().getType()) { case Type1: required.addAll(); break; ... default: break; } } //和用户所具有的的权限(即从userContext【根本上是从数据库里】中取 )比较,看用户是否有这个权限 return permService.hasPerms(required); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
接口上使用:
@GetMapping("/get") @PreAuthorize("hasPermission(#resourceId,'OPERATION', 'VIEW')") public List<Resurce> getResource(@RequestParam(value = "resourceId") Long resourceId){ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
权限类设置
import lombok.Value; @Value public class Access { //针对什么目标 Target target; //对这个目标有什么权限 Action action; @Value public static class Target { TargetType type; Long id; } public enum TargetType { USER, BOOK, PERMISSION, OPERATION } public enum Action { CREATE, EDIT, DELETE, VIEW, DOWNLOAD, } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
数据库权限类
@Table("role_perms") @Data @AllArgsConstructor public class Perm { @Id @Column("roleName") private String roleName; @Column("perm") private PermType perm; @Column("resId") private long resId; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
@AllArgsConstructor @Getter public enum PermType { ADMIN(false, AccessLevel.ADMIN), GUEST(false, AccessLevel.GUEST), USER_ADMIN(true, AccessLevel.ADMIN), USER_GUEST(true, AccessLevel.GUEST), BOOK_ADMIN(true, AccessLevel.ADMIN), ; private final boolean requireResId; private final AccessLevel accessLevel; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
public enum AccessLevel { /** ADMIN level. */ ADMIN, /** GUEST level. */ GUEST }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
参考博文:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40409260/category_11678122.html
http://www.javaboy.org/springsecurity/
https://blog.csdn.net/tq20160412/article/details/114655551
-
相关阅读:
Laravel 实现redis分布式锁
HTML5期末大作业dreamweaver作业静态HTML网页设计——甜点店(11页) 学生网页设计作品
(附源码)计算机毕业设计SSM焦作旅游网站
c 声明、定义、初始化的差别
动手学深度学习——循环神经网络的从零开始实现(原理解释+代码详解)
原来,BI数据分析也是有模板的
天龙八部服务端Public目录功能讲解
[Unity3D] C# 十进制、二进制、十六进制 之间进制的转换
深度学习入门(十四)数值稳定性和模型初始化
第十五章 观察者模式
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43604021/article/details/126948025
