-
SpringCloud
SpringCloud
视频参考尚硅谷 周阳 老师的微服务:尚硅谷-周阳微服务
该篇为上篇,下篇为 SpringCloud Alibaba
GitHub 源码已上传: github
JSON转换工具:
https://tool.lu/json
SpringBoot 与 SpringCloud 版本对应关系:

SpringCloud 目前使用的服务

开启 RunDashboard : 多模块运行
1、找到 .idea 目录中的 workspace.xml 文件
2、修改
<component name="RunDashboard"> <option name="configurationTypes"> <set> <option value="SpringBootApplicationConfigurationType" /> </set> </option> </component>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
隐藏 .idea 文件:
Ctrl + Alt + s 打开设置
找到 File Type

一、微服务架构搭建
微服务是一种架构风格,将一个单独的项目拆分成多个模块,每一个模块都是一个微服务。每个微服务都可以独立运行,部署,升级。

1.1 创建父工程
父工程只留下 pom.xml 文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion> <groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId> <artifactId>mscloudartifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion> <modules> <module>cloud-provider-payment8001module> modules> <packaging>pompackaging> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target> <junit.version>4.12junit.version> <log4j.version>1.2.17log4j.version> <lombok.version>1.18.16lombok.version> <mysql.version>8.0.16mysql.version> <druid.version>1.1.10druid.version> <mybatis.spring.boot.version>1.3.2mybatis.spring.boot.version> properties> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId> <version>2.2.2.RELEASEversion> <type>pomtype> <scope>importscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependenciesartifactId> <version>Hoxton.SR1version> <type>pomtype> <scope>importscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependenciesartifactId> <version>2.1.0.RELEASEversion> <type>pomtype> <scope>importscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> <version>${mysql.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibabagroupId> <artifactId>druidartifactId> <version>${druid.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId> <version>${mybatis.spring.boot.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junitgroupId> <artifactId>junitartifactId> <version>${junit.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4jartifactId> <version>${log4j.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <version>${lombok.version}version> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> dependencies> dependencyManagement> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId> <configuration> <fork>truefork> <addResources>trueaddResources> configuration> plugin> plugins> build> project>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
dependencyManagement 和 dependencies 的区别:
dependencyManagement 是用来管理版本依赖版本号的 ,出现在父工程中 。所有的子项目都统一使用同一个版本号。 dependencyManagement 并不会引入 jar 包 ,而是声明 jar 包,真正引入 jar 应该在 子工程的 dependencies 下 ,而在子工程中不需要写另外的版本号,如果需要新的版本号在子工程中重新指明 version 即可 !
1.2 支付模块
微服务模块流程:
- 建 module ---- cloud-provider-payment8001
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
POM :
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>mscloudartifactId> <groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion> parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion> <artifactId>cloud-provider-payment8001artifactId> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibabagroupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId> <version>1.2.9version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies> project>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
YML:
server: port: 8001 # 微服务模块名称 spring: application: name: cloud-payment-service datasource: type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 当前数据源操作类型 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver # mysql驱动包 com.mysql.jdbc.Driver druid: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2022?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=CST username: root password: 1234 /- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
主启动:
package com.atguigu.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; /** * 主启动类 * Handsome Man. ** Author: YZG * Date: 2022/5/19 16:55 * Description: */
@SpringBootApplication public class PaymentMain8001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8001.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
编写业务类:
Controller – Service – dao – mysql
前后端分离,前端不再关心后端的逻辑,后端只需要返回一个 JSON 字符串即可【状态码,错误信息】,因此在 Controller 层只需要返回 JSON
CREATE TABLE `payment` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'ID', `serial` varchar(200) DEFAULT '', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 =================================================================== 实体类 @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Payment implements Serializable { private Long id; private String serial ; } ======================================================================公共返回对象 /** * 公用的返回对象 --- 返回给前端的 JSON * Handsome Man. ** Author: YZG * Date: 2022/5/19 17:22 * Description: */
@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class CommonResult <T>{ private Integer code ; private String message ; // 指定返回的泛型 private T data; public CommonResult(Integer code, String message){ this(code,message,null); } } =========================================================================Dao @Mapper public interface PaymentDao { /** * 插入返回主键 ID * @param payment * @return */ int create(Payment payment); /** * 根据 ID 查询 * @param id * @return */ Payment getPaymentById(@Param("id") Long id); } =========================================================================映射文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.atguigu.springcloud.dao.PaymentDao"> <!-- useGeneratedKeys 开启自增主键 keyProperty 将 主键存放在哪个 属性中 --> <insert id="create" parameterType="Payment" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into payment(serial) values (#{serial}) </insert> <!-- resultType: 返回类型 --> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="Payment"> <id property="id" column="id" jdbcType="BIGINT"></id> <result property="serial" column="serial" jdbcType="VARCHAR"></result> </resultMap> <select id="getPaymentById" resultMap="BaseResultMap"> select * from payment where id = #{id}; </select> </mapper> ============================================================================ Service public interface PaymentService { /** * 插入返回主键 ID * @param payment * @return */ int create(Payment payment); /** * 根据 ID 查询 * @param id * @return */ Payment getPaymentById(@Param("id") Long id); } ============================================================================ @Service public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentService { @Autowired private PaymentDao paymentDao ; @Override public int create(Payment payment) { return paymentDao.create(payment); } @Override public Payment getPaymentById(Long id) { return paymentDao.getPaymentById(id); } } =========================================================================Controller @RestController @Log4j2 public class PaymentController { @Autowired private PaymentService paymentService; @PostMapping("/payment/create") public CommonResult create(@RequestBody Payment payment){ int result = paymentService.create(payment); log.info("====插入结果:" + result); if (result > 0){ return new CommonResult(200,"插入结果成功",result); }else { return new CommonResult(444,"插入结果失败",null); } } @GetMapping("/payment/get/{id}") public CommonResult getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ Payment payment = paymentService.getPaymentById(id); log.info("====查询结果:" + payment); if (payment != null){ return new CommonResult(200,"查询成功",payment); }else { return new CommonResult(444,"查询失败",null); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
1.3 订单模块
和 支付模块 流程一样,不需要在写 Dao、Service 层
订单模块使用 RestTemplate 调用 支付模块中的方法
什么是 RestTemplate ?
RestTemplate提供了多种便捷访问远程Http服务的方法,
是一种简单便捷的访问restful服务模板类,是Spring提供的用于访问Rest服务的客户端模板工具集编写配置类,将 RestTemplate 注册到 IOC 容器中:
@Configuration public class ApplicationContextConfig { @Bean public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Controller 层 :
@RestController @Log4j2 public class OrderController { public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate ; @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/create") public CommonResult<Payment> create(Payment payment){ // 发送POST 请求 // 第一个参数: url // 第二个参数: 参数 // 第三个参数: 返回类型 return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/create",payment,CommonResult.class); } @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/get/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> getPayment(@PathVariable("id") Long id){ // 发送 GET 请求 // 第一个参数: url // 第二个参数: 返回类型 return restTemplate.getForObject(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/get/" + id,CommonResult.class); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
测试的时候,不要忘记在 支付模块的 Controller 层的create方法中增加 @ReqeustBody 注解
1.4 工程重构
其实我们发现 支付模块和 订单模块都有共同的实体类,并没有得到复用。
因此我们可以在新建一个模块专门用于保存实体类以及通用工具包,将此安装到本地库中,只需要在使用的模块中引入 该 jar 包即可
公用模块 POM :
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>cn.hutoolgroupId> <artifactId>hutool-allartifactId> <version>5.1.0version> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
二、服务注册中心
什么是 RPC ?
2.1 Eureka
Eureka采用了CS的设计架构,Eureka Server 作为服务注册功能的服务器,它是服务注册中心。而系统中的其他微服务,使用 Eureka的客户端连接到 Eureka Server并维持心跳连接。这样系统的维护人员就可以通过 Eureka Server 来监控系统中各个微服务是否正常运行。
Eureka 和 Dubbo 架构对比:

服务提供者需要将服务注册到 服务注册中心
Eureka包含两个组件:Eureka Server 和 Eureka Client
-
Eureka Server 提供服务注册服务
- 各个微服务节点通过配置启动后,会在EurekaServer中进行注册,这样EurekaServer中的服务注册表中将会存储所有可用服务节点的信息,服务节点的信息可以在界面中直观看到。
-
EurekaClient 通过注册中心进行访问
- 是一个Java客户端,用于简化Eureka Server的交互,客户端同时也具备一个内置的、使用轮询(round-robin)负载算法的负载均衡器。在应用启动后,将会向Eureka Server发送心跳(默认周期为30秒)。如果Eureka Server在多个心跳周期内没有接收到某个节点的心跳,EurekaServer 将会从服务注册表中把这个服务节点移除(默认90秒)
Eureka 服务端安装 :
- 建 module ----cloud-eureka-server7001
- 该模块为服务注册中心
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-serverartifactId> <version>2.2.1.RELEASEversion> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId> <version>${project.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junitgroupId> <artifactId>junitartifactId> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
YAML 配置:
server: port: 7001 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost #eureka服务端的实例名称 client: #false表示不向注册中心注册自己。 register-with-eureka: false #false表示自己端就是注册中心,我的职责就是维护服务实例,并不需要去检索服务 fetch-registry: false service-url: #设置与Eureka Server交互的地址查询服务和注册服务都需要依赖这个地址。 defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
主启动类:
@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer// 表示该模块为服务注册中心 public class EurekaMain7001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaMain7001.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
访问: localhost:7001 Eureka网页端
将 payment8001 注册到 Eureka 服务注册中心,称为服务的提供者 :
改POM :
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
改YAML:
# 注册到 Eureka 服务中心 eureka: client: #表示是否将自己注册进EurekaServer默认为true。 register-with-eureka: true #是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true。单节点无所谓,集群必须设置为true才能配合ribbon使用负载均衡 fetchRegistry: true service-url: # Eureka 服务注册中心的 地址 defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
改启动类:
@SpringBootApplication // 表示该模块为客户端 @EnableEurekaClient public class PaymentMain8001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8001.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
启动 Payment8001 后,该模块成功注册到 Eureka 服务注册中心中了。

cloud-consumer-order 也可以注册到服务注册中心
2.1.2 Eureka 集群环境搭建

参考 eureka-server7001 新建一个 module : eureka-server7002
既然有俩个服务注册中心,那么他们的 hostname 就不能是一样的了,因此我们需要更改 Windows 中的 hosts 文件更改映射关系
- 127.0.0.1 eureka7001.com
- 127.0.0.1 eureka7002.com
Eureka7001 的 YAML :
server: port: 7001 eureka: instance: hostname: eureka7001.com #eureka服务端的实例名称 client: #false表示不向注册中心注册自己。 register-with-eureka: false #false表示自己端就是注册中心,我的职责就是维护服务实例,并不需要去检索服务 fetch-registry: false service-url: #设置与Eureka Server交互的地址查询服务和注册服务都需要依赖这个地址。 defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
Eureka7002 的 YAML :
server: port: 7002 eureka: instance: # hostname: localhost #eureka服务端的实例名称 hostname: eureka7002.com client: #false表示不向注册中心注册自己。 register-with-eureka: false #false表示自己端就是注册中心,我的职责就是维护服务实例,并不需要去检索服务 fetch-registry: false service-url: #设置与Eureka Server交互的地址查询服务和注册服务都需要依赖这个地址。 #defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/ # 集群版,注册到 7001 中 defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
通过hostname分别访问:
http://eureka7002.com:7002
http://eureka7001.com:7001/
将 80 和 8001 都加入到 7001 和 7002 中:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka # 集群版- 1
2.1.3 服务提供者 8001 集群搭建

创建module ,和 8001 一样: cloud-provide-payment8002
需要注意的是,俩个模块的端口号不一致。
cloud-provide-payment8002 端口号 8002
cloud-provide-payment8001 端口号 8001
由于我们在 order 模块中端口号是写死的,并没实现负载均衡,也就是说如果访问 8001 端口,一直都会由 8001 模块为我们提供服务,访问 8002 端口,一直都会有 8002 模块为我们服务。
显然这时不符合我们要求,我们需要根据 Eureka 中的服务名来区分谁为我们提供服务, 达到负载均衡的效果。
// public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001"; // 根据服务名称实现负载均衡 public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE";- 1
- 2
- 3

显然,这样还是不行的,虽然我们改了 是根据服务名区分的,但是你一个服务名下面是不止一个模块的,因此服务器并不知道用哪个。我们还需要开启 RestTemplate 的 负载均衡 @LoadBalanced
@Bean @LoadBalanced // 开启 RestTemplate 的负载均衡 public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
localhost/consumer/payment/get/1
此时就实现了负载均衡的功能!
2.1.4 actuator完善信息
前提是有这俩个依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
YAML 配置:
instance: instance-id: payment8001- 1
- 2

YAML 配置:
instance: instance-id: payment8002 prefer-ip-address: true #访问路径可以显示IP地址- 1
- 2
- 3

2.4.5 服务发现 Discovery
1、主程序类上增加 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解,开启服务发现
2、从 IOC 容器中取出
@Autowired // 服务发现 private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient ;- 1
- 2
3、
@GetMapping("/payment/discovery") public String discovery(){ // 获取所有的服务 List<String> services = discoveryClient.getServices(); for (String service : services) { log.info(service); } // 获取指定服务名的所有服务 List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE"); for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) { log.info(instance.getServiceId() + "\t" + instance.getInstanceId() + "\t" +instance.getHost() + "\t" + instance.getUri()); } return null ; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2.1.6 Eureka 自我保护机制
默认情况下,如果EurekaServer在一定时间内没有接收到某个微服务实例的心跳,EurekaServer将会注销该实例(默认90秒)。但是当网络分区故障发生(延时、卡顿、拥挤)时,微服务与EurekaServer之间无法正常通信,以上行为可能变得非常危险了——因为微服务本身其实是健康的,此时本不应该注销这个微服务。Eureka通过“自我保护模式”来解决这个问题——当EurekaServer节点在短时间内丢失过多客户端时(可能发生了网络分区故障),那么这个节点就会进入自我保护模式。
EMERGENCY! EUREKA MAY BE INCORRECTLY CLAIMING INSTANCES ARE UP WHEN THEY’RE NOT. RENEWALS ARE LESSER THAN THRESHOLD AND HENCE THE INSTANCES ARE NOT BEING EXPIRED JUST TO BE SAFE.
一句话:某时刻某一个微服务不可用了,Eureka不会立刻清理,依旧会对该微服务的信息进行保存
关闭自我保护机制:【当客户端down掉之后,Eureka 服务端会立马将他剔除掉】
服务端 cloud-eureka-server7001:
eureka: server: #关闭自我保护机制,保证不可用服务被及时踢除 enable-self-preservation: false eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
客户端:cloud-provider-payment8002
eureka: #心跳检测与续约时间 #开发时设置小些,保证服务关闭后注册中心能即使剔除服务 #Eureka客户端向服务端发送心跳的时间间隔,单位为秒(默认是30秒) lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 1 #Eureka服务端在收到最后一次心跳后等待时间上限,单位为秒(默认是90秒),超时将剔除服务 lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 2- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.2 Zookeeper
使用 Zookeeper 注册中心代替 Eureka 服务注册中心
2.2.1 服务提供者 注入到 Zookeeper 中
新建一个模块: cloud-provider-payment8004
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId> <version>${project.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discoveryartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
YAML :
#8004表示注册到zookeeper服务器的支付服务提供者端口号 server: port: 8004 #服务别名----注册zookeeper到注册中心名称 spring: application: name: cloud-provider-payment cloud: zookeeper: connect-string: 192.168.200.132:2181- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
主启动类:
@SpringBootApplication // 用于服务发现 @EnableDiscoveryClient public class PaymentMain8004 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8004.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
临时节点 Or 持久节点
当 服务 注销之后,Zookeeper 会将该服务删除,并不会向 Eureka 那样有心跳检测机制。
当服务重新开启后, 服务会重新注册进 Zookeeper,并且重新分配一个 ID 号,因此注册到 Zookeeper 中的 服务是一个 临时节点
2.2.2 服务消费者 注入到 Zookeeper 中

- 建 module ---- cloud-consumerzk-order80
- 改 Pom — 和 cloud-provider-payment8004 一样
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
YAML:
server: port: 80 spring: application: name: cloud-consumer-order cloud: #注册到zookeeper地址 zookeeper: connect-string: 192.168.200.132:2181- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Controller:
@RestController public class OrderZkController { // 可使用模块名进行服务区分 public static final String INVOKE_URL = "http://cloud-provider-payment"; @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @RequestMapping("/consumer/payment/zk") public String getPaymentInfo(){ String result = restTemplate.getForObject(INVOKE_URL + "/payment/zk", String.class); return result; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2.3 Consul
简介
Consul 是一套开源的分布式服务发现和配置管理系统,由 HashiCorp 公司用 Go 语言开发。
提供了微服务系统中的服务治理、配置中心、控制总线等功能。这些功能中的每一个都可以根据需要单独使用,也可以一起使用以构建全方位的服务网格,总之Consul提供了一种完整的服务网格解决方案。
它具有很多优点。包括: 基于 raft 协议,比较简洁; 支持健康检查, 同时支持 HTTP 和 DNS 协议 支持跨数据中心的 WAN 集群 提供图形界面 跨平台,支持 Linux、Mac、Windows
Consul 功能:
服务发现 : 提供 HTTP 和 DNS 俩中发现方式
健康检测:支持多种方式,HTTP、TCP
KV 存储:Key、Value 的存储方式
多数据中心
可视化 Web 界面
下载地址:
https://www.consul.io/downloads.html
下载后只有一个 exe 文件,使用 cmd 命令行查看 consul 版本信息:
consul -version- 1
使用开发者模式启动:
consul agent -dev- 1
访问 web 管理界面:
http://localhost:8500
2.3.1 服务提供者注入到 Consul 中
- 建 module ---- cloud-providerconsul-payment8006
- 改 Pom — 只是将 Zookeeper 依赖换成了 Consul
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discoveryartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
YAML:
###consul服务端口号 server: port: 8006 spring: application: name: consul-provider-payment ####consul注册中心地址 cloud: consul: host: localhost port: 8500 discovery: #hostname: 127.0.0.1 service-name: ${spring.application.name}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
启动类、Controller 和 8004 一样,最终启动8006 模块,服务已经注册进去了

2.3.2 服务消费者注入到 Consul 中
- 建 module ---- cloud-consumerconsul-order80
- 改 Pom — 和 服务提供者 一样
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
YAML:
###consul服务端口号 server: port: 80 spring: application: name: cloud-consumer-order ####consul注册中心地址 cloud: consul: host: localhost port: 8500 discovery: #hostname: 127.0.0.1 service-name: ${spring.application.name}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
如果显示 :java.net.UnknownHostException: consul-provider-payment
1、在远程调用时,调用的服务名 和 服务提供者的服务名保持一致

2、在配置 RestTemplate 时,没有加上 @LoadBalanced 注解
2.4 三个注册中心的异同


CAP 理论:
C
Consistency,一致性的意思。
一致性就是说,我们读写数据必须是一摸一样的。
比如一条数据,分别存在两个服务器中,server1和server2。
我们此时将数据a通过server1修改为数据b。此时如果我们访问server1访问的应该是b。
当我们访问server2的时候,如果返回的还是未修改的a,那么则不符合一致性,如果返回的是b,则符合数据的一致性。A
Availability,可用性的意思。
这个比较好理解,就是说,只要我对服务器,发送请求,服务器必须对我进行相应,保证服务器一直是可用的。P
Partition tolerance,分区容错的意思。
一般来说,分布式系统是分布在多个位置的。比如我们的一台服务器在北京,一台在上海。可能由于天气等原因的影响。造成了两条服务器直接不能互相通信,数据不能进行同步。这就是分区容错。我们认为,分区容错是不可避免的。也就是说 P 是必然存在的。CAP 是不能同时存在的,因此要么是 CP 要么是 AP :
因为目前都是基于分布式系统,因此每个模块之间的容错是非常重要的,因此 P 是必须满足的,那么怎么能够减少每个模块之间的错误呢?
就需要把一项数据分别复制到多个节点中,想要对每个节点都进行写操作,对数据的一致性是非常难满足的,就算满足了,也会影响数据的可用性,影响效率。因此 可用性 和 一致性 是不能同时满足的。
三、服务调用
3.1 Ribbon
Ribbon 是什么?
Spring Cloud Ribbon 是基于Netflix Ribbon实现的一套客户端 负载均衡的工具。
简单的说,Ribbon是Netflix发布的开源项目,**主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法和服务调用。**Ribbon客户端组件提供一系列完善的配置项如连接超时,重试等。简单的说,就是在配置文件中列出Load Balancer(简称LB)后面所有的机器,Ribbon会自动的帮助你基于某种规则(如简单轮询,随机连接等)去连接这些机器。我们很容易使用Ribbon实现自定义的负载均衡算法。
Ribbon 能干什么??
LB(负载均衡)
LB负载均衡(Load Balance)是什么
简单的说就是将用户的请求平摊的分配到多个服务上,从而达到系统的HA(高可用)。
常见的负载均衡有软件Nginx,LVS,硬件 F5等。Ribbon本地负载均衡客户端 VS Nginx服务端负载均衡区别
Nginx是服务器负载均衡,客户端所有请求都会交给nginx,然后由nginx实现转发请求。即负载均衡是由服务端实现的。Ribbon本地负载均衡,在调用微服务接口时候,会在注册中心上获取注册信息服务列表之后缓存到JVM本地,从而在本地实现RPC远程服务调用技术。
负载均衡包括:集中式LB、进程内LB
进程内LB
将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选择出一个合适的服务器。
Ribbon就属于进程内LB,它只是一个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址。
集中式LB:
即 在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施 (可以是硬件,如F5, 也可以是软件,如nginx), 由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方。

本质上 Ribbon 就是 负载均衡 + RestTemplate 远程调用
Ribbon其实就是一个软负载均衡的客户端组件,他可以和其他所需请求的客户端结合使用,和eureka结合只是其中的一个实例.

在引入 Eureka 客户端场景时,里面包含了 ribbon 依赖。
RestTemplate 中的 getForObject、getForEntity 、postForObject、postForEntity :
getForObject、getForEntity 发送 Get 请求
postForObject、postForEntity 发送 Post 请求
getForObject、postForObject : 返回对象为响应体中数据转化成的对象,基本上可以理解为 Json
getForEntity 、postForEntity : 返回对象为ResponseEntity对象,包含了响应中的一些重要信息,比如响应头、响应状态码、响应体等
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/getForEntity/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> getForEntity(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ // getForEntity 返回对象是 ResponseEntity 包含了响应中的一些重要信息 ResponseEntity<CommonResult> entity = restTemplate .getForEntity(PAYMENT_URL + "/payment/get/" + id, CommonResult.class); // 判断状态码是否是以 2 开头的 if (entity.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful()){ return entity.getBody(); }else{ return new CommonResult<>(444,"操作失败"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
3.1.1 Ribbon 核心组件 IRule
IRule:根据特定算法中从服务列表中选取一个要访问的服务
修改 RestTemplate 远程调用 各种服务时 采用的 轮询操作
IRule 接口结构图:


Ribbon 负载规则 替换:
注意:
这个自定义配置类不能放在 @ComponentScan 所扫描的当前包下以及子包下,
否则我们自定义的这个配置类就会被所有的Ribbon客户端所共享,达不到特殊化定制的目的了。也就是说,不能在 主程序类 同一包 或者 子包下。

配置类:
@Configuration public class MySelfRule { @Bean public IRule myRule(){ // 随机的负载算法 return new RandomRule(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
主程序类上加上:
// name 表示调用的微服务, configuration 自定义的规则 @RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE",configuration = MySelfRule.class)- 1
- 2
3.1.2 Ribbon 深入理解
Ribbon 默认 负载均衡 算法原理:
rest接口第几次请求数 % 服务器集群总数量 = 实际调用服务器位置下标
每次服务重启动后rest接口计数从 1 开始。
举例:
List instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(“CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE”);
如: List [0] instances = 127.0.0.1:8002
List [1] instances = 127.0.0.1:80018001+ 8002 组合成为集群,它们共计2台机器,集群总数为2, 按照轮询算法原理:
当总请求数为1时: 1 % 2 =1 对应下标位置为1 ,则获得服务地址为 127.0.0.1:8001
当总请求数位2时: 2 % 2 =0 对应下标位置为0 ,则获得服务地址为 127.0.0.1:8002
当总请求数位3时: 3 % 2 =1 对应下标位置为1 ,则获得服务地址为 127.0.0.1:8001
当总请求数位4时: 4 % 2 =0 对应下标位置为0 ,则获得服务地址为 127.0.0.1:8002
如此类推…Ribbon 源码分析:
public RoundRobinRule() { //原子整型值 初始化0 nextServerCyclicCounter = new AtomicInteger(0); } public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { if (lb == null) { log.warn("no load balancer"); return null; } Server server = null; int count = 0; while (server == null && count++ < 10) { // 获取所有可用的服务 List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers(); // 获取所有的服务,包括不可用的 List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers(); int upCount = reachableServers.size(); int serverCount = allServers.size(); if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) { log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb); return null; } // 获取下标 int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount); // 在 list 集合中获取对应下标的服务 server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex); if (server == null) { /* Transient. */ Thread.yield(); continue; } if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) { return (server); } // Next. server = null; } if (count >= 10) { log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " + lb); } return server; } // modulo : 所有的服务。 private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) { for (;;) { // 统计请求的次数 int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get(); int next = (current + 1) % modulo; // 比较并交换 if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next)) // 返回下标 return next; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
手写Ribbon轮询算法:
Ribbon为客户端提供负载均衡服务,首先注释掉@LoadBalanced 注解。
LoadBalancer 接口:
/** * 选取到列表中的某一个服务 * @param instanceList 服务列表 * @return */ ServiceInstance instance(List<ServiceInstance> instanceList);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
MyLB 实现类:
@Component public class MyLB implements LoadBalancer { // 原子整数型 private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0); // 获取访问的次数 private int incrementAndGetModulo() { int current; int next; do { current = this.atomicInteger.get(); next = current >= 2147483647 ? 0 : current + 1; // compareAndSet 比较并且转换, 将 current 转换成 next 值 } while (!this.atomicInteger.compareAndSet(current, next)); System.out.println("****** 第几次访问,next: " + next); return next ; } /** * * @param instanceList 服务列表 * @return 返回具体的服务 */ @Override public ServiceInstance instance(List<ServiceInstance> instanceList) { int index = incrementAndGetModulo() % instanceList.size(); return instanceList.get(index); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
OrderController:
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/lb") public String getLB(){ // 获取所有的服务 List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE"); if (instances == null || instances.size() == 0){ return null ; } // 通过自定义的轮询算法 获取到服务的具体实例 ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancer.instance(instances); URI uri = instance.getUri(); return restTemplate.getForObject(uri + "/payment/lb",String.class); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
3.2 OpenFeign
**官网:**https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign
Spring 社区: Spring Cloud OpenFeign
Feign 是一个声明式的Web服务客户端,让编写Web服务客户端变得非常容易,只需创建一个接口并在接口上添加注解即可
Feign旨在使编写 Java Http 客户端变得更容易。
前面在使用Ribbon+RestTemplate时,利用RestTemplate对http请求的封装处理,形成了一套模版化的调用方法。**但是在实际开发中,由于对服务依赖的调用可能不止一处,往往一个接口会被多处调用,所以通常都会针对每个微服务自行封装一些客户端类来包装这些依赖服务的调用。**所以,Feign在此基础上做了进一步封装,由他来帮助我们定义和实现依赖服务接口的定义。在 Feign 的实现下,我们只需创建一个接口并使用注解的方式来配置它 ( 以前是Dao接口上面标注Mapper注解,现在是一个微服务接口上面标注一个Feign注解即可),即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定,简化了使用Spring cloud Ribbon时,自动封装服务调用客户端的开发量。Feign集成了Ribbon 利用Ribbon维护了Payment的服务列表信息,并且通过轮询实现了客户端的负载均衡。而与Ribbon不同的是,通过feign只需要定义服务绑定接口且以声明式的方法,优雅而简单的实现了服务调用

OpenFeign 使用步骤:
OpenFeign 使用在消费端,在微服务调用接口中增加注解:@FeignClient,value 属性指明服务名
- 建 module ----cloud-consumer-feign-order80
- 改 Pom — 增加 OpenFeign的依赖
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
Pom:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeignartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId> <version>${project.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
YAML:
server: port: 80 eureka: client: # 不将自己注入到 服务中心 register-with-eureka: false service-url: # 注入到 eureka 集群中去 defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
主启动类:
使用哪个服务,就在主启动类上增加 @Enable… 这样的注解,OpenFeign 也不例外。
@SpringBootApplication // 开启Feign 服务 @EnableFeignClients public class OrderFeignMain { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderFeignMain.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
业务接口类:
该接口类与 服务提供者中的 Controller 相对应
@Component // 使用 Feign,指定调用的服务名 @FeignClient(value = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE") public interface PaymentFeignService { /** * 根据 ID 查询 * @param id * @return */ @GetMapping("/payment/get/{id}") // 向服务接口发送请求 CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13

Controller 层:
@RestController public class OrderFeignController { @Autowired private PaymentFeignService paymentFeignService; @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/get/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id")Long id){ return paymentFeignService.getPaymentById(id); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
使用 OpenFeign:
1、引入依赖
2、在主程序类上使用 @EnableFeignClients 注解 激活 OpenFeign
3、在service 层 使用 @FeignClient 注解使用 OpenFeign
Open Feign 更符合我们的编码习惯,还是 Controller 层调用 Service 层 ,只不过 Service 层需要调用远程服务的方法。。
3.2.1 OpenFeign 的超时控制
超时控制:
默认Feign客户端只等待一秒钟,但是服务端处理需要超过1秒钟,导致Feign客户端不想等待了,直接返回报错。
为了避免这样的情况,有时候我们需要设置Feign客户端的超时控制。演示超时控制:
服务提供方8001
/** * 演示 OpenFeign 服务提供方超时 * @return */ @GetMapping("/payment/feign/timeOut") public String PaymentFeignTimeOut(){ try { // 暂停 4S TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return serverPort; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
消费方80:
Service 层: /** * 演示 OpenFeign 超时控制 * @return */ @GetMapping("/payment/feign/timeOut") public String PaymentFeignTimeOut();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Controller层: /** *演示OpenFeign的超时控制 * @return */ @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/feign/timeOut") public String PaymentFeignTimeOut(){ return paymentFeignService.PaymentFeignTimeOut(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
由于调用服务时等待的时间超过了 1s ,Open Feign 自动报错:

OpenFeign 开启超时控制:
#设置feign客户端超时时间(OpenFeign默认支持ribbon) ribbon: #指的是建立连接所用的时间,适用于网络状况正常的情况下,两端连接所用的时间 ReadTimeout: 5000 #指的是建立连接后从服务器读取到可用资源所用的时间 ConnectTimeout: 5000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.2.2 OpenFeign 的日志打印功能
Feign 提供了日志打印功能,我们可以通过配置来调整日志级别,从而了解 Feign 中 Http 请求的细节。
说白了就是对Feign接口的调用情况进行监控和输出NONE:默认的,不显示任何日志;
BASIC:仅记录请求方法、URL、响应状态码及执行时间;
HEADERS:除了 BASIC 中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的头信息;
FULL:除了 HEADERS 中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的正文及元数据。
配置类:
@Configuration public class FeignConfig { /** * 开启 Feign 的日志 * @return */ @Bean Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() { return Logger.Level.FULL; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
在 YAML 中开启日志:
logging: level: # feign日志以什么级别监控哪个接口 -- 接口全类名 com.atguigu.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

四、服务降级
4.1 Hystrix
官网:
How To Use · Netflix/Hystrix Wiki · GitHub
Hystrix 已经停止更新进行维护当中
目前分布式系统面临的问题:
复杂分布式体系结构中的应用程序有数十个依赖关系,每个依赖关系在某些时候将不可避免地失败

服务雪崩
多个微服务之间调用的时候,假设微服务A调用微服务B和微服务C,微服务B和微服务C又调用其它的微服务,这就是所谓的 “扇出”。如果扇出的链路上某个微服务的调用响应时间过长或者不可用,对微服务A的调用就会占用越来越多的系统资源,进而引起系统崩溃,所谓的“雪崩效应”.
对于高流量的应用来说,单一的后端依赖可能会导致所有服务器上的所有资源都在几秒钟内饱和。比失败更糟糕的是,这些应用程序还可能导致服务之间的延迟增加,备份队列,线程和其他系统资源紧张,导致整个系统发生更多的级联故障。这些都表示需要对故障和延迟进行隔离和管理,以便单个依赖关系的失败,不能取消整个应用程序或系统。
所以,
通常当你发现一个模块下的某个实例失败后,这时候这个模块依然还会接收流量,然后这个有问题的模块还调用了其他的模块,这样就会发生级联故障,或者叫雪崩。Hystrix 是什么?
Hystrix 是一个用于 处理分布式系统的延迟和容错 的开源库,在分布式系统里,许多依赖不可避免的会调用失败,比如超时、异常等,Hystrix能够保证在一个依赖出问题的情况下,不会导致整体服务失败,避免级联故障,以提高分布式系统的弹性。
“断路器”本身是一种开关装置,当某个服务单元发生故障之后,通过断路器的故障监控(类似熔断保险丝),向调用方返回一个符合预期的、可处理的备选响应(FallBack),而不是长时间的等待或者抛出调用方无法处理的异常,这样就保证了服务调用方的线程不会被长时间、不必要地占用,从而避免了故障在分布式系统中的蔓延,乃至雪崩。
重要的概念:
服务降级:
服务器忙,请稍后再试,不让客户端等待并立刻返回一个友好提示,fallback
哪些情况下会发生服务降级,这四种情况都会由 fallback 处理:
- 程序运行异常
- 超时
- 服务熔断触发服务降级
- 线程池/信号量打满也会导致服务降级
服务熔断:
服务熔断会导致服务降级,但是和服务降级的区别就是服务熔断会恢复调用链路。
在互联网系统中,当下游服务因访问压力过大而响应变慢或失败,上游服务为了保护系统整体的可用性,可以暂时切断对下游服务的调用。 这种牺牲局部,保全整体的措施就叫做熔断。

一旦下游服务C因某些原因变得不可用,积压了大量请求,服务B的请求线程也随之阻塞。线程资源逐渐耗尽,使得服务B也变得不可用。紧接着,服务 A也变为不可用,整个调用链路被拖垮。
因此,需要服务熔断来确保整个系统的可用性
1. 开启熔断 在固定时间窗口内,接口调用超时比率达到一个阈值,会开启熔断。 进入熔断状态后,后续对该服务接口的调用不再经过网络,直接执行本地的默认方法,达到服务降级的效果。 2. 熔断恢复 熔断不可能是永久的。 当经过了规定时间之后,服务将从熔断状态回复过来,再次接受调用方的远程调用。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
服务限流:
秒杀高并发等操作,严禁一窝蜂的过来拥挤,大家排队,一秒钟N个,有序进行
构建支付模块:
- 建 module ----cloud-provider-hystrix-payment8001
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML
- 主启动 — 增加 @EnableEurekaClient 注解
- 业务类
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrixartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId> <version>${project.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
YAML:
server: port: 8001 spring: application: name: cloud-provider-hystrix-payment eureka: client: register-with-eureka: true fetch-registry: true service-url: #defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
注解类:
@Component public class PaymentService { /** * 正常 * @param id * @return */ public String paymentInfo_OK(Integer id){ return "线程池: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " paymentInfo_OK, id: " + id + "O(∩_∩)O哈哈~"; } /** * 超时 * @param id * @return */ public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(Integer id){ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "线程池: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " paymentInfo_TimeOut, id: " + id + "耗时3S"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
Controller 层 :
@RestController @Slf4j public class PaymentController { @Autowired private PaymentService paymentService; @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort ; @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}") public String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_OK(id); log.info("****info:" + result); return result; } @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/TimeOut/{id}") public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ String result = paymentService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id); log.info("****info:" + result); return result; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
当使用 Jmeter 对TimeOut进行压力测试,发现 ok 方法也变慢了,这是因为俩个方法都在一个服务内,当 TimeOut 有大量的请求时,会占满 Tomcat 的线程数,会集中大量的效率在 TimeOut 上。
这还仅仅是 服务提供者 进行自测,如果加上消费者,速度会更慢。
构建消费模块:
- 建 module ---- cloud-consumer-feign-hystrix-order80
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML
- 主启动 — // 激活 OpenFeign @EnableFeignClients
- 业务类
业务接口 + @FeignClient
@Component @FeignClient(value = "CLOUD-PROVIDER-HYSTRIX-PAYMENT") public interface PaymentHystrixService { @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}") String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id")Integer id); @GetMapping("/payment/hystrix/TimeOut/{id}") public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id")Integer id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Controller 层:
@RestController @Slf4j public class OrderHystrixController { @Autowired private PaymentHystrixService paymentHystrixService; @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}") String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ return paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_OK(id); } @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/TimeOut/{id}") public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ return paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
当我们增加一个消费者的时候,再去对 服务提供者的 TimeOut 方法进行压测,消费者再去访问时,会发现异常的慢,并且还可能会出现 超时控制。
正因为有上述故障或不佳表现 才有我们的降级/容错/限流等技术诞生
如何解决? 解决的要求?
- 超时导致服务器变慢(转圈)
- 超时不再等待
- 出错(宕机或程序运行出错)
- 出错要有兜底
- 对方服务(8001)超时了,调用者(80)不能一直卡死等待,必须有服务降级
- 对方服务(8001)down机了,调用者(80)不能一直卡死等待,必须有服务降级
- 对方服务(8001)OK,调用者(80)自己出故障或有自我要求(自己的等待时间小于服务提供者),自己处理降级
服务降级
降级配置:@HystrixCommand
1、先从 8001 服务提供方 进行服务降级:
设置自身调用超时时间的峰值,峰值内可以正常运行,超过了需要有兜底的方法处理,作服务降级fallback
/** * 超时 * * @param id * @return fallbackMethod : 设置兜底的处理方法 */ @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "paymentInfo_TimeOutHandler", commandProperties = { // 设置自身调用超时的时间峰值,超过这个时间使用兜底方法 paymentInfo_TimeOutHandler @HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds", value = "3000") }) public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(Integer id) { // try { // //TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); // } catch (Exception e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // 不管是服务超时 还是运行异常 都能由 fallback 进行处理 int age = 10 / 0; return "线程池: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " paymentInfo_TimeOut, id: " + id + "耗时3S"; } /** * fallback 兜底的方法 * * @return */ public String paymentInfo_TimeOutHandler(Integer id) { return "线程池: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 系统繁忙或者运行报错,请稍后再试, id: " + id + "╮(╯▽╰)╭"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
注意:
需要在主程序类上激活 :@EnableCircuitBreaker // 激活服务降级
**第一种方式:**为每一个远程调用的方法提供一个fallback方法
2、从消费端 80 进行服务降级:
YAML中开启 Hystrix :
# 开启 Hystrix feign: hystrix: enabled: true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
主程序类上增加注解:
// 开启Hystrix @EnableHystrix- 1
- 2
Controller 层:
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/TimeOut/{id}") // 服务降级 @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "paymentTimeOutFallbackMethod",commandProperties = { // 设置超时时间,超过1.5s 执行 兜底方法 fallback @HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value="1500") }) public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { return paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id); } public String paymentTimeOutFallbackMethod(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { return "我是消费者80,对方支付系统繁忙请10秒钟后再试或者自己运行出错请检查自己,o(╥﹏╥)o"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
目前存在的问题:
每个业务方法对应一个兜底的方法,代码膨胀
统一和自定义的分开
第二种方式: 使用 @DefaultProperties (defaultFallback = “”) 在 Controller 层 提供一个统一的 fallback 方法。
解决问题:
@DefaultProperties (defaultFallback = “”)
1:1 每个方法配置一个服务降级方法,技术上可以,实际上傻X
1:N 除了个别重要核心业务有专属,其它普通的可以通过 @DefaultProperties(defaultFallback = “”) 统一跳转到统一处理结果页面
@RestController @Slf4j // 全局的 fallback @DefaultProperties(defaultFallback = "payment_Global_FallbackMethod") public class OrderHystrixController { @Autowired private PaymentHystrixService paymentHystrixService; @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/ok/{id}") String paymentInfo_OK(@PathVariable("id")Integer id){ return paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_OK(id); } @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/hystrix/TimeOut/{id}") // 使用统一的服务降级 @HystrixCommand public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { return paymentHystrixService.paymentInfo_TimeOut(id); } public String paymentTimeOutFallbackMethod(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { return "我是消费者80,对方支付系统繁忙请10秒钟后再试或者自己运行出错请检查自己,o(╥﹏╥)o"; } /** * 处理全局的 fallback * @param id * @return */ public String payment_Global_FallbackMethod() { return "Global异常处理信息,请稍后再试,/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
虽然现在有了 @DefaultProperties 注解可以配置统一的 fallback,但是 Hystrix 代码与 Controller 混淆 显得很混乱。
**第三种方式:**利用远程调用微服务的接口,配置通用的 fallback
新建一个类实现远程调用微服务的接口
@Component public class PaymentFallbackService implements PaymentHystrixService{ @Override public String paymentInfo_OK(Integer id) { return "PaymentFallbackService --- paymentInfo_OK --- o(╥﹏╥)o"; } @Override public String paymentInfo_TimeOut(Integer id) { return "PaymentFallbackService --- paymentInfo_TimeOut --- o(╥﹏╥)o"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
在接口中指明该实现类:

注意:
前提是需要在 YAML 中开启 Hystrix
# 开启 Hystrix feign: hystrix: enabled: true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
服务熔断
熔断机制概述
熔断机制是应对雪崩效应的一种微服务链路保护机制。当扇出链路的某个微服务出错不可用或者响应时间太长时,会进行服务的降级,进而熔断该节点微服务的调用,快速返回错误的响应信息。
当检测到该节点微服务调用响应正常后,恢复调用链路。在Spring Cloud框架里,熔断机制通过Hystrix实现。Hystrix会监控微服务间调用的状况,
当失败的调用到一定阈值,缺省是5秒内20次调用失败,就会启动熔断机制。熔断机制的注解是**@HystrixCommand。**断路器的三个参数介绍:
circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds断路器的快照时间窗,也叫做窗口期。可以理解为一个触发断路器的周期时间值,默认为5秒(5000)。
这个参数大家应该不陌生,但是网上对他的解释有两种,**一种是说在这个时间内如果发生断路的请求数超过了设置数则会熔断;另一种是说如果发生了熔断,那么在这个时间后会成为半开状态。**其实以上两种都对,因为这两个时间都是一个窗口期
circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold断路器的窗口期内触发断路的请求阈值,默认为20。
当一个窗口期超过了20之后,则去看下面那个参数能够容忍的百分比阈值是否超过,若超过则熔断。假如某个窗口期内的请求总数都不到该配置值,那么断路器连发生的资格都没有。断路器在该窗口期内将不会被打开。circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage断路器的窗口期内能够容忍的错误百分比阈值,默认为50(也就是说默认容忍50%的错误率)。
假如一个窗口期内,发生了100次服务请求,其中50次出现了错误。在这样的情况下,断路器将会被打开。在下个窗口期结束之前,即使是之前可以正确访问得,也将被执行fallback逻辑。Service 层:
很简单的一个逻辑,正数成功,负数抛异常
// ===================================== 服务无熔断 @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "paymentCircuitBreaker_fallback", commandProperties = { // 是否开启断路器 @HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.enabled", value = "true"), // 请求次数 @HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold", value = "10"), // 时间窗口期 @HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds", value = "10000"), // 失败率达到多少后跳闸 @HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage", value = "60"), }) public String paymentCircuitBreaker(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { if (id < 0) { throw new RuntimeException("******id 不能负数"); } // 随机生成 UUID String serialNumber = IdUtil.simpleUUID(); return Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "调用成功,流水号: " + serialNumber; } public String paymentCircuitBreaker_fallback(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { return "id 不能负数,请稍后再试,/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~ id: " + id; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
@HystrixProperty 中的配置都在 HystrixCommandProperties 这个抽象类里。
Controller 层:
// =========================== 服务熔断 @GetMapping("/payment/circuit/{id}") public String paymentCircuitBreaker(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { String result = paymentService.paymentCircuitBreaker(id); log.info("****result: " + result); return result; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
当在一个时间窗口内,失败请求次数达到了 失败率,就会启动 断路器,也就是说一旦启动之后,就算输入正确,该服务也是无法使用的。

断路器开启或者关闭的条件:
- 当满足一定的阀值的时候(默认10秒内超过20个请求次数)
- 当失败率达到一定的时候(默认10秒内超过50%的请求失败)
- 到达以上阀值,断路器将会开启
- 当开启的时候,所有请求都不会进行转发
- 一段时间之后(默认是5秒),这个时候断路器是半开状态,会让其中一个请求进行转发。
如果成功,断路器会关闭,若失败,继续开启。重复4和5
服务限流后面讲解 !!!!!
工作原理

官网给出的步骤:
-
Construct a
HystrixCommandorHystrixObservableCommandObject构造一个 HystrixCommand 或 HystrixObservableCommand 对象
-
执行命令
-
响应是否缓存
-
断路器是否打开
-
Is the Thread Pool/Queue/Semaphore Full?
线程池/队列/信号量是否已满?
-
HystrixObservableCommand.construct()orHystrixCommand.run()HystrixObservableCommand.construct() 或 HystrixCommand.run()
-
计算电路健康
-
执行 fallback
-
Return the Successful Response
响应
服务监控hystrixDashboard
构建支付模块:
- 建 module ----cloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard9001
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML ---- 只需配置 9001 端口
- 主启动
- 业务类
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboardartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
主启动:
@SpringBootApplication // 开启 Hystrix 图形化界面 @EnableHystrixDashboard public class DashboardMain9001 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DashboardMain9001.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
被监控的服务需要有这个依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
启动访问: http://localhost:9001/hystrix

监控 8001 :
注意:新版 Hystrix 需要在 8001的主程序类中增加一个配置
/** *此配置是为了服务监控而配置,与服务容错本身无关,springcloud升级后的坑 *ServletRegistrationBean因为springboot的默认路径不是"/hystrix.stream", *只要在自己的项目里配置上下面的servlet就可以了 */ @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet() { HystrixMetricsStreamServlet streamServlet = new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet(); ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(streamServlet); registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1); registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/hystrix.stream"); registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet"); return registrationBean; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
如果不增加以上配置会报错:Unable to connect to Command Metric Stream
在 Hystrix 图形界面填写 监控地址:http://localhost:8001/hystrix.stream
断路器关闭:

断路器打开:

**实心圆:**共有两种含义。它通过颜色的变化代表了实例的健康程度,它的健康度从绿色<黄色<橙色<红色递减。
该实心圆除了颜色的变化之外,它的大小也会根据实例的请求流量发生变化,流量越大该实心圆就越大。所以通过该实心圆的展示,就可以在大量的实例中快速的发现故障实例和高压力实例。**曲线:**用来记录2分钟内流量的相对变化,可以通过它来观察到流量的上升和下降趋势。


五、服务网关
5.1 Gateway
Spring社区: Spring Cloud Gateway
基本介绍
Gateway是在Spring生态系统之上构建的API网关服务,基于
Spring 5,Spring Boot 2和Project Reactor等技术。
Gateway旨在提供一种简单而有效的方式来对API进行路由,以及提供一些强大的过滤器功能, 例如:熔断、限流、重试等SpringCloud Gateway 使用的Webflux中的reactor-netty响应式编程组件,底层使用了Netty通讯框架。
SpringCloud Gateway 作为 Spring Cloud 生态系统中的网关,目标是替代 Zuul,在Spring Cloud 2.0以上版本中,没有对新版本的Zuul 2.0以上最新高性能版本进行集成,仍然还是使用的Zuul 1.x非Reactor模式的老版本。而为了提升网关的性能,SpringCloud Gateway是基于
WebFlux框架实现的,而WebFlux框架底层则使用了高性能的Reactor模式通信框架Netty。Spring Cloud Gateway的目标提供统一的路由方式且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/指标,和限流。
微服务系统中 网关的位置:

有 Zuul 为什么使用 Gateway ?
- 一方面因为Zuul1.0已经进入了维护阶段,而且Gateway是 SpringCloud 团队研发的,是亲儿子产品,值得信赖。而且很多功能Zuul都没有用起来也非常的简单便捷。
- Gateway是基于异步非阻塞模型上进行开发的,性能方面不需要担心。虽然Netflix早就发布了最新的 Zuul 2.x,但 Spring Cloud 貌似没有整合计划。而且Netflix相关组件都宣布进入维护期;不知前景如何?
- Zuul 1.x 基于 Servlet 2. 5 使用阻塞架构它不支持任何长连接(如 WebSocket) Zuul 的设计模式和Nginx较像,每次 I/ O 操作都是从工作线程中选择一个执行,请求线程被阻塞到工作线程完成,但是差别是Nginx 用C++ 实现,Zuul 用 Java 实现,而 JVM 本身会有第一次加载较慢的情况,使得Zuul 的性能相对较差。
- Spring Cloud Gateway 建立 在 Spring Framework 5、 Project Reactor 和 Spring Boot 2 之上, 使用非阻塞 API。
- Spring Cloud Gateway 还 支持 WebSocket, 并且与Spring紧密集成拥有更好的开发体验
Gateway 中的概念:
- **Route 路由:**路由是构建网关的基本模块,它由ID,目标URI,一系列的断言和过滤器组成,如果断言为true则匹配该路由
- **Predicate(断言) :**参考的是Java8的java.util.function.Predicate
开发人员可以匹配HTTP请求中的所有内容(例如请求头或请求参数),如果请求与断言相匹配则进行路由 - **Filter (过滤):**指的是Spring框架中GatewayFilter的实例,使用过滤器,可以在请求被路由前或者之后对请求进行修改。

web请求,通过一些匹配条件,定位到真正的服务节点。并在这个转发过程的前后,进行一些精细化控制。
predicate就是我们的匹配条件;
而 filter,就可以理解为一个无所不能的拦截器。有了这两个元素,再加上目标uri,就可以实现一个具体的路由了工作流程

-
客户端向 Spring Cloud Gateway 发出请求。然后在 Gateway Handler Mapping 中找到与请求相匹配的路由,将其发送到 Gateway Web Handler。
-
Handler 再通过指定的过滤器链来将请求发送到我们实际的服务执行业务逻辑,然后返回。
过滤器之间用虚线分开是因为过滤器可能会在发送代理请求之前(“pre”)或之后(“post”)执行业务逻辑。 -
Filter在“pre”类型的过滤器可以做参数校验、权限校验、流量监控、日志输出、协议转换等,
在“post”类型的过滤器中可以做响应内容、响应头的修改,日志的输出,流量监控等有着非常重要的作用。
配置 Gateway
构建网关模块:
- 建 module ---- cloud-gateway-gateway9527
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
POM:
注意: spring-cloud-starter-gateway 依赖不要和 spring-boot-starter-web 和 spring-boot-starter-actuator 一起用,否则会报错
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gatewayartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId> <artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId> <version>${project.version}version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
YAML:
server: port: 9527 spring: application: name: cloud-gateway cloud: gateway: # 可以配置多个路由 routes: #路由的ID,没有固定规则但要求唯一,建议配合服务名 - id: payment_routh #payment_route #匹配后提供服务的路由地址 uri: http://localhost:8001 predicates: # ** 通配符 - Path=/payment/get/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由 #路由的ID,没有固定规则但要求唯一,建议配合服务名 - id: payment_routh2 #payment_route #匹配后提供服务的路由地址 uri: http://localhost:8001 predicates: # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由 - Path=/payment/lb/** eureka: instance: hostname: cloud-gateway-service client: #服务提供者provider注册进eureka服务列表内 service-url: register-with-eureka: true fetch-registry: true # 注册到 eureka 服务中心 defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
主启动类:
@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient public class GatewayMain9527 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(GatewayMain9527.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
配置网关前访问 8001 :
配置网关后:
类似于Nginx 的反向代理
Gateway 配置的俩种方式:
- 第一种:上面那种YAML 中进行配置
- 第二种:代码中注入RouteLocator的Bean
/** * 路由 ID :path_route_atguigu * 通过访问 9527 的 /guonei 路径 跳转到 http://news.baidu.com/guonei * @param builder * @return */ @Bean public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) { RouteLocatorBuilder.Builder routes = builder.routes(); routes.route("path_route_atguigu", r -> r.path("/guonei") .uri("http://news.baidu.com/guonei")).build(); return routes.build(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
Gateway 实现动态路由
默认情况下Gateway会根据注册中心注册的服务列表,以注册中心上微服务名为路径创建动态路由进行转发,从而实现动态路由的功能 达到一种负载均衡

9527 YAML 中配置:
spring: application: name: cloud-gateway cloud: gateway: discovery: locator: enabled: true #开启从注册中心动态创建路由的功能,利用微服务名进行路由 routes: - id: payment_routh # uri: http://localhost:8001 uri: lb://cloud-payment-service #匹配后提供服务的路由地址 predicates: - Path=/payment/get/** - id: payment_routh2 # uri: http://localhost:8001 uri: lb://cloud-payment-service # lb 负载均衡 + 服务名【小写】 predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/**- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
Gateway 常用 Predicate
启动网关模块 9527

RoutePredicateFactory 是什么?
Spring Cloud Gateway将路由匹配作为Spring WebFlux HandlerMapping基础架构的一部分。
Spring Cloud Gateway包括许多内置的 RoutePredicate工厂。所有这些Predicate都与HTTP请求的不同属性匹配。多个Route Predicate工厂可以进行组合Spring Cloud Gateway 创建 Route 对象时, 使用 RoutePredicateFactory 创建 Predicate 对象,Predicate 对象可以赋值给 Route。 Spring Cloud Gateway 包含许多内置的Route Predicate Factories。
所有这些谓词都匹配HTTP请求的不同属性。多种谓词工厂可以组合,并通过逻辑and。
简单来说 RoutePredicateFactory 里内置很多了断言方式,根据不同的方式匹配 路由进行转发
-
After Route Predicate
-
在指定的某个时间之后进行路由。
-
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - After=2020-02-05T15:10:03.685+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]- 1
- 2
- 3
-
- 时间串可通过 `ZonedDateTime zbj = ZonedDateTime.now();` 获取 - **Before Route Predicate** - 在指定的时间之前进行路由 - ```yaml predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Before=2020-02-05T15:10:03.685+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
-
Between Route Predicate
-
在俩个时间段之间进行路由,时间用 , 分开
-
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Between=2020-02-02T17:45:06.206+08:00[Asia/Shanghai],2020-03-25T18:59:06.206+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]- 1
- 2
- 3
-
- **Cookie Route Predicate** - Cookie Route Predicate需要两个参数,一个是 **Cookie name** ,一个是**正则表达式**。 路由规则会通过获取对应的 Cookie name 值和正则表达式去匹配,如果匹配上就会执行路由,如果没有匹配上则不执行 - ```yaml predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Cookie=username,yzg- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
-
使用 CMD 命令行 curl 访问:
- 不带 Cookie 访问:curl http://localhost:9527/payment/lb
- 带上 Cookie 访问:curl http://localhost:9527/payment/lb --cookie “username=yzg’”
-
Header Route Predicate
-
根据请求头,两个参数:一个是属性名称和一个正则表达式,这个属性值和正则表达式匹配则执行。
-
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进 - Header=X-Request-Id, \d+ # 请求头要有X-Request-Id属性并且值为整数的正则表达式- 1
- 2
- 3
-
- curl 测试: curl http://localhost:9527/payment/lb -H "X-Request-Id:123" - **Host Route Predicate** - Host Route Predicate 接收一组参数,一组匹配的域名列表,这个模板是一个 ant 分隔的模板,用 . 号作为分隔符。 它通过参数中的主机地址作为匹配规则。 - ```yaml predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Host=**.atguigu.com- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
-
Method Route Predicate
-
通过请求方式:GET、POST
-
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Method=GET- 1
- 2
- 3
-
- **Path Route Predicate** - 根据请求路径 - **Query Route Predicate** - 支持传入两个参数,一个是属性名,一个为属性值,属性值可以是正则表达式。 - ```yml predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Query=username, \d+ # 要有参数名username并且值还要是整数才能路由- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
说白了,Predicate就是为了实现一组匹配规则,让请求过来找到对应的Route进行处理。
不符合断言报错:

Filter 的使用
路由过滤器可用于修改进入的HTTP请求和返回的 HTTP 响应,路由过滤器只能指定路由进行使用。
Spring Cloud Gateway 内置了多种路由过滤器,他们都由GatewayFilter的工厂类来产生
生命周期: pre、Post
**种类:**GatewayFilter 、GlobalFilter
官方提供的过滤器种类非常多,有需要再去用: Spring Cloud Gateway
最常用的还是自定义过滤器’
自定义过滤器:
实现俩个接口:
Ordered, GlobalFilter@Component @Log4j2 public class MyLogGatewayFilter implements Ordered, GlobalFilter { @Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) { log.info("======== welcome to MyLogGatewayFilter"); // 获取参数 String age = exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("age"); if (age == null){ // 拒绝访问 exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE); // setComplete 表示设置完成 return exchange.getResponse().setComplete(); } return chain.filter(exchange); } /** * 返回优先级,数字越低 优先级越高 * @return */ @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
访问:
http://localhost:9527/payment/lb?age=22 √
http://localhost:9527/payment/lb 拒绝访问
六、服务配置
6.1 config
目前分布式系统存在的问题:
微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务。由于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能运行,所以一套集中式的、动态的配置管理设施是必不可少的。
SpringCloud提供了ConfigServer来解决这个问题,我们每一个微服务自己带着一个application.yml,上百个配置文件的管理…
/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~
是什么
SpringCloud Config为微服务架构中的微服务提供集中化的外部配置支持,配置服务器为各个不同微服务应用的所有环境提供了一个中心化的外部配置。
怎么玩
SpringCloud Config分为服务端和客户端两部分。服务端也称为分布式配置中心,它是一个独立的微服务应用,用来连接配置服务器并为客户端提供获取配置信息,加密/解密信息等访问接口客户端则是通过指定的配置中心来管理应用资源,以及与业务相关的配置内容,并在启动的时候从配置中心获取和加载配置信息配置服务器默认采用git来存储配置信息,这样就有助于对环境配置进行版本管理,并且可以通过git客户端工具来方便的管理和访问配置内容。能干嘛
- 集中管理配置文件
- 不同环境不同配置,动态化的配置更新,分环境部署比如dev/test/prod/beta/release
- 运行期间动态调整配置,不再需要在每个服务部署的机器上编写配置文件,服务会向配置中心统一拉取配置自己的信息
- 当配置发生变动时,服务不需要重启即可感知到配置的变化并应用新的配置
- 将配置信息以REST接口的形式暴露
Github 创建本地仓库 springcloud-config
创建 模块为 ConfigServer,服务端
- 建 module ---- cloud-config-center-3344
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-config-serverartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
YAML:
server: port: 3344 spring: application: name: cloud-config-center #注册进Eureka服务器的微服务名 cloud: config: server: git: uri: https://github.com/yangzhaoguang/springcloud-config.git #GitHub上面的git仓库名字 username: 994887644@qq.com password: q1209694409 ####搜索目录 search-paths: - springcloud-config ####读取分支 default-label: main #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
主启动:
@SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigServer @EnableEurekaClient public class ConfigCenterMain3344 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigCenterMain3344.class,args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
github 配置文件命名:严格遵守官网的规则
{name}-{profiles}.yml
label:分支(branch)
name :服务名
profiles:环境(dev/test/prod)访问规则:
- /{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
- /{application}-{profile}.yml
- /{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
ConfigClient 客户端模块:
新建cloud-config-client-3355
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-configartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
配置配文件不再是 application.yaml 而是 bootstrap.yaml
applicaiton.yml 是用户级的资源配置项
bootstrap.yml 是系统级的,优先级更加高Spring Cloud会创建一个“Bootstrap Context”,作为Spring应用的
Application Context的父上下文。初始化的时候,Bootstrap Context负责从外部源加载配置属性并解析配置。这两个上下文共享一个从外部获取的Environment。Bootstrap属性有高优先级,默认情况下,它们不会被本地配置覆盖。Bootstrap context和Application Context有着不同的约定,所以新增了一个bootstrap.yml文件,保证Bootstrap Context和Application Context配置的分离。要将 Client 模块下的application.yml文件改为 bootstrap.yml, 这是很关键的,
因为 bootstrap.yml 是比application.yml先加载的。bootstrap.yml优先级高于application.yml主启动类: @EnableEurekaClient + @SpringBootApplication
BootStrap.yaml:
server: port: 3355 spring: application: name: config-client cloud: #Config客户端配置 config: label: main #分支名称 name: config #配置文件名称 profile: dev #读取后缀名称 # 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址k #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
Controller 层:
@RestController public class ConfigClientController { // 该配置是 3344 从 github 上的 config-dev.yaml 配置文件读取的 @Value("${config.info}") private String configInfo; @GetMapping("/configInfo") public String getConfigInfo() { return configInfo; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
访问:http://localhost:3355/configInfo
当修改 GitHub 上的配置文件,3344 能够做到实时响应,但是3355需要重启才能获取到,每次修改配置文件,客户端都需要重启,那也太麻烦了。。。。
客户端动态刷新
POM:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
YAML:
# 暴露监控端点 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Controller 层: 增加 @RefreshScope 注解
但是这样,3355 还是做不到实时刷新,还需要发送一条 POST 请求。
curl -X POST “http://localhost:3355/actuator/refresh”
并且每次 配置文件更新后,都需要发送这样一条请求。
这样如果有很多个 客户端,其实就很麻烦了,当然可以写个脚本,依次执行所有,但是可以利用消息广播,一次通知,处处生效,因此需要下面的 消息总线 !!!
七、消息总线
Spring Cloud Bus 配合 Spring Cloud Config 使用可以实现配置的动态刷新。
7.1 Bus
是什么
Spring Cloud Bus 是用来将分布式系统的节点与轻量级消息系统链接起来的框架,
**它整合了 Java 的事件处理机制和消息中间件的功能。**Spring Cloud Bus目前支持RabbitMQ和Kafka。能干啥
Spring Cloud Bus能管理和传播分布式系统间的消息,就像一个分布式执行器,可用于广播状态更改、事件推送等,也可以当作微服务间的通信通道。
什么是总线
在微服务架构的系统中,通常会使用轻量级的消息代理来构建一个共用的消息主题,并让系统中所有微服务实例都连接上来。由于该主题中产生的消息会被所有实例监听和消费,所以称它为消息总线。在总线上的各个实例,都可以方便地广播一些需要让其他连接在该主题上的实例都知道的消息。基本原理
ConfigClient实例都监听MQ中同一个topic(默认是springCloudBus)。当一个服务刷新数据的时候,它会把这个信息放入到Topic中,这样其它监听同一Topic的服务就能得到通知,然后去更新自身的配置。新建 3366 模块:
- 建 module ---- cloud-config-client-3366
- 改 Pom
- 写 YML
- 主启动
- 业务类
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-configartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
YAML:
server: port: 3366 spring: application: name: config-client cloud: #Config客户端配置 config: label: main #分支名称 name: config #配置文件名称 profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址 #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka # 暴露监控端点 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
Controller 层:
@RestController public class ConfigClientController { @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort; @Value("${config.info}") private String configInfo; @GetMapping("/configInfo") public String configInfo() { return "serverPort: " + serverPort + "\t\n\n configInfo: " + configInfo; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
动态刷新配置文件的俩种设计思想:
1)利用消息总线触发一个客户端/bus/refresh,而刷新所有客户端的配置
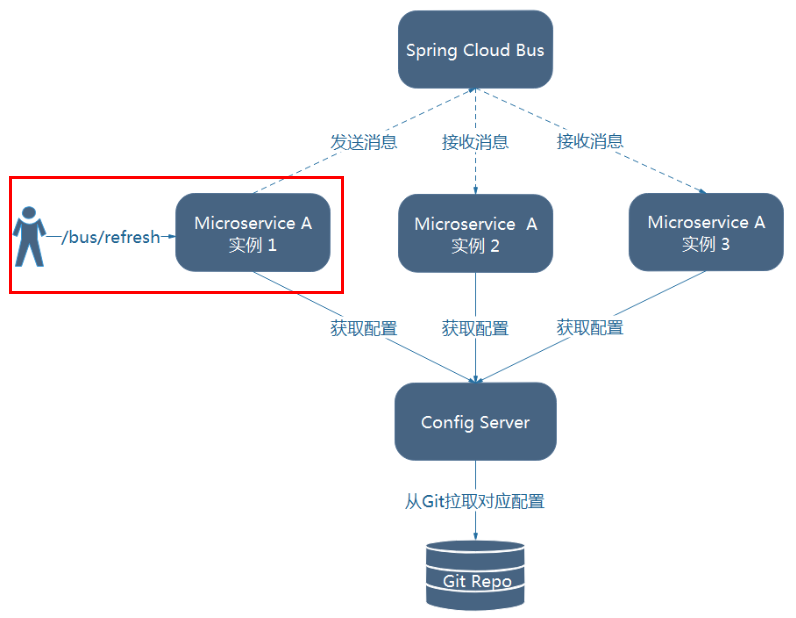
2)利用消息总线触发一个服务端ConfigServer的/bus/refresh端点,而刷新所有客户端的配置

图二的架构显然更加适合,图一不适合的原因如下:
- 打破了微服务的职责单一性,因为微服务本身是业务模块,它本不应该承担配置刷新的职责。
- 破坏了微服务各节点的对等性。
- 有一定的局限性。例如,微服务在迁移时,它的网络地址常常会发生变化,此时如果想要做到自动刷新,那就会增加更多的修改
因此目标就很明确了, 3344 作为服务中心,通知3355、3366 客户端
给cloud-config-center-3344配置中心服务端添加消息总线支持
POM:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqpartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
YAML:
server: port: 3344 spring: application: name: cloud-config-center #注册进Eureka服务器的微服务名 cloud: config: server: git: uri: https://github.com/yangzhaoguang/springcloud-config.git #GitHub上面的git仓库名字 ####搜索目录 search-paths: - springcloud-config username: yangzhaoguang password: q1209694409 timeout: 20 ####读取分支 default-label: main #rabbitmq相关配置 rabbitmq: host: 192.168.200.132 port: 5672 username: admin password: admin ##rabbitmq相关配置,暴露bus刷新配置的端点 management: endpoints: #暴露bus刷新配置的端点 web: exposure: include: 'bus-refresh' #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
3355、3366 POM一样增加一个 spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp 依赖,yaml 增加 RabbitMQ 的配置,业务类不要忘记加 @RefreshScope 注解
测试:
cmd命令行测试 3344 ,注意是刷新 3344 !
curl -X POST “http://localhost:3344/actuator/bus-refresh”
记录一个小坑: 发送 POST请求显示405,有可能是mq的依赖没有导入进去
只通知某一个客户端:
公式:http://localhost:配置中心的端口号/actuator/bus-refresh/{destination}
以 3355 为例:
curl -X POST “http://localhost:3344/actuator/bus-refresh/config-client:3355”
7.2 Spring Cloud Stream
什么是SpringCloudStream
官方定义 Spring Cloud Stream 是一个构建消息驱动微服务的框架。应用程序通过 inputs 或者 outputs 来与 Spring Cloud Stream中binder对象交互。
通过我们配置来binding(绑定) ,而 Spring Cloud Stream 的 binder对象负责与消息中间件交互。
所以,我们只需要搞清楚如何与 Spring Cloud Stream 交互就可以方便使用消息驱动的方式。通过使用Spring Integration来连接消息代理中间件以实现消息事件驱动。
Spring Cloud Stream 为一些供应商的消息中间件产品提供了个性化的自动化配置实现,引用了发布-订阅、消费组、分区的三个核心概念。目前仅支持RabbitMQ、Kafka。
简单来说,Stream 的作用:
屏蔽底层消息中间件的差异,降低切换成本,统一消息的编程模型官网文档:https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-stream#overview
中文文档:https://m.wang1314.com/doc/webapp/topic/20971999.html
为什么用到 Stream ? :
目前中间件的差异,比如 RabbitMQ 和 Kafka,二这皆为消息中间件,但是架构还是有区别的像RabbitMQ有exchange,kafka有Topic和Partitions分区,
这些中间件的差异性导致我们实际项目开发给我们造成了一定的困扰,我们如果用了两个消息队列的其中一种,后面的业务需求,我想往另外一种消息队列进行迁移,这时候无疑就是一个灾难性的,一大堆东西都要重新推倒重新做,因为它跟我们的系统耦合了,这时候springcloud Stream给我们提供了一种解耦合的方式。

Binder:
在没有绑定器这个概念的情况下,我们的 SpringBoot 应用要直接与消息中间件进行信息交互的时候,由于各消息中间件构建的初衷不同,它们的实现细节上会有较大的差异性,通过定义绑定器作为中间层,完美地实现了应用程序与消息中间件细节之间的隔离。Stream对消息中间件的进一步封装,可以做到代码层面对中间件的无感知,甚至于动态的切换中间件(rabbitmq切换为kafka),使得微服务开发的高度解耦,服务可以关注更多自己的业务流程。
INPUT对应于消费者
OUTPUT对应于生产者
Stream 标准化流程:

**Binder :**很方便的连接中间件,屏蔽差异
**Channel:**通道,是队列Queue的一种抽象,在消息通讯系统中就是实现存储和转发的媒介,通过Channel对队列进行配置
Source 和 Sink: 简单的可理解为参照对象是Spring Cloud Stream自身,
从Stream发布消息就是输出,接受消息就是输入。Stream 常用注解:


案例:新建三个模块:
cloud-stream-rabbitmq-provider8801,作为生产者进行发消息模块,
cloud-stream-rabbitmq-consumer8802,作为消息接收模块,
cloud-stream-rabbitmq-consumer8803 作为消息接收模块
cloud-stream-rabbitmq-provider8801 消费者:
POM:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbitartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId> <scope>runtimescope> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> <scope>testscope> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
YAML:
server: port: 8801 spring: application: name: cloud-stream-provider cloud: stream: binders: # 在此处配置要绑定的rabbitmq的服务信息; defaultRabbit: # 表示定义的名称,用于于binding整合 type: rabbit # 消息组件类型 environment: # 设置rabbitmq的相关的环境配置 spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.200.132 port: 5672 username: admin password: admin bindings: # 服务的整合处理 output: # 这个名字是一个通道的名称 destination: studyExchange # 表示要使用的Exchange名称定义 content-type: application/json # 设置消息类型,本次为json,文本则设置“text/plain” binder: {defaultRabbit} # 设置要绑定的消息服务的具体设置 eureka: client: # 客户端进行Eureka注册的配置 service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka instance: lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 2 # 设置心跳的时间间隔(默认是30秒) lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 5 # 如果现在超过了5秒的间隔(默认是90秒) instance-id: send-8801.com # 在信息列表时显示主机名称 prefer-ip-address: true # 访问的路径变为IP地址- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
Service:
/* 不需要加 @Service 注解,注意该实现类不在是之前的 service 层,而是和 RabbitMQ 打交道的 service 层 */ @EnableBinding(Source.class) // 定义消息的推送管道 public class MessageProviderImpl implements MessageProvider { @Autowired private MessageChannel output ; @Override public String send() { String serial = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); // 发送一条消息 output.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(serial).build()); return serial; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
Controller 层:
@RestController @Slf4j public class SendMessageController { @Autowired private MessageProvider messageProvider; @GetMapping(value = "/sendMessage") public String getMessage(){ // 发送 return messageProvider.send(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
在 Copy和 8802 一样的模块 8803
运行后存在的俩个问题:
有重复消费问题
消息持久化问题
分组消费与持久化
解决重复消费问题:

一个订单被多个服务处理,就会出错,因此利用 Stream 的分组 解决重复消费
同一个组只有一个能消费,是竞争关系,不同组是可以重复消费的。
进行分组:
binder 下面使用 group 分组,如果 8802、8803 俩个属于不同的组 还是会重复消费的。
只要将 8802、8803 都设置成相同的组就属于一个组,不会重复消费
bindings: # 服务的整合处理 input: # 接收消息 input 发送消息 output destination: studyExchange # 表示要使用的Exchange名称定义 content-type: application/json # 设置消息类型,本次为对象json,如果是文本则设置“text/plain” binder: {defaultRabbit} # 设置要绑定的消息服务的具体设置 group: atguiguA- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
注意: 同组之间的接收消息就采用轮询的机制
进行分组时,默认就会持久化,不进行分组就不会持久化
八、分布式请求链路跟踪
在微服务框架中,一个由客户端发起的请求在后端系统中会经过多个不同的的服务节点调用来协同产生最后的请求结果,每一个前段请求都会形成一条复杂的分布式服务调用链路,链路中的任何一环出现高延时或错误都会引起整个请求最后的失败。
Spring Cloud Sleuth提供了一套完整的服务跟踪的解决方案
在分布式系统中提供追踪解决方案并且兼容支持了zipkin
下载 zipkin:
Central Repository: io/zipkin/zipkin-server (maven.org)
执行 jar 包:
java -jar zipkin-server-2.12.9-exec.jar
访问:
http://localhost:9411/zipkin/
完整的调用链路:

一条链路通过Trace Id唯一标识,Span标识发起的请求信息,各span通过parent id 关联起来


拿 8001 和 80 举例,查看调用链路:
增加 依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkinartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
YAML配置:
spring: zipkin: base-url: http://localhost:9411 sleuth: sampler: probability: 1 #采样率值介于 0 到 1 之间,1 则表示全部采集- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
80端口 Controller :
// ====================> zipkin+sleuth @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/zipkin") public String paymentZipkin() { String result = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8001"+"/payment/zipkin/", String.class); return result; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
访问:http://localhost/consumer/payment/zipkin
: # 表示定义的名称,用于于binding整合
type: rabbit # 消息组件类型
environment: # 设置rabbitmq的相关的环境配置
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.200.132
port: 5672
username: admin
password: admin
bindings: # 服务的整合处理
output: # 这个名字是一个通道的名称
destination: studyExchange # 表示要使用的Exchange名称定义
content-type: application/json # 设置消息类型,本次为json,文本则设置“text/plain”
binder: {defaultRabbit} # 设置要绑定的消息服务的具体设置eureka:
client: # 客户端进行Eureka注册的配置
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
instance:
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 2 # 设置心跳的时间间隔(默认是30秒)
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 5 # 如果现在超过了5秒的间隔(默认是90秒)
instance-id: send-8801.com # 在信息列表时显示主机名称
prefer-ip-address: true # 访问的路径变为IP地址> **Service:** ```java /* 不需要加 @Service 注解,注意该实现类不在是之前的 service 层,而是和 RabbitMQ 打交道的 service 层 */ @EnableBinding(Source.class) // 定义消息的推送管道 public class MessageProviderImpl implements MessageProvider { @Autowired private MessageChannel output ; @Override public String send() { String serial = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); // 发送一条消息 output.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(serial).build()); return serial; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
Controller 层:
@RestController @Slf4j public class SendMessageController { @Autowired private MessageProvider messageProvider; @GetMapping(value = "/sendMessage") public String getMessage(){ // 发送 return messageProvider.send(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
在 Copy和 8802 一样的模块 8803
运行后存在的俩个问题:
有重复消费问题
消息持久化问题
分组消费与持久化
解决重复消费问题:
[外链图片转存中…(img-0NOYLCrt-1661664822463)]
一个订单被多个服务处理,就会出错,因此利用 Stream 的分组 解决重复消费
同一个组只有一个能消费,是竞争关系,不同组是可以重复消费的。
进行分组:
binder 下面使用 group 分组,如果 8802、8803 俩个属于不同的组 还是会重复消费的。
只要将 8802、8803 都设置成相同的组就属于一个组,不会重复消费
bindings: # 服务的整合处理 input: # 接收消息 input 发送消息 output destination: studyExchange # 表示要使用的Exchange名称定义 content-type: application/json # 设置消息类型,本次为对象json,如果是文本则设置“text/plain” binder: {defaultRabbit} # 设置要绑定的消息服务的具体设置 group: atguiguA- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
注意: 同组之间的接收消息就采用轮询的机制
进行分组时,默认就会持久化,不进行分组就不会持久化
-
相关阅读:
【微服务】Sentinel 控制台
Go语言的设计哲学
文件管理命令 ls,别名
MySQL主从复制与读写分离
Open3D 二维凸包计算
hevc sps 序列参数集
快速上手Django(七) -Django之登录cookie和session
【数据可视化】—大屏数据可视化展示
Unity3D教程:实现房产项目中的材质动态切换
面试官:你认为一个优秀的测试工程师需要具备哪些知识和经验?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/aetawt/article/details/126568999
