-
vuex 基础知识 (跨组件传值)
一、解释
vuex 状态(数据)管理工具 。 vuex 可以把整个项目的数据集中的管理起来 方便组件与组件的使用 (组件想使用数据 那么不需要使用 复杂的传递方式了 直接就可以去vuex中进行数据 的获取)
传统的vue 是单向数据流 如果是兄弟或者是跨层级的组件在进行传递的时候vue就非常的麻烦vuex就可以来进行上述传值 简化数据传递的复杂度。
二、vuex创建流程
①第一种 创建项目时选中Vuex
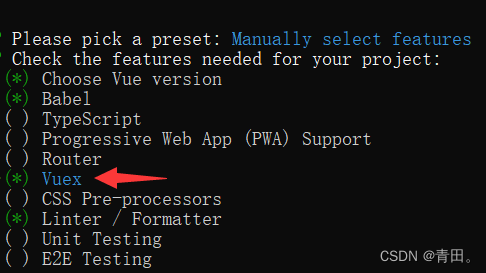
② 第二种 指令下载
npm install --save vuex
在src文件夹下新建store文件夹并且新建index.js
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- })
在main.js 中引用vuex文件 并且在vue实例上注册
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import App from './App.vue'
- import router from './router'
- import store from './store'//引用
- Vue.config.productionTip = false
- new Vue({
- router,
- store,//注册
- render: h => h(App)
- }).$mount('#app')
三、vuex的5大属性
1、state属性---数据源(创建数据的 类似于组件中的data)
vuex的所有数据都在state中进行创建
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- state: {
- text:"小王",
- age:18,
- arr:[111,222,333],
- obj:{
- love:"女"
- }
- },
- mutations: {
- },
- actions: {
- },
- modules: {
- }
- })
① 取值方式1 ----任意组件模板上直接使用 $store.state.xxx使用
- <template>
- <div>
- 拿text的值{{$store.state.text}}
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- export default {
- }
- script>
- <style>
- style>
②.取值方式2 ---使用计算属性来进行vuex的数据获取
- <template>
- <div>
- 拿age的值{{newage}}
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- export default {
- computed:{
- newage(){
- return this.$store.state.age
- }
- }
- }
- script>
- <style>
- style>
2、mutations属性---vuex的数据修改
vuex中state的数据不能直接修改 如果要触发mutations的修改动作 那么要使用commit这个方法来进行调用
比如把小王修改为小黑
第一步、通过事件触发commit来调用修改操作
- <template>
- <div>
- home页面{{$store.state.text}}
- <button @click="fun()">点我修改button>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- export default {
- methods:{
- fun(){
- // 需要触发这个函数之后把vuex的text变量进行修改
- // this.$store.commit("你要调用的mutations的名字",传递的参数)
- //第一种写法:
- this.$store.commit("uptext",{newtext:"小黑"})
- //第二种写法:推荐写对象的形式
- this.$store.commit({
- type:"uptext",
- newtext:"小白"
- })
- }
- }
- }
- script>
- <style>
- style>
第二步去store中编写对应的mutations修改动作
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- state: {//创建数据的类似于组件中的data
- text:"小王",
- age:18,
- arr:[111,222,333],
- obj:{
- love:"女"
- }
- },
- mutations: {
- // 第一个形参state就是指向上面的state数据源
- // 第二个形参接收的就是commit方法中的第二个参数
- uptext(state,payload){
- state.text = payload.newtext
- }
- },
- actions: {
- },
- modules: {
- }
- })
vuex数据修改后 刷新丢失
在vuex中如果我们修改数据之后 页面在刷新一次 那么页面的数据你会回复成默认值
- created() {
- //在页面加载时读取sessionStorage里的状态信息
- if (sessionStorage.getItem("store")) {
- this.$store.replaceState(
- Object.assign(
- {},
- this.$store.state,
- JSON.parse(sessionStorage.getItem("store"))
- )
- );
- }
- //在页面刷新时将vuex里的信息保存到sessionStorage里
- window.addEventListener("beforeunload", () => {
- sessionStorage.setItem("store", JSON.stringify(this.$store.state));
- });
- },
3、actions属性------触发异步操作
actions中是一个个的方法 每一个方法就是一个异步的动作 (异步请求)
actions调用的话 使用dispatch( ) 来进行调用
1.页面通过dispatch来触发actions
- <template>
- <div>
- user页面{{$store.state.text}}
- <button @click="fun()">点我触发异步操作button>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- export default {
- methods:{
- fun(){
- // 调用actions
- // this.$store.dispatch("你出发的actions的名字",{数据})
- //写法一:
- //this.$store.dispatch("demoLink",{url:"/data/data"})
- //写法二:推荐写为对象的形式
- this.$store.dispatch(
- {
- type:"getMenuList",
- url:"/data/list/menu"
- }
- )
- }
- }
- }
- script>
2、actions创建对应的方法
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- // 引用数据请求
- import getlink from "@/apis/getapi.js"
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- state: {//创建数据的类似于组件中的data
- text:"小王",
- age:18,
- arr:[111,222,333],
- obj:{
- love:"女"
- }
- },
- mutations: {
- uparr(state,payload){
- //把请求来的数据修改state
- state.arr=payload.arrdata
- }
- },
- actions: {
- // context形参 就是store对象
- // 第二个形参接收的就是dispatch
- demoLink(context,payload){
- console.log("context")
- //发送异步操作
- getlink(payload.url).then((res)=>{
- console.log(res.data.data)
- //把请求来的数据交给mutations来修改state
- context.commit("uparr",{arrdata:res.data.data})
- })
- }
- },
- modules: {
- }
- })
3、在页面展示请求来的新的arr
- <template>
- <div>
- {{newarr}}
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- export default {
- computed:{
- newarr(){
- return this.$store.state.arr
- }
- },
- }
- script>
- <style>
- style>
4、getters属性 -- 类似于计算属性
getters 可以对一个数据在不同位置展示出不同的形态时候用
getters 处理的数据 任何组件都能用
vue的计算属性处理的数据 只能当前组件使用
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- state: {//创建数据的类似于组件中的data
- demo:"abcde"
- },
- mutations: {
- },
- actions: {
- },
- modules: {
- },
- getters:{
- // 里面就一个形参 state代表的就是数据源
- newdemo(state){
- return state.demo.toUpperCase()
- }
- }
- })
把demo的小写处理为大写后在页面去用(组件里使用getters时不加模块名)
- <template>
- <div>
- home页面
- <h1>{{$store.getters.newdemo}}h1>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- export default {
- }
- script>
- <style>
- style>
5、module 模块
可以把上面写在一起的数据 修改 异步操作 计算属性 按照页面等进行分类管理
第一步 home页面user页面分开管理

第二步 在index.js把模块注入到vuex中
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- // 引用模块
- import Home from "./modules/home.js"
- import User from "./modules/user.js"
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- // 注入
- modules: {
- Home ,
- User
- }
- })
第三步 使用数据 $store.state.模块名.xxx
- <template>
- <div>
- home页面
- <h1>{{$store.state.Home.text}}h1>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- export default {
- }
- script>
- <style>
- style>
问题:如果home和user两个模块里有相同action(mutation)的名字


结果是两个都会调用,那么如何区分????
添加
namespaced: true的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块
两个都要开启。开启后变为严格模式必须加模块名字

getters重名区分的话 也要加模块名
{{$store.getters["Home/newdemo"]}}
{{$store.getters["User/newdemo"]}}
问题:这样写太繁琐(冗余)

辅助函数 http:// https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/state.html
mapState, mapGetters (这两个在computed里映射)
mapMutations, mapActions(这两个在methods里映射)
假如index.js 里 (没分模块化)
- import axios from "axios";
- import Vue from "vue";
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- import Home from "./home.js"
- import User from "./user.js"
- // 1.安装
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- // 2.创建对象
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- state: {
- demo:"abc",
- num:0,
- num1:"1",
- num2:"2",
- num3:"2",
- age:18,
- },
- mutations: {
- },
- actions: {
- },
- getters: {
- newDemo(state){
- return state.demo.toUpperCase()
- }
- },
- modules: {
- Home,
- User
- }
- })
使用辅助函数
- <template>
- <div>
- demoVuex:
- <h3>{{num1}}h3>
- <h3>{{num2}}h3>
- <h3>{{num3}}h3>
- <h3>newDemo:{{newDemo}}h3>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- import { mapState,mapGetters } from "vuex";
- export default {
- data(){
- return{
- }
- },
- methods:{
- },
- computed:{
- ...mapState(['num1','num2','num3']),
- ...mapGetters(["newDemo"])
- },
- //这种写法也可以但(不能再写其它计算属性)
- // computed:mapState({
- // num:state=> state.num
- // }),
- }
- script>
区分模块化
- <template>
- <div>
- demoVuex
- <h4>{{newDemo}}h4>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- import { mapState,mapGetters } from "vuex";
- export default {
- data(){
- return{
- }
- },
- methods:{
- },
- computed:{
- // 未加模块名
- ...mapState(['num1','num2','num3']),
- ...mapGetters(["newDemo"]),
- // 加了模块名
- // ...mapGetters(["模块名",[模块里的getters]])
- ...mapGetters(["Home",["newdemo"]])
- },
- }
- script>
mapActions
① 不区分模块index.js
- actions: {
- getMenuList(){
- axios({
- url:'/data/list/menu'
- }).then(res=> {
- console.log('res',res);
- })
- }
- },
使用时候
- <template>
- <div>
- <input type="button" value="按钮" @click="handleAxios()">
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- import { mapState,mapGetters,mapActions } from "vuex";
- export default {
- data(){
- return{
- }
- },
- methods:{
- // 把getMenuList映射到当前组件的methods中
- ...mapActions(["getMenuList"]),
- handleAxios(){
- this.getMenuList({id:123}) //类似this.$store.dispatch()
- },
- }
- }
- script>
区分模块化 ...mapActions({"名字":"模块名/actions下的方法名"}),
- <template>
- <div>
- <input type="button" value="按钮" @click="handleAxios()">
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- import { mapState,mapGetters,mapActions } from "vuex";
- export default {
- data(){
- return{
- }
- },
- methods:{
- // 把getIndexAction映射到当前组件的methods中
- ...mapActions(["getIndexAction"]),
- // ...mapActions({"getMenuList":"Home/getMenuList"}),
- ...mapActions(['getMenuList', ['Home/getMenuList']]),
- handleAxios(){
- this.getIndexAction({id:123}) //类似this.$store.dispatch()
- this.getMenuList() //类似this.$store.dispatch()
- },
- }
- }
- script>
mapMutations
不区分模块index.js
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- state: {
- word:"hello word",
- },
- mutations: {
- upWord(state,payload) {
- state.word = payload.newWord
- }
- },
- })
使用
- <template>
- <div>
- demoVuex:
- <h5>{{ $store.state.word }}h5>
- <button @click="changeWord()">点我修改button>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- import { mapState, mapGetters, mapActions,mapMutations } from 'vuex'
- export default {
- data() {
- return {}
- },
- methods: {
- ...mapMutations(['upWord']),
- changeWord(){
- this.upWord({newWord:'hi'})
- }
- }
- }
- script>
区分模块home.js
- export default {
- state:{
- homeText:'home的hello'
- },
- mutations:{
- homeText(state,payload) {
- state.homeText = payload.homeText
- }
- }
- }
使用
- <template>
- <div>
- demoVuex:
- <h5>{{ $store.state.word }}h5>
- <h5>{{$store.state.home.homeText}}h5>
- <button @click="changeWord()">点我修改button>
- div>
- template>
- <script>
- import { mapState, mapGetters, mapActions,mapMutations } from 'vuex'
- export default {
- methods: {
- ...mapMutations(['homeText',['home/homeText']]),
- changeWord(){
- this.homeText({homeText:'heihei'})
- }
- }
- }
- script>
dispatch触发actions通过commit调用mutations修改state

-
相关阅读:
MATLAB算法实战应用案例精讲-【优化算法】沙丁鱼优化算法(SOA)(附MATLAB代码实现)
数据库中的数据
Docker -- 01实践:使用Docker 快速安装Jenkins
csdn 格式规范
结构化数据和非结构化数据
认识物联网
Java获取dbcp连接池
export default 导出的对象,不能解构问题,和module.exports的区别
Linux之从进程角度来理解文件描述符
SpringCloud - Spring Cloud Alibaba 之 Seata分布式事务服务详解;部署(十八)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Tianxiaoxixi/article/details/126216431
