-
LeetCode #104.二叉树的最大深度
题目截图

方法一:深度优先搜索(递归)
将二叉树不断分解,直到左子树和右子树的最大深度即可知道二叉树的最大深度。
每个字数又可以不断分解成新的字数,直到没有结点,每一次分解,加一层。
- class Solution:
- def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
- if not root :
- return 0
- return max(self.maxDepth(root.left),self.maxDepth(root.right))+1
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
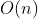 其中
其中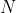 为二叉树节点的个数。每个节点在递归中只被遍历一次。
为二叉树节点的个数。每个节点在递归中只被遍历一次。空间复杂度:
 其中
其中 表示二叉树的高度。
表示二叉树的高度。完整测试代码
- from typing import Optional
- class TreeNode:
- def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
- self.val = val
- self.left = left
- self.right = right
- class Solution:
- def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
- if not root :
- return 0
- return max(self.maxDepth(root.left),self.maxDepth(root.right))+1
- class main:
- a = Solution()
- node1 = TreeNode(3)
- node2 = TreeNode(9)
- node3 = TreeNode(20)
- node4 = TreeNode(15)
- node5 = TreeNode(7)
- node1.left = node2
- node1.right = node3
- node3.left = node4
- node3.right = node5
- b = a.maxDepth(node1)
- print(b)
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
方法二:广度优先搜索
利用队列保存每一层的所有结点,把队列里的所有结点出队列,然后把出队列的结点的子节点加入队列。
如例题中的二叉树

刚开始,深度为0。
先加入第一层的3,然后第一层的3出队列,第一层所有结点出队列,深度+1。
加入第二层的9和20,然后9出队列,由于9没有子节点,不添加新的结点进入队列。
再让20出队列,此时第二层所有结点已经出队列,深度+1。
加入第三层的15和7。
再分别让15和7出队列,由于没有子节点,不添加任何新节点,此时所有结点出队列,队列为空,深度+1。
最终返回深度,深度为3。
- class Solution:
- def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
- if root == None:
- return 0
- queue = [root]
- depth = 0
- while queue:
- n = len(queue)
- for i in range(n):
- node = queue.pop(0)
- if node.left:
- queue.append(node.left)
- if node.right:
- queue.append(node.right)
- depth += 1
- return depth
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
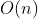
空间复杂度:
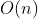
-
相关阅读:
若依微服务版集成华东验证码AJ-Captcha
纷享销客CRM为虎邦辣酱的第二次增长插上数字化翅膀
详解GaussDB(DWS) 资源监控
【QML】QML中的ui文件
如何报考华为网络工程师?
ubuntu开机系统出错且无法恢复。请联系系统管理员。
Qt实现微信截图功能(一)
并发编程CompletableFuture用法
Shape Completion Enabled Robotic Grasping
【python入门篇】元组、字典和集合(3)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42112343/article/details/126232991
