-
神经网络原理及代码实现
1.深度学习
机器学习流程: 数据获取、特征工程 、建立模型、评估与应用

特征工程的作用:
数据特征决定了模型的上限
预处理和特征提取是最核心的算法与参数选择决定了如何逼近这个上限
传统特征提取方法:

深度学习特征提取方式:

2.线性函数
从输入-->输出的映射
 每个类别的得分
每个类别的得分数学表示:

计算方法:
 多组权重参数构成了决策边界
多组权重参数构成了决策边界

3.损失函数
损失函数其实有很多种,我们来实验一个

如何损失函数的值相同,那么意味着两个模型一样吗?

 我们可以看到,不同的权重的损失函数值相同,因此,我们引入正则化消减权重的影响
我们可以看到,不同的权重的损失函数值相同,因此,我们引入正则化消减权重的影响损失函数 = 数据损失 + 正则化惩罚项
 正则化惩罚项:
正则化惩罚项:
4.Softmax分类器
将得分值转换为概率值


归一化:

计算损失值:


前向传播

如何更新模型呢?这个就交给反向传播了(梯度下降)
反向传播的链式法则




梯度是一步一步传的

复杂的例子:


可以一大块一大块的计算吗?

加法门单元:均等分配
MAX门单元:给最大的
乘法门单元:互换的感觉

6.正则化的作用
惩罚力度对结果的影响:
加大惩罚力度,可以减小过拟合的风险

参数个数对结果的影响:
参数越多,一般情况下,拟合效果越好

7.激活函数
常用的激活函数(Sigmoid,Relu,Tanh 等)

Sigmoid:梯度消失现象

Relu:

8.数据预处理
不同的预处理结果会使得模型的效果发生很大的差异,通常要对数据进行归一化处理

9.代码实现
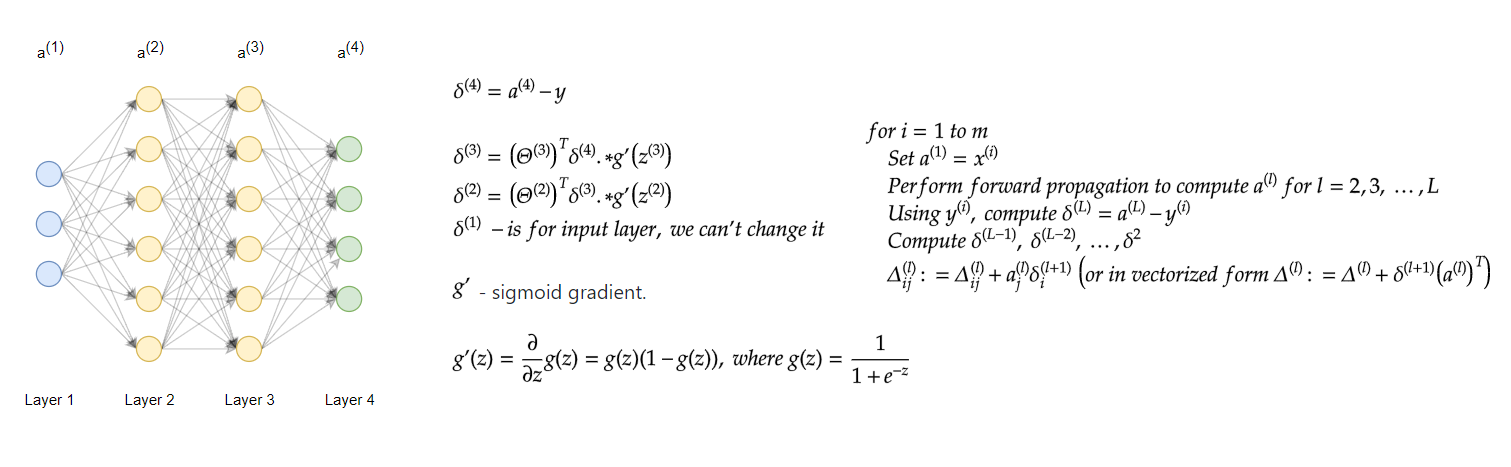
神经网络最重要的部分为反向传播,反向传播公式如图所示:
代码实现:
- import numpy as np
- from utils.features import prepare_for_training
- from utils.hypothesis import sigmoid, sigmoid_gradient
- class MultilayerPerceptron:
- def __init__(self,data,labels,layers,normalize_data =False):
- data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,normalize_data = normalize_data)[0]
- self.data= data_processed
- self.labels= labels
- self.layers= layers #784 25 10
- self.normalize_data= normalize_data
- self.thetas = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_init(layers)
- def predict(self,data):
- data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,normalize_data = self.normalize_data)[0]
- num_examples = data_processed.shape[0]
- predictions = MultilayerPerceptron.feedforward_propagation(data_processed,self.thetas,self.layers)
- return np.argmax(predictions,axis=1).reshape((num_examples,1))
- def train(self,max_iterations=1000,alpha=0.1):
- unrolled_theta = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_unroll(self.thetas)
- (optimized_theta,cost_history) = MultilayerPerceptron.gradient_descent(self.data,self.labels,unrolled_theta,self.layers,max_iterations,alpha)
- self.thetas = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_roll(optimized_theta,self.layers)
- return self.thetas,cost_history
- @staticmethod
- def thetas_init(layers):
- num_layers = len(layers)
- thetas = {}
- for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
- """
- 会执行两次,得到两组参数矩阵:25*785 , 10*26
- """
- in_count = layers[layer_index]
- out_count = layers[layer_index+1]
- # 这里需要考虑到偏置项,记住一点偏置的个数跟输出的结果是一致的
- thetas[layer_index] = np.random.rand(out_count,in_count+1)*0.05 #随机进行初始化操作,值尽量小一点
- return thetas
- @staticmethod
- def thetas_unroll(thetas):
- num_theta_layers = len(thetas)
- unrolled_theta = np.array([])
- for theta_layer_index in range(num_theta_layers):
- unrolled_theta = np.hstack((unrolled_theta,thetas[theta_layer_index].flatten()))
- return unrolled_theta
- @staticmethod
- def gradient_descent(data,labels,unrolled_theta,layers,max_iterations,alpha):
- optimized_theta = unrolled_theta
- cost_history = []
- for _ in range(max_iterations):
- cost = MultilayerPerceptron.cost_function(data,labels,MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_roll(optimized_theta,layers),layers)
- cost_history.append(cost)
- theta_gradient = MultilayerPerceptron.gradient_step(data,labels,optimized_theta,layers)
- optimized_theta = optimized_theta - alpha* theta_gradient
- return optimized_theta,cost_history
- @staticmethod
- def gradient_step(data,labels,optimized_theta,layers):
- theta = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_roll(optimized_theta,layers)
- thetas_rolled_gradients = MultilayerPerceptron.back_propagation(data,labels,theta,layers)
- thetas_unrolled_gradients = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_unroll(thetas_rolled_gradients)
- return thetas_unrolled_gradients
- @staticmethod
- def back_propagation(data,labels,thetas,layers):
- num_layers = len(layers)
- (num_examples,num_features) = data.shape
- num_label_types = layers[-1]
- deltas = {}
- #初始化操作
- for layer_index in range(num_layers -1 ):
- in_count = layers[layer_index]
- out_count = layers[layer_index+1]
- deltas[layer_index] = np.zeros((out_count,in_count+1)) #25*785 10*26
- for example_index in range(num_examples):
- layers_inputs = {}
- layers_activations = {}
- layers_activation = data[example_index,:].reshape((num_features,1))#785*1
- layers_activations[0] = layers_activation
- #逐层计算
- for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
- layer_theta = thetas[layer_index] #得到当前权重参数值 25*785 10*26
- layer_input = np.dot(layer_theta,layers_activation) #第一次得到25*1 第二次10*1
- layers_activation = np.vstack((np.array([[1]]),sigmoid(layer_input)))
- layers_inputs[layer_index + 1] = layer_input #后一层计算结果
- layers_activations[layer_index + 1] = layers_activation #后一层经过激活函数后的结果
- output_layer_activation = layers_activation[1:,:]
- delta = {}
- #标签处理
- bitwise_label = np.zeros((num_label_types,1))
- bitwise_label[labels[example_index][0]] = 1
- #计算输出层和真实值之间的差异
- delta[num_layers - 1] = output_layer_activation - bitwise_label
- #遍历循环 L L-1 L-2 ...2
- for layer_index in range(num_layers - 2,0,-1):
- layer_theta = thetas[layer_index]
- next_delta = delta[layer_index+1]
- layer_input = layers_inputs[layer_index]
- layer_input = np.vstack((np.array((1)),layer_input))
- #按照公式进行计算
- delta[layer_index] = np.dot(layer_theta.T,next_delta)*sigmoid_gradient(layer_input)
- #过滤掉偏置参数
- delta[layer_index] = delta[layer_index][1:,:]
- for layer_index in range(num_layers-1):
- layer_delta = np.dot(delta[layer_index+1],layers_activations[layer_index].T)
- deltas[layer_index] = deltas[layer_index] + layer_delta #第一次25*785 第二次10*26
- for layer_index in range(num_layers -1):
- deltas[layer_index] = deltas[layer_index] * (1/num_examples)
- return deltas
- @staticmethod
- def cost_function(data,labels,thetas,layers):
- num_layers = len(layers)
- num_examples = data.shape[0]
- num_labels = layers[-1]
- #前向传播走一次
- predictions = MultilayerPerceptron.feedforward_propagation(data,thetas,layers)
- #制作标签,每一个样本的标签都得是one-hot
- bitwise_labels = np.zeros((num_examples,num_labels))
- for example_index in range(num_examples):
- bitwise_labels[example_index][labels[example_index][0]] = 1
- bit_set_cost = np.sum(np.log(predictions[bitwise_labels == 1]))
- bit_not_set_cost = np.sum(np.log(1-predictions[bitwise_labels == 0]))
- cost = (-1/num_examples) *(bit_set_cost+bit_not_set_cost)
- return cost
- @staticmethod
- def feedforward_propagation(data,thetas,layers):
- num_layers = len(layers)
- num_examples = data.shape[0]
- in_layer_activation = data
- # 逐层计算
- for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
- theta = thetas[layer_index]
- out_layer_activation = sigmoid(np.dot(in_layer_activation,theta.T))
- # 正常计算完之后是num_examples*25,但是要考虑偏置项 变成num_examples*26
- out_layer_activation = np.hstack((np.ones((num_examples,1)),out_layer_activation))
- in_layer_activation = out_layer_activation
- #返回输出层结果,结果中不要偏置项了
- return in_layer_activation[:,1:]
- @staticmethod
- def thetas_roll(unrolled_thetas,layers):
- num_layers = len(layers)
- thetas = {}
- unrolled_shift = 0
- for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
- in_count = layers[layer_index]
- out_count = layers[layer_index+1]
- thetas_width = in_count + 1
- thetas_height = out_count
- thetas_volume = thetas_width * thetas_height
- start_index = unrolled_shift
- end_index = unrolled_shift + thetas_volume
- layer_theta_unrolled = unrolled_thetas[start_index:end_index]
- thetas[layer_index] = layer_theta_unrolled.reshape((thetas_height,thetas_width))
- unrolled_shift = unrolled_shift+thetas_volume
- return thetas
10.测试效果
使用mnist数据集进行测试
数据集展示:

效果展示:



-
相关阅读:
VQ-VAE torch 实现
面试又被问高并发,哑口无言?一份高并发核心文档助你吊打面试官
新人FPGA验证书籍推荐
Vue3实现粒子动态背景
Golang处理gRPC请求/响应元数据
地球人口承载力估计(c++基础)
设计模式-策略模式
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 的实现类为什么可以在初始化Web容器的时候被调用
系统架构设计师-大数据
flutter 使用FlutterJsonBeanFactory工具遇到的问题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52053775/article/details/126094711