-
【Python-pyecharts】全国数据分析岗招聘信息可视化
实验数据集:全国工作情况数据集下载
运行工具:jupyter notebook一、数据预处理
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from pyecharts.charts import * from pyecharts import options as opts from pyecharts.commons.utils import JsCode from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType from pyecharts.components import Table import textwrap- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
path = r'2022年数据分析岗招聘数据.csv'#修改文件存储目录 data = pd.read_csv(path) data.head()- 1
- 2
- 3

# 城市数据处理 data['城市'] = data['地点'].apply(lambda x:x.split('-')[0]) data.head()- 1
- 2
- 3

# 薪资数据处理 # 去除非范围类数据 data2 = data[data['薪资范围'] != '面议'] data2 = data2[~data2.薪资范围.str.contains('/天')] data2 = data2[~data2.薪资范围.str.contains('以下')] data2['薪资下限'] = data2.薪资范围.apply(lambda x:x.split('-')[0]) data2['薪资上限'] = data2.薪资范围.apply(lambda x:x.split('-')[1]) # 定义函数将薪资转化为数字形式 def salary_handle(word): if word[-1] == '万': num = float(word.strip('万')) * 10000 elif word[-1] == '千': num = float(word.strip('千')) * 1000 return num data2['薪资下限'] = data2.薪资下限.apply(lambda x:salary_handle(x)) data2['薪资上限'] = data2.薪资上限.apply(lambda x:salary_handle(x)) data2['薪资均值'] = round((data2.薪资上限 + data2.薪资下限)/2,2) data2.head()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

print('不规范数据量为:',data.shape[0] - data2.shape[0])- 1
不规范数据量为: 330
# 去除异常值 data2 = data2.reset_index(drop = True) # data2[data2['工作经验']=='10年以上'] data2 = data2.drop(index = 5860)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
在数据预处理部分,做了如下事情。
首先导入数据,查看数据基本情况。由于数据是自己爬的,所以每个字段的数据情况基本上都了解了,这部分就进行了省略。 然后处理城市数据。企业发布的招聘信息中,工作地点的信息大部分都精确到了具体的市区。因此这里将工作地区中的城市提取出来,方便后续统计。 然后对数据中的薪资范围进行处理。由于薪资范围的数据是‘1万-2万’或者是‘7千-9千’或者是'面议'或者是‘200元/天’这样的形式,因此要对薪资数据进行处理。查看薪资数据,发现大部分薪资的数据都是以‘7千-9千’这样的范围形式出现的,仅有少部分数据是‘面议’或者是‘200/天’这样的形式,这样不规范的数据总计330条,占比不是很大,因此将这部分数据直接进行去除。并且将范围中的7千、1万这样形式的数据都转换成具体的数值型数据,方便后续统计分析。并且去薪资的上限和下限的均值作为新字段进行分析。- 1
- 2
- 3
二、岗位需求
1. 哪个城市的数据分析岗岗位需求较多呢?
我们首先来看看,哪个城市的数据分析岗的岗位需求最多呢?
绘制各城市岗位需求榜单如下。# 绘制圆角柱状图函数 def echarts_bar(x,y,title = '主标题',subtitle = '副标题',label = '图例'): """ x: 函数传入x轴标签数据 y:函数传入y轴数据 title:主标题 subtitle:副标题 label:图例 """ bar = Bar( init_opts=opts.InitOpts( # bg_color='#080b30', # 设置背景颜色 theme='shine', # 设置主题 width='1000px', # 设置图的宽度 height='700px' # 设置图的高度 ) ) bar.add_xaxis(x) bar.add_yaxis(label,y, label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True) # 是否显示数据 ,category_gap="50%" # 柱子宽度设置 ) bar.reversal_axis() bar.set_series_opts( # 自定义图表样式 label_opts=opts.LabelOpts( is_show=True, position='right', # position 标签的位置 可选 'top','left','right','bottom','inside','insideLeft','insideRight' font_size=15, color= '#333333', font_weight = 'bolder', # font_weight 文字字体的粗细 'normal','bold','bolder','lighter' font_style = 'oblique', # font_style 文字字体的风格,可选 'normal','italic','oblique' ), # 是否显示数据标签 itemstyle_opts={ "normal": { "color": JsCode( """new echarts.graphic.LinearGradient(0, 0, 0, 1, [{ offset: 0,color: '#FC7D5D'} ,{offset: 1,color: '#C45739'}], false) """ ), # 调整柱子颜色渐变 'shadowBlur': 6, # 光影大小 "barBorderRadius": [100, 100, 100, 100], # 调整柱子圆角弧度 "shadowColor": "#999999", # 调整阴影颜色 'shadowOffsetY': 2, 'shadowOffsetX': 2, # 偏移量 } } ) bar.set_global_opts( # 标题设置 title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title=title, # 主标题 subtitle=subtitle, # 副标题 pos_left='center', # 标题展示位置 title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20,font_weight='bolder') ), # 图例设置 legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts( is_show=True, # 是否显示图例 pos_left='right', # 图例显示位置 pos_top='3%', #图例距离顶部的距离 orient='horizontal' # 图例水平布局 ), tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( is_show=True, # 是否使用提示框 trigger='axis', # 触发类型 trigger_on='mousemove|click', # 触发条件,点击或者悬停均可出发 axis_pointer_type='cross', # 指示器类型,鼠标移动到图表区可以查看效果 ), yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( is_show=True, splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=False), # 分割线 axistick_opts=opts.AxisTickOpts(is_show=False), # 刻度不显示 axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts( # 坐标轴标签配置 font_size=13, # 字体大小 font_weight='bolder' # 字重 ), ), # 关闭Y轴显示 xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( boundary_gap=True, # 两边不显示间隔 axistick_opts=opts.AxisTickOpts(is_show=True), # 刻度不显示 splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=False), # 分割线不显示 axisline_opts=opts.AxisLineOpts(is_show=True), # 轴不显示 axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts( # 坐标轴标签配置 font_size=13, # 字体大小 font_weight='bolder' # 字重 ), ), ) return bar- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
job_demand = data2.城市.value_counts().sort_values(ascending = True) echarts_bar(job_demand.index.tolist(),job_demand.values.tolist(),title = '全国各地数据分析岗岗位需求排名',subtitle = ' ', label = '岗位需求量').render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
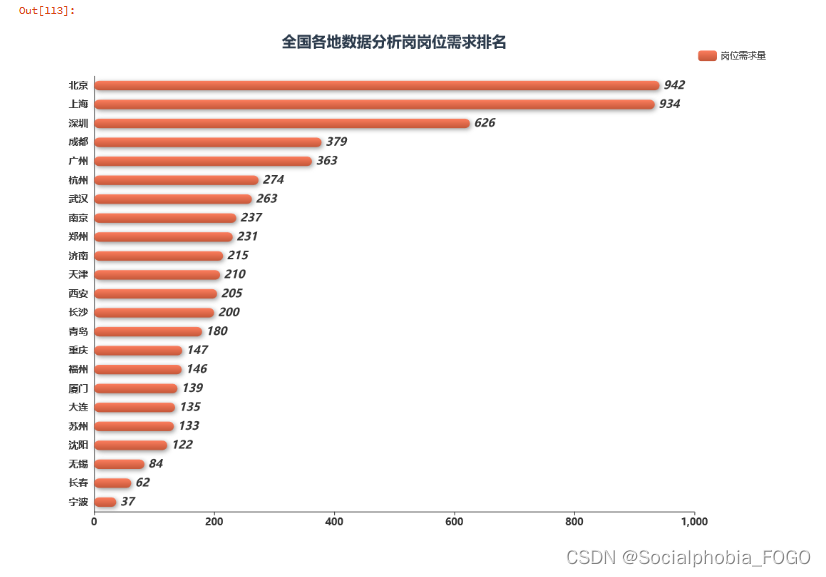 通过全国各地数据分析岗岗位需求排名可以发现,北京上海的岗位需求是最多的。其次是深圳。在北上广深四个一线城市中,广州的数据分析岗位需求是最少的。而成都的数据分析岗的岗位需求量近几年增长较快,甚至超过了广州。其次是杭州、武汉、南京等城市。
通过全国各地数据分析岗岗位需求排名可以发现,北京上海的岗位需求是最多的。其次是深圳。在北上广深四个一线城市中,广州的数据分析岗位需求是最少的。而成都的数据分析岗的岗位需求量近几年增长较快,甚至超过了广州。其次是杭州、武汉、南京等城市。
因此要找数据分析岗工作或者实习的小伙伴,还是推荐去北上广深这样的一线城市。2. 岗位需求较多的城市中,哪个区的岗位需求更多呢?
我们进一步查看北上广深以及成都、杭州等数据分析岗岗位需求排名前9的城市,其数据分析岗岗位需求主要分别分布在哪些区。
# 北上广深和成都杭州各个地区岗位需求量 beijing_demand = data[data['城市'] == '北京']['地点'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending = False) shanghai_demand = data[data['城市'] == '上海']['地点'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending = False) shenzhen_demand = data[data['城市'] == '深圳']['地点'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending = False) guangzhou_demand = data[data['城市'] == '广州']['地点'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending = False) chengdu_demand = data[data['城市'] == '成都']['地点'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending = False) hangzhou_demand = data[data['城市'] == '杭州']['地点'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending = False)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
def bar_chart(desc, title_pos): df_t = data[(data['城市'] == desc)&(data['地点'] != desc)]['地点'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending = False).reset_index() df_t.columns = [desc,'岗位需求量'] df_t[desc] = df_t[desc].apply(lambda x:x.split('-')[1]) # 新建一个Bar chart = Bar( init_opts=opts.InitOpts( # bg_color='#2C3B4C', # 设置背景颜色 theme='white', # 设置主题 width='400px', # 设置图的宽度 height='400px' ) ) chart.add_xaxis( df_t[desc].tolist() ) chart.add_yaxis( '', df_t['岗位需求量'].tolist() ) chart.set_series_opts( # 自定义图表样式 label_opts=opts.LabelOpts( is_show=True, position='top', # position 标签的位置 可选 'top','left','right','bottom','inside','insideLeft','insideRight' font_size=15, color= '#727F91', font_weight = 'bolder', # font_weight 文字字体的粗细 'normal','bold','bolder','lighter' font_style = 'oblique', # font_style 文字字体的风格,可选 'normal','italic','oblique' ), # 是否显示数据标签 itemstyle_opts={ "normal": { 'shadowBlur': 10, # 光影大小 "barBorderRadius": [100, 100, 0, 0], # 调整柱子圆角弧度 "shadowColor": "#94A4B4", # 调整阴影颜色 'shadowOffsetY': 6, 'shadowOffsetX': 6, # 偏移量 } } ) # Bar的全局配置项 chart.set_global_opts( xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( name='地区', is_scale=True, axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate = 45), # 网格线配置 splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts( is_show=False, linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts( type_='dashed')) ), yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( is_scale=True, name='岗位需求量', type_="value", # 网格线配置 splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts( is_show=False, linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts( type_='dashed')) ), # 标题配置 title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title=desc, pos_left=title_pos[0], pos_top=title_pos[1], title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20) ), tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( is_show=True, # 是否使用提示框 trigger='axis', # 触发类型 # is_show_content = True, trigger_on='mousemove|click', # 触发条件,点击或者悬停均可出发 axis_pointer_type='cross', # 指示器类型,鼠标移动到图表区可以查看效果 ), ) return chart grid = Grid( init_opts=opts.InitOpts( theme='white', width='1200px', height='1200px', ) ) # 依次添加不同属性下价格对比Bar grid.add( bar_chart('北京', ['15%', '3%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', # 指定Grid中子图的位置 pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('上海', ['50%', '3%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('广州', ['85%', '3%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('深圳', ['15%', '33%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('成都', ['50%', '33%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('杭州', ['85%', '33%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('武汉', ['15%', '63%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('南京', ['50%', '63%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('郑州', ['85%', '63%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177

通过绘制柱状图可以发现,北京作为岗位需求最多的城市,其数据分析岗主要分布在朝阳区和海淀区,而其他区仅有这两个区的不到三分之一的岗位需求。
上海数据分析岗岗位需求最多的区是浦东新区,其次是徐汇区,而徐汇区的岗位需求也不及浦东新区的一半。
广州的数据分析岗岗位需求主要分布在天河区,海珠越秀黄埔也有一部分数据分析岗,但是最主要的还是再天河区。
深圳的数据分析岗岗位需求主要分布在南山区、福田区以及龙岗区。
…三、薪资
下边看大部分小伙伴都比较关心的问题,就是薪资水平。这里的计算采用的都是企业发布的招聘的薪资范围的均值。
1. 各个城市平均薪资水平排名
city_salary = data2[['城市','薪资均值']].groupby('城市').mean().round(0).sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = True).reset_index() echarts_bar(city_salary['城市'].tolist(),city_salary['薪资均值'].tolist(),title = '全国各城市数据分析岗平均薪资水平排名', subtitle = '',label = '平均薪资').render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3

查看各个城市的薪资水平可以发现,北上广深身为经济最发达的四个一线城市,薪资水平也是最高的。数据分析岗薪资最高的城市是上海,而四个城市中薪资最低的城市是广州。南京和苏杭二州的薪资是紧随其后的,值得一提的是,岗位需求量超过广州的成都,薪资水平却处于中等水平。2. 各工作经验和学历的薪资水平对比
知道了哪个城市薪资水平较高以后,我们看看不同工作经验和不同学历的薪资水平分布是怎么样的吧
# 不同学历、不同经验、大专-不同经验交叉分析、本科-不同经验交叉分析、硕士-不同经验交叉分析、学历不限-不同经验交叉分析 job_exp = data2[['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() job_edu = data2[['学历要求','薪资均值']].groupby('学历要求').mean().round(0).sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() benke_exp = data2[data2['学历要求'] == '本科'][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).\ sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() dazhuan_exp = data2[data2['学历要求'] == '大专'][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).\ sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() shuoshi_exp = data2[data2['学历要求'] == '硕士'][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).\ sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() buxian_exp = data2[data2['学历要求'] == '学历不限'][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).\ sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() boshi_exp = data2[data2['学历要求'] == '博士'][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).\ sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() gaozhong_exp = data2[data2['学历要求'] == '高中'][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).\ sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index() zhongzhuan_exp = data2[data2['学历要求'] == '中专/中技'][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).\ sort_values(by = '薪资均值',ascending = False).reset_index()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
def bar_chart2(x,y,title_pos,title = '主标题',subtitle = '副标题'): # 新建一个Bar chart = Bar( init_opts=opts.InitOpts( # bg_color='#2C3B4C', # 设置背景颜色 theme='white', # 设置主题 width='400px', # 设置图的宽度 height='400px' ) ) chart.add_xaxis( x ) chart.add_yaxis( '', y ) chart.set_series_opts( # 自定义图表样式 label_opts=opts.LabelOpts( is_show=True, position='top', # position 标签的位置 可选 'top','left','right','bottom','inside','insideLeft','insideRight' font_size=15, color= '#727F91', font_weight = 'bolder', # font_weight 文字字体的粗细 'normal','bold','bolder','lighter' font_style = 'oblique', # font_style 文字字体的风格,可选 'normal','italic','oblique' ), # 是否显示数据标签 itemstyle_opts={ "normal": { 'shadowBlur': 10, # 光影大小 "barBorderRadius": [100, 100, 0, 0], # 调整柱子圆角弧度 "shadowColor": "#94A4B4", # 调整阴影颜色 'shadowOffsetY': 6, 'shadowOffsetX': 6, # 偏移量 } } ) # Bar的全局配置项 chart.set_global_opts( xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( name=' ', is_scale=True, axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate = 45), # 网格线配置 splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts( is_show=False, linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts( type_='dashed')) ), yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( is_scale=True, name='薪资均值', type_="value", # 网格线配置 splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts( is_show=False, linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts( type_='dashed')) ), # 标题配置 title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title=title, subtitle = subtitle, pos_left=title_pos[0], pos_top=title_pos[1], title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20) ), tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( is_show=True, # 是否使用提示框 trigger='axis', # 触发类型 # is_show_content = True, trigger_on='mousemove|click', # 触发条件,点击或者悬停均可出发 axis_pointer_type='cross', # 指示器类型,鼠标移动到图表区可以查看效果 ), ) return chart- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
grid = Grid( init_opts=opts.InitOpts( theme='white', width='1200px', height='1200px', ) ) # 依次添加不同属性下价格对比Bar grid.add( bar_chart2(job_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), job_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['15%', '3%'], title='不同工作经验薪资对比', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', # 指定Grid中子图的位置 pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(job_edu['学历要求'].tolist(), job_edu['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['50%', '3%'], title='不同学历要求薪资对比', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(buxian_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), buxian_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['85%', '3%'], title='学历不限', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(dazhuan_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), dazhuan_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['15%', '33%'], title='大专', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(benke_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), benke_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['50%', '33%'], title='本科', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(shuoshi_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), shuoshi_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['85%', '33%'], title='硕士', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(boshi_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), boshi_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['15%', '63%'], title='博士', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(gaozhong_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), gaozhong_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['50%', '63%'], title='高中', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart2(zhongzhuan_exp['工作经验'].tolist(), zhongzhuan_exp['薪资均值'].tolist(), ['85%', '63%'], title='中专/中技', subtitle=' '), grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100

总的来看工作经验、学历和薪资的关系,可以发现,工作经验和学历越高,相应的薪资也越高,这是毋庸置疑的。
通过不同学历背景下,不同的工作经验与薪资的交叉分析,不难看出,学历越高,相应的薪资的上升空间也是越高的。3. 各城市不同工作经验薪资水平对比
def bar_chart(desc, title_pos): df_t = data2[data2['城市'] == desc][['工作经验','薪资均值']].groupby('工作经验').mean().round(0).sort_values(by = '薪资均值', ascending = False).reset_index() # 新建一个Bar chart = Bar( init_opts=opts.InitOpts( # bg_color='#2C3B4C', # 设置背景颜色 theme='white', # 设置主题 width='400px', # 设置图的宽度 height='400px' ) ) chart.add_xaxis( df_t['工作经验'].tolist() ) chart.add_yaxis( '', df_t['薪资均值'].tolist() ) chart.set_series_opts( # 自定义图表样式 label_opts=opts.LabelOpts( is_show=True, position='top', # position 标签的位置 可选 'top','left','right','bottom','inside','insideLeft','insideRight' font_size=15, color= '#727F91', font_weight = 'bolder', # font_weight 文字字体的粗细 'normal','bold','bolder','lighter' font_style = 'oblique', # font_style 文字字体的风格,可选 'normal','italic','oblique' ), # 是否显示数据标签 itemstyle_opts={ "normal": { 'shadowBlur': 10, # 光影大小 "barBorderRadius": [100, 100, 0, 0], # 调整柱子圆角弧度 "shadowColor": "#94A4B4", # 调整阴影颜色 'shadowOffsetY': 6, 'shadowOffsetX': 6, # 偏移量 } } ) # Bar的全局配置项 chart.set_global_opts( xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( name='工作经验', is_scale=True, axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate = 45), # 网格线配置 splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts( is_show=False, linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts( type_='dashed')) ), yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts( is_scale=True, name='薪资均值', type_="value", # 网格线配置 splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts( is_show=False, linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts( type_='dashed')) ), # 标题配置 title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title=desc, pos_left=title_pos[0], pos_top=title_pos[1], title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20) ), tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts( is_show=True, # 是否使用提示框 trigger='axis', # 触发类型 # is_show_content = True, trigger_on='mousemove|click', # 触发条件,点击或者悬停均可出发 axis_pointer_type='cross', # 指示器类型,鼠标移动到图表区可以查看效果 ), ) return chart grid = Grid( init_opts=opts.InitOpts( theme='white', width='1200px', height='1200px', ) ) # 依次添加不同属性下价格对比Bar grid.add( bar_chart('北京', ['15%', '3%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', # 指定Grid中子图的位置 pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('上海', ['50%', '3%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('广州', ['85%', '3%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='10%', pos_bottom='70%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('深圳', ['15%', '33%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('成都', ['50%', '33%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('杭州', ['85%', '33%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='40%', pos_bottom='40%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('武汉', ['15%', '63%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='5%', pos_right='70%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('南京', ['50%', '63%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='40%', pos_right='35%' ) ) grid.add( bar_chart('郑州', ['85%', '63%']), # is_control_axis_index=False, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts( pos_top='70%', pos_bottom='10%', pos_left='75%', pos_right='0%' ) ) grid.render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176

看各城市相应的薪资下限和上限,可以发现,北上广深的下限和上限都是很高的,做数据分析去一线城市是没毛病的~四、岗位要求
1. 数据分析岗对工作经验和学历的需求情况
了解了薪资以后,接下来我们看下数据分析岗有哪些岗位需求吧~
pie1 = data[['工作经验','职位名称']].groupby('工作经验').count().sort_values(by = '职位名称',ascending = False).reset_index() pie2 = data[['学历要求','职位名称']].groupby('学历要求').count().sort_values(by = '职位名称',ascending = False).reset_index() pie1 = (Pie() .add('', [list(z) for z in zip(pie1['工作经验'], pie1['职位名称'])]) .set_global_opts( title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title='工作经验需求量', title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20) ) ) ) pie2 = (Pie() .add('', [list(z) for z in zip(pie2['学历要求'], pie2['职位名称'])]) .set_global_opts( title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title='学历需求量', title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20) ) ) ) page = Page() page.add(pie1,pie2) page.render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23


首先看工作经验。数据分析岗在工作经验的要求上边,1-3年工作经验是最多的,而不限工作经验和3-5年工作经验的需求也相对较多。
在学历需求上边,本科和大专占了绝大部分,仅有较少一部分是要求硕士和博士学历的。因此数据分析岗对于学历的要求并不是很高。2. 数据分析岗技能需求
接下来我们看下数据分析岗要具备哪些技能吧~
这里的数据是爬取自公司发布的职位信息中的职位标签,而非岗位JDtag_array = data['岗位标签'].apply(lambda x:eval(x)).tolist() tag_lis = [] for tag in tag_array: tag_lis += tag tag_df = pd.DataFrame(tag_lis,columns = ['职位标签']) tag_df_cnt = tag_df['职位标签'].value_counts().reset_index() tag_df_cnt.columns = ['职位标签','计数'] word_cnt_lis = [tag for tag in zip(tag_df_cnt['职位标签'],tag_df_cnt['计数'])] wc = ( WordCloud() .add("", word_cnt_lis, ) .set_global_opts( title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="岗位标签词云图"), ) ) wc.render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
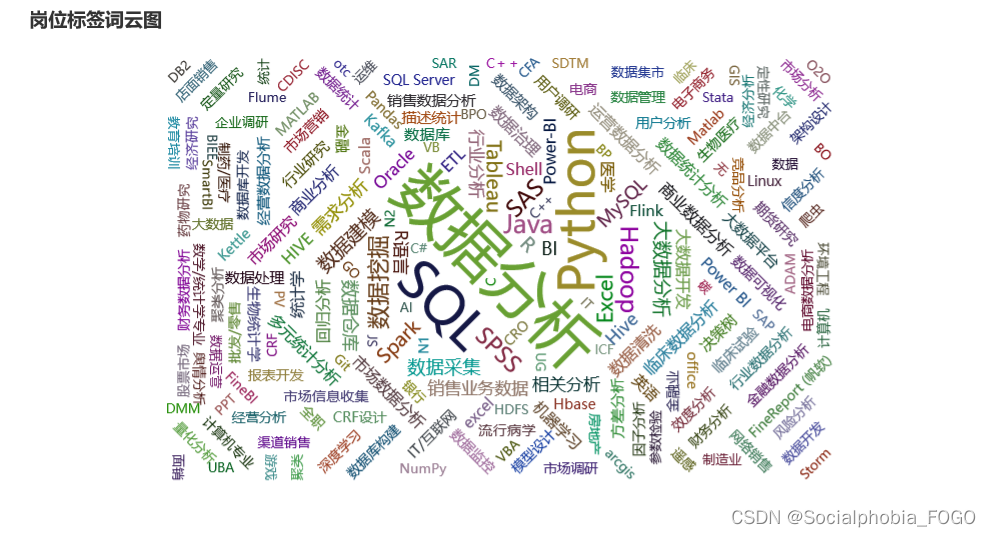
绘制词云图我们可以发现,众多的岗位标签中,出现次数最频繁的就是python和sql了,因此可以说明,sql和python是数据分析岗必备的技能,当然excel技能在日常工作中使用同样很频繁。
词云中数据挖掘、数据清洗、SPSS、BI工具等一些词汇出现的也较多,具体的还要看各岗位的具体需求。五、公司情况
1. 公司类型、公司规模统计
接下来我们看看招聘数据分析岗的企业中,主要都是哪些类型的企业,以及公司规模都是如何的。
company_type_cnt = data[['公司类型','公司规模']].groupby('公司类型').count().sort_values(by = '公司规模',ascending = False).reset_index() # 删除空值 company_type_cnt = company_type_cnt.drop(index = 10) company_type_cnt.columns = ['公司类型','数量'] company_size_cnt = data[['公司类型','公司规模']].groupby('公司规模').count().sort_values(by = '公司类型',ascending = False).reset_index() company_size_cnt.columns = ['公司规模','数量'] pie1 = (Pie() .add('', [list(z) for z in zip(company_type_cnt['公司类型'], company_type_cnt['数量'])]) .set_global_opts( title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title='各类型公司数据分析岗需求量', title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20) ) ) ) pie2 = (Pie() .add('', [list(z) for z in zip(company_size_cnt['公司规模'], company_size_cnt['数量'])]) .set_global_opts( title_opts=opts.TitleOpts( title='各规模公司数据分析岗需求量', title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#2C3B4C', font_size=20) ) ) ) page = Page() page.add(pie1,pie2) page.render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
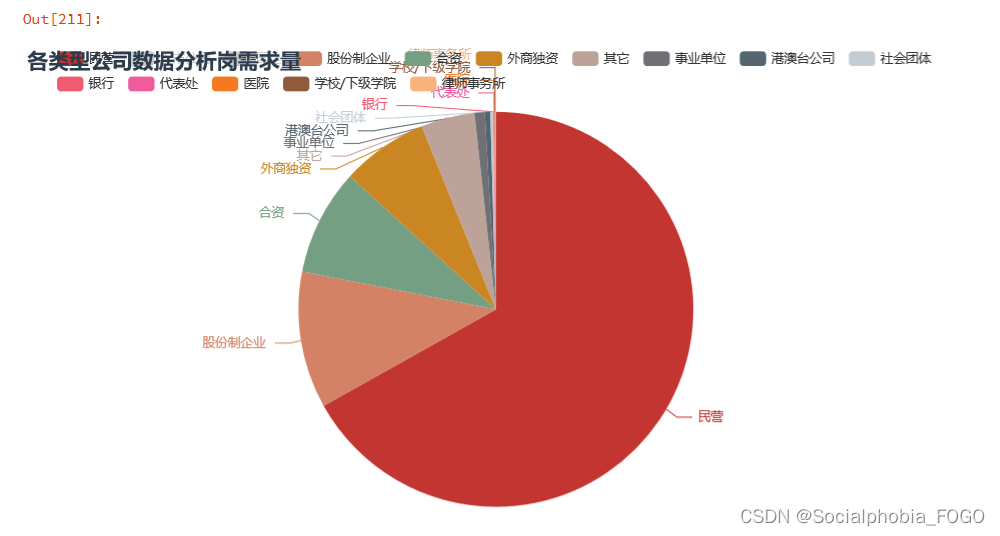

我们可以发现,招聘数据分析岗的企业中,以民营企业为主,占了一大半以上。
公司规模以1000-9999以及10000人以上的大型企业为主,大厂的数字化建设较为完善和成熟,因此会有较多的数据分析需求。同样也有部分中小企业,有可能是一些外包企业等。2. 公司薪资待遇综合排名top50
接下来,我们统计出薪资待遇top前50的企业,希望可以为各位小伙伴提供一些参考的依据~
company_rank = data2[['职位名称','公司名称','薪资均值','公司规模']].groupby(['公司名称','公司规模','职位名称']).mean().\ sort_values(by = ['薪资均值'],ascending = False).reset_index() table = Table() table_rows = [company_rank.iloc[i,:].tolist() for i in range(50)] table.add(company_rank.columns.tolist(), table_rows) table.render_notebook()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
相关阅读:
L1-002 打印沙漏分数 20
大白话 K8S(03):从 Pause 容器理解 Pod 的本质
day1| 704. 二分查找、27. 移除元素
【算法刷题day37】Leetcode:738. 单调递增的数字、968. 监控二叉树
炫酷动漫游戏网站页面设计html页面前端源码
Python自动化办公小程序:实现报表自动化和自动发送到目的邮箱
个人如何用时间管理软件提升效率
删除C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsA\python.exe
【区块链 + 智慧政务】一体化政务数据底座平台 | FISCO BCOS应用案例
并发编程之volatile与JMM多线程内存模型
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46043195/article/details/125395707