-
单调性约束与反单调性约束的区别 monotonicity and anti-monotonicity constraint
▚ 01 Monotone Constraints 单调性约束
1.1 Definitions 定义
【Monotone Constraints | SpringerLink 】
A constraint C is monotone if and only if for all itemsets S and S′:
if S ⊇ S′ and S violates C, then S′ violates C.1.2 Key Points 要点
Monotone constraints possess the following property. If an itemset S violates a monotone constraint C, then any of its subsets also violates C. Equivalently, all supersets of an itemset satisfying a monotone constraint C also satisfy C (i.e., C is upward closed). By exploiting this property, monotone constraints can be used for reducing computation in frequent itemset mining with constraints. As frequent itemset mining with constraints aims to find frequent itemsets that satisfy the constraints, if an itemset S satisfies a monotone constraint C, no further constraint checking needs to be applied to any superset of S because all supersets of S are guaranteed to satisfy C. Examples of monotone constraints include min(S. Price) ≤ $30, which expresses that the minimum price of all items in an itemset S is at most $30. Note that, if the minimum price of all items in S is at most $30, adding more items to S would not increase its minimum price (i.e., supersets of S would also satisfy such a monotone constraint).

▚ 02 Anti-monotone Constraints 反单调性约束
2.1 Definitions 定义
【Anti-monotone Constraints | SpringerLink】
A constraint C is anti-monotone if and only if for all itemsets S and S′:
if S ⊇ S′and S satisfies C, then S′ satisfies C.2.2 Key Points 要点
Anti-monotone constraints possess the following nice property. If an itemset S satisfies an anti-monotone constraint C, then all of its subsets also satisfy C (i.e., C is downward closed). Equivalently, any superset of an itemset violating an anti-monotone constraint C also violates C. By exploiting this property, anti-monotone constraints can be used for pruning in frequent itemset mining with constraints. As frequent itemset mining with constraints aims to find itemsets that are frequent and satisfy the constraints, if an itemset violates an anti-monotone constraint C, all its supersets (which would also violate C) can be pruned away and their frequencies do not need to be counted. Examples of anti-monotone constraints include min(S. Price) ≥ $20 (which expresses that the minimum price of all items in an itemset S is at least $20) and the usual frequency constraint support(S) ≥ minsup (i.e., frequency(S) ≥ minsup). For the former, if the minimum price of all items in S is less than $20, adding more items to S would not increase its minimum price (i.e., supersets of S would not satisfy such an anti-monotone constraint). For the latter, it is widely used in frequent itemset mining, with or without constraints. It states that (i) all subsets of a frequent itemset are frequent and (ii) any superset of an infrequent itemset is also infrequent. This is also known as the Apriori property.

▚ 03 Explanation 解释
假设:我们将S violates C作为事件A,S′ violates C作为事件B;则 S satisfies C为事件not A,then S′ satisfies C为事件not B.
此时,根据Monotone Constraints定义知(A → B),也即(not B → not A);
根据Anti-monotonicity Constraints定义知(not A → not B),也即(B → A);因为(A → B)并不一定意味着(B → A),所以这两者 (Monotone Constraints & Anti-monotonicity Constraints) 的声明是不同的。

▚ 04 Example 示例
For an example. Consider- C1 = Sum of elements is greater than 5 C2 = Sum of elements is at most 5 U(universe) = Set of non-negative real numbers- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
In case of C1,
If S violates C1, then S’ obviously violates C1 as well (S being a superset of S’)
Eg. S = {1, 2}, S’ = {2}
Hence C1 is monotonic.In case of C2,
If S satisfies C2, then S’ obviously satisfies C2 as well (S being a superset of S’)
Eg. S = {1, 2}, S’ = {2}
Hence C2 is anti-monotonic.
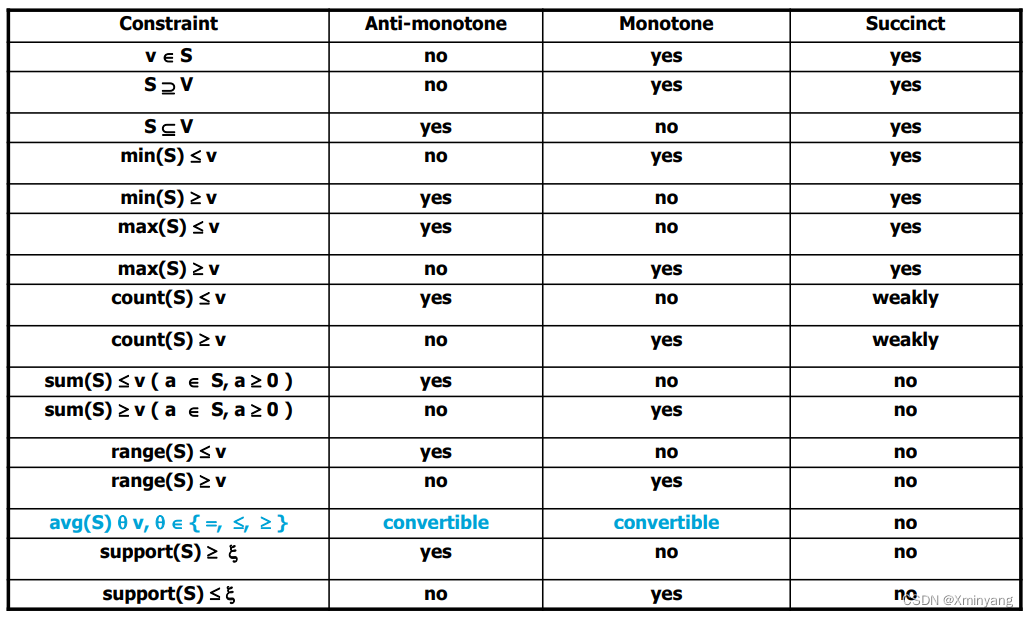
▚ 05 数据挖掘的约束限制
Constraint-Based Mining — A General Picture

参考文章
-
相关阅读:
介绍java中Pair和Map的区别
vue3使用Element ui plus中MessageBox消息框+radio框配合使用
【元宇宙欧米说】音频+PFP,做一只web3最勤劳的猫咪
Nacos docker实现nacos高可用集群项目
Opencv!!在树莓派上安装Opencv!
Doris学习笔记之优化
C++核心编程(持续更新)
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition浅读与实现
Spring——五大类注解和方法注解详解
巧用 redis 实现点赞功能,它不比 mysql 香吗?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Xminyang/article/details/125453967