-
【数据结构】这些栈、队列的经典面试题你还不知道吗?
一.用队列实现栈
在做这道题前,我们需要有 栈 的先驱知识,可以参考本人的这篇博客
(41条消息) 【数据结构】栈_Living_Amethyst的博客-CSDN博客
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
- void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
- int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
- int top() 返回栈顶元素。
- boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
分析:
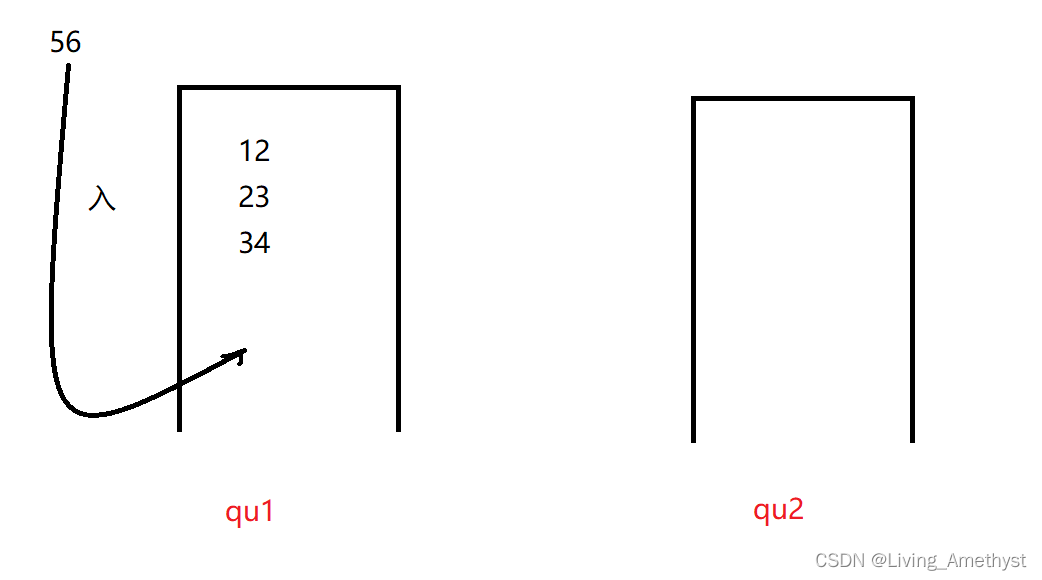
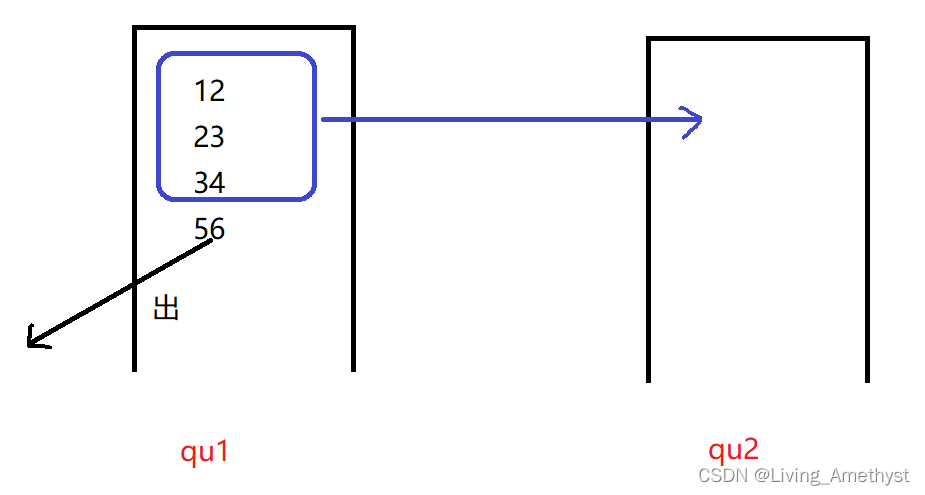
由于队列的特点是“先进先出”,而栈的特点是“后入先出”,所以用队列实现栈 仅用一个队列是不能实现的,需要两个队列
我们的思路是:入的时候都入到不为空的队列里,出的时候就把不为空的队列里的除了要出的元素之外的其他(size-1)个元素都移到为空的队列里
- import java.util.LinkedList;
- import java.util.Queue;
- class MyStack {
- private Queue<Integer> qu1;
- private Queue<Integer> qu2;
- public MyStack() {
- qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
- qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
- }
- /**
- * 入到不为空的队列中
- * 如果都为空,就入到qu1中
- * @param x
- */
- public void push(int x) {
- if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
- qu1.offer(x);
- }else if(qu2.isEmpty()){
- qu2.offer(x);
- }else{
- qu1.offer(x);
- }
- }
- public int pop() {
- //1.判断当前“栈”是否为空
- if(empty()){
- return -1;
- }
- if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
- //从不为空的队列里出 size-1 个元素
- int size = qu1.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {
- /*
- int tmp = qu1.poll();
- qu2.offer(tmp);
- */
- qu2.offer(qu1.poll());
- }
- return qu1.poll();
- }else{
- //从不为空的队列里出 size-1 个元素
- int size = qu2.size();
- for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++) {
- /*
- int tmp = qu1.poll();
- qu2.offer(tmp);
- */
- qu1.offer(qu2.poll());
- }
- return qu2.poll();
- }
- }
- public int top() {
- //1.判断当前“栈”是否为空
- if(empty()){
- return -1;
- }
- if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
- //从不为空的队列里出 size个元素
- int size = qu1.size();
- int tmp = -1;
- for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
- tmp = qu1.poll();
- qu2.offer(tmp);
- }
- return tmp;
- }else{
- //从不为空的队列里出 size个元素
- int size = qu2.size();
- int tmp = -1;
- for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
- tmp = qu2.poll();
- qu1.offer(tmp);
- }
- return tmp;
- }
- }
- public boolean empty() {
- if (qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty()) {
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- }
二.用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
- void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
- int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
- int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
- boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
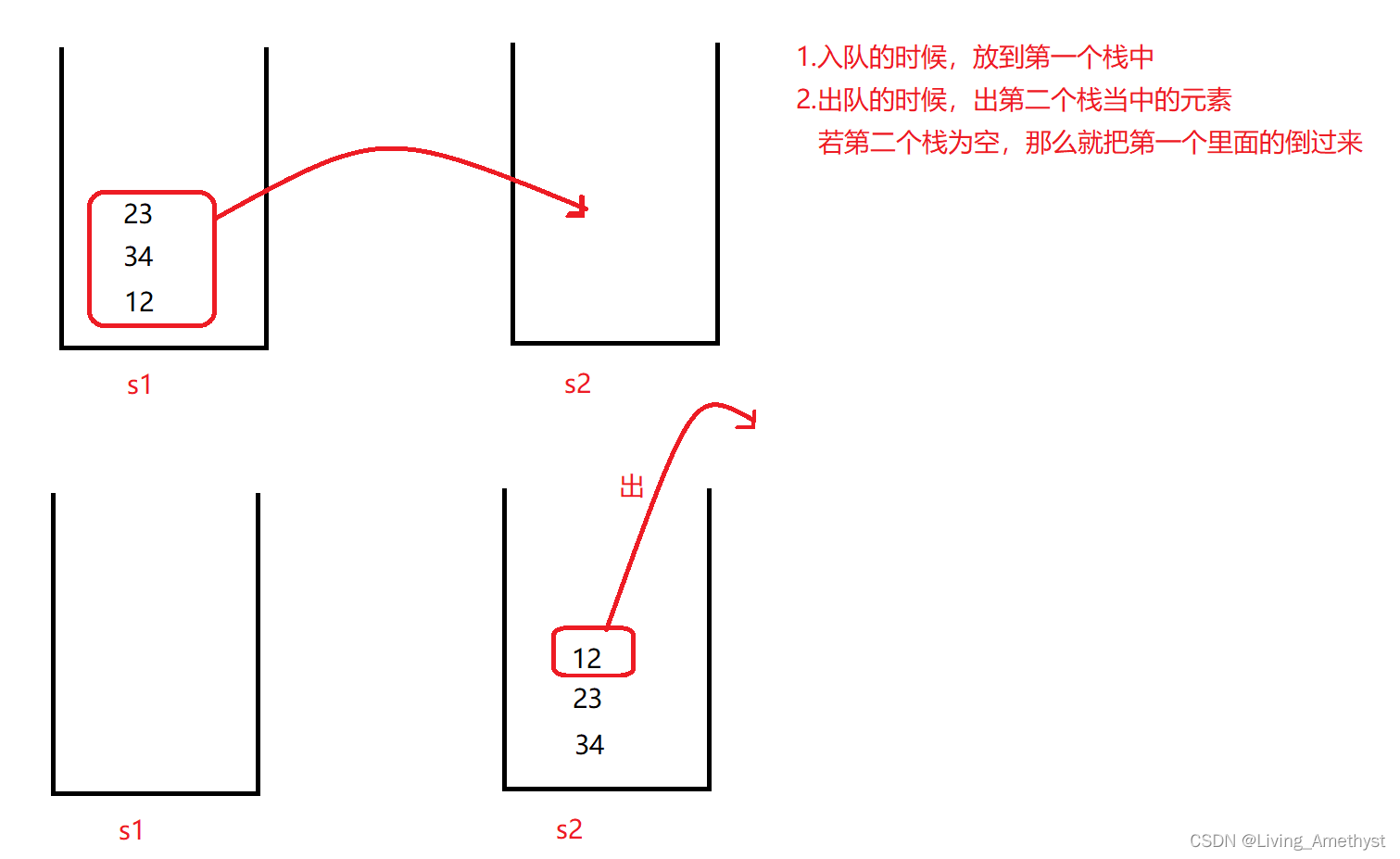
分析:和上一题类似,若要用栈实现队列,我们需要两个栈
- import java.util.Stack;
- class MyQueue {
- private Stack<Integer> s1;
- private Stack<Integer> s2;
- public MyQueue() {
- s1 = new Stack<>();
- s2 = new Stack<>();
- }
- public void push(int x) {
- //入队的逻辑是把元素统一放到第一个栈中
- s1.push(x);
- }
- //如果第二个栈不为空,则出栈顶元素,否则把第一个栈的元素全部导入第二个栈
- public int pop() {
- if(empty()){
- return -1;//两个栈都是空
- }
- if (s2.empty()){
- //把第一个栈的元素全部导入第二个栈
- while(!s1.empty()){
- s2.push(s1.pop());
- }
- }
- //s2一定是不为空的
- return s2.pop();
- }
- public int peek() {
- if(empty()){
- return -1;//两个栈都是空
- }
- if (s2.empty()){
- //把第一个栈的元素全部导入第二个栈
- while(!s1.empty()){
- s2.push(s1.pop());
- }
- }
- //s2一定是不为空的
- return s2.peek();
- }
- public boolean empty() {
- return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
- }
- }
三.实现一个最小栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
实现 MinStack 类:
- MinStack() 初始化堆栈对象。
- void push(int val) 将元素val推入堆栈。
- void pop() 删除堆栈顶部的元素。
- int top() 获取堆栈顶部的元素。
- int getMin() 获取堆栈中的最小元素。
分析:
- 定义两个栈,s1 和 minStack
- 入栈时,s1这个栈是一定会放元素的,
- 而对于minStack这个栈,如果minStack为空,则把元素放入minStack
- 若不为空就把放入s1的元素与minStack的元素比较
- 若大于minStack栈中元素,就不放入minStack栈,若小于minStack栈中元素就放入。
- 出栈时,s1一定要出栈,同时要与minStack栈中元素比较,如果一样,那么minStack中的元素也要出栈
- import java.util.Stack;
- class MinStack {
- private Stack<Integer> s1;
- private Stack<Integer> minStack;
- public MinStack() {
- s1 = new Stack<>();
- minStack = new Stack<>();
- }
- public void push(int val) {
- s1.push(val);//s1这个栈是一定会放元素的
- if(minStack.empty()){
- minStack.push(val);
- }else{
- int x = minStack.peek();
- if(val <= x){ //这里必须加等号
- minStack.push(val);
- }
- }
- }
- public void pop() {
- int x = s1.pop();
- int x2 = minStack.peek();
- if(x == x2){
- minStack.pop();
- }
- }
- //获取当前栈顶元素不删除
- public int top() {
- return s1.peek();
- }
- public int getMin() {
- return minStack.peek();
- }
- }
-
相关阅读:
市场调研团体怎么使用无人系统生产更安全
洛谷-官方题单版【入门篇】
c++builder6.0 数据库查询函数select * into 功能的实现
Linux 命令行——Shell 环境变量的查看、配置、激活
【Python大数据笔记_day10_Hive调优及Hadoop进阶】
贫血模型与充血模型
从javascript到vue再到react的演变
Linux0.11-内核中断体系
Docker详解(上)
【Vue插件】一款很好用的vue日历插件——vue-sweet-calendar
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Living_Amethyst/article/details/125399993