-
【力扣 - 和为K的子数组】
题目描述
给你一个整数数组
nums和一个整数k,请你统计并返回 该数组中和为k的子数组的个数 。子数组是数组中元素的连续非空序列。
示例 1:
输入:
nums = [1,1,1], k = 2
输出:2示例 2:
输入:
nums = [1,2,3], k = 3
输出:2提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 10^4
-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
-10^7 <= k <= 10^7方法一:枚举
思路和算法
考虑以
i结尾和为k的连续子数组个数,我们需要统计符合条件的下标j的个数,其中0≤j≤i且[j..i]这个子数组的和恰好为k。我们可以枚举
[0..i]里所有的下标j来判断是否符合条件,可能有读者会认为假定我们确定了子数组的开头和结尾,还需要 O(n) 的时间复杂度遍历子数组来求和,那样复杂度就将达到 O(n3) 从而无法通过所有测试用例。但是如果我们知道[j,i]子数组的和,就能 O(1) 推出[j−1,i]的和,因此这部分的遍历求和是不需要的,我们在枚举下标j的时候已经能 O(1) 求出[j,i]的子数组之和。代码
/** * Function to count the number of subarrays that sum up to the target value k * @param nums: array of integers * @param numsSize: size of the input array * @param k: target sum value * @return the number of subarrays that sum up to k */ int subarraySum(int* nums, int numsSize, int k) { int count = 0; // Initialize the count of subarrays that sum up to k // Iterate through each index as the starting point of the subarray for(int leftindex = 0; leftindex < numsSize; ++leftindex) { int sum = 0; // Initialize the sum of the subarray starting at leftindex // Calculate the sum of subarrays starting from leftindex and ending at different points for(int rightindex = leftindex; rightindex >= 0; --rightindex) { sum = sum + nums[rightindex]; // Add the element at rightindex to the sum // Check if the current sum equals the target value k if(sum == k) { count++; // Increment the count as a subarray with sum k is found } } } return count; // Return the total count of subarrays with sum equal to k }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
方法二:前缀和 + 哈希表优化
思路和算法
我们可以基于方法一利用数据结构进行进一步的优化,我们知道方法一的瓶颈在于对每个
i,我们需要枚举所有的j来判断是否符合条件,这一步是否可以优化呢?答案是可以的。



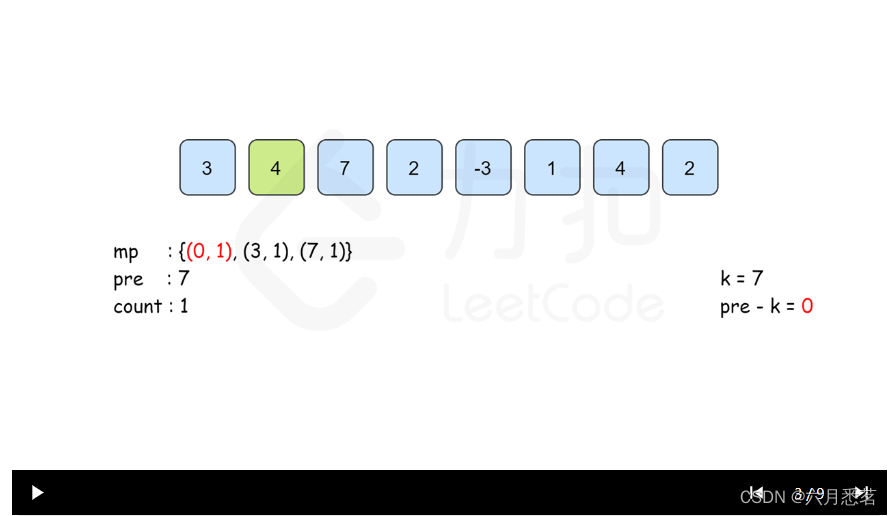






代码
// Structure to represent a node in the hash table struct Node { int key; int value; struct Node* next; }; // Function to create a new node for the hash table struct Node* createNode(int key, int value) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->key = key; newNode->value = value; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; } // Function to count the number of subarrays that sum up to the target value k int subarraySum(int* nums, int numsSize, int k) { // Initialize an array of pointers to nodes for the hash table struct Node* map[numsSize + 1]; for (int i = 0; i <= numsSize; i++) { map[i] = NULL; } // Initialize the first node in the hash table map[0] = createNode(0, 1); int count = 0, pre = 0; // Iterate through the input array to calculate subarray sums for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { pre += nums[i]; // Calculate the key for the current subarray sum int key = pre - k; int index = (key % (numsSize + 1) + numsSize + 1) % (numsSize + 1); // Ensure non-negative index struct Node* current = map[index]; // Traverse the linked list at the computed index while (current != NULL) { if (current->key == key) { count += current->value; } current = current->next; } // Calculate the new index for the current sum int newIndex = (pre % (numsSize + 1) + numsSize + 1) % (numsSize + 1); // Ensure non-negative index if (map[newIndex] == NULL) { map[newIndex] = createNode(pre, 1); } else { struct Node* temp = map[newIndex]; while (temp->next != NULL) { temp = temp->next; } temp->next = createNode(pre, 1); } } return count; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
方法三:哈希表(不超时)
前面两个方法都超时了。
利用malloc动态开辟一个数组空间,作为哈希表,数组下标代表哈希key值,数组下标对应的值代表key值指向的元素值,再对数组求前缀和,将前缀和将key值存入哈希数组中,前缀和 p[i] - p[j] = k 就表示数组i - j 满足要求,即p[i] - k = p[j],每次求出当前前缀和,就在哈希数组中判断是否存在p[j],累加p[j]存在个数,并返回// Function to count the number of subarrays that sum up to the target value k int subarraySum(int *nums, int numsSize, int k) { int count = 0; // Create a large array to act as a simple hash table, initialized to all zeros int *maps = (int *)calloc(10000001 * 2, sizeof(int)); // Set the pointer to the middle position to accommodate negative prefix sums int *map = maps + 10000001 * 1; // Initialize the prefix sum with an additional sum at index 0 int sum = 0; map[sum]++; // Calculate prefix sums and count subarrays with target sum k for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { sum += nums[i]; // Check if a previous prefix sum exists that can form a subarray with sum k if (map[sum - k] > 0) { count += map[sum - k]; } // Update the count of prefix sums encountered map[sum]++; } // Free the memory allocated for the hash table array free(maps); return count; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
-
相关阅读:
FPGA-结合协议时序实现UART收发器(四):串口驱动模块uart_drive、例化uart_rx、uart_tx
shell脚本的条件判断3:探究[[]]和[]的区别
使用uncompyle6反编译pyc文件(附报KeyError和Error: uncompyle6 requires Python 2.6-3.8的解决方法)
01背包的变形-最后一块石头重量。
请简要说明 Mysql 中 MyISAM 和 InnoDB 引擎的区别
Shell脚本攻略:循环语句for
react面试题笔记整理
PINN期刊推荐总结
Element UI表格的序号递增(点击分页后)
MySQL数据库连接失败
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/shuting7/article/details/136620811
