-
Activiti监听器
学习链接
- 5.2 activiti任务监听器TaskListener
- 5.1 activiti执行监听器ExecutionListener
- 5.3 activiti工作流程事件监听ActivitiEventListener
任务监听器 TaskListener
任务监听器用于在特定的任务相关事件发生时,执行自定义的Java逻辑或表达式
- 任务监听器是处理业务逻辑的重要的地方,当任务创建、设定负责人、完成任务时都可以监听的到,从而来处理自己的业务
- 常用于监听Assignment事件,设置完负责人给负责人发一个消息来通知提示。注意:
任务监听器只能用在UserTask上使用。
监听的事件
-
String EVENTNAME_CREATE = “create”;创建):当任务已经创建,并且所有任务参数都已经设置时触发
-
String EVENTNAME_ASSIGNMENT = “assignment”;(指派):当任务已经指派给某人时触发。请注意:当流程执行到达用户任务时,create事件触发前,首先触发assignment事件。这看起来不是自然顺序,但是有实际原因的:当收到create事件时,我们通常希望查看任务的所有参数,包括办理人。
-
String EVENTNAME_COMPLETE = “complete”(完成):当任务已经完成,从运行时数据中删除前触发。
-
String EVENTNAME_DELETE = “delete”(删除):在任务即将被删除前触发。请注意当任务通过completeTask正常完成时也会触发
注意:assignment事件比create先执行。
TaskListener 接口
TaskListener接口继承自BaseTaskListener 接口
public interface BaseTaskListener extends Serializable { String EVENTNAME_CREATE = "create"; String EVENTNAME_ASSIGNMENT = "assignment"; String EVENTNAME_COMPLETE = "complete"; String EVENTNAME_DELETE = "delete"; /** * Not an actual event, used as a marker-value for {@link BaseTaskListener}s that should be called for all events, including {@link #EVENTNAME_CREATE} , {@link #EVENTNAME_ASSIGNMENT} and * {@link #EVENTNAME_COMPLETE} and {@link #EVENTNAME_DELETE}. */ String EVENTNAME_ALL_EVENTS = "all"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
TaskListener接口定义,只有notify方法,传入DelegateTask
public interface TaskListener extends BaseTaskListener { void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
监听器委托类DelegateTask
我们在监听方法中,能够拿到DelegateTask对象,因此,我们要熟悉这个对象的相关方法
package org.activiti.engine.delegate; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Set; import org.activiti.engine.ActivitiObjectNotFoundException; import org.activiti.engine.task.DelegationState; import org.activiti.engine.task.IdentityLink; import org.activiti.engine.task.IdentityLinkType; /** * @author Joram Barrez */ public interface DelegateTask extends VariableScope { /** DB id of the task. */ String getId(); /** Name or title of the task. */ String getName(); /** Change the name of the task. */ void setName(String name); /** Free text description of the task. */ String getDescription(); /** Change the description of the task */ void setDescription(String description); /** indication of how important/urgent this task is with a number between * 0 and 100 where higher values mean a higher priority and lower values mean * lower priority: [0..19] lowest, [20..39] low, [40..59] normal, [60..79] high * [80..100] highest */ int getPriority(); /** indication of how important/urgent this task is with a number between * 0 and 100 where higher values mean a higher priority and lower values mean * lower priority: [0..19] lowest, [20..39] low, [40..59] normal, [60..79] high * [80..100] highest */ void setPriority(int priority); /** Reference to the process instance or null if it is not related to a process instance. */ String getProcessInstanceId(); /** Reference to the path of execution or null if it is not related to a process instance. */ String getExecutionId(); /** Reference to the process definition or null if it is not related to a process. */ String getProcessDefinitionId(); /** The date/time when this task was created */ Date getCreateTime(); /** The id of the activity in the process defining this task or null if this is not related to a process */ String getTaskDefinitionKey(); /** Indicated whether this task is suspended or not. */ boolean isSuspended(); /** The tenant identifier of this task */ String getTenantId(); /** The form key for the user task */ String getFormKey(); /** Change the form key of the task */ void setFormKey(String formKey); /** Returns the execution currently at the task. */ DelegateExecution getExecution(); /** Returns the event name which triggered the task listener to fire for this task. */ String getEventName(); /** The current {@link org.activiti.engine.task.DelegationState} for this task. */ DelegationState getDelegationState(); /** Adds the given user as a candidate user to this task. */ void addCandidateUser(String userId); /** Adds multiple users as candidate user to this task. */ void addCandidateUsers(Collection<String> candidateUsers); /** Adds the given group as candidate group to this task */ void addCandidateGroup(String groupId); /** Adds multiple groups as candidate group to this task. */ void addCandidateGroups(Collection<String> candidateGroups); /** The {@link User.getId() userId} of the person responsible for this task. */ String getOwner(); /** The {@link User.getId() userId} of the person responsible for this task.*/ void setOwner(String owner); /** The {@link User.getId() userId} of the person to which this task is delegated. */ String getAssignee(); /** The {@link User.getId() userId} of the person to which this task is delegated. */ void setAssignee(String assignee); /** Due date of the task. */ Date getDueDate(); /** Change due date of the task. */ void setDueDate(Date dueDate); /** The category of the task. This is an optional field and allows to 'tag' tasks as belonging to a certain category. */ String getCategory(); /** Change the category of the task. This is an optional field and allows to 'tag' tasks as belonging to a certain category. */ void setCategory(String category); /** * Involves a user with a task. The type of identity link is defined by the given identityLinkType. * @param userId id of the user involve, cannot be null. * @param identityLinkType type of identityLink, cannot be null (@see {@link IdentityLinkType}). * @throws ActivitiObjectNotFoundException when the task or user doesn't exist. */ void addUserIdentityLink(String userId, String identityLinkType); /** * Involves a group with group task. The type of identityLink is defined by the given identityLink. * @param groupId id of the group to involve, cannot be null. * @param identityLinkType type of identity, cannot be null (@see {@link IdentityLinkType}). * @throws ActivitiObjectNotFoundException when the task or group doesn't exist. */ void addGroupIdentityLink(String groupId, String identityLinkType); /** * Convenience shorthand for {@link #deleteUserIdentityLink(String, String)}; with type {@link IdentityLinkType#CANDIDATE} * @param userId id of the user to use as candidate, cannot be null. * @throws ActivitiObjectNotFoundException when the task or user doesn't exist. */ void deleteCandidateUser(String userId); /** * Convenience shorthand for {@link #deleteGroupIdentityLink(String, String, String)}; with type {@link IdentityLinkType#CANDIDATE} * @param groupId id of the group to use as candidate, cannot be null. * @throws ActivitiObjectNotFoundException when the task or group doesn't exist. */ void deleteCandidateGroup(String groupId); /** * Removes the association between a user and a task for the given identityLinkType. * @param userId id of the user involve, cannot be null. * @param identityLinkType type of identityLink, cannot be null (@see {@link IdentityLinkType}). * @throws ActivitiObjectNotFoundException when the task or user doesn't exist. */ void deleteUserIdentityLink(String userId, String identityLinkType); /** * Removes the association between a group and a task for the given identityLinkType. * @param groupId id of the group to involve, cannot be null. * @param identityLinkType type of identity, cannot be null (@see {@link IdentityLinkType}). * @throws ActivitiObjectNotFoundException when the task or group doesn't exist. */ void deleteGroupIdentityLink(String groupId, String identityLinkType); /** * Retrieves the candidate users and groups associated with the task. * @return set of {@link IdentityLink}s of type {@link IdentityLinkType#CANDIDATE}. */ Set<IdentityLink> getCandidates(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
任务监听实现方式 — 类class
绘制流程图

给经理审批节点设置如下任务监听器

自定义任务监听器
SiteReportUserTaskListener
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.activiti.engine.delegate.DelegateTask; import org.activiti.engine.delegate.TaskListener; /** * 任务监听器用于在特定的任务相关事件发生时,执行自定义的Java逻辑或表达式 * * 任务监听器支持下列属性: * event(事件)(必填):任务监听器将被调用的任务事件类型。可用的事件有: * create(创建):当任务已经创建,并且所有任务参数都已经设置时触发。 * assignment(指派):当任务已经指派给某人时触发。请注意:当流程执行到达用户任务时,create事件触发前,首先触发 * assignment事件。这看起来不是自然顺序,但是有实际原因的:当收到create事件时,我们通常希望查看任务的所有参数,包括 * 办理人。 * complete(完成):当任务已经完成,从运行时数据中删除前触发。 * delete(删除):在任务即将被删除前触发。请注意当任务通过completeTask正常完成时也会触发 * * class:需要调用的代理类。这个类必须实现 org.activiti.engine.delegate.TaskListener 接口 * * * expression:(不能与class属性一起使用):指定在事件发生时要执行的表达式。可以为被调用的对象传递 DelegateTask 对象与事件名(使用 task.eventName )作为参数 * * * * delegateExpression:可以指定一个能够解析为 TaskListener 接口实现类对象的表达式。与服务任务类似 * * */ @Slf4j public class SiteReportUserTaskListener implements TaskListener { /* 启动流程时候(按顺序) 收到事件通知: assignment 收到事件通知: create 完成经理审批任务时候(按顺序) 收到事件通知: complete 收到事件通知: delete */ @Override public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) { log.info("收到事件通知: {}", delegateTask.getEventName()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
测试
- 先部署该流程
- 然后,发起1个流程时,它会收到assignment、create
- 然后,部门经理完成该任务,它会收到complete、delete
监听实现方式 — 表达式expression
使用activiti:taskListener元素的expression属性来指定监听器
绘制流程图

如下图给经理审批节点添加任务监听器,设置Expression为${taskListenerExpression.execute(task)}
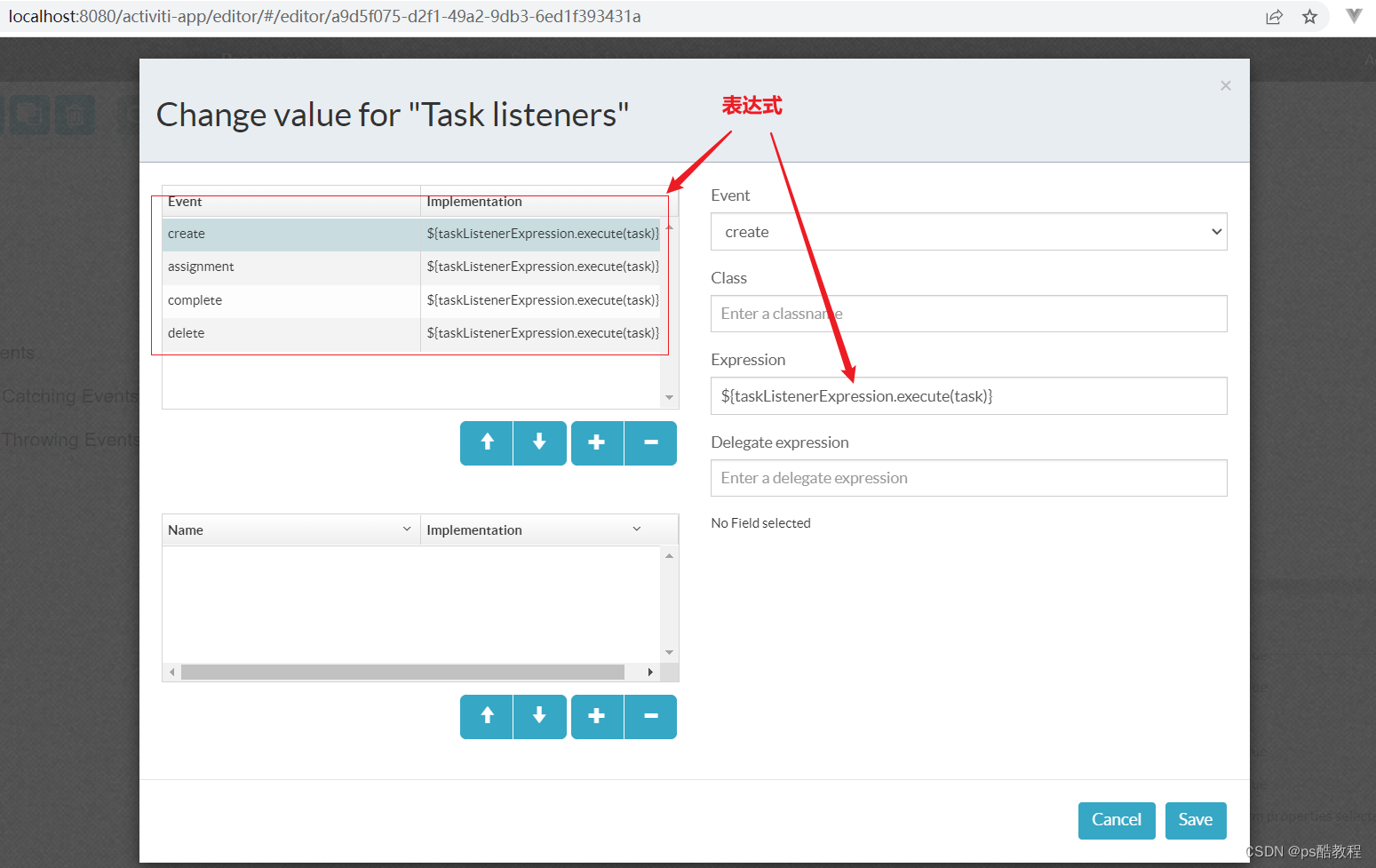
自定义 TaskListenerExpression
注意:这个的TaskListenerExpression 需要实现Serializable接口。
@Slf4j public class TaskListenerExpression implements Serializable { public void execute(DelegateTask delegateTask) { log.info("收到事件通知: {}", delegateTask.getEventName()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
测试
-
先部署该流程
-
然后,发起1个流程时,注意发起流程时,这里需要设置taskListenerExpression,然后它会收到assignment、create
ProcessEngine engine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine(); // 发起流程 需要通过 runtimeService来实现 RuntimeService runtimeService = engine.getRuntimeService(); HashMap<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // 在流程执行到某个阶段,或者启动流程实例的时候,用下面代码调用 HashMap<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>(); variables.put("taskListenerExpression", new TaskListenerExpression()); ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("listener1", variables);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
-
然后,部门经理完成该任务,它会收到complete、delete
spring表达式
在上面,我们在开启流程时,自己new了1个TaskListenerExpression,并且把它放入了流程变量中。在spring中,我们只需要将此bean定义在spring容器中即可(此处案例定义在activiti.cfg.xml中),在启动流程时,就不需要把它放入流程变量中了,就可以启动流程(注意:一定要把这个bean定义在容器中,否则启动流程时会报错,因为此时不能解析表达式了。当任务执行到该节点的时候,会直接调用该spring管理的bean)。
监听器实现方式——委托表达式delegateExpression
委托表达式 和 表达式区别:
-
委托表达式需要实现TaskListener和序列化接口
-
xml中直接写实现类的变量名,不用写方法名称,默认调取接口方法名
绘制流程图

设置经理审批节点,当经理审批后,触发表达式的执行
自定义 TaskListenerDelegateExpression
需要同时实现TaskListener接口 和 Serializable接口
@Slf4j public class TaskListenerDelegateExpression implements TaskListener, Serializable { @Override public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) { log.info("TaskListenerDelegateExpression#收到事件通知: {}", delegateTask.getEventName()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
测试
-
先部署该流程
-
然后,发起1个流程时,注意发起流程时,这里需要设置taskListenerDelegateExpression
ProcessEngine engine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine(); // 发起流程 需要通过 runtimeService来实现 RuntimeService runtimeService = engine.getRuntimeService(); HashMap<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>(); variables.put("taskListenerDelegateExpression", new TaskListenerDelegateExpression()); // 通过流程定义ID来启动流程 返回的是流程实例对象 ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("listener1", variables); System.out.println("processInstance.getId() = " + processInstance.getId()); System.out.println("processInstance.getDeploymentId() = " + processInstance.getDeploymentId()); System.out.println("processInstance.getDescription() = " + processInstance.getDescription());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
-
然后,部门经理完成该任务,委托表达式执行,它会收到complete
ProcessEngine engine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine(); TaskService taskService = engine.getTaskService(); List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskAssignee("zhangsan").list(); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Task task = list.get(0); // 完成经理审批 taskService.complete(task.getId(), map);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
字段属性使用
下面这种只能用类这种方式来给类中的某个属性赋值

自定义类SiteReportUserTaskListener
@Slf4j public class SiteReportUserTaskListener implements TaskListener { /* 注意:这里写的类型!否则可能会报错 */ private Expression fieldNameA; /* 完成经理审批任务时候 收到事件通知: complete */ @Override public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) { log.info("收到事件通知: {}, {}", delegateTask.getEventName(), fieldNameA); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
通过多次设置字段的值可以得知:fieldNameA取值优先级:
第1个 字符串>第3个 字符串> 第二个 表达式总结
- 一个用户任务节点可以创建多个监听器
- class类方式实现监听器,不需要在流程变量中加入监听器对象
- expression方式,监听器可以是一个普通的java类,但要实现序列化接口,需要在流程变量中加入监听器类的对象,或者加入spring容器中
- delegateExpression,监听器要同时实现TaskListener和序列化接口,需要在流程变量中加入监听器类的对象
执行监听器 ExecutionListener
执行监听器的使用场景
人员动态分配
- 节点审批人员需要在流程运行过程中动态分配
- 当前任务节点完成的时候,需要指定下一个节点的处理人(比如,一个请假流程,a员工请假,需要指定下一步需要处理请假流程的领导)
任务节点调取业务
-
任务节点完成的时候,需要一些复杂业务,(比如当前节点完成的时候,需要调用我们的jms消息系统发送消息)。
-
任务流转到当前的节点的时候,需要监控当前任务节点的一些信息或者其他的业务信息。
-
当前的任务节点分配处理人的时候,需要触发自定义的一些业务。
流程上处理业务
- 流程开始结束的时候,需要处理业务信息。
连线上处理业务
- 经过任务节点的出线,也就是连线的时候,需要触发自定义的业务。
监听的事件
ExecutionListener 接口
ExecutionListener 继承自BaseExecutionListener 接口
/* Callback interface to be notified of execution events like starting a process instance, ending an activity instance, taking a transition. */ public interface BaseExecutionListener extends Serializable { String EVENTNAME_START = "start"; String EVENTNAME_END = "end"; String EVENTNAME_TAKE = "take"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
ExecutionListener 接口如下
public interface ExecutionListener extends BaseExecutionListener { void notify(DelegateExecution execution); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
DelegateExecution
public interface DelegateExecution extends VariableScope { /** * Unique id of this path of execution that can be used as a handle to provide external signals back into the engine after wait states. */ String getId(); /** Reference to the overall process instance */ String getProcessInstanceId(); /** * The 'root' process instance. When using call activity for example, the processInstance * set will not always be the root. This method returns the topmost process instance. */ String getRootProcessInstanceId(); /** * Will contain the event name in case this execution is passed in for an {@link ExecutionListener}. */ String getEventName(); /** * Sets the current event (typically when execution an {@link ExecutionListener}). */ void setEventName(String eventName); /** * The business key for the process instance this execution is associated with. */ String getProcessInstanceBusinessKey(); /** * The process definition key for the process instance this execution is associated with. */ String getProcessDefinitionId(); /** * Gets the id of the parent of this execution. If null, the execution represents a process-instance. */ String getParentId(); /** * Gets the id of the calling execution. If not null, the execution is part of a subprocess. */ String getSuperExecutionId(); /** * Gets the id of the current activity. */ String getCurrentActivityId(); /** * Returns the tenant id, if any is set before on the process definition or process instance. */ String getTenantId(); /** * The BPMN element where the execution currently is at. */ FlowElement getCurrentFlowElement(); /** * Change the current BPMN element the execution is at. */ void setCurrentFlowElement(FlowElement flowElement); /** * Returns the {@link ActivitiListener} instance matching an {@link ExecutionListener} * if currently an execution listener is being execution. * Returns null otherwise. */ ActivitiListener getCurrentActivitiListener(); /** * Called when an {@link ExecutionListener} is being executed. */ void setCurrentActivitiListener(ActivitiListener currentActivitiListener); /* Execution management */ /** * returns the parent of this execution, or null if there no parent. */ DelegateExecution getParent(); /** * returns the list of execution of which this execution the parent of. */ List<? extends DelegateExecution> getExecutions(); /* State management */ /** * makes this execution active or inactive. */ void setActive(boolean isActive); /** * returns whether this execution is currently active. */ boolean isActive(); /** * returns whether this execution has ended or not. */ boolean isEnded(); /** * changes the concurrent indicator on this execution. */ void setConcurrent(boolean isConcurrent); /** * returns whether this execution is concurrent or not. */ boolean isConcurrent(); /** * returns whether this execution is a process instance or not. */ boolean isProcessInstanceType(); /** * Inactivates this execution. This is useful for example in a join: the execution still exists, but it is not longer active. */ void inactivate(); /** * Returns whether this execution is a scope. */ boolean isScope(); /** * Changes whether this execution is a scope or not. */ void setScope(boolean isScope); /** * Returns whather this execution is the root of a multi instance execution. */ boolean isMultiInstanceRoot(); /** * Changes whether this execution is a multi instance root or not. * @param isMultiInstanceRoot */ void setMultiInstanceRoot(boolean isMultiInstanceRoot); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
使用方法与上面大致相同,只不过ExecutionListener还可以设置在开始和结束节点、连线上。
执行监听器与任务监听器区别
介绍
执行监听器与任务监听器的基本原理和使用方法。当流程途径连线或者节点的时候,会触发对应的事件类型。执行监听器与任务监听器在生产中经常会用在几个方面:
- 动态分配节点处理人。通过前一个节点设置的变量,在运行到下一个节点时设置对应的处理人;
- 当流程运行到某个节点时,发送邮件或短信给待办用户;
- 统计流程处理时长,是否超时等;
- 业务层面数据处理。
任务监听器顾名思义是监听任务的。任务监听器的生命周期如下图所示,会经历assignment、create、complete、delete。当流程引擎触发这四种事件类型时,对应的任务监听器会捕获其事件类型,再按照监听器的处理逻辑进行处理。
执行监听器则监听流程的所有节点和连线。主要有start、end、take事件。其中节点有start、end两种事件,而连线则有take事件。下图是执行监听器的生命周期:

接下来通过代码去演示监听器效果。 首先我们创建一个执行监听器的类:package listener; import org.activiti.engine.delegate.DelegateExecution; import org.activiti.engine.delegate.ExecutionListener; public class MyExecutionListener implements ExecutionListener { public void notify(DelegateExecution execution) throws Exception { System.out.println("============executionListener start============"); String eventName = execution.getEventName(); String currentActivitiId = execution.getCurrentActivityId(); System.out.println("事件名称:" + eventName); System.out.println("ActivitiId:" + currentActivitiId); System.out.println("============executionListener end============"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
自定义执行监听器需要实现ExecutionListener接口,并且实现notify方法。这里我们打印对应的事件和活动节点id
接下来创建一个自定任务监听器:
package listener; import org.activiti.engine.delegate.DelegateTask; import org.activiti.engine.delegate.TaskListener; public class MyTaskListener implements TaskListener{ public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) { System.out.println("============TaskListener start============"); String taskDefinitionKey = delegateTask.getTaskDefinitionKey(); String eventName = delegateTask.getEventName(); System.out.println("事件名称:" + eventName); System.out.println("taskDefinitionKey:" + taskDefinitionKey); System.out.println("============TaskListener end============"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
自定义任务监听器需要实现TaskListener接口,并且实现notify方法。这里我们打印对应的事件和任务节点键值(即bpmn图里userTask的id)。
之后新建一个bpmn图:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <definitions xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/MODEL" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:activiti="http://activiti.org/bpmn" xmlns:bpmndi="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/DI" xmlns:omgdc="http://www.omg.org/spec/DD/20100524/DC" xmlns:omgdi="http://www.omg.org/spec/DD/20100524/DI" typeLanguage="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" expressionLanguage="http://www.w3.org/1999/XPath" targetNamespace="http://www.activiti.org/test"> <process id="listenerBpmProcess" name="My process" isExecutable="true"> <startEvent id="startevent1" name="Start"></startEvent> <userTask id="usertask1" name="myTask1" activiti:assignee="张三"> <extensionElements> <activiti:executionListener event="start" class="listener.MyExecutionListener"></activiti:executionListener> <activiti:executionListener event="end" class="listener.MyExecutionListener"></activiti:executionListener> <activiti:taskListener event="all" class="listener.MyTaskListener"></activiti:taskListener> </extensionElements> </userTask> <endEvent id="endevent1" name="End"></endEvent> <sequenceFlow id="flow1" sourceRef="startevent1" targetRef="usertask1"></sequenceFlow> <sequenceFlow id="flow2" sourceRef="usertask1" targetRef="endevent1"></sequenceFlow> </process> <bpmndi:BPMNDiagram id="BPMNDiagram_listenerBpmProcess"> <bpmndi:BPMNPlane bpmnElement="listenerBpmProcess" id="BPMNPlane_listenerBpmProcess"> <bpmndi:BPMNShape bpmnElement="startevent1" id="BPMNShape_startevent1"> <omgdc:Bounds height="41.0" width="35.0" x="505.0" y="40.0"></omgdc:Bounds> </bpmndi:BPMNShape> <bpmndi:BPMNShape bpmnElement="usertask1" id="BPMNShape_usertask1"> <omgdc:Bounds height="55.0" width="105.0" x="470.0" y="150.0"></omgdc:Bounds> </bpmndi:BPMNShape> <bpmndi:BPMNShape bpmnElement="endevent1" id="BPMNShape_endevent1"> <omgdc:Bounds height="35.0" width="35.0" x="505.0" y="240.0"></omgdc:Bounds> </bpmndi:BPMNShape> <bpmndi:BPMNEdge bpmnElement="flow1" id="BPMNEdge_flow1"> <omgdi:waypoint x="522.0" y="81.0"></omgdi:waypoint> <omgdi:waypoint x="522.0" y="150.0"></omgdi:waypoint> </bpmndi:BPMNEdge> <bpmndi:BPMNEdge bpmnElement="flow2" id="BPMNEdge_flow2"> <omgdi:waypoint x="522.0" y="205.0"></omgdi:waypoint> <omgdi:waypoint x="522.0" y="240.0"></omgdi:waypoint> </bpmndi:BPMNEdge> </bpmndi:BPMNPlane> </bpmndi:BPMNDiagram> </definitions>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
这里我们给userTask1添加了执行监听器和任务监听器。部署bpmn图后,我们观察流程运转时监听器的触发时机和作用,启动流程:
public void startProcessById() { RuntimeService runtimeService = pe.getRuntimeService(); ProcessInstance pi = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceById("listenerBpmProcess:1:4"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
流程启动后,从开始节点运转到userTask1节点,观察控制台输出:
============executionListener start============ 事件名称:start ActivitiId:usertask1 ============executionListener end============ ============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:assignment taskDefinitionKey:usertask1 ============TaskListener end============ ============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:create taskDefinitionKey:usertask1 ============TaskListener end============- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
可以看到流程走到userTask1节点时,首先触发start事件,调用我们自定义的执行监听器,随后触发assignment和create事件,执行自定义任务监听器的内容。注意这里是先触发assignment进行人员分配,再触发create事件,与一般的认知有些差异。
接下来通过taskService的complete方法完成userTask1节点上流程的提交,观察控制台输出:
============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:complete taskDefinitionKey:usertask1 ============TaskListener end============ ============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:delete taskDefinitionKey:usertask1 ============TaskListener end============ ============executionListener start============ 事件名称:end ActivitiId:usertask1 ============executionListener end============- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
可以看到userTask1节点提交的时候,首先触发complete事件再触发delete事件,最后触发end事件。
以上就是执行监听器与任务监听器的基本使用方式。实际工程中,由于流程节点十分多,并且流程和业务常常需要进行微调,通常是不会在bpmn图上逐个节点添加监听器的,往往是在解析bpmn对象期间利用对象解析器动态添加监听器。
手动测试
画如下的流程图,
-
给开始节点、经理审批节点、开始节点到经理审批节点之间的连线上都添加MyExecutionListener,3种类型包括start、task、end都加上。
-
给经理审批节点加上MyTaskListener,4种类型包括assignment、create、complete、delete都加上。因为TaskListener只能添加给userTask节点
bpmn文件如下:<definitions xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/MODEL" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:activiti="http://activiti.org/bpmn" xmlns:bpmndi="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/DI" xmlns:omgdc="http://www.omg.org/spec/DD/20100524/DC" xmlns:omgdi="http://www.omg.org/spec/DD/20100524/DI" typeLanguage="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" expressionLanguage="http://www.w3.org/1999/XPath" targetNamespace="http://www.activiti.org/processdef"> <process id="listener2" name="listener2" isExecutable="true"> <documentation>listener2documentation> <startEvent id="startEvent1"> <extensionElements> <activiti:executionListener event="start" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> <activiti:executionListener event="end" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> <activiti:executionListener event="take" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> extensionElements> startEvent> <userTask id="pmNode" name="经理审批" activiti:assignee="zhangsan"> <extensionElements> <activiti:executionListener event="start" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> <activiti:executionListener event="end" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> <activiti:executionListener event="take" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> <activiti:taskListener event="create" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyTaskListener">activiti:taskListener> <activiti:taskListener event="assignment" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyTaskListener">activiti:taskListener> <activiti:taskListener event="complete" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyTaskListener">activiti:taskListener> <activiti:taskListener event="delete" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyTaskListener">activiti:taskListener> <modeler:initiator-can-complete xmlns:modeler="http://activiti.com/modeler">modeler:initiator-can-complete> extensionElements> userTask> <userTask id="HrNode" name="人事审批" activiti:assignee="lisi"> <extensionElements> <modeler:initiator-can-complete xmlns:modeler="http://activiti.com/modeler">modeler:initiator-can-complete> extensionElements> userTask> <endEvent id="sid-95094C86-3D9A-4AF0-9575-26BF6EE37AF0">endEvent> <sequenceFlow id="sid-CF295D96-0BAD-44EF-8461-8D0CEA5D60EF" sourceRef="HrNode" targetRef="sid-95094C86-3D9A-4AF0-9575-26BF6EE37AF0">sequenceFlow> <sequenceFlow id="sid-D3BAAF86-675D-49CC-A831-1403C117D883" sourceRef="startEvent1" targetRef="pmNode"> <extensionElements> <activiti:executionListener event="start" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> <activiti:executionListener event="end" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> <activiti:executionListener event="take" class="com.zzhua.listener.MyExecutionListener">activiti:executionListener> extensionElements> sequenceFlow> <sequenceFlow id="sid-6A9C7D82-BFA1-449D-A280-649024CDA85A" sourceRef="pmNode" targetRef="HrNode">sequenceFlow> process> <bpmndi:BPMNDiagram id="BPMNDiagram_listener2"> ... bpmndi:BPMNDiagram> definitions>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
先部署流程,然后开启1个流程,输出如下,这说明开始节点:没有take,只有start和end,连线:有start、take、end,userTask:有start,然后顺序是任务监听器的assignment、create
============executionListener start============ 事件名称:start ActivitiId:startEvent1 ============executionListener end============ ============executionListener start============ 事件名称:end ActivitiId:startEvent1 ============executionListener end============ ============executionListener start============ 事件名称:start ActivitiId:sid-D3BAAF86-675D-49CC-A831-1403C117D883 ============executionListener end============ ============executionListener start============ 事件名称:take ActivitiId:sid-D3BAAF86-675D-49CC-A831-1403C117D883 ============executionListener end============ ============executionListener start============ 事件名称:end ActivitiId:sid-D3BAAF86-675D-49CC-A831-1403C117D883 ============executionListener end============ ============executionListener start============ 事件名称:start ActivitiId:pmNode ============executionListener end============ ============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:assignment taskDefinitionKey:pmNode ============TaskListener end============ ============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:create taskDefinitionKey:pmNode ============TaskListener end============- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
完成经理审批节点时的,输入如下,先是任务监听器的complete,然后是delete
============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:complete taskDefinitionKey:pmNode ============TaskListener end============ ============TaskListener start============ 事件名称:delete taskDefinitionKey:pmNode ============TaskListener end============ ============executionListener start============ 事件名称:end ActivitiId:pmNode ============executionListener end============- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
工作流程事件监听 ActivitiEventListener
在流程运转的过程中,流程引擎会发出很多不同的事件,前面的文章,我们通过执行监听器和任务监听器捕获到对应事件并进行处理。除了这两个监听器以外,
activiti从5.15版开始加入了全局事件监听器,这样很多重复的监听器就不需要在每个活动上去绑定。添加全局监听器有几种方式,包括 通过流程引擎文件方式进行配置、通过流程文档进行配置、动态添加全局事件监听器等方式,下面分别展示这几种方法:
可监听事件类型

配置方式
MyCfgActivitiEventListener
直接设置SpringProcessEngineConfiguration#eventListeners属性,即可
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activiti2?characterEncoding=utf-8&nullCatalogMeansCurrent=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> <property name="maxActive" value="3"/> <property name="maxIdle" value="1"/> bean> <bean id="processEngineConfiguration" class="org.activiti.spring.SpringProcessEngineConfiguration"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/> <property name="databaseSchemaUpdate" value="true"/> <property name="eventListeners"> <list> <bean class="com.zzhua.listener.acti.MyCfgActivitiEventListener"/> list> property> <property name="typedEventListeners"> <map> <entry key="TASK_CREATED"> <list> <bean class="com.zzhua.listener.acti.MyCfgTypeActivitiEventListener"/> list> entry> <entry key="PROCESS_COMPLETED"> <list> <bean class="com.zzhua.listener.acti.MyCfgTypeActivitiEventListener"/> list> entry> map> property> bean> <bean id="processEngine" class="org.activiti.spring.ProcessEngineFactoryBean"> <property name="processEngineConfiguration" ref="processEngineConfiguration"/> bean> <bean id="repositoryService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getRepositoryService"/> <bean id="runtimeService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getRuntimeService"/> <bean id="taskService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getTaskService"/> <bean id="historyService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getHistoryService"/> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> bean> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="get*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/> tx:attributes> tx:advice> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
public class MyCfgActivitiEventListener implements ActivitiEventListener { @Override public void onEvent(ActivitiEvent event) { System.out.println("【cfg-eventName】:" + event.getType().name()); } @Override public boolean isFailOnException() { return false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
MyCfgTypeActivitiEventListener
直接设置SpringProcessEngineConfiguration#typedEventListeners属性,即可,配置同上,这种方式可以为指定的事件类型添加一批监听器,这种属于动态添加,在spring或springboot中,就直接在ProcessEngineConfiguration创建时添加监听器即可。
如果需要禁用,可以设置
ProcessEngineConfiguration#enableEventDispatcher为false来关闭事件派发器。事实上,在ProcessEngineConfiguration上有很多可以设置的属性,后面可以探究下。
public class MyCfgTypeActivitiEventListener implements ActivitiEventListener { @Override public void onEvent(ActivitiEvent event) { System.out.println("【cfg-type-eventName】:" + event.getType().name()); } @Override public boolean isFailOnException() { return false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
MyBpmnActivitiEventListener
在bpmn画图工具中设置

public class MyBpmnActivitiEventListener implements ActivitiEventListener { @Override public void onEvent(ActivitiEvent event) { System.out.println("【bpmn-eventName】:" + event.getType().name()); } @Override public boolean isFailOnException() { return false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
MyRuActivitiEventListener
使用RuntimeService#addEventListener添加,也可以
public class MyRuActivitiEventListener implements ActivitiEventListener { @Override public void onEvent(ActivitiEvent event) { System.out.println("【ru-eventName】:" + event.getType().name()); } @Override public boolean isFailOnException() { return false; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
-
相关阅读:
esxi 6.7下安装黑裙
ArcGis地图
c++中类和对象(1)
#边学边考 必修5 高项:对人管理 第1章 项目人力资源管理
Python输入与输出(文件读取、json格式转换)
【MediaSoup】mediasoup-sfu-cp vs2022 构建
10 Minimax估计和Bayes估计
初学python非常实用的10个小技巧,先收藏再说~
airflow重启
Redash和Metabase深度比较之四:可视化种类
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16992475/article/details/134235921
