-
Springboot学习笔记——1
Springboot学习笔记——1
一、快速上手Springboot
1.1、Springboot入门程序开发
1.1.1、IDEA创建Springboot项目
- SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程
- 创建新模块,选择Spring Initializr,并配置模块相关基础信息

- 选择当前模块需要使用的技术集

- 开发控制器类
//Rest模式 @RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class BookController { @GetMapping public String getById(){ System.out.println("springboot is running..."); return "springboot is running..."; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 运行自动生成Application类

-
最简SpringBoot程序所包含的基础文件
- pom.xml文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId> <version>3.1.4version> <relativePath/> parent> <groupId>com.SmulllgroupId> <artifactId>springboot_01_02artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion> <name>springboot_01_02name> <description>springboot_01_02description> <properties> <java.version>17java.version> properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> dependencies> project>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- Application类
@SpringBootApplication public class Springboot0102Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot0102Application.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
Spring程序与SpringBoot程序对比
类/配置文件 Spring SpringBoot pom文件中的坐标 手工添加 勾选添加 web3.0配置类 手工制作 无 Spring/SpringMVC配置类 手工制作 无 控制器 手工制作 手工制作 1.1.2、官网创建Springboot项目
创建项目也可以通过官网进行创建
springboot项目创建官网
1.1.3、阿里云创建Springboot项目
通过阿里云进行创建项目
阿里云创建项目官网
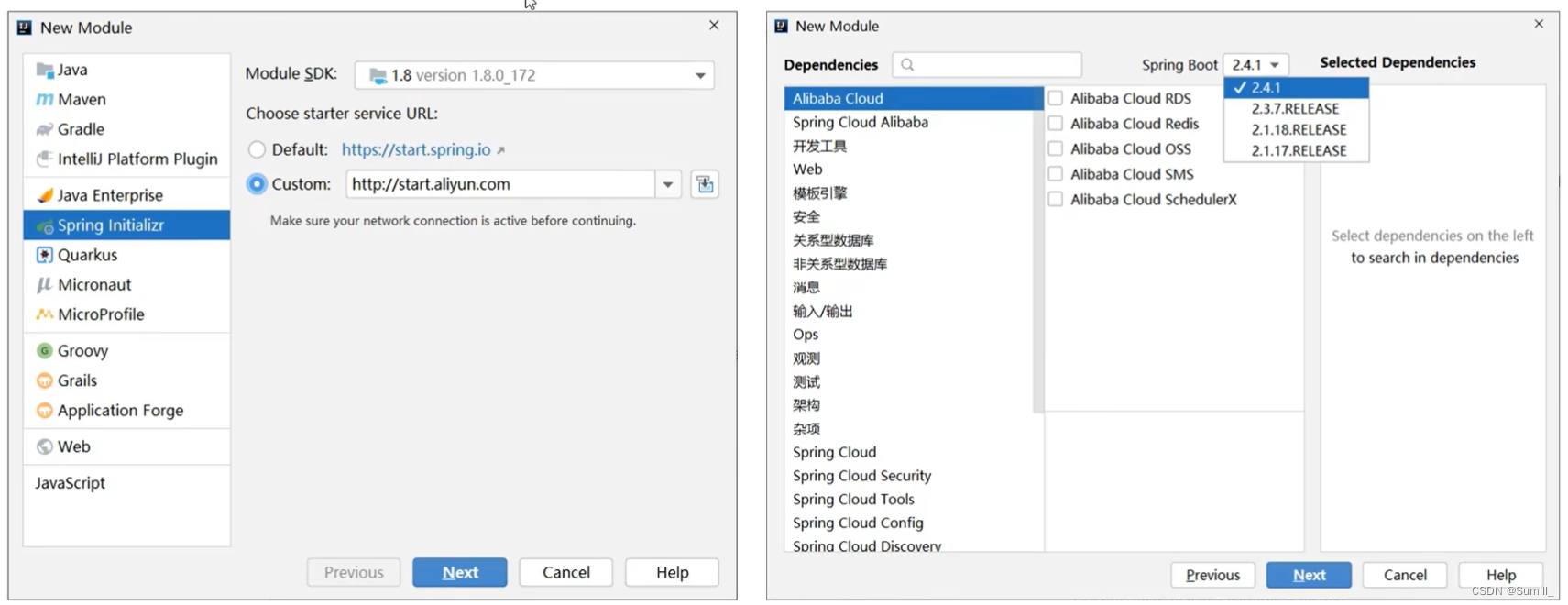
阿里云提供的坐标版本较低,如果需要使用高版本,进入工程后手工切换SpringBoot版本阿里云提供的工程模板与Spring官网提供的工程模板略有不同
1.1.4、手工制作Springboot项目
- 手工创建项目(手工导入坐标)
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId> <version>3.1.4version> <relativePath/> parent> <groupId>com.SmulllgroupId> <artifactId>springboot_01_02artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> dependencies> project>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 手工创建项目(手工制作引导类)
@SpringBootApplication public class Springboot0102Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot0102Application.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.2、隐藏文件或文件夹

1.3、入门案例解析
-
SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程
-
Spring程序缺点
- 依赖设置繁琐
- 配置繁琐
-
SpringBoot程序优点
- 起步依赖(简化依赖配置)
- 自动配置(简化常用工程相关配置)
- 辅助功能(内置服务器,…)
1.3.1、parent

将依赖合并

再进行统一管理

- 开发SpringBoot程序要继承
spring-boot-starter-parent spring-boot-starter-parent中定义了若干个依赖管理- 继承parent模块可以避免多个依赖使用相同技术时出现依赖版本冲突
- 继承parent的形式也可以采用引入依赖的形式实现效果
1.3.2、starter
- spring-boot-starter-web.pom
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcatartifactId> <version>2.5.4version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>springwebartifactId> <version>5.3.9version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId> <version>5.3.9version> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
-
starter
- SpringBoot中常见项目名称,定义了当前项目使用的所有依赖坐标,以达到减少依赖配置的目的
-
parent
- 所有SpringBoot项目要继承的项目,定义了若干个坐标版本号(依赖管理,而非依赖),以达到减少依赖冲突的目的
- spring-boot-starter-parent各版本间存在着诸多坐标版本不同
-
实际开发
- 使用任意坐标时,仅书写GAV中的G和A,v由SpringBoot提供,除非SpringBoot未提供对应版本V
- 如发生坐标错误,再指定Version(要小心版本冲突)
1.3.3、引导类
- 启动方式
@SpringBootApplication public class Springboot0102Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboot0102Application.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- SpringBoot的引导类是Boot工程的执行入口,运行main方法就可以启动项目
- SpringBoot工程运行后初始化Spring容器,扫描引导类所在包加载bean
1.3.4、内嵌tomact
- 辅助功能
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
在其内部导入一个
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcatartifactId> <version>2.5.4version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
其内部有个核心包进行运行
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embedgroupId> <artifactId>tomcat-embed-coreartifactId> <version>9.0.52version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
内置服务器
- tomcat(默认) :apache出品,粉丝多,应用面广,负载了若干较重的组件
- jetty :更轻量级,负载性能远不及tomcat
- undertow :undertow,负载性能勉强跑赢tomcat
1.4、REST开发
1.4.1、REST风格介绍
-
REST (Representational State Transfer),表现形式状态转换
- 传统风格资源描述形式
http://localhost/user/getById?id=1
http:/ localhost/user/saveUser - REST风格描述形式
http:/ localhost/user/1
http:/ localhost/user
- 传统风格资源描述形式
-
优点:
- 隐藏资源的访问行为,无法通过地址得知对资源是何种操作
- 书写简化
-
按照REST风格访问资源时使用行为动作区分对资源进行了何种操作
- http://localhost/users 查询全部用户信息 GET(查询)
- http://localhost/users/1 查询指定用户信息 GET(查询)
- http://localhost/users 添加用户信息 POST(新增/保存)
- http://localhost/users 修改用户信息 PUT(修改/更新)
- http://localhost/users/1 删除用户信息 DELETE(删除)
-
根据REST风格对资源进行访问称为RESTful
注意事项
上述行为是约定方式,约定不是规范,可以打破,所以称REST风格,而不是REST规范描述模块的名称通常使用复数,也就是加s的格式描述,表示此类资源,而非单个资源,例如: users、books、accounts…
1.4.2、入门案例
- 设定http请求动作(动词)
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.PUT) @ResponseBody public String update(@RequestBody User user){ System.out.println("user update..."+user); return "{'module':'user update'}"; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 设定请求参数(路径变量)
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("user getById..."+id); return "{'module':'user getById'}"; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 名称:@RequestMapping
- 类型:方法注解
- 位置:SpringMVC控制器方法定义上方
- 作用:设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public String save(){ System.out.println("user save..."); return "{'module':'user save'}"; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 属性
- value(默认):请求访问路径
- method:http请求动作,标准动作(GET/POST/PUT/DELETE)
- 名称:@PathVariable
- 类型:形参注解
- 位置: SpringMVC控制器方法形参定义前面
- 作用:绑定路径参数与处理器方法形参间的关系,要求路径参数名与形参名一一对应
- 范例:
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) @ResponseBody public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("user delete..."+id); return "{'module':'user delete'}"; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
接收参数的三种方式
@RequestBody @RequestRaram @PathVariable
- 区别
- @RequestParam用于接收url地址传参或表单传参
- @RequestBody用于接收json数据
- @PathVariable用于接收路径参数,使用{参数名称}描述路径参数
- 应用
- 后期开发中,发送请求参数超过1个时,以json格式为主,@RequestBody应用较广
- 如果发送非json格式数据,选用@RequestParam接收请求参数
- 采用RESTful进行开发,当参数数量较少时,例如1个,可以采用@PathVariable接收请求路径变量,通常用于传递id值
1.4.3、RESTful快速开发
@RequestMapping(value = "/books",method=RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public String save(@RequestBody Book book){ system.out.println("book save. . ." + book); return "{'module':'book save'}"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/books",method=RequestMethod.PUT) @ResponseBody public String update(@RequestBody Book book){ system.out.println( "book update. . . "+book); return "{'module':'book update'}"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 名称:@RestController
- 类型:类注解
- 位置:基于SpringMNC的RESTful开发控制器类定义上方
- 作用:设置当前控制器类为RESTful风格,等同于@Controller与@ResponseBody两个注解组合功能
- 范例:
@RestController public class BookController{ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 名称:@GetMapping@PostMapping @PutMapping@DeleteMapping
- 类型:方法注解
- 位置:基于SpringMVC的RESTful开发控制器方法定义上方
- 作用:设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径与请求动作,每种对应一个请求动作,例如@GetMapping对应GET请求
- 范例:
@GetMapping("/{id}") public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ System.out.println("user getById..."+id); return "{'module':'user getById'}"; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 属性
- value(默认):请求访问路径
二、基础配置
复制工程
- 原则
- 保留工程基础结构
- 抹掉原始工程痕迹
- 在工作空间中复制对应工程,并修改工程名称
- 删除与Idea相关配置文件,仅保留src目录与pom. xml文件
- 修改pom.xml文件中的artifactId与新工程/模块名相同删除name标签(可选)
- 保留备份工程供后期使用
2.1、属性配置
-
修改服务器端口
-
SpringBoot默认配置文件application.properties,通过键值对配置对应属性
-
修改配置
- 修改服务器端口
server.port=80- 1
- 关闭运行日志图标(banner)
spring.main.banner-mode=off- 1
- 设置日志相关
logging.level.root = error- 1
-
SpringBoot内置属性查询
2.2、三种属性配置方式
- application.properties
server.port=80- 1
- application. yml
server: port: 81- 1
- 2
- application. yaml
server: port: 82- 1
- 2
-
SpringBoot配置文件加载顺序
- application.
properties> application.yml>application.yaml
- application.
-
不同配置文件中相同配置按照加载优先级相互覆盖,不同配置文件中不同配置全部保留
2.3、yaml
- YAML ( YAML Ain 't Markup Language) ,一种数据序列化格式
- 优点:
- 容易阅读
- 容易与脚本语言交互
- 以数据为核心,重数据轻格式
- YAML文件扩展名
- .yml(主流)
- .yaml
yaml语法规则
- 大小写敏感
- 属性层级关系使用多行描述,每行结尾使用冒号结束
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不允许使用Tab键)
- 属性值前面添加空格(属性名与属性值之间使用冒号+空格作为分隔)
#表示注释
- 核心规则:数据前面要加空格与冒号隔开
- 字面值表示方式
boolean: TRUE #TRUE ,true ,True ,FALSE,false ,False均可 float: 3.14 #6.8523015e+5#支持科学计数法 int: 123 #0b1010_0111_0100_1010_1110#支持二进制、八进制、十六进制 null: ~ #使用~表示null string: Helloworld #字符串可以直接书写 string2: "Hello world" #可以使用双引号包裹特殊字符 date: 2018-02-17 #日期必须使用yyyy-MM-dd格式 datetime: 2018-02-17T15:02:31+08:00 #时间和日期之间使用T连接,最后使用+代表时区- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 数组表示方式:在属性名书写位置的下方使用减号作为数据开始符号,每行书写一个数据,减号与数据间空格分隔
likes: - game - sleep - music user1: name: zhangsan age: 23 likes: - Java - 前端 - 大数据 likes1: [game,sleep,music]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
2.3.1、读取yaml单一属性数据
- 使用@Value读取单个数据,属性名引用方式∶
${一级属性名.二级属性名...}
likes: - game - sleep - music user1: name: zhangsan age: 23- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
@RestController @RequestMapping("/Books") public class BookController { @Value("${country}") private String country1; @Value("${user1.name}") private String name1; @Value("${likes[1]}") private String likes; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
2.3.2、yaml文件中的变量引用
- 在配置文件中可以使用属性名引用方式引用数据
baseDir: /usr/ local/fire center: dataDir: ${baseDir}/data tmpDir: ${baseDir}/tmp logDir: ${baseDir}/log msgDir: ${baseDir}/msgDir- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 属性值中如果出现转义字符,需要使用双引号包裹
lession: "Spring\tboot\nlesson"- 1
2.3.3、读取yaml全部属性数据
@RestController @RequestMapping("/Books") public class BookController { @Autowired private Environment environment; @GetMapping public void Books(){ System.out.println(environment.getProperty("user1.name")); System.out.println(environment.getProperty("likes[1]")); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
likes: - game - sleep - music user1: name: zhangsan age: 23- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 使用Environment对象封装全部配置信息
- 使用@Autowired自动装配数据到Environment对象
2.3.4、读取yaml引用类型属性数据
- 自定义对象封装指定类
datasource: driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/springboot_db username: root password: 123456- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
@Component @ConfigurationProperties("datasource") public class Datasource { private String driver; private String url; private String username; private String password; public Datasource() { } public Datasource(String driver, String url, String username, String password) { this.driver = driver; this.url = url; this.username = username; this.password = password; } public String getDriver() { return driver; } public void setDriver(String driver) { this.driver = driver; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String toString() { return "Datasource{driver = " + driver + ", url = " + url + ", username = " + username + ", password = " + password + "}"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
@RestController @RequestMapping("/Books") public class BookController { @Autowired private Datasource datasource; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定配置信息到封装类中
- 封装类需要定义为Spring管理的bean,否则无法进行属性注入
三、整合第三方技术
3.1、整合Junit
- SpringBoot整合Junit
@SpringBootTest class Springboot0101ApplicationTests { @Autowired private BooksDao booksDao; @Test void contextLoads() { booksDao.save(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 名称: @SpringBootTest
- 类型:测试类注解
- 位置:测试类定义上方
- 作用:设置JUnit加载的SpringBoot启动类
- 范例:
@SpringBootTest class Springboot0101ApplicationTests {} @SpringBootTest(classes = Springboot0101Application.class ) class Springboot0101ApplicationTests {}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 相关属性
- classes:设置SpringBoot启动类
注意事项
如果测试类在SpringBoot启动类的包或子包中,可以省略启动类的设置,也就是省略classes的设定
步骤:
- 导入测试对应的starter
- 测试类使用@SpringBootTest修饰
- 使用自动装配的形式添加要测试的对象
3.2、整合Mybatis
- 核心配置:数据库连接相关信息(练什么?连谁?什么权限)
- 映射配置:SQL映射(XML/注解)
- 创建一个全新的模块,选择Spring初始化,并配置模块相关基础信息
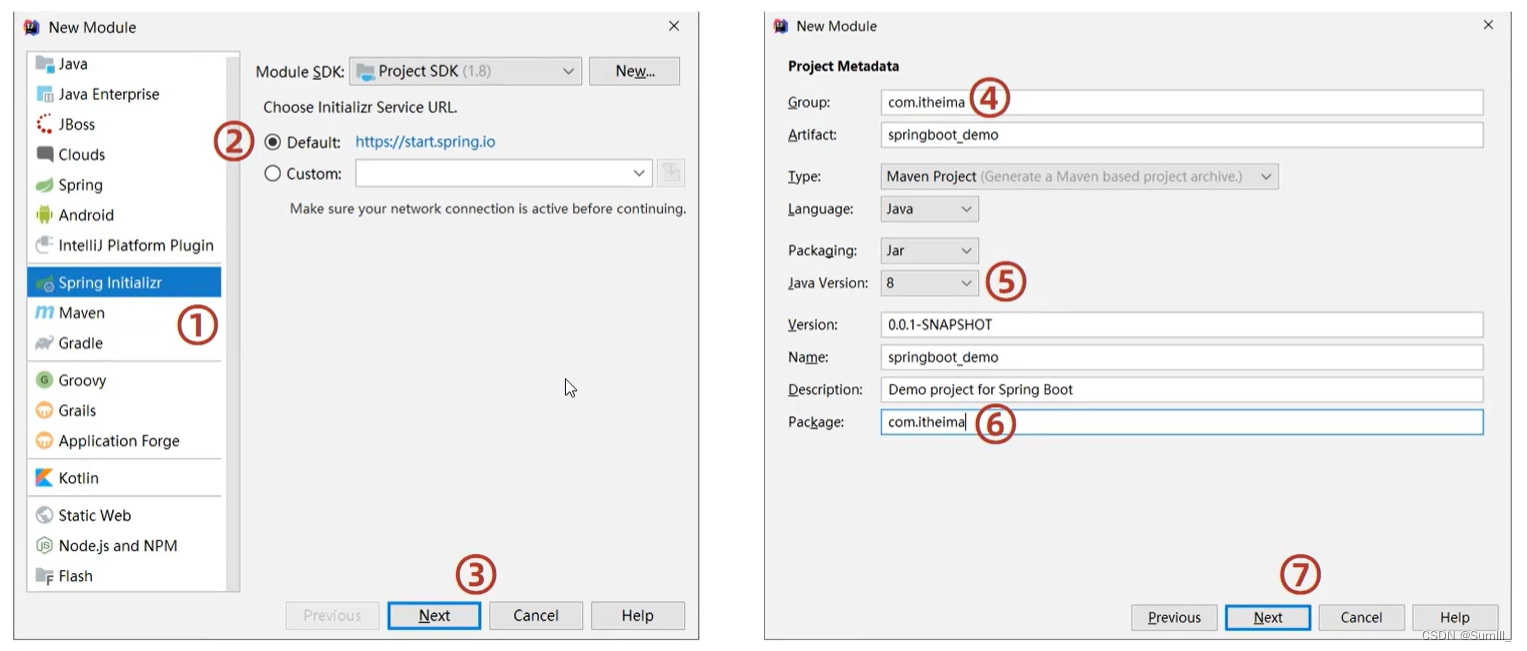
- 选择当前模块需要使用的技术集(MyBatis,MySQL)

- 设置数据源参数
spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbase username: root password: xxxxxx- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 定义数据层接口与映射配置
@Mapper public interface AccountDao { @Select("select * from tb_account where id = #{id}") public Account SelectById(Integer id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 测试类中注入dao接口,测试功能
@SpringBootTest class Springboot03MybatisApplicationTests { @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao; @Test void contextLoads() { Account account = accountDao.SelectById(1); System.out.println(account); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
注意:
-
MySQL 8.X驱动强制要求设置时区
- 修改url,添加serverTimezone设定
- 修改MySQL数据库配置(略)
-
驱动类过时,提醒更换为
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
3.3、整合Mybatis-Plus
- 手工添加SpringBoot整合MyBatis-Plus的坐标,可以通过mvnrepository获取
<dependency> <groupId>com.baomidougroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId> <version>3.5.3.1version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
注意事项:
由于SpringBoot中未收录MyBatis-plus的坐标版本,需要指定对应的Version
- 定义数据层接口与映射文件,继承BaseMapper
@Mapper public interface AccountDao extends BaseMapper<Account> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
3.4、整合Druid
- 指定数据源类型
spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbase?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123456 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 导入Druid对应的starter
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibabagroupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId> <version>1.2.19version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 变更Druid的配置方式
spring: datasource: druid: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbase?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123456- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
四、基于SpringBoot的SSMP整合案例
- 案例实现方案分析
- 实体类开发——使用Lombok快速制作实体类
- Dao开发–整合MyBatisPlus,制作数据层测试类
- service开发——基于MyBatisPlus进行增量开发,制作业务层测试类
- Controller开啊发——基于Restful开发,使用PostMan测试接口功能
- Controller开发——前后端开发协议制作
- 页面开发——基于VUE+ElementUI制作,前后端联调,页面数据处理,页面消息处理
- 列表、新增、修改、删除、分页、查询
- 项目异常处理
- 按条件查询——页面功能调整、Controller修正功能、Service修正功能
4.1、模块开发

- 勾选springMVC与MySQL坐标
- 修改配置文件为yml格式
- 设置端口为80方便访问
4.2、实体类快速开发
- Lombok,一个Java类库,提供了一组注解,简化POJ0实体类开发
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- lombok版本由SpringBoot提供,无需指定版本
- 常用注解@Data
@Data public class Book { private Integer id; private String type; private String name; private String description; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 为当前实体类在编译期设置对应的get/set方法,toString方法,hashCode方法,equals方法等
4.3、数据层开发(基础CUBD)
- 技术实现方案
- MyBatisPlus
- Druid
- 导入MyBatisPlus与Druid对应的starter
<dependency> <groupId>com.baomidougroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId> <version>3.5.3.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibabagroupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId> <version>1.2.19version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 配置数据源与MyBatisPlus对应的基础配置(id生成策略使用数据库自增策略)
server: port: 80 spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootbase?serverTimezone=UTC username: root password: 123456 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource mybatis-plus: global-config: db-config: table-prefix: tb_ id-type: auto- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 继承BaseMapper并指定泛型
@Mapper public interface bookDao extends BaseMapper<Book> { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 制作测试类测试结果
@SpringBootTest public class bookTestCase { @Autowired private bookDao bookDao; @Test void TestSelectById(){ Book book = bookDao.selectById(1); System.out.println(book); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.3.1、开启MP运行日志
- 为方便调试可以开启MyBatisPlus的日志
mybatis-plus: configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl- 1
- 2
- 3

4.3.2、分页
- 分页操作需要设定分页对象IPage
@Test void TestGetPage(){ Page page = new Page(1,5); bookDao.selectPage(page,null); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
-
IPage对象中封装了分页操作中的所有数据
- 数据
- 当前页码值
- 每页数据总量
- 最大页码值
- 数据总量
-
分页操作是在MNyBatisPlus的常规操作基础上增强得到,内部是动态的拼写SQL语句,因此需要增强对应的功能,使用MyBatisPlus拦截器实现
@Configuration public class MPConfig { @Bean public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){ //定义MP拦截器 MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor(); //添加具体的拦截器 mybatisPlusInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor()); return mybatisPlusInterceptor; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
4.3.3、数据层标准开发(按条件查询)
- 使用Querywrapper对象封装查询条件,推荐使用LambdaQuerywrapper对象,所有查询操作封装成方法调用
@Test void TestGetBy(){ QueryWrapper<Book> qw = new QueryWrapper<>(); qw.like("name", "Spring"); bookDao.selectList(qw); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 支持动态拼写查询条件
@Test void TestGetBy2(){ String name = "Spring"; LambdaQueryWrapper<Book> lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); //当name不等于null时走该语句 lqw.like(name!=null,Book::getName, name); //执行分页查询加上条件查询 Page page = new Page(1,5); bookDao.selectPage(page,lqw); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.4、业务层开发(基础CUBD)
-
Service层接口定义与数据层接口定义具有较大区别,不要混用
selectByUserNameAndPassword (String username,String password);login (String username,String password);
-
定义接口
public interface BookService { Boolean save(Book book); Boolean update(Book book); Boolean delete(Integer id); Book getById(Integer id); List<Book> getAll(); IPage<Book> getByPage(Integer current,Integer size); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 实现类定义
@Service public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService { @Autowired private bookDao bookDao; @Override public Boolean save(Book book) { return bookDao.insert(book)>0; } @Override public Boolean update(Book book) { return bookDao.updateById(book)>0; } @Override public Boolean delete(Integer id) { return bookDao.deleteById(id)>0; } @Override public Book getById(Integer id) { return bookDao.selectById(id); } @Override public List<Book> getAll() { return bookDao.selectList(null); } @Override public IPage<Book> getByPage(Integer current, Integer size) { Page<Book> bookPage = new Page<>(current, size); bookDao.selectPage(bookPage,null); return bookPage; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 测试类定义
@SpringBootTest public class bookServiceTestCase { @Autowired private BookService bookService; @Test void getById(){ Book byId = bookService.getById(1); System.out.println(byId); } @Test void getAll(){ List<Book> all = bookService.getAll(); System.out.println(all); } @Test void testPage(){ IPage<Book> byPage = bookService.getByPage(0, 5); System.out.println(byPage.getPages()); System.out.println(byPage.getCurrent()); System.out.println(byPage.getSize()); System.out.println(byPage.getTotal()); System.out.println(byPage.getRecords()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
4.4.1、业务层快速开发(基于MyBatisPlus框架)
-
快速开发方案
- 使用MyBatisPlus提供有业务层通用接口(
ISerivce)与业务层通用实现类(ServiceImpl) - 在通用类基础上做功能重载或功能追加
- 注意重载时不要覆盖原始操作,避免原始提供的功能丢失

- 使用MyBatisPlus提供有业务层通用接口(
-
定义接口
public interface IBookService extends IService<Book> { }- 1
- 2
- 如果不满足使用需要,可以自行添加
public interface IBookService extends IService<Book> { Boolean delete(Book book); Boolean insert(Book book); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 实现类定义
@Service public class BookServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<bookDao,Book> implements IBookService { @Override public Boolean delete(Book book) { return null; } @Override public Boolean insert(Book book) { return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
4.5、表现层开发
- 基于Restful进行表现层接口开发
- 使用Postman测试表现层接口功能
- 功能测试
@RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class bookController { @Autowired private IBookService iBookService; @GetMapping public List<Book> GetAll(){ return iBookService.list(); } @PostMapping public Boolean save(@RequestBody Book book){ boolean save = iBookService.save(book); return save; } @PutMapping public Boolean update(@RequestBody Book book){ boolean b = iBookService.updateById(book); return b; } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public Boolean delete(@PathVariable Integer id){ boolean b = iBookService.removeById(id); return b; } @GetMapping("/{id}") public Book getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ return iBookService.getById(id); } @GetMapping("{current}/{size}") public IPage<Book> getPage(@PathVariable Integer current,@PathVariable Integer size){ return iBookService.getPage(current,size); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- getPage在Service层重写
@Override public Page<Book> getPage(Integer current, Integer size) { Page<Book> bookPage = new Page<>(current, size); return bookDao.selectPage(bookPage, null); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 接收参数
- 实体数据:@RequestBody
- 路径变量:@PathVariable
4.5.1、表现层消息一致性处理
- 增删改
true- 1
- 查单条
{ "id": 5, "type": "操作系统", "name": "深入理解计算机系统", "description": "这本书是一本导论型作品,并不单单的讲操作系统,它创造性的把操作系统,体系结构,数字逻辑,以及编译原理这些计算机基础学科知识有机的结合起来。" }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 查多条
[ { "id": 1, "type": "计算机理论", "name": "Spring实战 第五版", "description": "Spring经典入门教学,深入理解Spring理解技术内幕" }, { "id": 2, "type": "计算机理论", "name": "Spring实战 第五版", "description": "Spring经典入门教学,深入理解Spring理解技术内幕" }, { "id": 3, "type": "计算机理论", "name": "Spring实战 第五版", "description": "Spring经典入门教学,深入理解Spring理解技术内幕" }, { "id": 4, "type": "操作系统", "name": "现代操作系统", "description": "本书虽然是理论的书,但是里面的一些操作系统算法介绍都挺非常的详细,有关操作系统的各种理论也是非常详实。" }, { "id": 5, "type": "操作系统", "name": "深入理解计算机系统", "description": "这本书是一本导论型作品,并不单单的讲操作系统,它创造性的把操作系统,体系结构,数字逻辑,以及编译原理这些计算机基础学科知识有机的结合起来。" } ]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32

- 设计表现层返回结果的模型类,用于后端与前端进行数据格式统一,也称为前后端数据协议
@Data public class R { private Boolean flag; private Object data; public R(Boolean flag) { this.flag = flag; } public R() { } public R(Boolean flag, Object data) { this.flag = flag; this.data = data; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 表现层接口统一返回值类型结果
@RestController @RequestMapping("/books") public class bookController { @Autowired private IBookService iBookService; @GetMapping public R GetAll(){ return new R(true,iBookService.list()); } @PostMapping public R save(@RequestBody Book book){ return new R(iBookService.save(book)); } @PutMapping public R update(@RequestBody Book book){ return new R(iBookService.updateById(book)); } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public R delete(@PathVariable Integer id){ return new R(iBookService.removeById(id)); } @GetMapping("/{id}") public R getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ return new R(true,iBookService.getById(id)); } @GetMapping("{current}/{size}") public R getPage(@PathVariable Integer current,@PathVariable Integer size){ return new R(true,iBookService.getPage(current,size)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
4.6、前后端协议联调
- 前后端分离结构设计中页面归属前端服务器
- 单体工程中页面放置在resources目录下的static目录中(建议执行clean)
- 前端发送异步请求,调用后端接口
//列表 getAll(){ axios.get("/books").then((res)=>{ console.log(res.data) }) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 单体项目中页面放置在resources /static目录下
- created钩子函数用于初始化页面时发起调用
- 页面使用axios发送异步请求获取数据后确认前后端是否联通
4.6.1、添加功能
//添加 handleAdd () { //发送异步请求 axios.post("/books",this.formData).then((res)=>{ //如果操作成功,关闭弹层,显示数据 if(res.data.flag) this.dialogFormVisible = false; this.$message.success("添加成功"); }else { this.$message.error("添加失败"); } }).finally(()=>{ this.getAl1(); }); },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 请求方式使用POST调用后台对应操作
- 添加操作结束后动态刷新页面加载数据
- 根据操作结果不同,显示对应的提示信息
- 弹出添加Div时清除表单数据
4.6.2、删除功能
//删除 handleDelete(row){ axios.delete("/books/"+row.id).then((res)=>{ if(res.data.flag){ this.$message.success("删除成功"); }else{ this.$message.error("数据同步失败,自动刷新"); } }).finally(()=>{ this.getAll(); }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
改进删除操作
handleDelete(row) { //1.弹出提示框 this.$confirm("此操作永久删除当前数据,是否继续? ","提示",{ type:'info' }).then(()=>{ //2.做删除业务 axios.delete("/books/"+row.id).then((res)=>{ ...... }).finally(()=>{ this.getAl1(); }); }).catch(()=>{ //3.取消删除 this.$message.info("取消删除操作"); }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 请求方式使用Delete调用后台对应操作
- 删除操作需要传递当前行数据对应的id值到后台
- 删除操作结束后动态刷新页面加载数据
- 根据操作结果不同,显示对应的提示信息
- 删除操作前弹出提示框避免误操作
4.6.3、修改功能
//弹出编辑窗口 handleUpdate(row){ axios.get("/books/"+row.id).then((res)=>{ if(res.data.flag){ //展示弹层,加载数据 this.formData = res.data.data; this.dialogFormVisible4Edit = true; }else{ this.$message.error("数据同步失败,自动刷新"); } }); },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 加载要修改数据通过传递当前行数据对应的id值到后台查询数据
- 利用前端数据双向绑定将查询到的数据进行回显
//修改 handleAdd () { //发送异步请求 axios.put("/books",this.formData).then((res)=>{ //如果操作成功,关闭弹层,显示数据 if(res.data.flag) this.dialogFormVisible4Edit = false; this.$message.success("修改成功"); }else { this.$message.error("修改失败"); } }).finally(()=>{ this.getAl1(); }); },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 取消添加和修改
cancel(){ this.dialogFormVisible = false; this.dialogFormVisible4Edit = false; this.$message.info("操作取消"); },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 请求方式使用PUT调用后台对应操作
- 修改操作结束后动态刷新页面加载数据(同新增)
- 根据操作结果不同,显示对应的提示信息(同新增)
4.6.4、异常消息处理
- 业务操作成功或失败返回数据格式
{ "flag": true, "data": null }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
{ "flag": false, "data": null }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 后台代码BUG导致数据格式不统一性
{ "timestamp": "2021-09-15T03:27:31.038+00:00", "status": 500, "error": "Internal Server Error", "path": "/books" }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 对异常进行统一处理,出现异常后,返回指定信息
//作为SpringMVC的异常处理器 @ControllerAdvice @RestControllerAdvice public class ProjectExceptionAdvice { @ExceptionHandler public R doException(Exception ex){ //记录日志 //通知运维 //通知开发 ex.printStackTrace(); return new R("服务器故障,请稍后重试"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 修改表现层返回结果的模型类,封装出现异常后对应的信息
- flag: false
- Data: null
- 消息(msg):要显示信息
@Data public class R { private Boolean flag; private Object data; private String Message; public R(Boolean flag, String message) { this.flag = flag; this.Message = message; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 可以在表现层Controller中进行消息统一处理
@PostMapping public R save(@RequestBody Book book){ boolean flag = iBookService.save(book); return new R(flag,flag?"添加成功^_^":"添加失败-_-!"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 目的:国际化
- 使用注解@RestControllerAdvice定义SpringMVC异常处理器用来处理异常的
- 异常处理器必须被扫描加载,否则无法生效
- 表现层返回结果的模型类中添加消息属性用来传递消息到页面
4.6.5、分页
- 页面上使用el分页组件添加分页功能
<div class="pagination-container"> <el-pagination class="pagiantion" @current-change="handleCurrentChange" :current-page="pagination.currentPage" :page-size="pagination.pageSize" layout="total,prev, pager,next,jumper" :total="pagination.total"> el-pagination> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 定义分页组件需要使用的数据并将数据绑定到分页组件
data:{ pagination: { //分页相关模型数据 currentPage: 1, //当前页码 pageSize:10, //每页显示的记录数 total:0, //总记录数 } },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 替换查询全部功能为分页功能
getAll(){ axios.get("/books/"+this.pagination.currentPage+"/"+this.pagination.pageSize).then((res)=>{ }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 加载分页数据
getAll(){ axios.get("/books/"+this.pagination.currentPage+"/"+this.pagination.pageSize).then((res)=>{ this.pagination.total = res.data.data.total; this.pagination.currentPage = res.data.data.current; this.pagination.pagesize = res.data.data.size; this.datalist = res.data.data.records; }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 分页页码值切换
//切换页码 handleCurrentChange(currentPage) { this.pagination.currentPage = currentPage; this.getAll(); },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
4.6.6、删除功能维护
- 对查询结果进行校验,如果当前页码值大于最大页码值,使用最大页码值作为当前页码值重新查询
@GetMapping("{current}/{size}") public R getPage(@PathVariable Integer current,@PathVariable Integer size){ Page<Book> page = iBookService.getPage(current, size); if (current>page.getPages()){ page = iBookService.getPage((int)page.getPages(), size); } return new R(true,page ); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
4.6.7、按条件查询
- 查询条件数据封装
- 单独封装
- 与分页操作混合封装
pagination: { //分页相关模型数据 currentPage: 1, //当前页码 pagesize:10, //每页显示的记录数 total:0, //总记录数 name: "", type: "", description: "" }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 页面数据模型绑定
<div class="filter-container"> <el-input placeholder="图书类别"v-model="pagination.type" class="filter-item"/> <el-input placeholder="图书名称"v-model="pagination.name" class="filter-item" /> <el-input placeholder="图书描述"v-model="pagination.description" class="filter-item" /> <el-button @click="getAll()" class="dalfBut">查询el-button> <el-button type="primary" class="butT" @click="handleCreate()">新建el-button> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 组织数据成为get请求发送的数据
getAll() { //1.获取查询条件,拼接查询条件 param = "?name="+this.pagination.name; param += "&type="+this.pagination.type; param += "&description="+this.pagination.description; console.log("-----------------"+param) ; axios.get("/books/"+this.pagination.currentPage+"/"+this.pagination.pageSize+param) .then((res) => { this.dataList = res.data.data.records; }); },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- Controller接收参数
@GetMapping("{current}/{size}") public R getPage(@PathVariable Integer current,@PathVariable Integer size,Book book){ Page<Book> page = iBookService.getPage(current, size,book); if (current>page.getPages()){ page = iBookService.getPage((int)page.getPages(), size,book); } return new R(true,page ); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 业务层接口功能开发
@Override public Page<Book> getPage(Integer current, Integer size, Book book) { LambdaQueryWrapper<Book> lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); lqw.like(Strings.isNotEmpty(book.getType()),Book::getType,book.getType()); lqw.like(Strings.isNotEmpty(book.getName()),Book::getName,book.getName()); lqw.like(Strings.isNotEmpty(book.getDescription()),Book::getDescription,book.getDescription()); Page<Book> bookPage = new Page<>(current, size); return bookDao.selectPage(bookPage, lqw); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.7、案例基本步骤
- pom. xml
配置起步依赖 - application.yml
设置数据源、端口、框架技术相关配置等 - dao
继承BaseMapper、设置@Mapperdao测试类 - service
调用数据层接口或MyBatis-Plus提供的接口快速开发 - service测试类
- controller
基于Restful开发,使用Postman测试跑通功能 - 页面
放置在resources目录下的static目录中
-
相关阅读:
基于复旦微的FMQL45T900全国产化ARM核心模块(100%国产化)
数据结构链表力扣例题AC(2)——代码以及思路记录
SOLIDWORKS Flow Simulation阀门内流体仿真
蓝桥杯成绩已出
《Weisfeiler and Leman Go Neural Higher-order Graph Neural Networks》阅读笔记
分布式事务-Seata-详细图文讲解
【开源】物联网智慧消防云平台系统,前后端分离,微服务框架带文档,源码分享
机器人过程自动化(RPA)入门 1. 什么是机器人过程自动化?
RPA处理重复工作,助力高效资金管理
【Vue】watch 和 watchEffect 的使用和差异性(1)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_74155781/article/details/133209523
