-
QT 字符串操作常用接口函数
经过该简单设置可以防止msvc环境下使用qdebug打印输出时出现中文乱码的问题。
#include "learn.h" #include#include #include #include // 解决qdebug 输出中文乱码的情况 #pragma execution_character_set("utf-8") - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
常见字符串处理函数
接口定义 接口功能 QString &QString::sprintf(const char *cformat, …) 支持的格式定义符和C++中的sprintf功能类似,返回值是一个QString对象 QString QString::arg(const QString &a, int fieldWidth = 0, QChar fillChar = QLatin1Char(’ ')) const 字符串组合方式输出一个QString对象,提供一个支持多种数据类型重载的arg函数 QString::insert 指定位置插入字符串 QString::prepend 头插一个字符串 QString::replace(const QString &before, const QString &after) 使用after 替换掉before //格式输出一个字符串 qDebug() << QString().sprintf("%s", "1111111"); # out: "1111111" qDebug() << QString("%1来自%2今年%3岁了").arg("张三") .arg("新疆").arg("21"); # out: "张三来自新疆今年21岁了" //指定位置插入字符串 QString tmp = "11"; tmp.insert(0,"10_"); qDebug() << tmp; # out: "10_11" //头插字符串 tmp.prepend("日期:"); qDebug() << tmp; # out: "日期:10_11" //字符串替换 tmp.replace(QString("1"), QString("2")); qDebug() << tmp; # out: "日期:20_22"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
空白字符串处理函数
接口定义 接口功能 QByteArray QByteArray::trimmed() const 删除字符串的两端的空白字符 QByteArray QByteArray::simplified() const 删除字符串的两端的空白字符,使用单个空格替换字符串中出现的空白字符 //移除字符串的两边空格 QString str = " welcome \t to \n you"; qDebug() << str.trimmed(); # out:"welcome \t to \n you" //移除字符串的全部空格 qDebug() << str.simplified(); #out:"welcome to you"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
查询字符串数据
函数定义 函数功能 bool QByteArray::startsWith(const QByteArray &ba) const 如果此字节数组以字节数组ba开头,则返回true;否则返回false, CaseInsensitive为可选择参数,可以设置此参数从而区分大小写,否则默认是不区分大小写的。 bool QByteArray::endsWith(const QByteArray &ba) const 从结尾开始查找 bool QByteArray::contains(const QByteArray &ba) const 判断一个指定的字符串是否出现过 //查找第一次出现的字符串 QString str = "Welcome to you"; //CaseInsensitive: 不区分大小写 qDebug() << str.startsWith("Welcome", Qt::CaseInsensitive); qDebug() << str.startsWith("to", Qt::CaseInsensitive); #out: true false //查找最后一次出现的字符串 str = "Welcome to you"; //区分大小写 qDebug() << str.endsWith("you"); qDebug() << str.endsWith("You"); #out: true false QString str = "Welcome to you"; //不区分大小写 qDebug() << str.contains("to"); qDebug() << str.contains("Welcome"); qDebug() << str.contains("you"); # out: true true true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
字符串比较
函数定义 功能说明 int QString::localeAwareCompare(const QString &s1, const QString &s2) 比较s1与s2,如果s1小于、等于或大于s2,则返回一个小于、等于或大于零的整数。 int QByteArray::compare(QString&,QString&, Qt::CaseSensitivity cs = Qt::CaseSensitive) const 可以设置是否区分大小写进行字符串的比较 //比较两个字符串的大小,小于返回负数,相等返回0,大于返回正数 QString str1 = "Welcome to you"; QString str2 = "Welcome to you"; qDebug() << QString::localeAwareCompare(str1, str2); // compare 函数可以指定是否区分大小写来进行比较 str1 = "Welcome to You"; str2 = "Welcome to you"; qDebug() << QString::compare(str1, str2, Qt::CaseInsensitive);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
字符串的转换
QString提供的字符编码集的转换函数将会返回一个const char* 类型版本的QByteArray,即构造函数QByteArray(const char*)构造的QByteArray对象。
QByteArray类具有一个字节数组,它既可以存储原始字节(原始字节),也可以存储传统的以“\0”结尾的8位的 字符串。在Qt中,使用QByteArray比使用const char * 存储传统的以“\0”结尾的8位的字符串.在Qt中,使用QByteArray比使用Const char*更方便,QByteArray也支 持隐式共享。转换函数有以下几种。
函数定义 函数功能 toAscill 返回一个Ascill 编码的8位字符串, 返回值都是QByteArray toLatin1 返回一个toLatin-1编码的8位字符串, 返回值都是QByteArray toUtf8 返回一个Utf8编码的8位字符串, 返回值都是QByteArray toLocal8Bit 返回一个系统本地编码的8位字符串, 返回值都是QByteArray QString str = "Welcome to you"; auto utf = str.toUtf8(); auto Latin1 = str.toLatin1(); auto Local8Bit = str.toLocal8Bit(); qDebug() << utf; qDebug() << Latin1; qDebug() << Local8Bit; #out: "Welcome to you" "Welcome to you" "Welcome to you"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
QT版本的STL
-
QList是迄今为止最常用的容器类,它存储给定数据类型T的一列数值。
-
QList维护了一个指针数组,该数组存储的指针指向QList存储的列表维护了一个指针数组,该数组存储的指针指向QList存储的列表项的内容。
对于不同的数据类型,QList采取不同的存储策略,存储策略有以下几种.
-
如果T是一个指针类型或指针大小的基本类型(即该基本类型占有的字节数和指针类型占有的字节数相同),QList 会将数值直接存储在它的数组中。
-
如果QList存储对象的指针,则该指针指向实际存储的对象。
//直接存储对象 QList<QString> list1; list1 << QString("%1来自%2今年%3岁了").arg("张三"). arg("新疆").arg("21"); qDebug() << sizeof(list1); # out: 8 //存储对象的指针 auto s = QString("%1来自%2今年%3岁了").arg("张三").arg("新疆").arg("21"); QList<QString*> list2; list2 << &s; qDebug() << sizeof(list2); # out: 8- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
通过结果可以得知qlist最终不管T是什么类型,但是最终存储的一定是指针类型,即使直接存储一个对象和存储一个对象的指针二者的qlist对象大小都是一样的
QLinkedList和QVector的区别
QLinkedList类
QLinkedList是一个链式列表,它以非连续的内存块保存数据。
QLinkedList不能使用下标,只能使用迭代器访问它的数据项。QVector类
QVector在相邻的内存中存储给定数据类型T的一组数值。
QVector既可以使用下标访问数据项,也可以使用迭代器访问数据项。QT提供的STL命名风格的迭代器

QMap和QHash
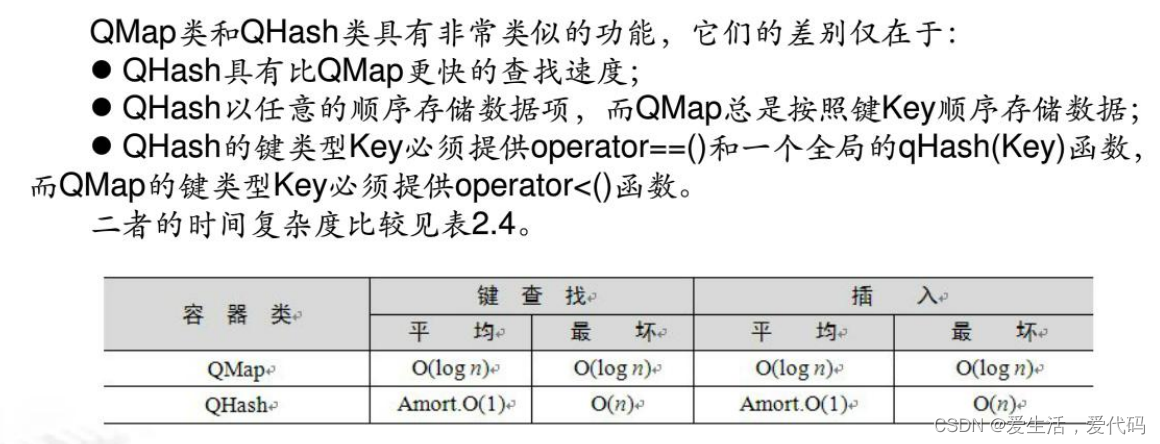
QMap和QHash的简单使用QMap<QString, QString> map; map.insert("小8", "11"); map.insert("小9", "12"); map.insert("小7", "13"); //构造一个Qmap的迭代器 QMap<QString, QString>::iterator it = map.begin(); while (it != map.end()) { qDebug() << "key:" << it.key() << "val:" << it.value(); it++; } //讲小王的年龄修改 for (auto it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); it++) if (it.key() == "小王") it.value() = "20"; qDebug() << "--------------------------------------"; it = map.begin(); while (it != map.end()) { qDebug() << "key:" << it.key() << "val:" << it.value(); it++; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
输出:
key: "小7" val: "13" key: "小8" val: "11" key: "小9" val: "12" -------------------------------------- key: "小7" val: "13" key: "小8" val: "11" key: "小9" val: "12"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
QHash 并不根据key的值大小进行排序,而是随机的无序的
QHash<QString, QString> has; has.insert("小8", "11"); has.insert("小9", "12"); has.insert("小7", "13"); //构造一个Qmap的迭代器 QHash<QString, QString>::iterator it = has.begin(); while (it != has.end()) { qDebug() << "key:" << it.key() << "val:" << it.value(); it++; } //讲小王的年龄修改 for (auto it = has.begin(); it != has.end(); it++) if (it.key() == "小王") it.value() = "20"; qDebug() << "--------------------------------------"; it = has.begin(); while (it != has.end()) { qDebug() << "key:" << it.key() << "val:" << it.value(); it++; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
输出
key: "小9" val: "12" key: "小7" val: "13" key: "小8" val: "11" -------------------------------------- key: "小9" val: "12" key: "小7" val: "13" key: "小8" val: "11"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
-
相关阅读:
面试打底稿⑤ 项目一的第一部分
redis的解决分布式锁的bug 和 redis面试题
npm报证书过期 certificate has expired问题(已解决)
Pytorch CIFAR10图像分类 工具函数utils更新v2.0篇
音视频开发基础概念
最近一段时间的规划
JSON和全局异常处理
pinia基本使用介绍
生态系统服务——水源涵养水源涵养分布
win10你的设备遇到问题,需要重启的五种解决方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_53421868/article/details/127965874
