-
Java的自动装箱与拆箱详细分析
Java的自动装箱与拆箱详细分析
1. 既然说是装箱与拆箱,那么到底是装的什么,拆的什么?
装箱:将基本数据类型封装起来,用他对应的引用类(包装类)来处理
拆箱:就是把引用类里面的基本数据拆出来
2. 说到了基础数据类型,Java中的基础数据类型有哪些?
基础数据类型 默认值 占用内存大小 取值范围 数据包装类 boolean false 8位 false / true Boolean byte 0 8位 -128 ~ 127 (-2^7 ~ 2^7 - 1) Byte short 0 16位 -32768 ~ 32767 (-2^15 ~ 2^15 - 1) Short int 0 32位 -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 (-2^31 ~ 2^31 - 1) Integer long 0 64位 -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 (-2^63 ~ 2^63 - 1) Long char ‘\u0000’ 16位 0 ~ 65535 (‘\u0000’~‘\uffff’) Character float 0.0f 32位 满足 IEEE 754 的计算 Float double 0.0 64位 满足 IEEE 754 的计算 Double 这些基础数据类型为什么是这么个取值范围?内存占用为什么会是这么大呢?
肯定是Java虚拟机规范定义的。那么,Java的这些基础数据类型的内存占用大小的具体实现是如何实现的?这就要去看hotspot虚拟机实现了:
在jni.h 中如下定义:
typedef unsigned char jboolean; // 说明Java的boolean其实是c语言的无符号char类型 typedef unsigned short jchar; // 说明Java的char其实是C语言的无符号short类型 typedef short jshort; // 说明Java的short就是C语言的short类型 typedef float jfloat; // 说明Java的float就是C语言的float类型 typedef double jdouble; // 说明Java的double就是C语言的double类型- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
而 int 类型 和 long 类型 在jni.h中并没有直接给出,而是在jni_md.h中:
typedef int jint; // 说明Java中的int就是C语言的int类型 // 以下说明 在Java中,long的实现分两种:在64位机上是C语言的long类型;在32位机上是C语言的long long类型 #ifdef _LP64 /* 64-bit */ typedef long jlong; #else typedef long long jlong; #endif- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
3. 那么为什么要装箱和拆箱呢?
装箱是为了把基础数据用对应的包装类封装起来,这样就可以让这些基础数据类型具有面向对象的相关属性,方便按照面向对象思想操作。
4. 什么是自动装箱?
举个例子:
public static void main(String[] args) { Integer a = 5; }- 1
- 2
- 3
明明 5 是一个基础数据类型,为什么能直接变成一个Integer包装类?
经过javap命令查看字节码如下:

可以看到编译成字节码后会调用一个
Integer.valueOf()方法那么我们需要去看看Integer这个类在执行这个方法的时候干了个什么事:
public static Integer valueOf(int i) { if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) // 为了优化性能,在不需要新的Integer实例时会先拿缓存中的值 return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); // 返回一个新的Integer对象 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Integer对象中包含一个value属性
private final int value; public Integer(int value) { this.value = value; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
其他基础数据类型同样如此
因此,自动装箱总结如下:
在编译类似直接将基础数据类型赋值给包装类对象的时候,javac编译器会在编译过程中自动添加 包装类.valueOf方法,将创建一个新的包装类对象并将传入的基础数据类型存放到该对象的value属性中
5. 什么是自动拆箱?
在进行包装类与基础数据类型进行数据比较的时候
Integer b1 = 1000; Integer b2 = 2000; int b3 = 1500; System.out.println("包装类与包装类的比较"); System.out.println(b1 > b2); // false System.out.println("包装类与基础数据类型比较"); System.out.println(b3 > b2); // false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
在进行比较操作时,这种基础数据类型的包装类可以直接用对象进行比较,为啥?
编译成字节码后研究如下

发现编译器会帮你创建一个intValue的方法
看看intValue方法干了什么事?
public int intValue() { return value; }- 1
- 2
- 3
就是把包装类中value属性值返回出去了
因此,自动拆包总结如下:
基础数据类型的包装类在对象比较等操作时,javac编译器会自动添加xxxValue方法将包装类对象中的属性返回出来还原成一个基础数据类型
6. 经过上述描述,那么我们可以写上一大堆代码进行验证学习这些个包装好的类
测试1:
Integer a1 = 5; int a2 = 5; Integer a3 = 5; System.out.println("包装类 与 基础数据 直接通过==比较: "); System.out.println(a1==a2); // true System.out.println("包装类 与 基础数据 直接通过equals比较: "); System.out.println(a1.equals(a2)); // true System.out.println("包装类 与 包装类 直接通过==比较: "); System.out.println(a1==a3); // true System.out.println("包装类 与 包装类 直接通过equals比较: "); System.out.println(a1.equals(a3)); // true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
测试2:
// 当两个值大于缓存时: Integer b1 = 1000; Integer b2 = 1000; System.out.println("直接通过==比较:"); System.out.println(b1==b2); // false System.out.println("通过equals比较:"); System.out.println(b1.equals(b2)); // true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
测试3:
Integer c1 = new Integer(100); Integer c2 = new Integer(100); System.out.println("直接通过==比较:"); System.out.println(c1==c2); // false System.out.println("通过equals比较:"); System.out.println(c1.equals(c2)); // true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
经过上述测试,我们可以得出如下结论:
- 当数值较小时,会将值缓存起来,每次获取都是同一个对象
- 当数值超出缓存时,每次都会创建出新的对象
- 直接new的对象其地址也不会相同,直接==比较地址肯定就会返回false
7. 包装类的valueOf详细分析
Integer类
public static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException { // radix用来表示用什么进制来解析s字符串 再转换成 int return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s,radix)); // 再执行 valueOf(int) } public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException { // 直接用10进制解析s字符串 return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10)); // 再执行 valueOf(int) } // 重点在此方法 public static Integer valueOf(int i) { if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) // -128 ~ 127 return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); // 创建一个新的Integer对象 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
IntegerCache类
private static class IntegerCache { static final int low = -128; static final int high; static final Integer cache[]; static { // high值可以通过属性来配置 int h = 127; // 通过VM返回系统初始化时保存的"java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"的系统属性。 String integerCacheHighPropValue = sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) { try { int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue); // 系统中的虚拟机配置 i = Math.max(i, 127); // 如果配置小于127则将high设置为 // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1); // 如果配置的值大于Integer最大值则设置为 0x7fffff7e } catch( NumberFormatException nfe) { // If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it. } } high = h; cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; // 创建cache数组的大小 int j = low; for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++) cache[k] = new Integer(j++); // 循环,将cache数组中的每个下标都设置值,0位置设置-128 // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7) assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; } private IntegerCache() {} }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
看了这个类了之后发现:
- 这个缓存的大小是可以通过虚拟机参数进行设置的,而且能存的数为 -128 到 127(默认)
- 缓存是一个数组,并且将从 -128~127的所有值产生了对应的对象进行存储
我们到底如何给虚拟机设置参数来改变最大的那个缓存数呢?
IntegerCache类的注释如下:
cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between
-128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by jls.缓存 支持 JLS 要求的 -128 和 127(含)之间的值的自动装箱的对象标识语义。
The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache
may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=} option.
During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property
may be set and saved in the private system properties in the
sun.misc.VM class.缓存在第一次使用时被初始化。缓存的大小可以由 {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=} 选项控制。在VM初始化时,可以设置java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high属性并保存在sun.misc.VM类的私有系统属性中。
所以想要通过虚拟机设置参数来改变这个大小就可以使用
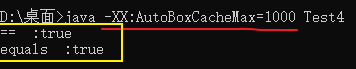
-XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=来设置测试代码:
/** * @author: XuJiaKai * @createTime: 2022/11/11-18:04 */ public class Test4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer b1 = 1000; Integer b2 = 1000; System.out.println("== :" + (b1==b2)); System.out.println("equals :" + (b1.equals(b2))); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
执行:
不携带参数:

携带参数:
其他类的分析方法与此相同。
Boolean类
public static Boolean valueOf(String s) { return parseBoolean(s) ? TRUE : FALSE; } public static Boolean valueOf(boolean b) { return (b ? TRUE : FALSE); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
布尔类型就俩值,所以不需要像int类型一样使用缓存,而是直接在属性中保存两个Boolean对象
public static final Boolean TRUE = new Boolean(true); public static final Boolean FALSE = new Boolean(false);- 1
- 2
Byte类
public static Byte valueOf(byte b) { final int offset = 128; // 设置偏移量,用于与传入值进行计算获取到对应ByteCache数组的下标 return ByteCache.cache[(int)b + offset]; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
ByteCache类
private static class ByteCache { private ByteCache(){} static final Byte cache[] = new Byte[-(-128) + 127 + 1]; static { for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) cache[i] = new Byte((byte)(i - 128)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Character 类
public static Character valueOf(char c) { if (c <= 127) { // must cache return CharacterCache.cache[(int)c]; } return new Character(c); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
CharacterCache类
private static class CharacterCache { private CharacterCache(){} static final Character cache[] = new Character[127 + 1]; static { for (int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) cache[i] = new Character((char)i); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Double类 / Float类
public static Double valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException { return new Double(parseDouble(s)); } public static Double valueOf(double d) { return new Double(d); } ========================================================================== public static Float valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException { return new Float(parseFloat(s)); } public static Float valueOf(float f) { return new Float(f); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
说明:Java中的Double类/Float类每次自动装箱都会创建新的对象
Double b1 = 10.0; Double b2 = 10.0; System.out.println("直接通过==比较:"); System.out.println(b1==b2); // false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Long类
public static Long valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException { return Long.valueOf(parseLong(s, 10)); } public static Long valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException { return Long.valueOf(parseLong(s, radix)); } public static Long valueOf(long l) { final int offset = 128; if (l >= -128 && l <= 127) { // will cache return LongCache.cache[(int)l + offset]; } return new Long(l); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
LongCache类
private static class LongCache { private LongCache(){} static final Long cache[] = new Long[-(-128) + 127 + 1]; static { for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) cache[i] = new Long(i - 128); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Short类
public static Short valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException { return valueOf(parseShort(s, radix)); } public static Short valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException { return valueOf(s, 10); } public static Short valueOf(short s) { final int offset = 128; int sAsInt = s; if (sAsInt >= -128 && sAsInt <= 127) { // must cache return ShortCache.cache[sAsInt + offset]; } return new Short(s); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
ShortCache类
private static class ShortCache { private ShortCache(){} static final Short cache[] = new Short[-(-128) + 127 + 1]; static { for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) cache[i] = new Short((short)(i - 128)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
8. 总结
- 包装类 和 基本数据类型 之间可以进行比较:包装类会自动拆箱后与基本数据类型比较
- 在用包装类对象变量去接收一个基础数据类型时,会自动调用valueOf方法返回一个封装的对象
- 大部分的整型包装类对象都会有一个缓存,保存从 -128~127 的值,并且可以通过虚拟机参数设置Integer类型的缓存数组大小
- 布尔类型的包装类不主动创建时,只有两个对象
- 在比较包装类对象的时候尽量不要使用 == 号进行比较,因为缓存区域外的对象会创建不同的对象
-
相关阅读:
java集合list map set
数学建模——插值拟合
JVM调优:JVM中常见的垃圾回收算法详解
SpringBoot getpost请求详解
Log4j 漏洞还没忙完,新的漏洞又出现了
头文件和编译的问题
第三方在线地图源有哪些?
HTTPDNS
恭喜你~遇到了最有趣的算法(三)数论篇
scrollIntoView锚点跳转 超好用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41755616/article/details/127815329
