-
初阶数据结构 堆(二)
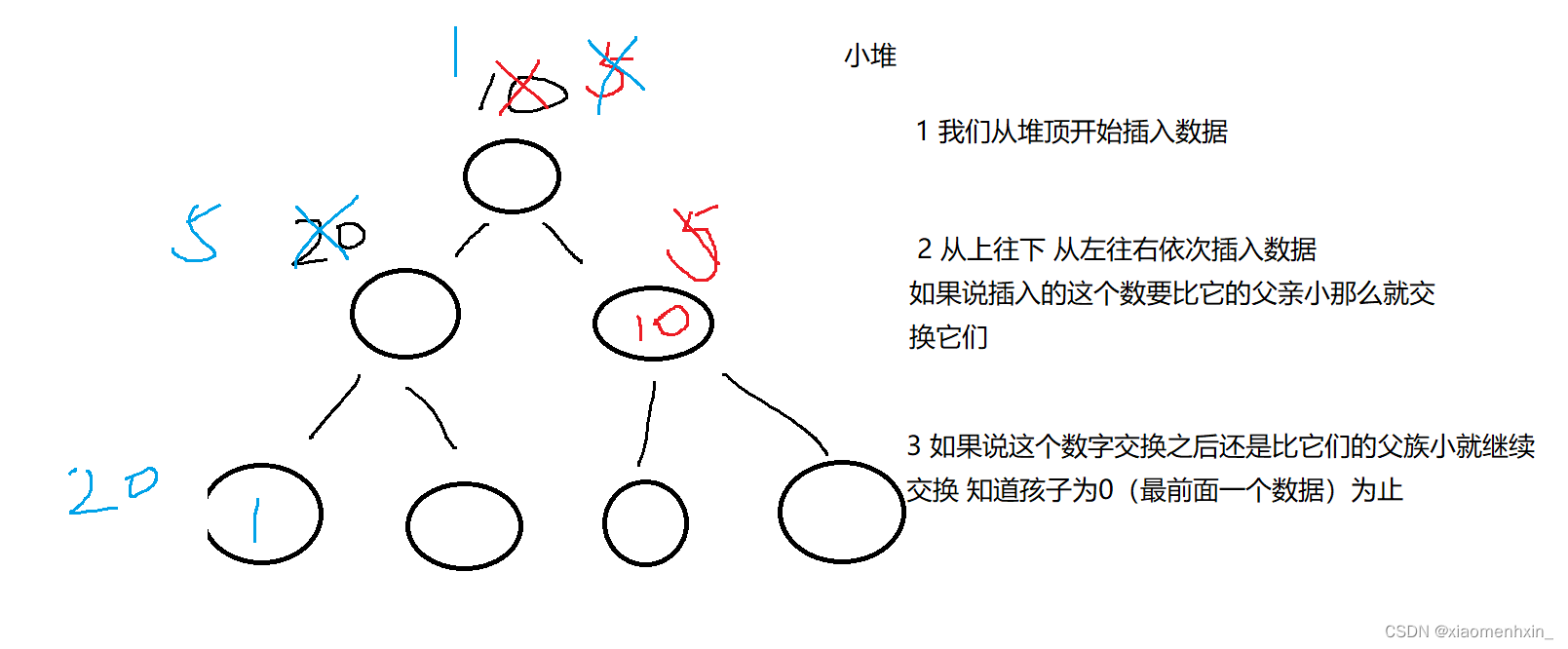
一. 堆的接口函数(续)
虽然我们的上一篇博客已经写过了堆的前面一些接口函数
这里我们再重复一遍
1. 结构体形式
我们这里形式上使用一个数组来表示一个逻辑上的二叉树
// 为了方便复用 我们这里将int重定义下 typedef int HeapType; // 结构体定义一下 typedef struct Heap { HeapType* arr; int size; int capacity; }Hp;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
2. 初始化和销毁
这里的两个接口函数都很简单 我们直接连起来动手实现一下
初始化
void HeapInit(Hp* obj) { //assert assert(obj); // main obj->arr = NULL; obj->size = 0; obj->capacity = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
销毁
void HeapDestroy(Hp* obj) { // assert assert(obj); // main free(obj->arr); obj->arr = NULL; obj->size = 0; obj->capacity = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
3. 添加数据(小堆为例)
void HeapPush(Hp* obj, HeapType x) { // assert assert(obj); //开辟空间 if (obj->size==obj->capacity) { int newcapacity; //第一次*2为0 newcapacity = obj->capacity * 2 + 4; //注意这里的sizeof 以及最后的更新capacity HeapType* tmp = realloc(obj->arr, sizeof(HeapType) * newcapacity); if (tmp=NULL) { printf("HeapPush realloc error"); exit(-1); } else { obj->arr = tmp; obj->capacity = newcapacity; } } //开始插入数据 obj->arr[obj->size] = x; //判断是否需要调整 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
这里因为判断是否需要调整这个函数要使用很多次
所以说我们单独写出一个函数出来
void HeapAdjust(Hp* obj, int seat) { // assert assert(obj); //循环判断孩子是否大于父亲 终止条件是孩子等于0(这个时候孩子就是最前面的位置了)或者不需要调整了 int child = seat; int father = (seat - 1) / 2; while (child) { // 小堆 上面的最小 所以说如果孩子小就要向上调整 if (obj->arr[child]<obj->arr[father]) { HeapType tmp; tmp = obj->arr[father]; obj->arr[father] = obj->arr[child]; obj->arr[child] = tmp; //迭代条件 child = father; father = (child - 1) / 2; } else { break; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
小堆的调整方式如上
整体代码如下
void HeapPush(Hp* obj, HeapType x) { // assert assert(obj); //开辟空间 if (obj->size==obj->capacity) { int newcapacity; //第一次*2为0 newcapacity = obj->capacity * 2 + 4; //注意这里的sizeof 以及最后的更新capacity HeapType* tmp = realloc(obj->arr, sizeof(HeapType) * newcapacity); if (tmp=NULL) { printf("HeapPush realloc error"); exit(-1); } else { obj->arr = tmp; obj->capacity = newcapacity; } } //开始插入数据 obj->arr[obj->size] = x; obj->size++; //判断是否需要调整 注意这里不能使用-- 因为这样子使用了就改变size的值了 HeapAdjust(obj, obj->size - 1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
4. 打印数据
这个很简单 直接打印数组的顺序就可以
简单来实现一下
void HeapPrint(Hp* obj) { //assert assert(obj); //按照数组顺序一个个打印数据就可以 int i = 0; for ( i = 0; i < obj->size; i++) { printf("%d ", obj->arr[i]); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
下面让我们来测试一下

我们发现出现了一个这样子的错误到底怎么回事呢?
我们debug看看
这里显示obj->arr是一个空指针
难道是我们前面的tmp写错了?
回去一看
果然
HeapType* tmp = realloc(obj->arr, sizeof(HeapType) * newcapacity);- 1
忘记强制转换类型了
我们强制转换下类型再试试
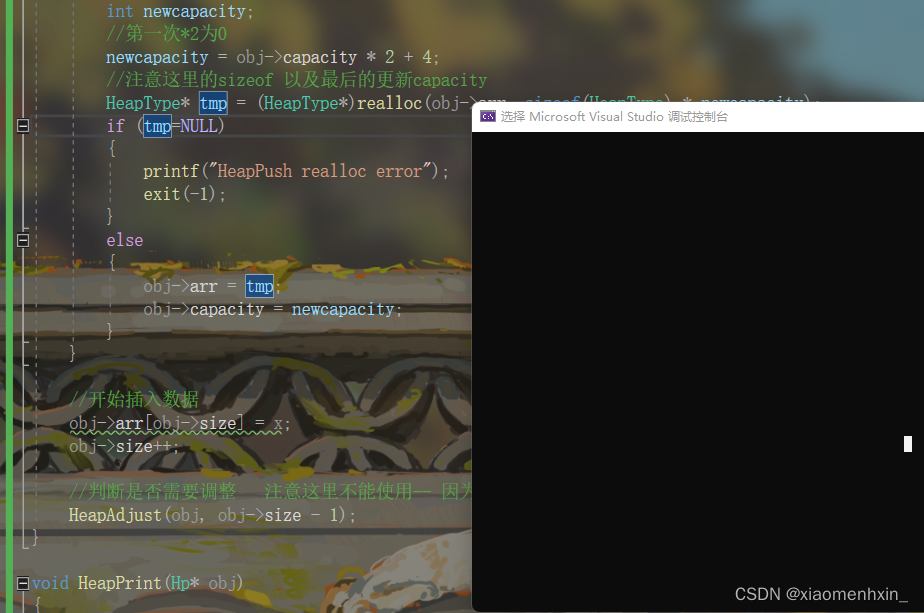
我们发现这里程序还是崩溃了再debug一下我们就发现了
原来是这一行的条件
if (tmp=NULL)- 1
这里要改一下
改成
if (tmp==NULL)- 1
这样子就可以啦
我们再来看看效果

5. 删除数据
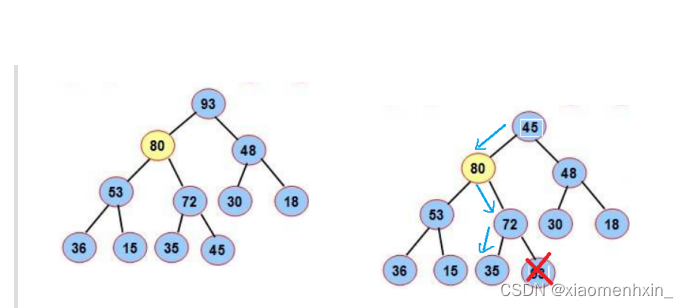
我们想要删除堆中的一个数据 还要不改变这个堆的结构 这个时候怎么办呢这个时候我们这里给出一种很巧妙的解法
我们先将最前面的元素和最后面的元素交换位置
然后再删除掉堆最后面的元素
之后开始向下调整这个堆
如上图所示
下面是删除数据的大体逻辑
void HeapDelete(Hp* obj) { // assert assert(obj); assert(obj->arr); assert(obj->size > 0); // 交换头尾元素 HeapType tmp = obj->arr[0]; obj->arr[0] = obj->arr[obj->size - 1]; obj->arr[obj->size - 1] = tmp; //删除尾元素 obj->size--; //向下调整 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
这里我们还需要再写一个函数向下调整
void HeapAdjustDown(Hp* obj,int size) { // assert assert(obj); // set孩子父亲 比较 int father = 0; int child = 2 * father + 1; // 孩子大于等于size的时候结束 while (child < size) { // 右孩子存在 比较两个大小 if (child + 1 < size && obj->arr[child + 1] < obj->arr[child]) { child++; } else { break; } //父亲和最大的孩子比较大小 如果大于就交换 如果小于就结束 if (obj->arr[father] > obj->arr[child]) { HeapType tmp = obj->arr[father]; obj->arr[father] = obj->arr[child]; obj->arr[child] = tmp; // 交换完迭代 father = child; child = 2 * father + 1; } else { break; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
调整函数如上
我们再来整体看看这个函数
void HeapDelete(Hp* obj) { // assert assert(obj); assert(obj->arr); assert(obj->size > 0); // 交换头尾元素 HeapType tmp = obj->arr[0]; obj->arr[0] = obj->arr[obj->size - 1]; obj->arr[obj->size - 1] = tmp; //删除尾元素 obj->size--; //向下调整 HeapAdjustDown(obj,obj->size); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
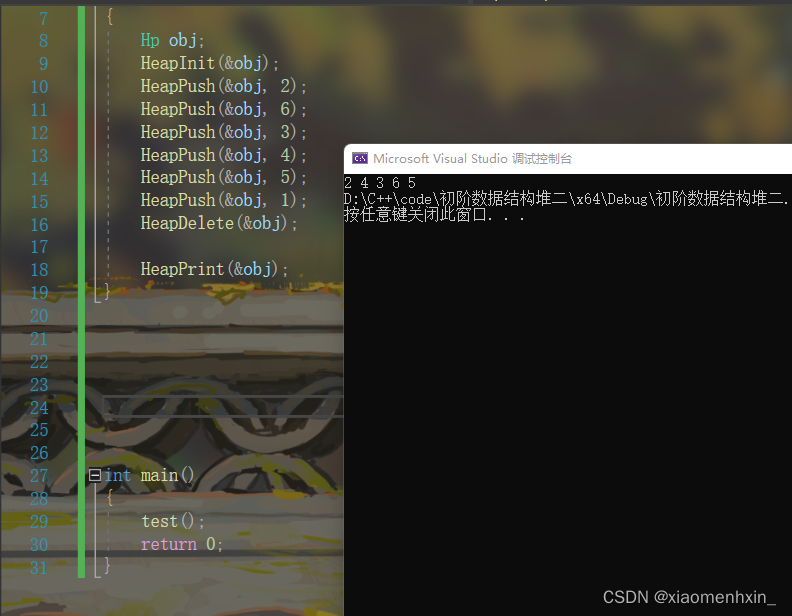
测试一下试试
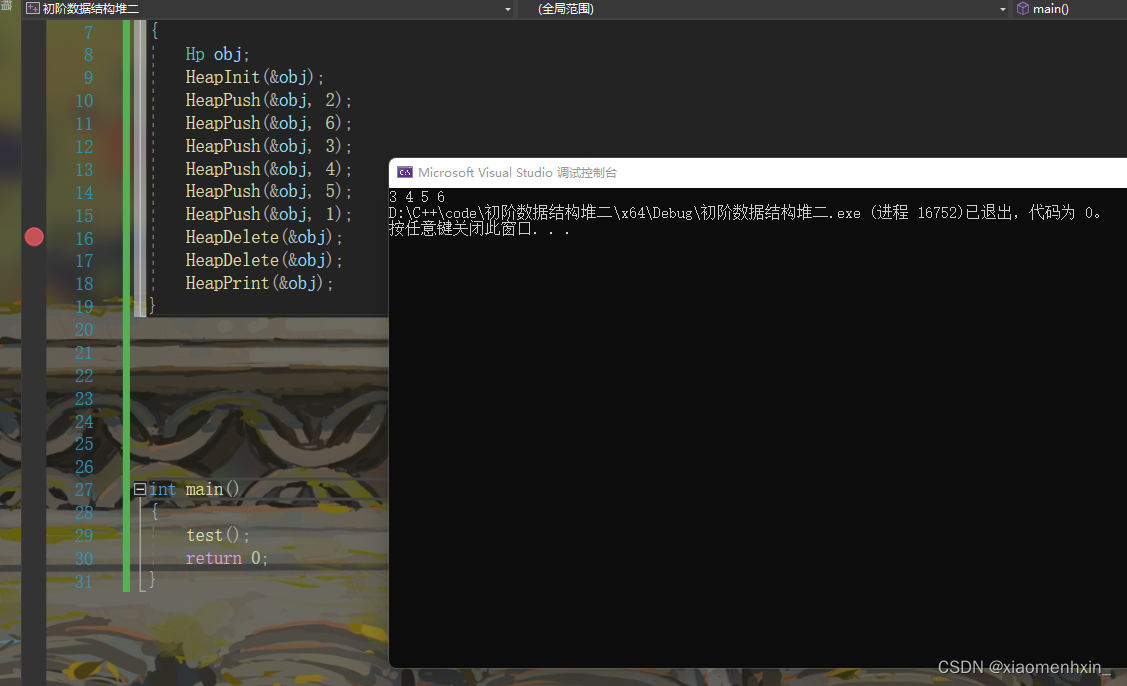
6. 返回大小
这个很简单 返回size大小
int HeapSize(Hp* obj) { return obj->size; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
7. 判断为空
bool HeapEmpty(Hp* obj) { return obj->size == 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
以上就是本篇博客的全部内容啦 由于博主才疏学浅 所以难免会出现纰漏 希望大佬们看到错误之后能够
不吝赐教 在评论区或者私信指正 博主一定及时修正
那么大家下期再见咯
-
相关阅读:
windows解决ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘cython_bbox‘问题,亲测可用
快速删除MySQL服务 。
OccuSeg: Occupancy-aware 3D Instance Segmentation
突破从0到1后,鲜花电商2.0时代怎么走?
接口测试关键技术
使用jenkins自动打包构建Maven项目
第三方支付接口响应超时处理方法【杭州多测师】【杭州多测师_王sir】
【JavaSe】断言 assert 到底怎么用?
打造自己的前端组件库(奶妈版,超详细)
解放双手!无需注解快速生成API文档,跟SpringBoot绝配!
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/meihaoshy/article/details/127414899
