-
面试基础篇——ArrayList扩容机制
引言
要注意的是,以下所有代码中用反射方式来更直观地反映 ArrayList 的扩容特征,但从 JDK 9 由于模块化的影响,对反射做了较多限制,需要在运行测试代码时添加 VM 参数
--add-opensjava.base/java.util=ALL-UNNAMED方能运行通过扩容规则
1. ArrayList() 无参构造扩容
ArrayList() 无参构造会使用长度为零的数组
ArrayList()源码
/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2. ArrayList(int initialCapacity)扩容
ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 使用指定容量的数组初始化ArrayList()
ArrayList(int initialCapacity)源码
/** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity * is negative */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
3. public ArrayList(Collection c) 扩容
public ArrayList(Collection c) 会使用 c 集合 的大小作为数组容量
ArrayList(Collection c) 源码
/** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); if ((size = a.length) != 0) { if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) { elementData = a; } else { elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class); } } else { // replace with empty array. elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
4. add(Object o)扩容
add(Object o) 首次扩容为 10,再次扩容为上次容量的 1.5 倍(使用移位相加的规则即 (原容量 > > 1 ) + 原容量 (原容量>>1)+ 原容量 (原容量>>1)+原容量 )
无参构造ArryList()
-
首次添加元素a
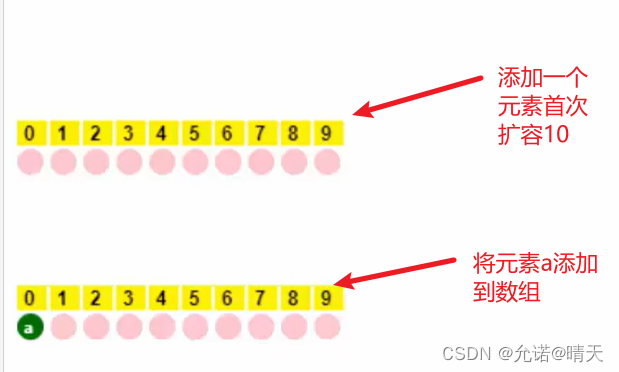
-
当数组容量满时添加b
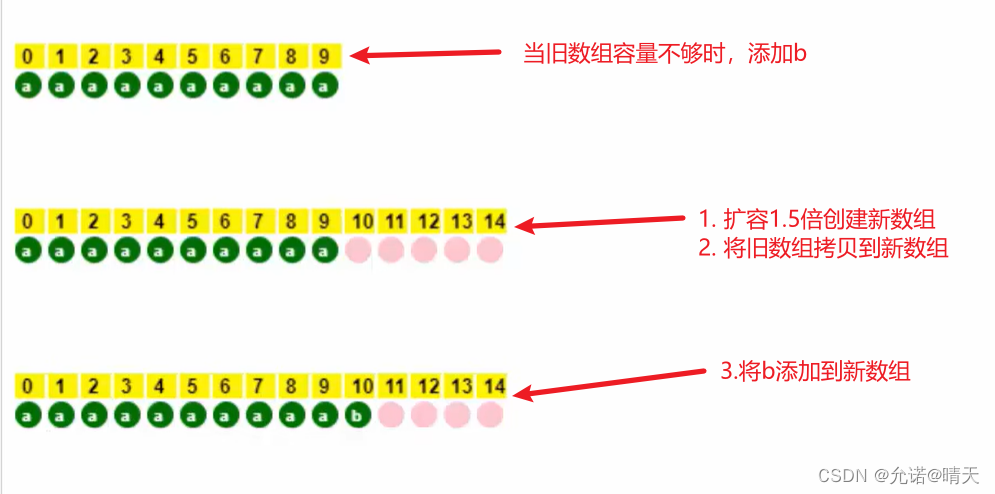
代码演示:
演示扩容10次的ArrayList的长度
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class TestArrayList { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(arrayListGrowRule(10)); } private static List<Integer> arrayListGrowRule(int n) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); int init = 0; list.add(init); if (n >= 1) { init = 10; list.add(init); } for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { init += (init) >> 1; list.add(init); } return list; } } // 执行结果:[0, 10, 15, 22, 33, 49, 73, 109, 163, 244, 366]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
5. addAll(Collection c) 扩容
addAll(Collection c) 没有元素时,扩容为 Math.max(10, 实际元素个数),有元素时为 Math.max(原容量 1.5 倍, 实际元素个数)
代码演示:
- 无初始容量时扩容
import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; // --add-opens java.base/java.util=ALL-UNNAMED public class TestArrayList { public static void main(String[] args) { testAddAllGrowEmpty(); } private static void testAddAllGrowEmpty() { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3)); // list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11)); System.out.println(length(list)); } public static int length(ArrayList<Integer> list) { try { Field field = ArrayList.class.getDeclaredField("elementData"); field.setAccessible(true); return ((Object[]) field.get(list)).length; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return 0; } } } //当执行 list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3)); 时运行结果为:10 //当执行 list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11)); 时结果为:11- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 有初始容量(10) 时扩容
import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; // --add-opens java.base/java.util=ALL-UNNAMED public class TestArrayList { public static void main(String[] args) { testAddAllGrowNotEmpty(); } private static void testAddAllGrowNotEmpty() { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { list.add(i); } list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3)); // list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)); System.out.println(length(list)); } public static int length(ArrayList<Integer> list) { try { Field field = ArrayList.class.getDeclaredField("elementData"); field.setAccessible(true); return ((Object[]) field.get(list)).length; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return 0; } } } //当执行 list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3)); 时运行结果为:15 //当执行 list.addAll(List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11)); 时结果为:16- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
其他
-
相关阅读:
SEO方案尝试--Nuxtjs项目基础配置
matlab 方向向量约束的PCA快速粗配准
C语言堆排序
一场深刻的开源聚会:KCC@北京 9.2 活动回顾
qt历史数据管理模块(模块化程序)功能块复制直接使用不冲突
Vue中的路由介绍以及Node.js的使用
yaml编写规则以及YAML和JSON对比
zabbix6.4告警配置(短信告警和邮件告警),脚本触发
氮化镓(GaN)中碳相关缺陷的迁移机制和扩散势垒
Jetson Xavier NX远程桌面VNC使用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52006948/article/details/127326420
