-
【Android-实战】1、Room 使用 Flow 和 collect() 监听数据库的变化、动态更新页面
一、准备工作
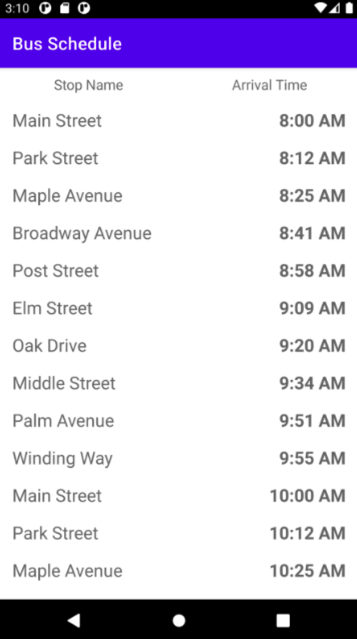
通过 Room,可以开发数据库,而 Flow 是 Kotlin 的一项技术,通过本文将学习二者怎么结合运用,我们希望实现如下效果:
首先,在 build.gradle(Project) 中添加 room 的依赖:
buildscript { ext { kotlin_version = "1.6.20" room_version = '2.4.3' nav_version = '2.5.2' } }在 build.gradle(app) 中添加 room 依赖:
dependencirs { implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version" kapt "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" // optional - Kotlin Extensions and Coroutines support for Room implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version" }二、创建 Entity
我们的 schedule 表有如下3个字段:
- id:一个整数,提供用作主键的唯一标识符
- stop_name:一个字符串
- arrival_time:一个整数
目录结构如下:
在 database/schedule/Schedule.kt 中定义 Entity,如下:
package com.example.busschedule.database.schedule import androidx.annotation.NonNull import androidx.room.ColumnInfo import androidx.room.Entity import androidx.room.PrimaryKey /** * Represents a single table in the database. Each row is a separate instance of the Schedule class. * Each property corresponds to a column. Additionally, an ID is needed as a unique identifier for * each row in the database. */ @Entity data class Schedule( @PrimaryKey val id: Int, @NonNull @ColumnInfo(name = "stop_name") val stopName: String, @NonNull @ColumnInfo(name = "arrival_time") val arrivalTime: Int )三、创建 Dao
Dao 是数据访问对象,包含读取和操作数据的函数,调用 Dao 相当于 调用 SQL,目录结构如下:
在 database/schedule/ScheduleDao.kt 中定义 Dao,如下:
package com.example.busschedule.database.schedule import androidx.room.Dao import androidx.room.Query import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.Flow /** * Provides access to read/write operations on the schedule table. * Used by the view models to format the query results for use in the UI. */ @Dao interface ScheduleDao { @Query("SELECT * FROM schedule ORDER BY arrival_time ASC") fun getAll(): Flow<List<Schedule>> @Query("SELECT * FROM schedule WHERE stop_name = :stopName ORDER BY arrival_time ASC") fun getByStopName(stopName: String): Flow<List<Schedule>> }在 Dao 的函数中,我们可在 Query 中用
:引用函数参数(如上文中的 :stopName 即引用了 stopName: String 参数)四、定义 ViewModel
有了 Entity 和 Dao 我们就可访问数据库并获取数据了,但通常 App 的 UI 层每个页面需要的是不同的接口,我们不应将数据层和 UI 层耦合在一起。
因此拆分出 ViewModel 层,其有如下2个优点:
- 其封装了各种数据层操作,并对外暴露 UI 层的接口,解耦
- 其具备生命周期感知能力,即当Activity/Fragment 被销毁并重建时,因为 ViewModel 不会被销毁,所以不需要重新创建 ViewModel。
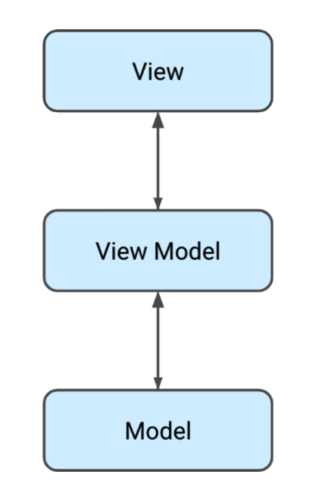
所以,最佳实践是,用 ViewModel 把加载数据的责任,从Activity、Fragment 中分离出来,其架构如下:
在 viewmodels 文件夹下,新建 ScheduleListViewModel.kt,目录结构如下:

ScheduleListViewModel.kt 的代码如下:
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider import com.example.busschedule.database.schedule.Schedule import com.example.busschedule.database.schedule.ScheduleDao import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.Flow class BusScheduleViewModel(private val scheduleDao: ScheduleDao) : ViewModel() { fun fullSchedule(): Flow<List<Schedule>> = scheduleDao.getAll() fun scheduleForStopName(name: String): Flow<List<Schedule>> = scheduleDao.getByStopName(name) }因为 ViewModel 需要能感知生命周期变化,所以应由可响应生命周期事件的对象来对其实例化。(如果在某个 Activity、Fragment 中对其实例化,那么该 Activity、Fragment 就不得不处理所有任务(如内存管理任务),这超出了Activity、Fragment 的职责范围)。因此需要用工厂类,来实例化 ViewModel,代码如下:
- 首先,继承自 ViewModelProvider.Factory 类,代码如下:
class BusScheduleViewModelFactory(private val scheduleDao: ScheduleDao) : ViewModelProvider.Factory { }- 其次,override fun create(),使得 BusScheduleViewModelFactory 可创建出 BusScheduleViewModel,代码如下:
class BusScheduleViewModelFactory(private val scheduleDao: ScheduleDao) : ViewModelProvider.Factory { override fun <T : ViewModel> create(modelClass: Class<T>): T { if (modelClass.isAssignableFrom(BusScheduleViewModel::class.java)) { @Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST") return BusScheduleViewModel(scheduleDao) as T } throw IllegalArgumentException("Unknown ViewModel class") } }五、创建 Database
因为一个 App 可能操作多个 sqlite 文件,所以需要 Database 层。Database 类继承自 RoomDatabase,其负责:指定 Entity、访问各个 Dao 、对 Database 做预填充(createFromAsset)和升级(Migration),代码如下:
package com.example.busschedule.database import android.content.Context import androidx.room.Database import androidx.room.Room import androidx.room.RoomDatabase import com.example.busschedule.database.schedule.Schedule import com.example.busschedule.database.schedule.ScheduleDao /** * Defines a database and specifies data tables that will be used. * Version is incremented as new tables/columns are added/removed/changed. * You can optionally use this class for one-time setup, such as pre-populating a database. */ @Database(entities = [Schedule::class], version = 1) abstract class AppDatabase : RoomDatabase() { abstract fun scheduleDao(): ScheduleDao companion object { @Volatile private var INSTANCE: AppDatabase? = null fun getDatabase(context: Context): AppDatabase { return INSTANCE ?: synchronized(this) { val instance = Room.databaseBuilder(context, AppDatabase::class.java, "app_database") .createFromAsset("database/bus_schedule.db") .build() INSTANCE = instance instance } } } }六、创建 Application
Application 类会使用 Database 类,创建 BusScheduleApplication 类,创建的文件位置如下:
BusScheduleApplication.kt 的代码如下:
import android.app.Application import com.example.busschedule.database.AppDatabase class BusScheduleApplication : Application() { val database: AppDatabase by lazy { AppDatabase.getDatabase(this) } }为了确保使用的是 BusScheduleApplication 类,而不是默认的基类 Application 类,需要在 AndroidManifest.xml 设置 android:name 属性,设置如下:
<application android:name="com.example.busschedule.BusScheduleApplication" ...> application>七、创建 ListAdapter
使用 RecyclerView 时,有如下2种方式:
- 若用 Adapter,则只要有一项数据被改变,就会刷新整个 RecyclerView。
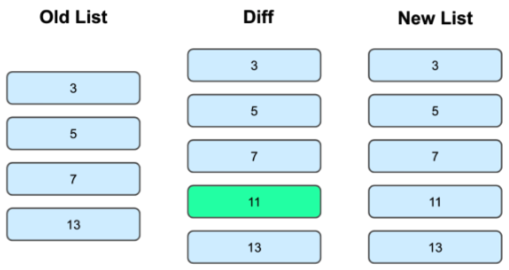
- 若用 ListAdapter,则当新旧数据列表有差异(如下图)时,才会刷新 RecyclerView,性能更高。
首先,在 BusStopListAdapter.kt 中创建 BusStopAdapter 类,该类传入 onItemClicked() 函数参数,并继承自 ListAdapter 类,代码如下:
class BusStopAdapter(private val onItemClicked: (Schedule) -> Unit) : ListAdapter<Schedule, BusStopAdapter.BusStopViewHolder>(DiffCallback) {然后,创建 class BusStopViewHolder,其 bind() 函数会将数据显示在 UI布局的控件上,代码如下:
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): BusStopViewHolder { val viewHolder = BusStopViewHolder( BusStopItemBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.context), parent, false) ) viewHolder.itemView.setOnClickListener { val position = viewHolder.adapterPosition onItemClicked(getItem(position)) } return viewHolder }接下来,创建并实现 onCreateViewHolder(),并膨胀布局,设置 viewHolder.itemView.setOnClickListener,为调用当前位置项的 onItemClicked() 函数,代码如下:
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): BusStopViewHolder { val viewHolder = BusStopViewHolder( BusStopItemBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.context), parent, false) ) viewHolder.itemView.setOnClickListener { val position = viewHolder.adapterPosition onItemClicked(getItem(position)) } return viewHolder }然后,替换并实现 onBindViewHolder() 来讲数据绑定到某位置,代码如下:
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: BusStopViewHolder, position: Int) { holder.bind(getItem(position)) }最后,创建名为 DiffCallback 的 companion object,用于对比新旧列表的差异,代码如下:
companion object { private val DiffCallback = object : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Schedule>() { override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: Schedule, newItem: Schedule): Boolean { return oldItem.id == newItem.id } override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: Schedule, newItem: Schedule): Boolean { return oldItem == newItem } } }八、在 Activity、Fragment 中使用 ListAdapter
新建 FullScheduleFragment.kt,其位置如下:
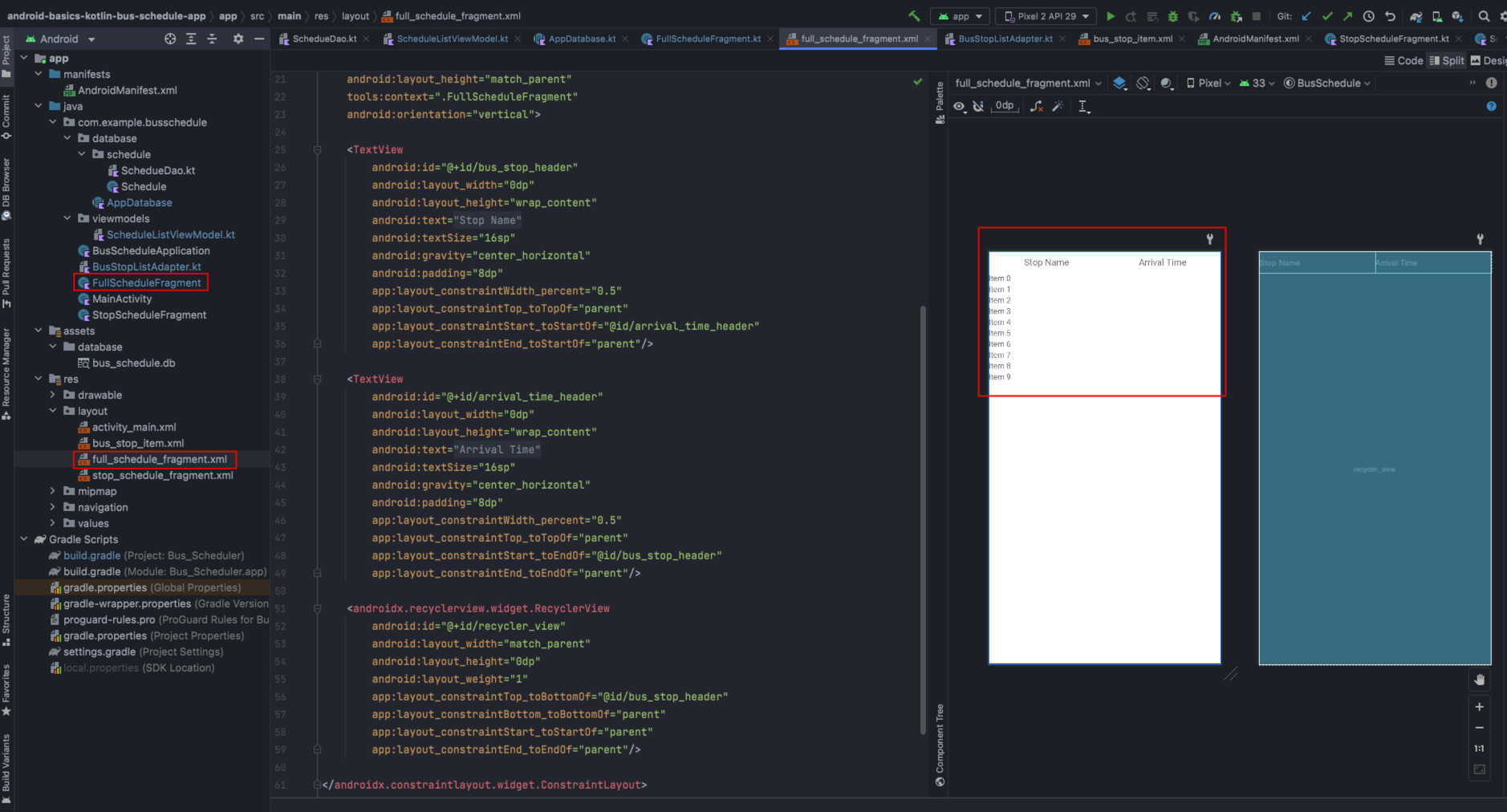
其对应的 full_schedule_fragment.xml 布局文件如下图:
在 FullScheduleFragment.kt 中,创建 ViewModel,代码如下:
class FullScheduleFragment : Fragment() { private val viewModel: BusScheduleViewModel by activityViewModels { BusScheduleViewModelFactory( (activity?.application as BusScheduleApplication).database.scheduleDao() ) } }在 FullScheduleFragment.kt 中的 onViewCreated() 中通过如下代码,设置 recyclerView 并分配其布局管理器,代码如下:
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState) recyclerView = binding.recyclerView recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(requireContext()) }然后,设置 recyclerView 的 adapter 属性为导航到下一个 Fragment,代码如下:
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState) recyclerView = binding.recyclerView recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(requireContext()) val busStopAdapter = BusStopAdapter { val action = FullScheduleFragmentDirections.actionFullScheduleFragmentToStopScheduleFragment(stopName = it.stopName) view.findNavController().navigate(action) } recyclerView.adapter = busStopAdapter }最终,通过 submitList() 更新视图,代码如下:
// submitList() is a call that accesses the database. To prevent the // call from potentially locking the UI, you should use a // coroutine scope to launch the function. Using GlobalScope is not // best practice, and in the next step we'll see how to improve this. GlobalScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) { busStopAdapter.submitList(viewModel.fullSchedule()) }运行后,效果如下:
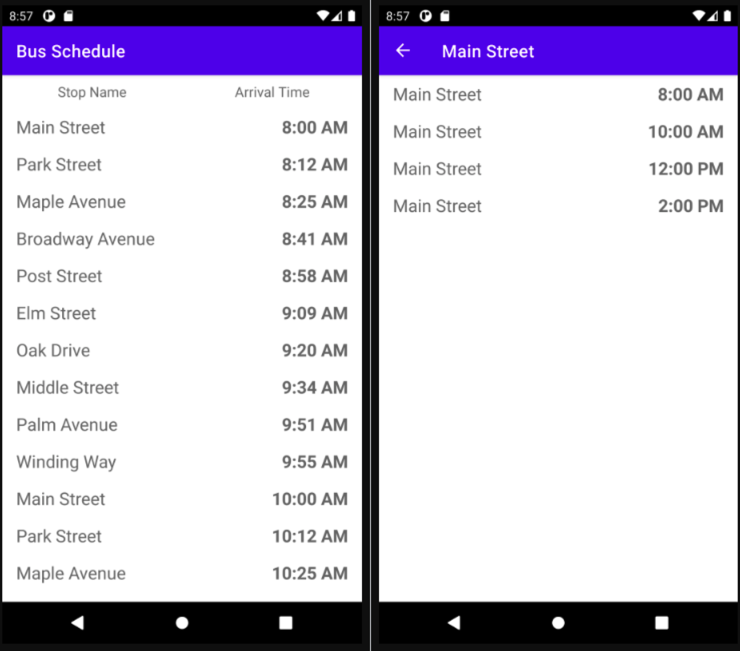
九、用 Flow 响应数据库的变化
目前,UI 无法动态处理数据库的变化,例如通过如下 sql
INSERT INTO schedule VALUES (null, 'Winding Way', 1617202500)向数据库增加一条,示例如下: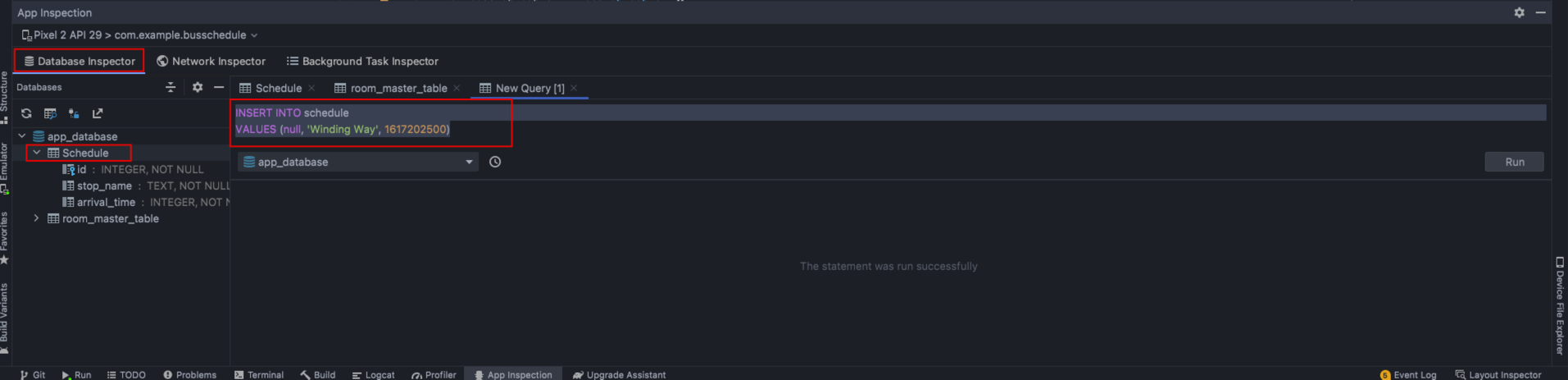
因为系统智慧从每个 Dao 返回一次 List,所以虽然数据库已变化,但系统也不会通过 submitList() 来更新 UI。
可用 Kotlin 的 Flow 功能解决此问题,使用 Flow 后,Dao 会持续监听数据库,当增删改数据后,其会向Activity、Fragment 发数据,Activity、Fragment 通过 collect() 函数接收,并调用 submitList() 让 ListAdapter 更新 UI。
将 ScheduleDao.kt 的代码改为如下 Flow 的形式:
package com.example.busschedule.database.schedule import androidx.room.Dao import androidx.room.Query import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.Flow /** * Provides access to read/write operations on the schedule table. * Used by the view models to format the query results for use in the UI. */ @Dao interface ScheduleDao { @Query("SELECT * FROM schedule ORDER BY arrival_time ASC") fun getAll(): Flow<List<Schedule>> @Query("SELECT * FROM schedule WHERE stop_name = :stopName ORDER BY arrival_time ASC") fun getByStopName(stopName: String): Flow<List<Schedule>> }将 BusScheduleViewModel 的类型改为 Flow 封装的,代码如下:
class BusScheduleViewModel(private val scheduleDao: ScheduleDao) : ViewModel() { fun fullSchedule(): Flow<List<Schedule>> = scheduleDao.getAll() fun scheduleForStopName(name: String): Flow<List<Schedule>> = scheduleDao.getByStopName(name) }在 Fragment 中,通过 fullSchedule() 启动协程,通过 collect() 收集数据,最终更新界面,代码如下:
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState) recyclerView = binding.recyclerView recyclerView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(requireContext()) val busStopAdapter = BusStopAdapter { val action = FullScheduleFragmentDirections.actionFullScheduleFragmentToStopScheduleFragment(stopName = it.stopName) view.findNavController().navigate(action) } recyclerView.adapter = busStopAdapter lifecycle.coroutineScope.launch { viewModel.fullSchedule().collect() { busStopAdapter.submitList(it) } } }运行后,当数据库改变时,UI 即更新,效果如下:

-
相关阅读:
AI智剪:批量剪辑实战,技巧与实例
vulhub靶场搭建
面经 - 高频难
18-Linux系统服务
某物联网数智化园区行业基于 KubeSphere 的云原生实践
M1 Pro MacBook Pro下载Android11源码
简洁的 Markdown 文本编辑器 Typora
MyBatis简介测试
使用asyncua模块的call_method方法调用OPC UA的Server端方法报错:asyncio.exceptions.TimeoutError
干货 | 一文搞定 uiautomator2 自动化测试工具使用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jiaoyangwm/article/details/127106606