-
AQS源码解读
AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)抽象队列同步器,JUC的基础工具类,是实现 ReentrantLock、CountDownLatch、Semaphore、FutureTask 等类的基础。核心属性
/** * Head of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Except for * initialization, it is modified only via method setHead. Note: * If head exists, its waitStatus is guaranteed not to be * CANCELLED. */ //等待队列的头结点,延迟初始化,初始化后仅可以通过setHead方法进行修改,如果头结点已存在,它的waitStatus不会变成CANCELLED取消状态 //头结点可以直接理解为当前持有锁的线程 private transient volatile Node head; /** * Tail of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Modified only via * method enq to add new wait node. */ //等待队列的尾结点,延迟初始化,只能通过enq方法来添加等待结点 //一个线程参与竞争如果需要加入队列,都将线程结点插入到等待队列尾部 private transient volatile Node tail; /** * The synchronization state. */ //当前锁状态,0代表没有被占用,大于等于1则表示被线程占用,由于可重入,因此每次重入state++ private volatile int state; /** * The current owner of exclusive mode synchronization. */ //当前独占锁线程(继承自AbstractOwnableSynchronizer) private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;阻塞队列不包含head
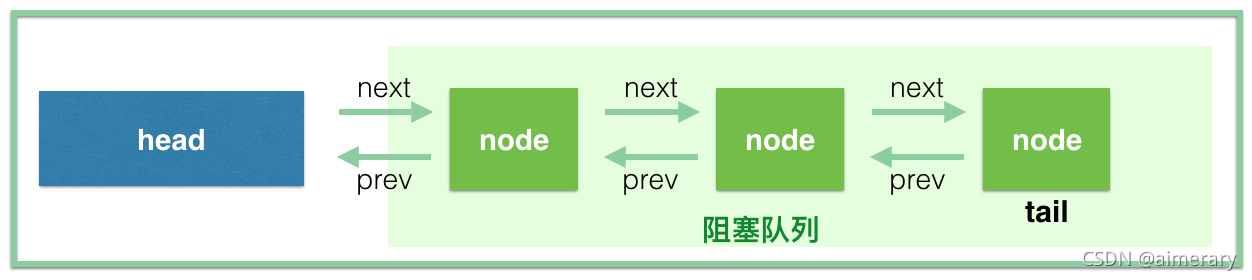
等待队列的Node结点是对线程的包装,数据结构是链表//标识当前结点是否为共享模式 static final Node SHARED = new Node(); //标识当前结点是否为独占模式 static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */ //表示线程已取消 static final int CANCELLED = 1; /** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */ //表示当前结点的后继结点需要被唤醒 static final int SIGNAL = -1; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */ static final int CONDITION = -2; /** * waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should * unconditionally propagate */ static final int PROPAGATE = -3; //当前结点的等待状态 volatile int waitStatus; //前驱结点的引用 volatile Node prev; //后继结点的引用 volatile Node next; //当前结点线程 volatile Thread thread; //如果是独占锁则为null Node nextWaiter;ReentrantLock源码(公平锁)
static final class FairSync extends Sync { //争抢锁 final void lock() { acquire(1); } }acquire方法
public final void acquire(int arg) { //首先调用tryAcquire尝试获取锁,如果获取成功直接返回 if (!tryAcquire(arg) && //如果tryAcquire失败,执行addWaiter添加等待者将当前线程封装为Node插入队列尾部 //当前结点插入队列后,进行获取队列acquireQueued acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); }tryAcquire方法
/** * Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless * recursive call or no waiters or is first. */ protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { //获得当前获取锁的线程 final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); //获得锁的状态 int c = getState(); //1、判断锁的状态是否空闲 if (c == 0) { //由于是公平锁,空闲还需要去判断等待队列是否存在正在等待的线程 //如果判断队列为非空且CAS改变状态成功 // hasQueuedPredecessors方法等效于: //getFirstQueuedThread() != Thread.currentThread() &&hasQueuedThreads() if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { //改变状态成功了就设置独占锁线程为当前线程,获取锁成功 setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } //2、否则不为空闲,就判断当前线程是否与获得锁的线程相等,相等则进行重入 //进行重入说明是同一个线程进行,不可能存在并发问题 else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { //相当于c+1 int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } //返回false说明1、锁被占用 2、锁未被占用但队列存在其他线程将竞争 3、不是同一线程不能被重入 return false; }addWaiter方法
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); //尝试以快捷的方式插入队列尾,如果失败则将node传入完整的enq方法执行 //获取当前队尾结点,将当前结点与队尾结点连接 //即当前结点前驱=队尾,队尾结点后继=当前结点,期间将当前结点设置为新队尾 Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) { node.prev = pred; //CAS方式将当前结点设置为新队尾,成功才进行正式的结点插入 if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } //进入enq方法的两种情况:1、多线程竞争导致CAS失败,结点插入队列失败 2、tail结点为null,意味着队列不存在 enq(node); return node; }private Node enq(final Node node) { for (;;) { Node t = tail; //尾结点为空说明队列为空,对队列进行CAS初始化,使tail=head=new Node() if (t == null) { // Must initialize if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) tail = head; //队列初始化完成不返回值,tail未初始化,继续循环进行结点插入 } else { //与上文addWaiter的快捷插入方式一样,区别是进行了自旋直到插入结点成功 node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { t.next = node; return t; } } } }队列初始化!=head和tail初始化
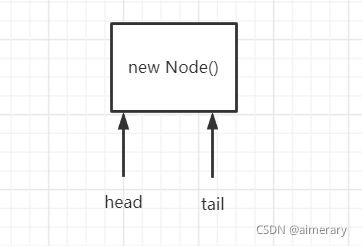
假设为队列初始化,head和tail都是延时初始化的,进行队列初始化后head和tail并未初始化,并未指向实际的结点
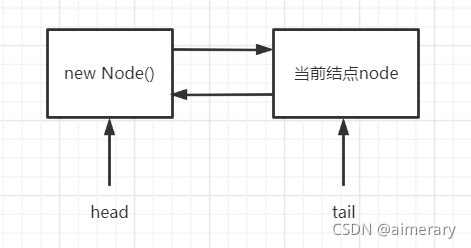
在插入结点后tail进行了初始化,指向了当前结点,但head并未初始化,并未指向实际的结点,head并未设置任何线程,即还没有线程获取锁
acquireQueued方法
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); //判断p==head且尝试获取锁,能进入当前语句有这种情况: //队列刚刚进行初始化,插入了结点,head并未初始化,说明锁还没有被获取 //node为队列中的第一个结点,因此node的前驱结点为head,因此可以进行尝试获取锁 if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } -
相关阅读:
【Java技术专题】「原理分析系列」Lambda表达式实现原理分析
安卓7原生相机切到视频崩溃
计算机毕业设计Java高校设备采购审批管理系统(源码+系统+mysql数据库+Lw文档)
Eyeshot Ultimate参数化建模升级
初识reactor响应式编程
jvm-sandbox-repeater时间mock插件设计与实现
Ansys Speos | SPEOS 在HUD杂光分析中的应用
SpringBoot简单入门
Jetpack Compose - Button按钮使用
API自动化(四)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/aimerary/article/details/120374820